Structural Kinesiology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
scaphoid
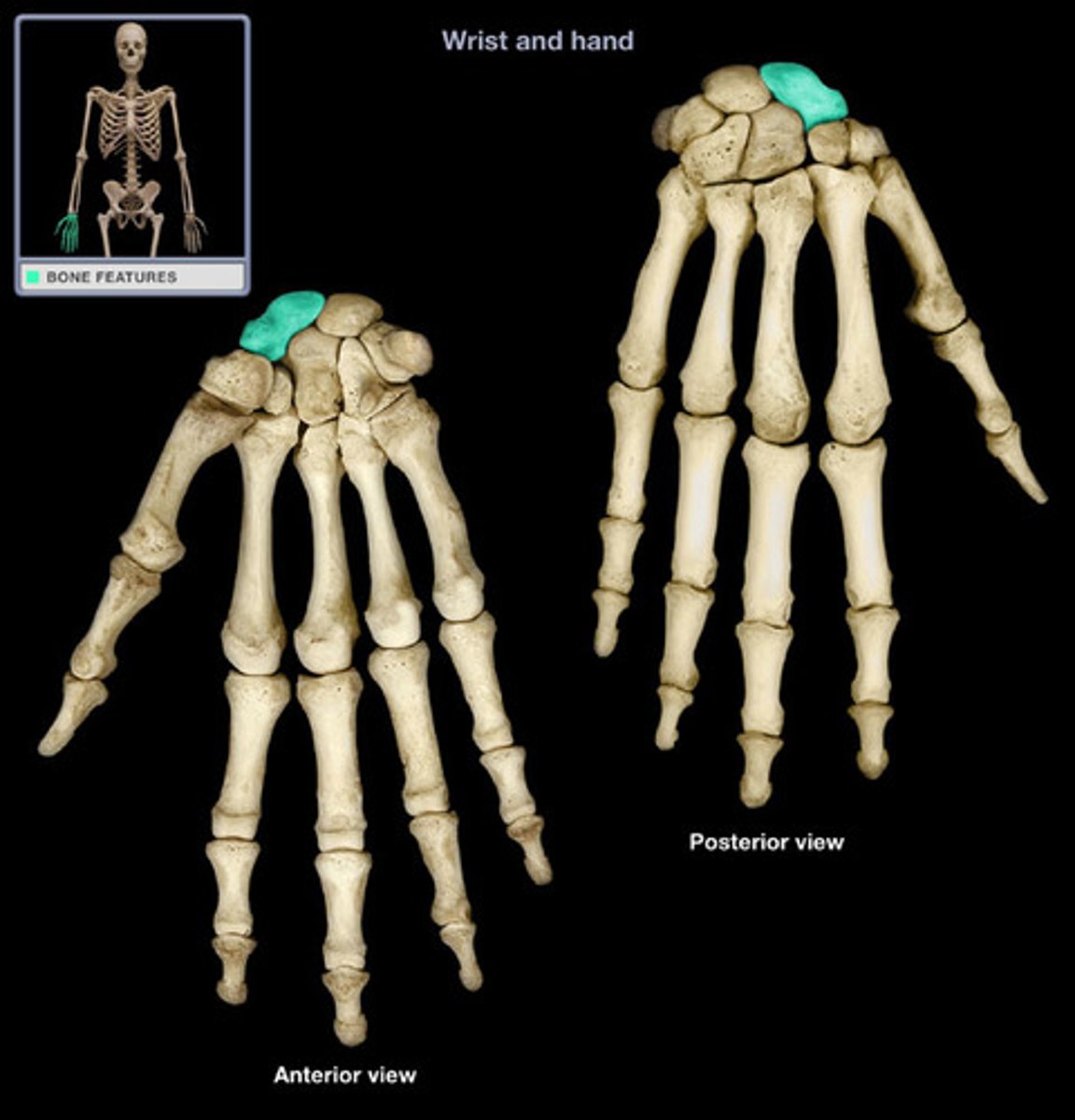
Lunate
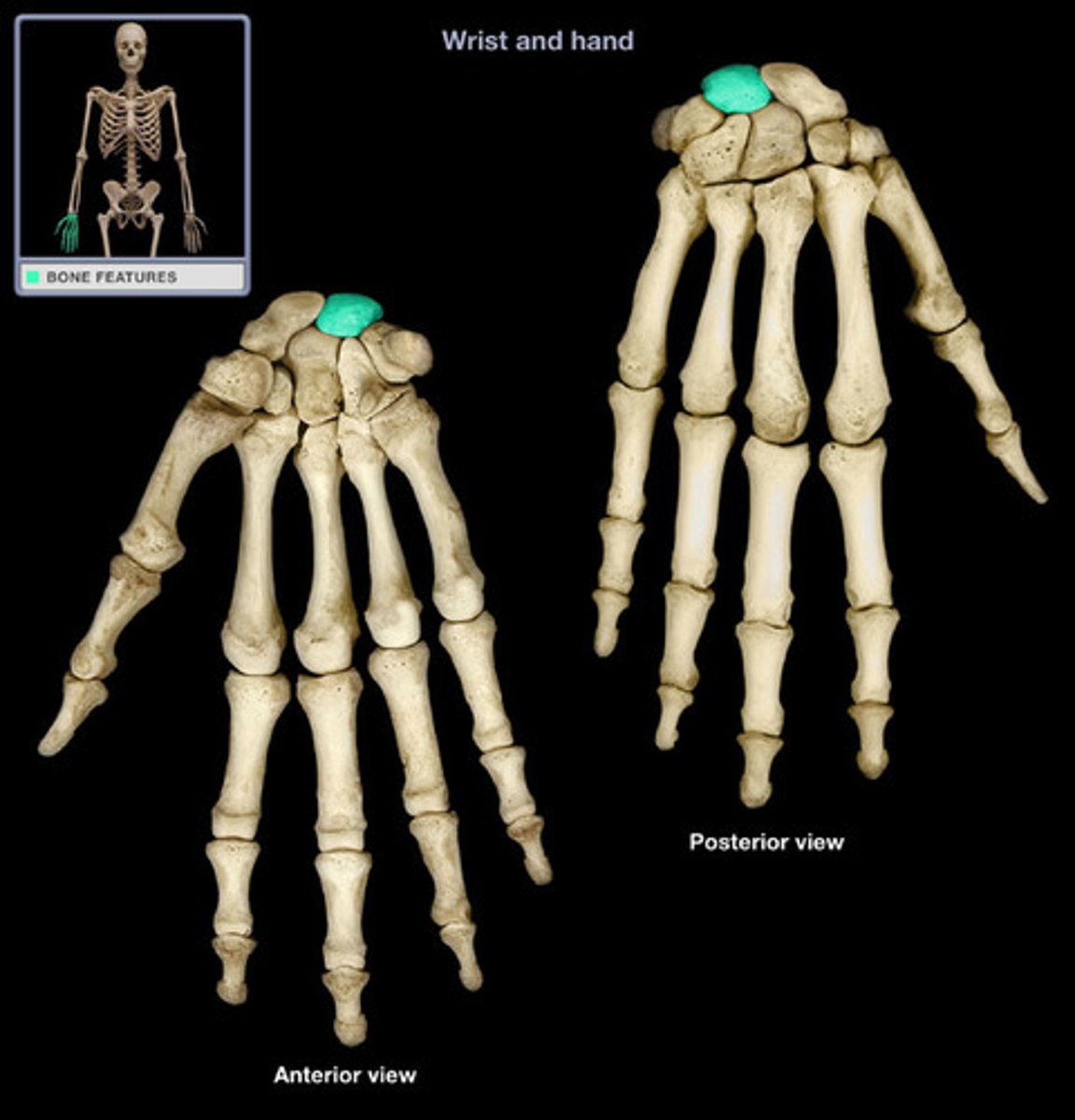
Triquetrium
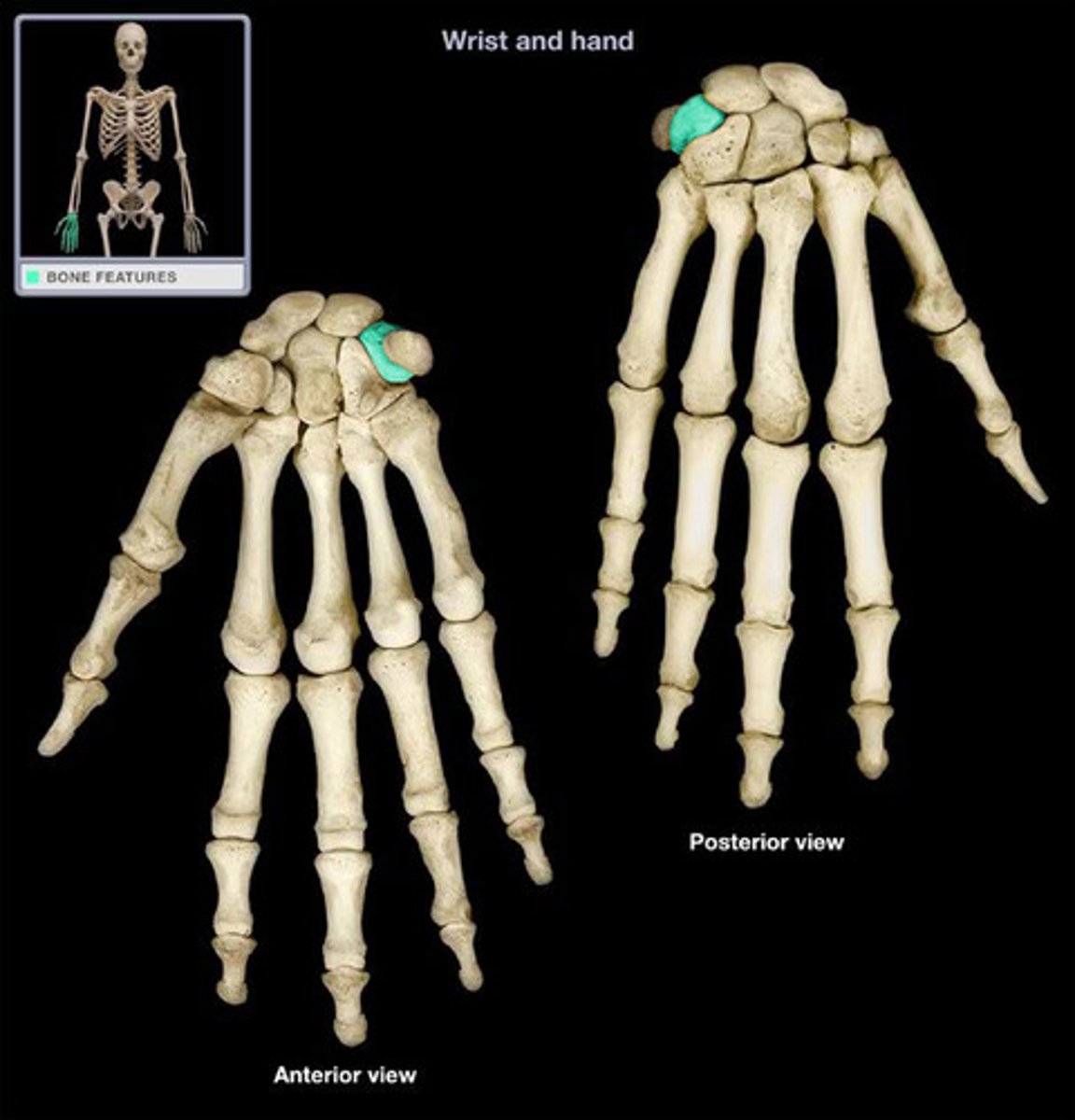
Pisiform
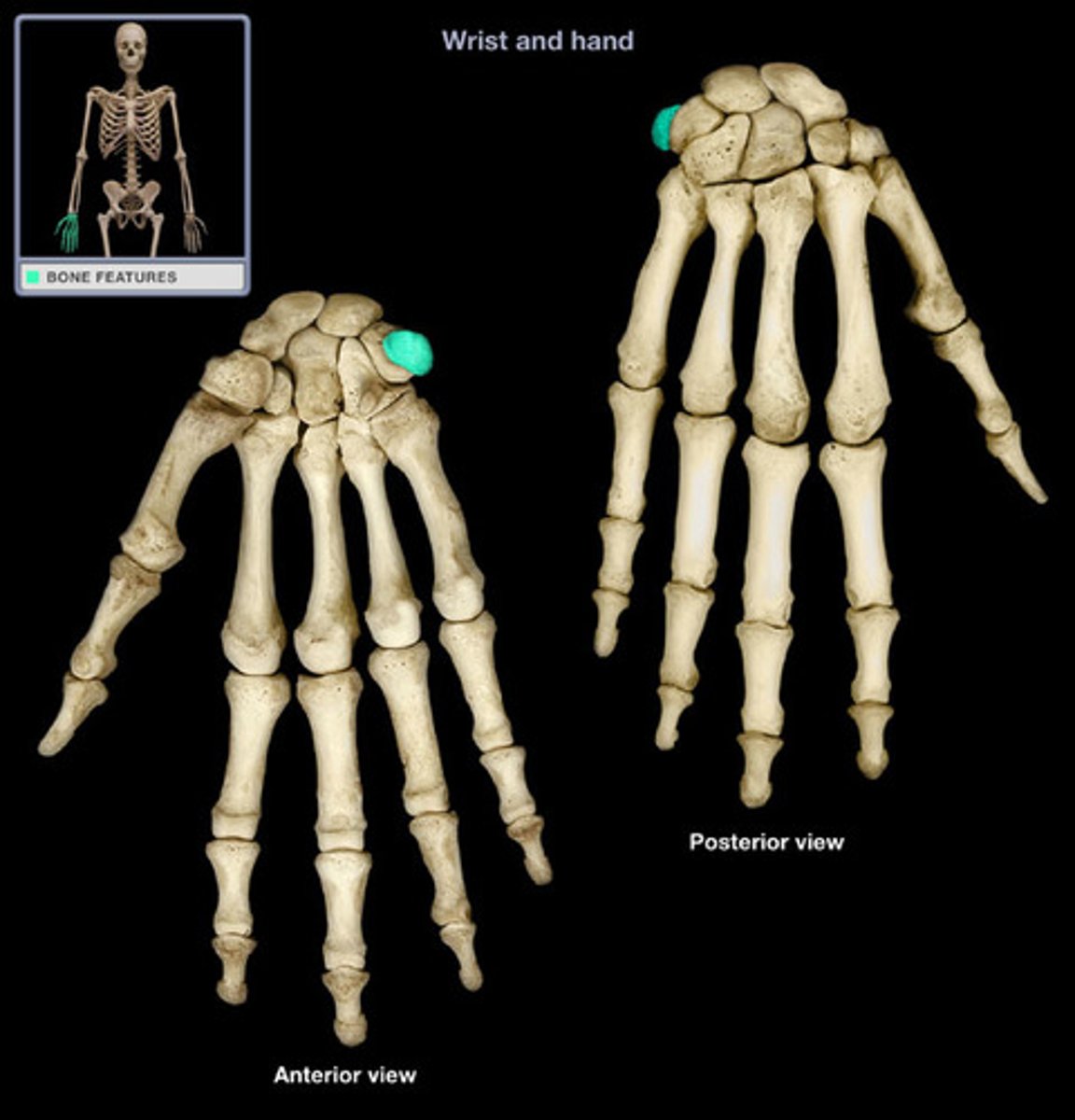
Trapezium
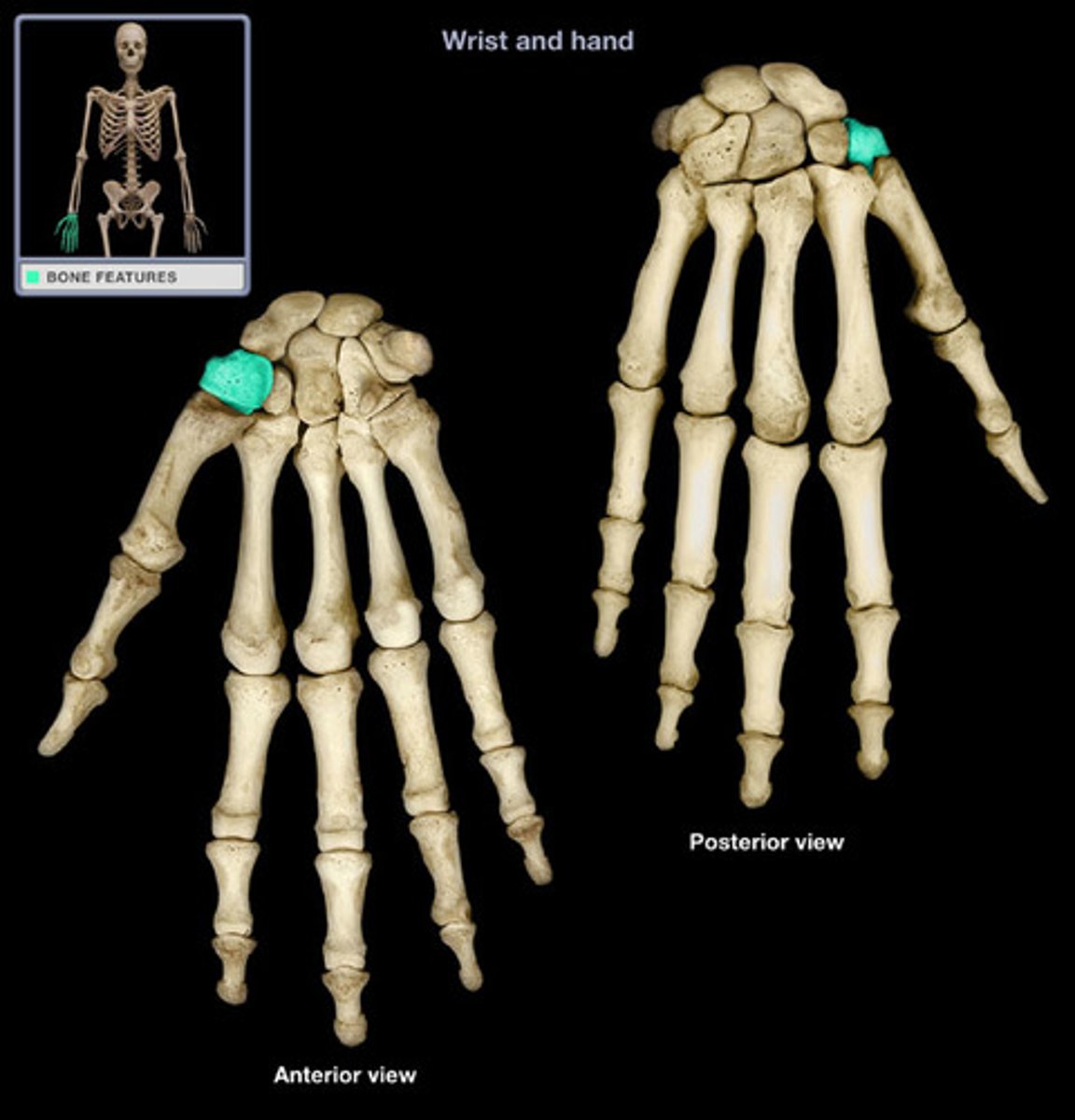
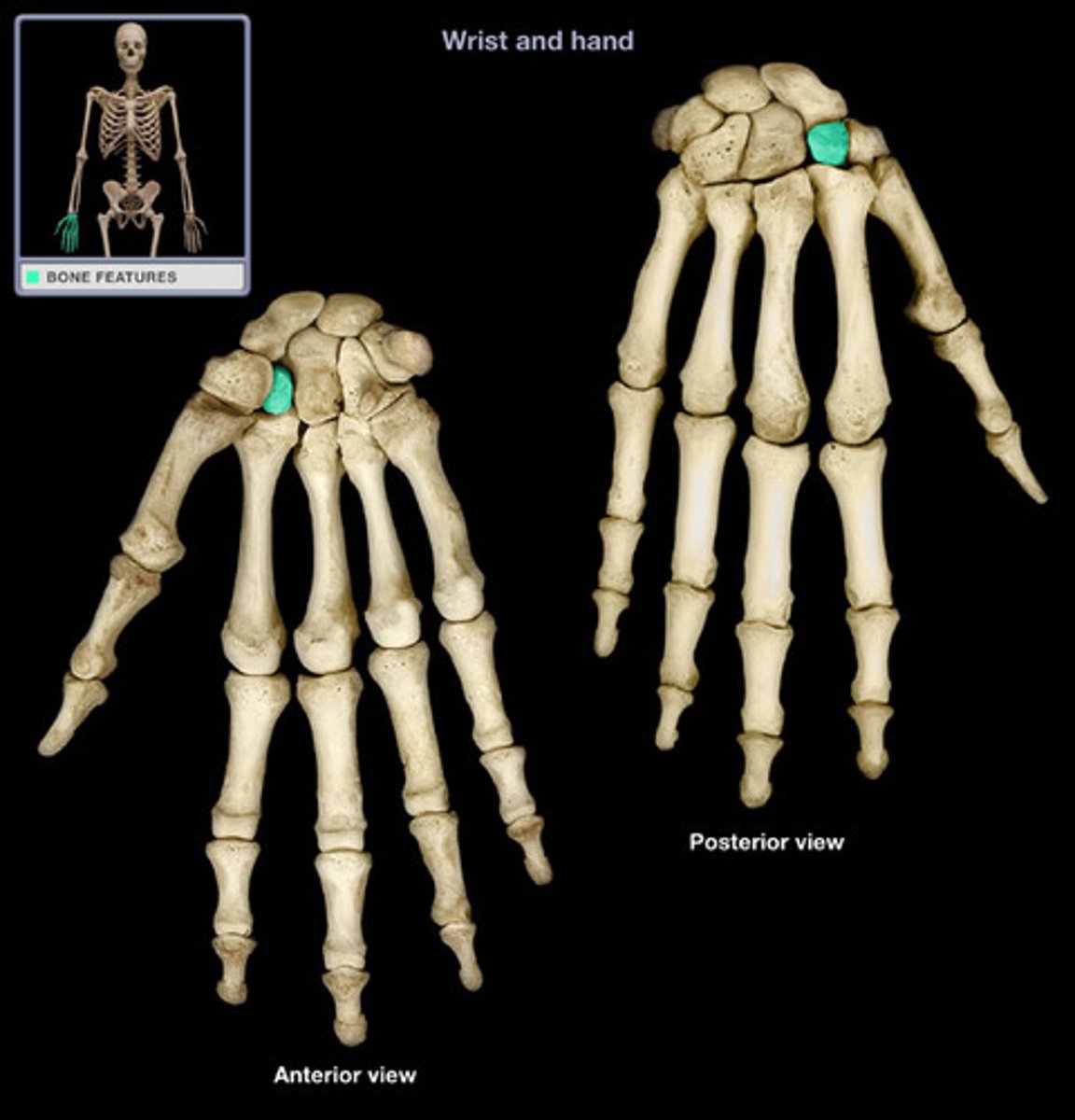
capitate
trapezoid
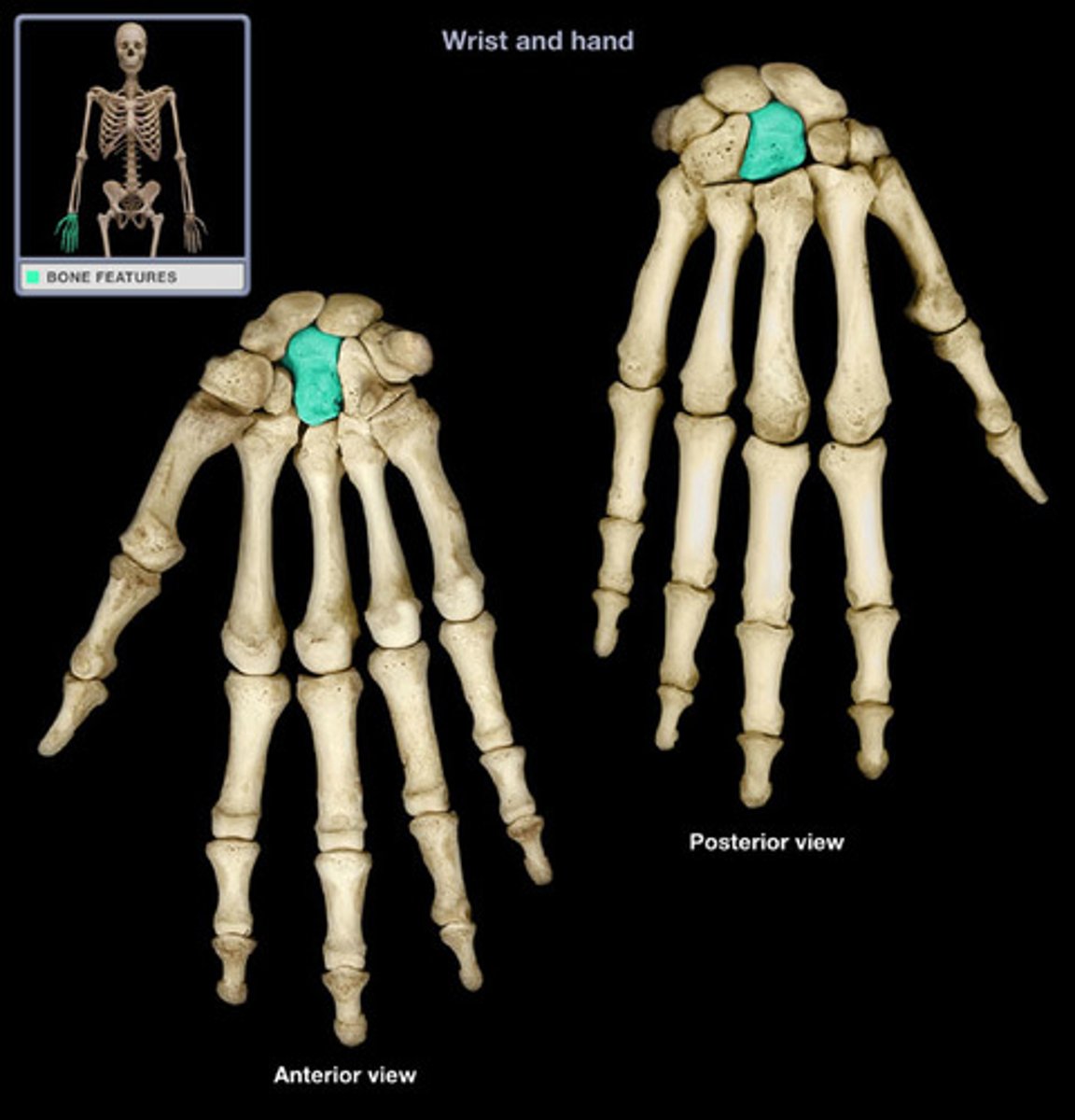
hamate
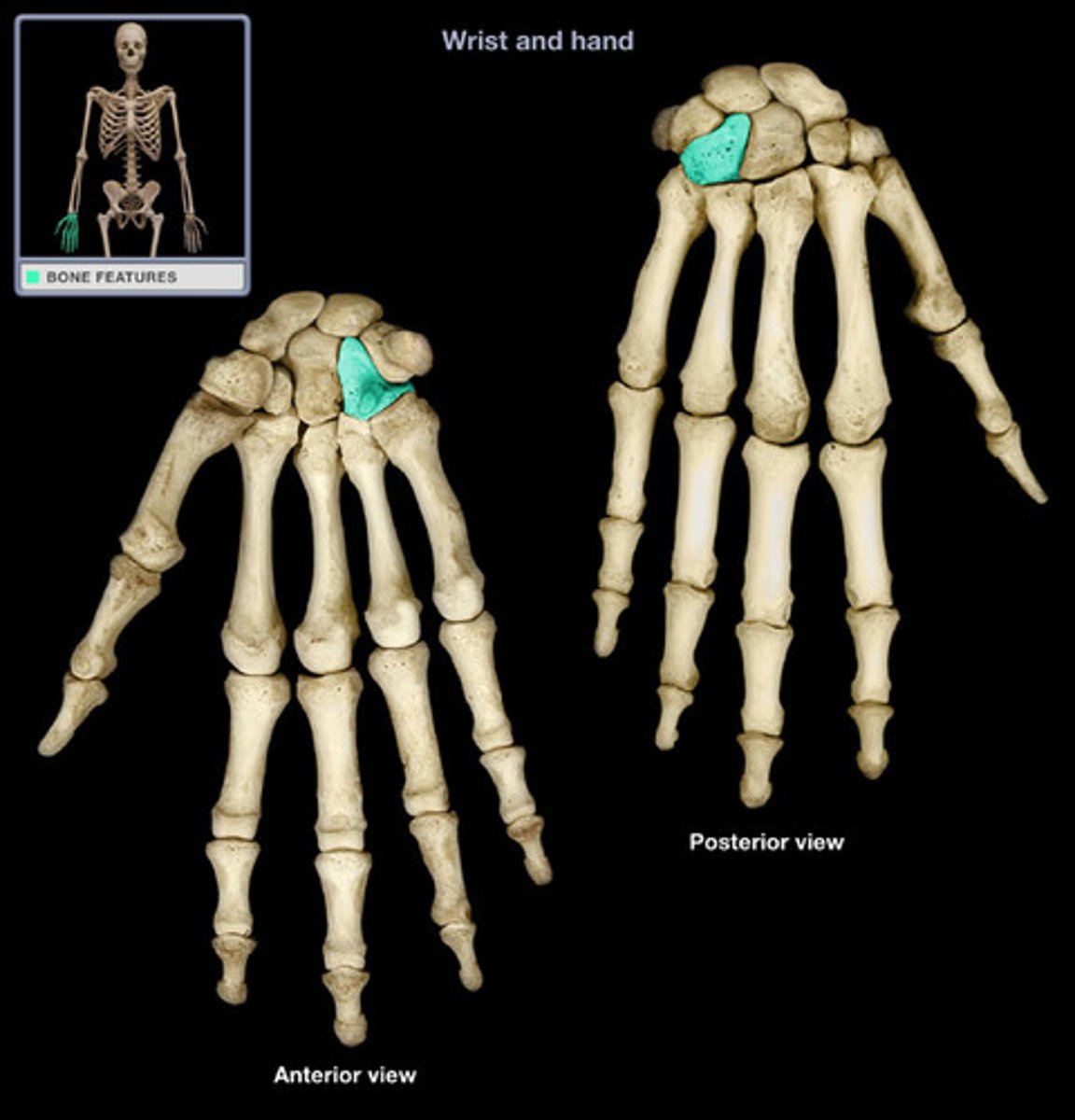
Distal: Trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Proximal: scaphoid, lunate, triquetrium, pisiform
What are all the carpal bones? Which ones are distal and which ones are proximal?
Base Shaft Head
What are the three parts of a metacarpal?
The 4th and 5th are mobile and the 2nd and 3rd are immobile. The ability to grasp objects of varying shapes and sizes is because of the mobility of the 4th and 5th metacarpal. The gripping and pinching motions are stable due to the 2nd and 3rd metacarpal.
Which metacarpals are mobile and which are immobile? Why is this important and how does it show the design of the Creator?
synoival pivot
What is the joint classification of the distal radioulnar joint?
Head of the ulna
ulnar notch of radius
What are the articulating surfaces of the distal radioulnar joint?
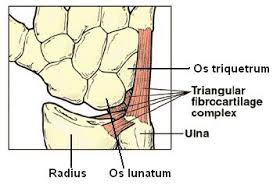
TFCC- Triangular Fibrocartilage complex
interosseous membrane
Movements: forearm pronation and supination
What are the stabilizing ligaments/structures of the distal radioulnar joint and what are this joints movements?
Synovial condyloid joint
Surfaces: distal radius and TFCC and proximal row of carpal bones
What is the joint classification of the radiocarpal (wrist) joint and what are the articulating surfaces?
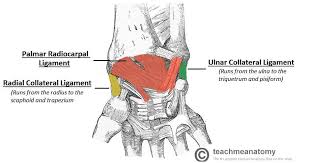
Palmer radiocarpal ligament
Dorsal radiocarpal ligament
Radial collateral ligament
Ulnar collateral ligament
Movements:flexion, extension, radial and ulnar deviation, circumduction
What are the stabilizing ligaments and movements of the radiocarpal joint?
synovial condyloid
Head of metacarpals with the bases of proximal phalanges
what are the articulating surfaces and joint classification of the metcarpophalangeal joint?
collateral ligaments
Volar plates (prevent hyperextension)
Flexion and extension
Adduction and abduction
what are the movements and stabilizing ligaments of the metacarpophalangeal MCP joints
synovial hinge joints
Head and bases of phalanges (of adjacent phalanges)
What type of joint are the DIP and PIP joints and what are the articulating surfaces?
collateral ligaments
Volar palmer plates
Flexion and extension
What are the movements and stabilizing ligaments of the DIP and PIP ligaments?
synovial saddle joint
Movements occur around oblique axis
Flexion and extension
Adduction and abduction
Opposition and reposition
what is the joint classification and movements of the 1st carpometacarpal CMC joint
Radial
What nerve innervates all the muscles that extend the wrist and fingers?
Median Nerve
What nerve innervates most of the muscles that flex the wrist and fingers?
O- medial epicondyle of the humerus
I- slips from base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal (palmer side)
A- flexion, radial deviation (abduction)
N-median nerve
Flexor carpi radialis OIAN
O: medial epicondyle of humerus
I: palmar aponeurosis
A: tenses aponeurosis and weakly assist with wrist flexion
This muscle may be absent from one or both arms in around 15% of the population
Palmaris Longus OIA
O: Medial epicondyle of the humerus and proximal ulna
I: base of 5th metacarpal; hamate and pisiform
A: flexion and ulnar deviation (cutting with a knife or hammering)
N: ulnar nerve
Flexor carpi Ulnaris OIAN
Flexor carpi radialis and flexor carpi ulnaris
What muscles would need to be working to act PURE WRIST FLEXION (with no deviation)?
O: medial epicondyle of the humerus
I: sides of the middle phalanges, digits 2-5
N: median nerve
Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) OIN
O: proximal ulna
I: Base of distal phalanges of digits 2-5
N: Lateral part (digits 2 and 3)- median nerve
medial part (digits 4 and 5)- ulnar nerve
Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) OIN
MCP and PIP joint flexion (digits 2-5)
wrist flexion
(DIP joint flexion is an additional action of FDP)
What are the actions of both the FDS and FDP?
1) Synovial sheaths- surround the flexor tendons of each finger
2) Fibrous sheaths- surround the synovial sheaths and consist of multiple pulleys
Job: reduce friction and hold the long finger flexor tendons close to prevent bowstringing
What are the two types of sheaths found in the hand and what is their job?
Floor and sides: carpal bones and ligaments
Roof: flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament)
What structures form the floor and sides of the carpal tunnel and what structure form the roof?
wrist and finger flexor tendond (FDS and FDP)
median nerve
What are the contents of the tunnel?
Radial: scaphoid and trapezium
Ulnar: pisiform and hook of hamate
continuous with the palmar aponeurosis
What are the attachments of the flexor retinaculum? Radial and Ulnar side? what is this retinaculum continuous with?
O: lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
I: base of 2nd metacarpal, dorsal surface
Extensor carpi radialis longus OI
O: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
I: Base of 3rd metacarpal, dorsal surface
Extensor carpi radialis brevis OI
wrist extension
radial deviation
What are the actions of the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis?
O: lateral epicondyle of the humerus and posterior border of the ulna
I: base of the 5th metacarpal, dorsal surface
A: wrist extension and ulnar deviation
Extensor carpi ulnaris OIA
O: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
I: Central slip- base of middle phalanges
lateral bands- distal phalanges (digits 2-5)
A: extension of MCP, DID, PIP jpints and wrist extension
Extensor digitorum OIA
help to stablize the tendons and they reduce friction
What are intertendinous connections?
Extensor retinaculum and it helps to hold the tendons in place and prevent bow stringing
Extensor tendons pass under what? and what does this structure do?