GI Radiology 1 and 2
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What is the most common imaging method for the GI tract?
Fluoroscopy (left) and MRI (right) are common, but by far the most common is a CT Scan
How does GI Fluoroscopy work? What are the four kinds
Contrast is placed into the tube in order to fill the tract and take pictures via an X-ray. Barium is the most common contrast
1) Fluoroscopy Barium Swallow
→ fluoroscopy imaging method where patients will swallow barium contrast allowing us to see if the contrast properly goes down the esophagus
2) Fluoroscopy Upper GI
→ fluoroscopy technique used to image the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
3) Fluoroscopy Small Bowel Follow Through
→ allows us to see the movement of the contrast through the stomach and small intestine
4) Fluoroscopy Barium Enema
→ screening tool for colon cancer
→ distend the colon with air and then shoot barium into their asshole in order to see the features of the large intestine
What are the three kinds of CT imaging for GI?
Coronal (front to back) and Sagittal (cross sections from side to side) and Transverse (top down)
What is a CT Angiogram?
Computed Tomography method
→ administration of contrast into the blood vessels that allows us to image our blood vessels - the blood vessels will look bright white
→ used to see if there are any clots or issues with the vessels
What is Stranding?
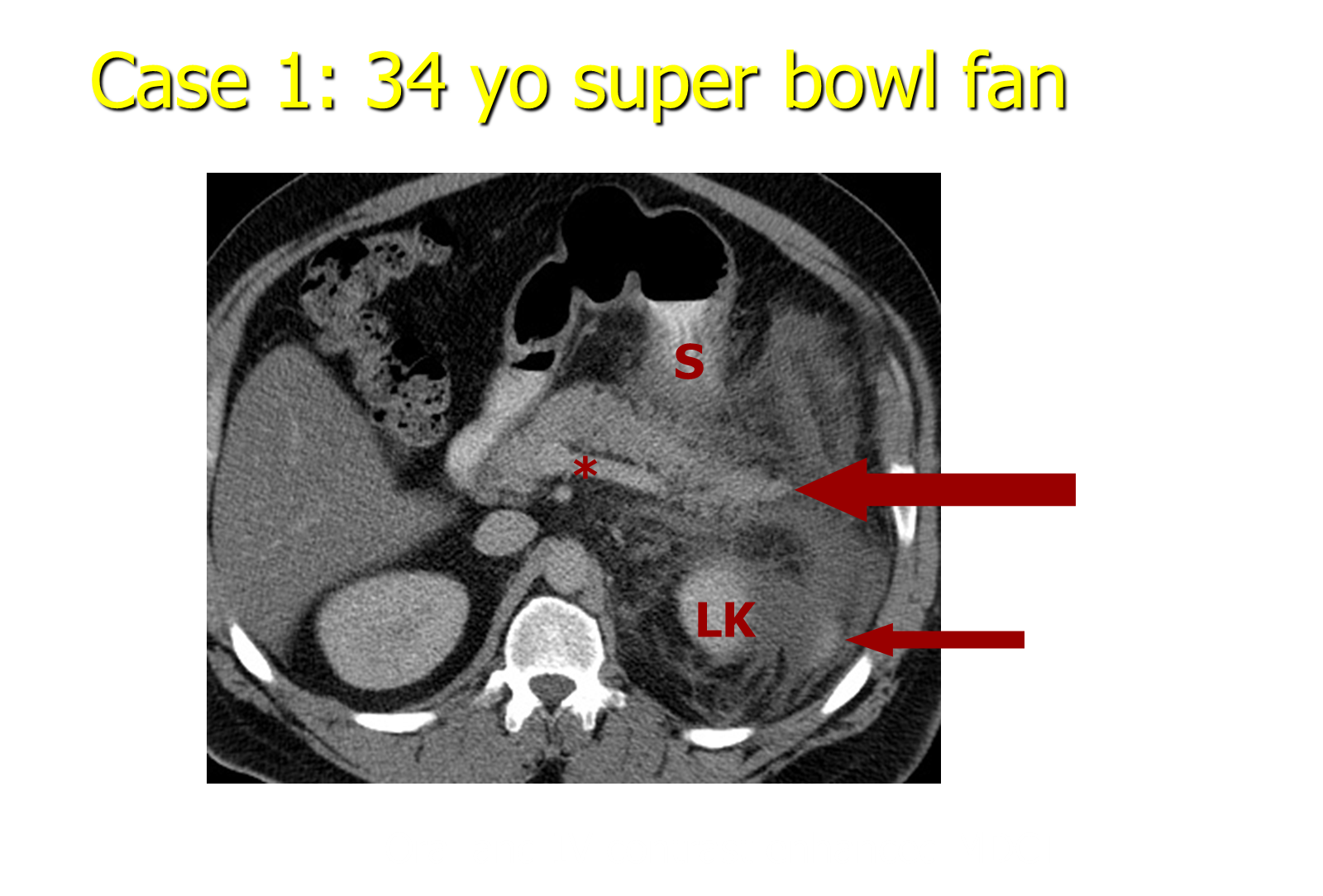
Stranding is a radiology term
→ bright stuff that is “strand like” and indicates inflammatory change and the presence of fluid where it is not supposed to be
What is the difference between IV and oral contrast
IV (intravenous) contrast is injected into a vein to enhance the visualization of blood vessels and solid organs, while oral contrast is taken by mouth to help differentiate the bowel from other abdominal structures