DNA TRANSCRIPTION + TRANSLATION
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is this?
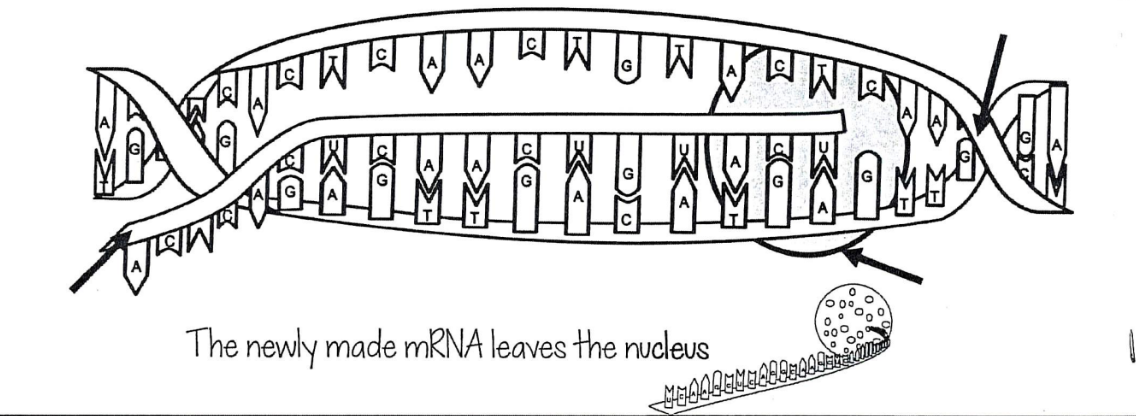
transcription (DNA → mRNA) location: nucleus | players involved: RNA polymer, TF, promoter
mRNA is also…
messenger
rNA is also…
ribosomal
tRNA is also…
transfer
what is this?
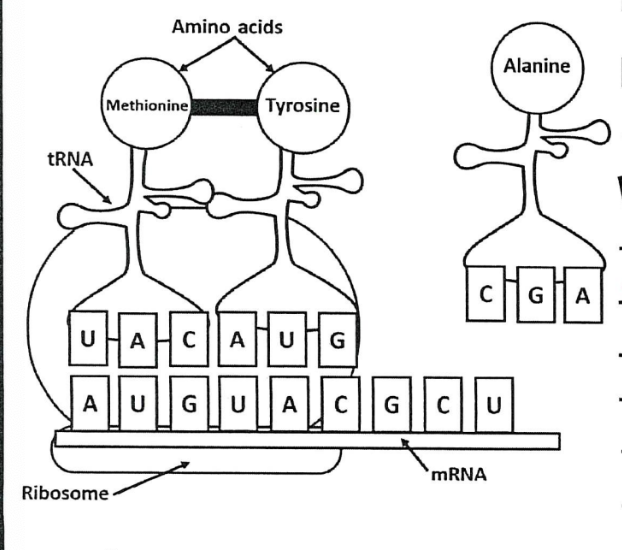
translation (mRNA → protein) location: cytoplasm / ER | players involved: ribosome, mRNA, tRNA)
what is transcription?
copying of DNA into RNA; RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and creates a complementary RNA molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA)
what is translation?
decoding of RNA into a protein; takes place in ribosomes, where mRNA is decoded into a sequence of amino acids. each three nucleotide sequence in mRNA, called codon, specifies a particular amino acid. transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the correct amino acids to the ribosome during translation
what is gene activation?
the process of turning on a gene so it can be transcribed
ribosomes
read mRNA from 5 to 3. uses that info to synthesize a protein by connecting the correct amino acids in the correct order.
what is the start codon?
AUG
coding (DNA sequence)
contains information for how to make a protein. gets read and transcribed by RNA polymerase. will complement/base pair with a specific mRNA
promoter (DNA sequence)
found directly 3’ of coding regions. attract and bind RNA polymerase, telling it where to start reading and transcribing
enhancer (DNA sequence)
bind transcription factors to help activate RNA polymerase. can found basically anywhere in the genome
RNA polymerase (DNA binding protein)
binds to promoter sequences, reads coding DNA from 3 to 5, and builds a complementary mRNA strand from 5 to 3
transcription factor (TF) (DNA binding protein)
proteins that help regulate which genes are being used when activating RNA polymerase when bound
repressors (DNA binding protein)
bind enhancers or promoters blocking TFs or polymerase, preventing that gene from being transcribed
central dogma of molecular bio
information stored in DNA gets transcribed into mRNA, and then translated into proteins; every gene codes for a specific mRNA sequence that codes for a specific protein
RNA
short single stranded nucleotide chains. contains A,U,G, and C bases. there are several types of RNA, tRNA, mRNA (t = transfer, m = messenger)
mRNA (messenger RNA)
a transcription of a DNA coding region (bases pairs with the coding sequence)> made by RNA polymerase, which reads the DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand
non coding DNA
does not contain protein information. these areas interact with DNA binding proteins to help regulate transcription (the making of mRNA)
DNA mutations
typos made by DNA polymerase while it replicates/synthesizes DNA. happen randomly all the time. most have little to no effect. some are helpful, some are harmful. mutations create all of the alleles and phenotype variation we see.
point mutations
changes to a single nucleotide, a T gets swapped out for a G, etc. or we swap out a single codon (set of 3 bases that get read together) for another. both of these change only one codon, and do not cause a frame shift.
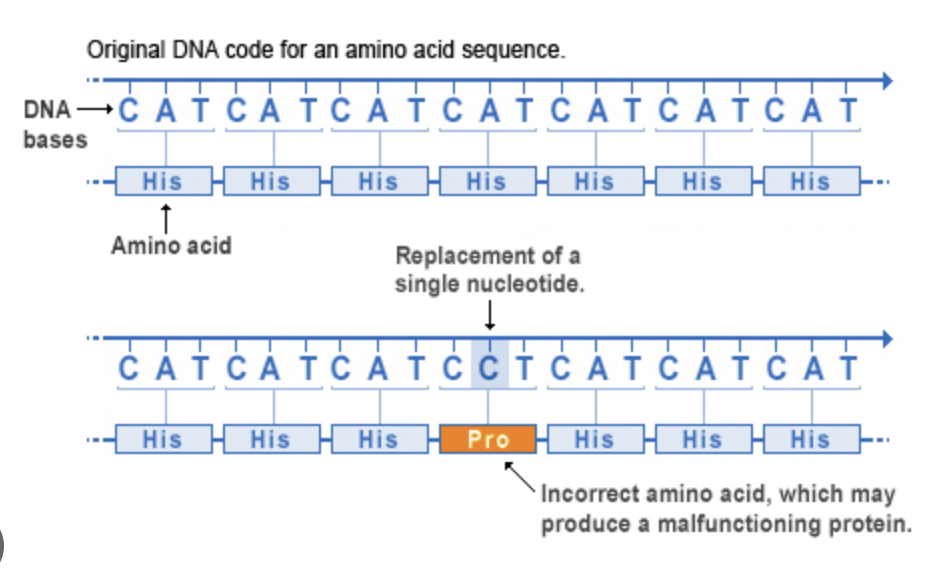
miss sense (point mutations)
changes to a base or bases that result in a single codon change, one different amino acid in your protein, does NOT cause frame shift
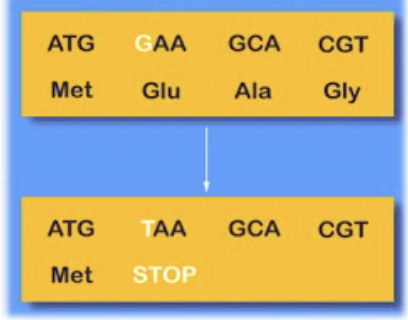
nonsense (point mutation)
change to a single base or bases that creates a stop codon where there previously was none. can be very impactful if early in the gene, does NOT cause frame shift
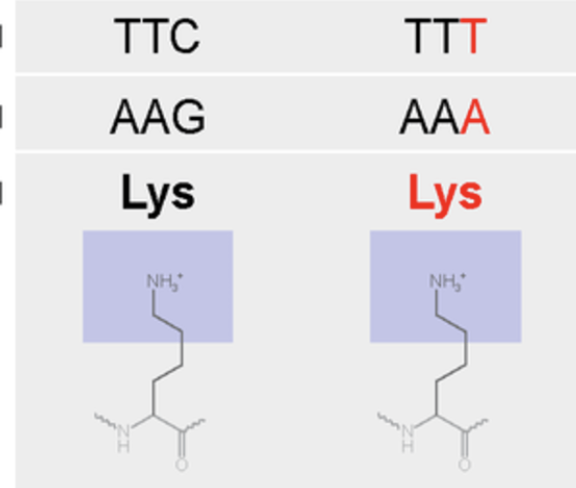
silent (protein mutations)
changes to a base or bases that don’t impact the amino acid sequence (changing out one codon that codes for valine for another codon that codes for valine), does NOT cause frame shift
frame shift mutations
adding or removing nucleotides where they were not present before. causes all of the bases after to shift position, changing multiple codons
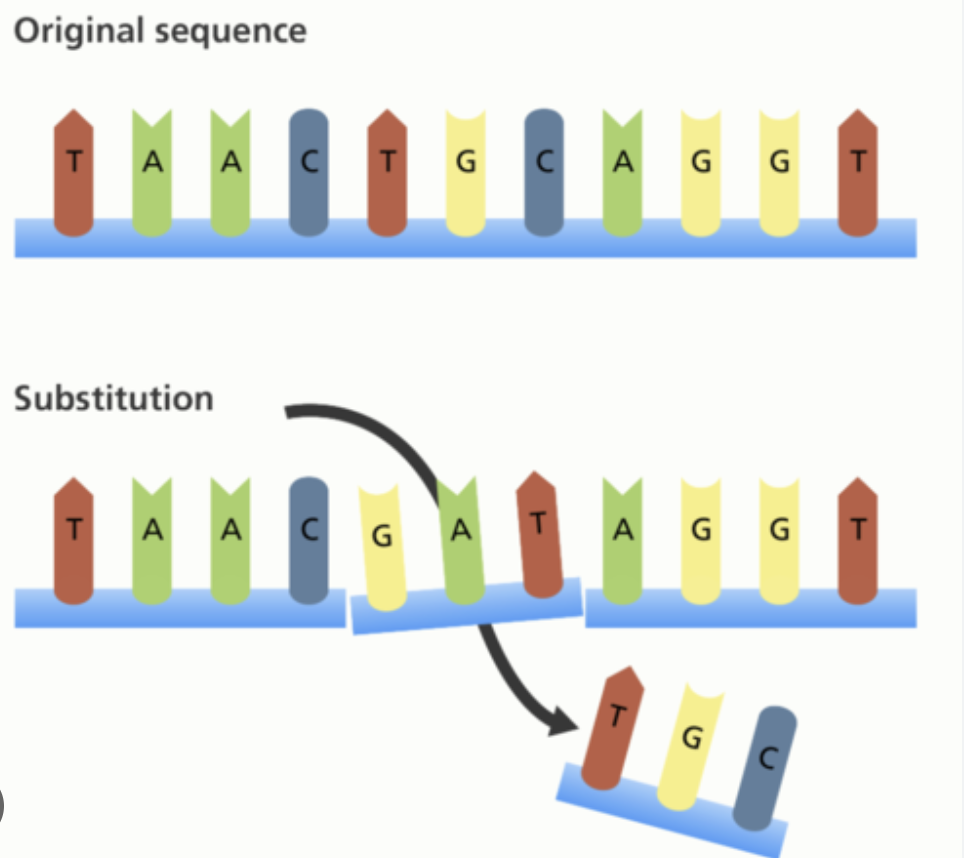
insertion (frame shift mutations)
adding a base or bases where they don’t belong (DOES cause frame shift)
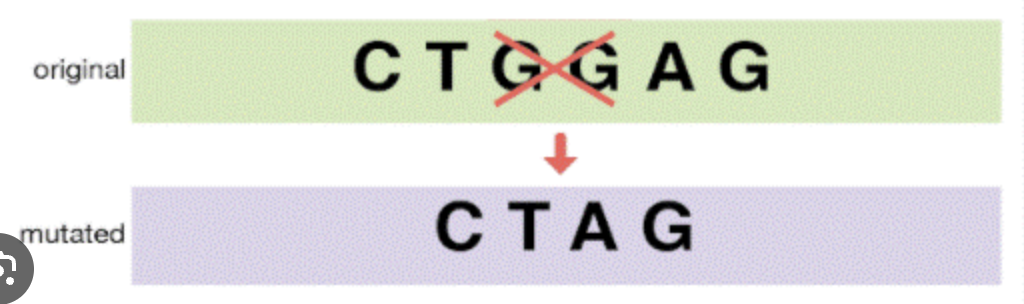
deletion
removing a base or bases (DOES cause frame shift)
loss of function mutation
any mutation that causes a large enough change in the final protein that it cannot perform its typical function (frame shifts, nonsense)