Exam 1 Quiz 2
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
glial cells/glia/neuroglia
nonneuronal brain cells that provide structural, nutritional, and other types of support to the brain
thought that neurons were continuous with one another, forming a nearly endless network of connected tubes through which information flowed
Was each neuron in the brain a discrete information-processing component? Or did cells of the nervous system become fused together?
Camillo Golgi (1843-1926)
exploiting Golgi’s staining techniques, to create precise pen-and-ink studies of neurons, he proposed that although neurons come very close to one another (i.e. they are contiguous), they are not quite continuous with one another. At each point of contact between neurons, a tiny gap keeps the cells separate
Was each neuron in the brain a discrete information-processing component? Or did cells of the nervous system become fused together?
Santiago Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934)
neuron doctrine
neurons and other cells of the brain are structurally, metabolically, and functionally independent
information is transmitted from neuron to neuron across tiny gaps
synapses
the tiny gap between neurons where information is passed from one to the other
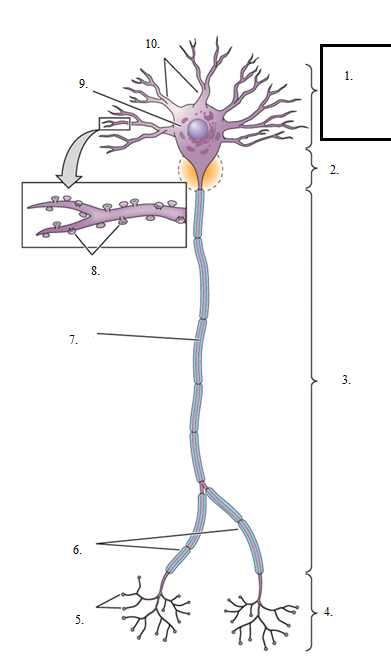
cell body/soma
the region of a neuron that is defined by the presence of the cell nucleus
input zone
where neurons collect and process information, either from the environment or from other cells
dendrites
one of the extensions of the cell body through which synaptic inputs are received; some neurons have very elaborately branched ones, providing room for many synapses
integration zone
where the decision to produce a neural signal is made by combining the information the neuron has received; contains the cell body
conduction zone
where information can be electrically transmitted over great distances/may be actively propagated; usually corresponds to the cell’s axon
axon
a single extension from the nerve cell that carries action potentials from the cell body to other neurons
axon collaterals
a branch of an axon from a single neuron
output zone
the part of a neuron, usually corresponding to the axon terminals, at which the cell sends information to another cell; where the neuron transfers information to other cells
axon terminals/synaptic bouton
the end of an axon or axon collateral, which forms a synapse on a neuron or other target cell
motor neurons/motoneurons
a nerve cell in the brain or spinal cord that transmits motor messages, stimulating a muscle or gland
sensory neurons
a neuron that is directly affected by changes in the environment, such as light, odor, or touch; carry messages from peripheral tissue back to the spinal cord and brain
interneurons
a neuron that is neither a sensory nor a motor neuron; it receives input from and sends output to other neurons; the vast majority of neurons in the brain, featuring complex dendrites and relatively short axons
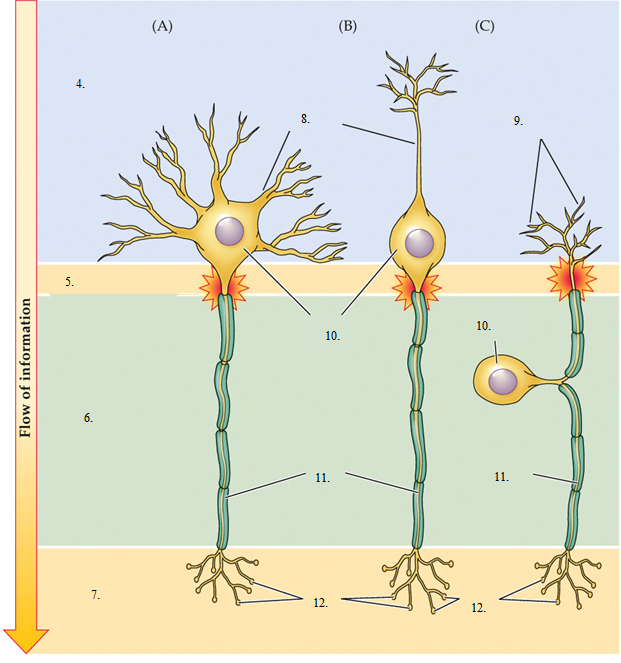
multipolar neurons
a nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon; the most common type of neuron
bipolar neurons
a nerve cell that has a single dendrite at one end and a single axon at the other end; especially common in sensory systems
unipolar/monopolar neuron
a nerve cell with a single branch that leaves the cell body and then extends in two directions; one end is the receptive pole, the other end the output zone; transmit touch information from the body into the spinal cord
cell body
In multipolar and bipolar cells, the …. also receives synapses and so is also part of the input zone
arborization
the elaborate branching of the dendrites of some neurons; this reflects the complexity of the neuron’s information-processing
presynaptic
referring to the region of a synapse that releases neurotransmitter
postsynaptic
referring to the region of a synapse that receives and responds to neurotransmitters
presynaptic membrane
the specialized membrane of the axon terminal of the neuron that transmits information by releasing neurotransmitter
synaptic cleft
the space (20-40 nm) between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
postsynaptic membrane
the specialized membrane on the surface of the cell that receives information by responding to neurotransmitters from a presynaptic neuron
synaptic vesicles
a small, spherical structure that contains molecules of neurotransmitters (30-140 nm)
synaptic transmitter/chemical transmitter/transmitter
the chemical released from the presynaptic axon terminal that serves as the basis of communication between neurons
neurotransmitter receptors
specialized protein molecules that stud the postsynaptic membrane, where they capture and react to molecules of the neurotransmitter
cognate
matching receptor of a neurotransmitter molecule
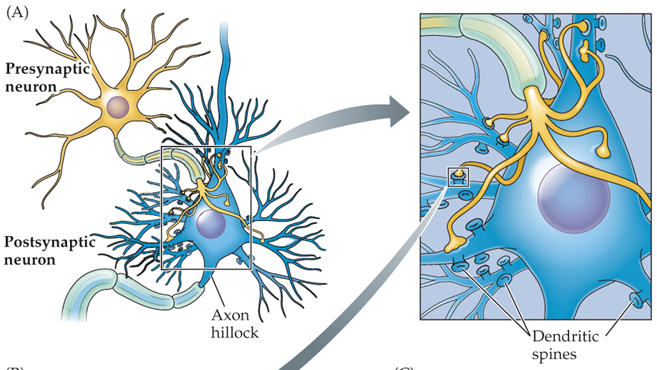
dendritic spines
outgrowths studding the dendrites of many neurons that effectively increase the surface area of the dendrites, allowing for extra synaptic contacts
axon hillock
a cone-shaped area from which the axon originates out of the cell body; functionally the integration zone of the neuron
innervate
to provide neural input
usually one per neuron, with many terminal branches
Number of Axons
usually many per neuron
Number of Dendrites
uniform until start of terminal branching
Diameter of Axons
tapering progressively toward ending
Diameter of Dendrites
present
Presence of Hillock in axons
no hillock-like region
Presence of Hillock on Dendrites
usually covered with myelin
Sheathing on Axons
no myelin sheath
Sheathing on Dendrites
ranging from practically nonexistent to several meters long
Length of Axons
often much shorter than axons
Length of Dendrites
axonal transport
the transport of materials between the neuronal cell body and axon terminals
anterograde transport
moves materials toward the axon terminals; same direction as electrical signal
retrograde transport
moves materials back to the cell body
The rapid transmission of electrical signals along the outside of the axon (like a wire)
The much slower transportation of substances through the inside of the axon, to and from the axon terminals
2 Main Functions of the Axon
astrocyte
a star-shaped glial cell with numerous processes that extend in all directions; monitor neuronal activity and regulate blood flow to meet neural demand
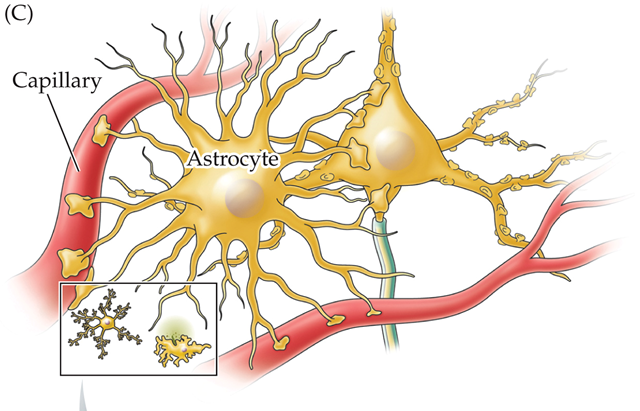
end feet
some astrocytes form these sucker-like things on blood vessels, regulating blood flow to provide more supplies to neurons when they are active
microglial cell/microglia
extremely small glial cells that remove cellular debris from injured or dead cells
oligodendrocytes
a type of glial cell that forms myelin in the central nervous system; each cell myelinates several nearby axons
Schwann cells
a glial cell that forms myelin in the peripheral nervous system; each cell ensheathes a limited length of a single axon
myelination
the process of ensheathing axons in myelin
myelin
the fatty insulation around an axon, formed by glial cells, that speeds the conduction of action potentials
nodes of Ranvier
a gap between successive segments of the myelin sheath where the axon membrane is exposed needed to propagate electrical signals
edema
the swelling of tissue, such as in the brain, in response to injury
multiple sclerosis
literally, “many scars.” A disorder characterized by widespread degeneration of myelin; demyelinating disease
within, between
Information flows …. a neuron via electrical signals. Information passes …. neurons through (most often) chemical signals
Input zone - where neurons collect and process information, either from the environment or from other cells
Integration zone - where the decision to produce a neural signal is made
Conduction zone - where information can be electrically transmitted over great distances
Output zone - where the neuron transfers information to other cells
Axon terminals
Axon collaterals
Axon
Dendritic spines
Cell body
Dendrites
Multipolar neuron
Bipolar neuron
Unipolar neuron
Input zone
Integration zone
Conduction zone
Output zone
Dendrites
Dendritic branches
Cell body
Axon
Axon terminals
axon hillock
Action potential generation is initiated at the ….
myelinated
insulated, fast-conducting
unmyelinated
non-insulated, slow conducting
Presynaptic axon terminal
Mitochondrion
Synaptic vesicles
Presynaptic membrane
Neurotransmitter molecules
Synaptic cleft
Postsynaptic membrane
Dendritic spine
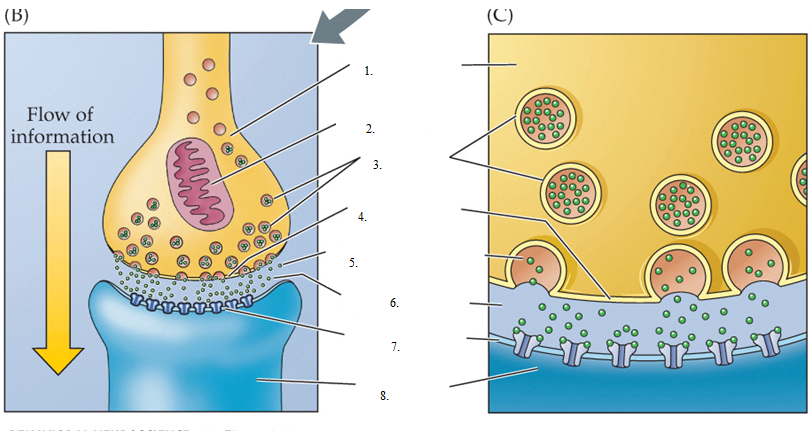
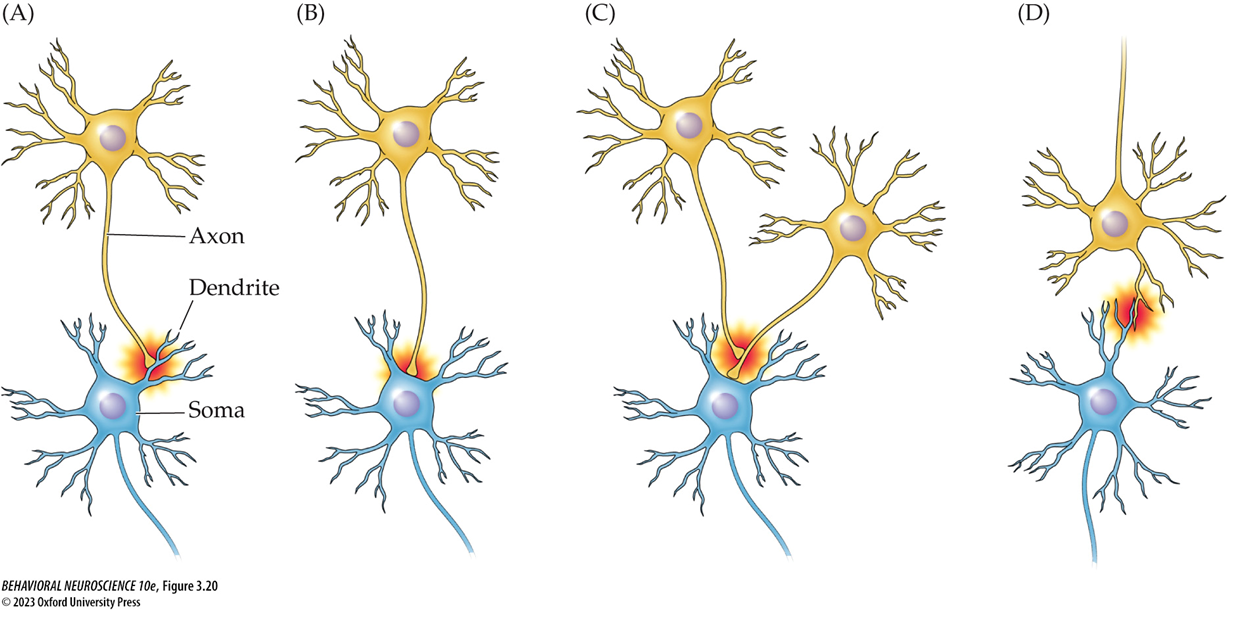
axodendritic synapse
most synapses are formed here, between a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
A) Axodendritic
B) Axosomatic
C) Axoaxonic
D) Dendrodendritic
nondirected synapses
like drip irrigation; neurotransmitters released along large sections of tissue from axonal swellings called varicosities
1. Electrostatic pressure - the force that causes oppositely charged particles to come together and causes particles with the same electrical charge to repel one another
2. Diffusion - the tendency of molecules of a substance to spread away from regions of high concentrations to regions of low concentration
3. Selectively permeable membranes - allows certain ions (like K+) to cross freely, but normally prevents other ions (like Na+) from passing through