Infectious Diseases and Immunology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What term describes the physical & chemical barriers and cellular defences e.g. skin, mucus, tears, digestive enzymes?
Innate (general) immune system
What term describes active & passive immunity?
Adaptive (specialised) immune system
Do the eyes have a low innate immunity? Why/why not?
Yes as the inflammatory immune response is limited to prevent vision impairment
What is present in both the innate & adaptive immune system?
White blood cells
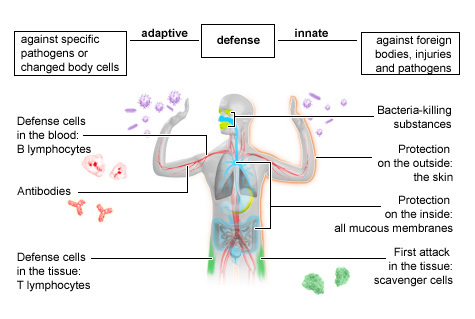
What term describes the body’s rapid, non-specific defence against pathogens?
Immediate response
What term describes the quicker response due to memory cells?
Learned response
Which cell causes inflammation by releasing chemicals e.g. histamine & recruits other cells to the location?
Mast
Which cell carries out phagocytosis & recruits other cells to the location?
Neutrophil
Which cell carries out phagocytosis & digests pathogens, dead cells, and debris?
Macrophage
Which cell identifies cells that have been infected by pathogens i.e. infected host cells, & tumour cells and destroy them?
Natural killer (NK)
Which cell moves from the site of infection to the lymphoid system & activates the adaptive immune system (what vaccinations mainly rely on)?
Dendritic
Which cell activates the adaptive immune system by travelling to the site of infection & interacting with the innate immune system?
T-helper lymphocyte (CD4+)
Which cell is similar to NK cells but require activation?
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CD8+)
Which cell remembers the interaction made by CD4+ cells when the same infection returns and matures into cytotoxic cells?
T-memory lymphocyte
Why do we need booster vaccines?
Because T-memory cells tend to forget the interaction made by CD4+ cells
Which cell interacts with CD4+ cells and matures into plasma cells which quickly produce specific antibodies to particular antigens, and memory cells?
B cells
What term describes any pathogenic microorganism/entity that can invade a host & trigger an immune response, potentially leading to disease?
Infectious agent
What do infectious agents possess in order to be recognised by the host’s immune system?
Antigens
What gives a positive result in a Gram stain test (retains crystal violet dye & remains purple) as it has a thick peptidoglycan cell we all & no outer membrane?
Gram-positive bacteria
What gives a negative result in a Gram stain test (appears red/pink) as it has a thinner peptidoglycan cell wall and an outer membrane?
Gram-negative bacteria
What term describes an acellular nucleic material that contain either DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat (capsid)?
Virus
Why are viruses considered non-living?
Requires a host to reproduce
Which viruses are most common?
Polyhedral & spherical
What term describes no-phototropic eukaryotic microorganisms with a rigid cell wall?
Fungi
Some fungi are?
Symbiotic
What are fungal infections caused by?
Yeast or mould
When do fungal infections occur?
When immunocompromised
Where are fungal infections most commonly found?
In the nails or the skin
What is ‘furry tongue’ caused by?
Smoking
What term describes eukaryotic, unicellular, motile microbes?
Protozoa
How are protozoa classified?
By their means of locomotion (movement or the ability to move from one place to another)
What type of disease do protozoa cause a lot of?
Water-borne
What term describes dynamic relationships where the host & pathogens influence each other’s survival, often leading to disease?
Host-pathogen interactions
What do host-pathogen interactions involve?
Complex molecular, cellular, immunological responses from the host’s immune system to combat invading microbes
Why are immunosuppressants sometimes given?
Due to overactivity of the immunological response which may damage host cells e.g. myelin sheath of nerve cells
What term describes a set of six intertwined links that allow for communicable diseases to spread?
Chain of infection
What does the chain of infection include?
Infectious agent
Reservoir
Port of exit
Mode of transmission
Portal of entry
Susceptible host
What term describes a microorganism that can cause disease/infection?
Infectious agent
What term describes where microorganisms live without causing infection to humans e.g. cholera in water, Covid-19 in bats?
Reservoir
What term describes how microorganisms leave the reservoir e.g. sneezing in influenza?
Port of exit
What term describes the action that causes microorganisms to enter the body e.g. hands touching the eyes after touching a surface infected by influenza?
Mode of transmission
What term describes the opening where the pathogen may enter e.g. nose, eyes, mouth, wounds?
Portal of entry
What term describes someone at risk of infection?
Susceptible host
What will happen if the chain of infection is broken at any time?
Infection will not occur
The earlier the chain of infection is broken…?
The less risk & more cost-effective