Quarter 3 Study Guide
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is the most important thing you do when trying to control severe bleeding?
Apply direct pressure with a gloved hand immediately
What is the last vital sign to change when a patient develops shock?
Blood pressure only drops significantly as the body's compensatory mechanisms fail to maintain adequate perfusion to tissues and organs
When treating injuries to the neck, what should you be most concerned about?
Neck contains many structures that are susceptible to injuries from trauma that could be deadly.
o Trachea may become torn or swell = airway problems
o JVD or tracheal deviation
o The neck also contains large BVs that supply the brain w/ blood. Injury may cause swelling and prevent blood flow to the brain or injure the CNS.
o Penetrating neck injuries may cause significant bleeding or air may be drawn into the circulatory system = air embolism = cardiac arrest
• When treating neck injuries, the most crucial concern is preventing or minimizing damage to the spinal cord. This includes securing the airway, maintaining cervical spine immobilization, and assessing neurological deficits. Early identification and management of potential spinal cord injuries are vital, as they can lead to paralysis or even death
What are the signs of intercranial bleeding?
• can manifest with a variety of symptoms, often related to the location and size of the bleeding. Common signs include severe, sudden headaches, nausea, vomiting, weakness, tingling, or numbness, especially on one side of the body. Other symptoms may include slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, vision changes, seizures, loss of consciousness, and altered mental status
Epidural hematoma:
accumulation of blood between skull & dura mater, nearly always a result of a blow to the head that produces a linear fracture of the thin temporal bone. Arterial bleed so rapidly progressing symptoms.
Pt often has immediate loss of consciousness, followed by a brief lucid interval, and then back to unconsciousness. As ICP increases, pupil on side of hematoma becomes fixed & dilated.
Subdural hematoma:
accumulation of blood beneath the dura mater but outside the brain. Usually occurs after falls or injuries involving strong deceleration forces.
Venous bleeding, so signs of ICP develop more gradually. Fluctuating LOC/slurred speech
Subarachnoid hemorrhage:
bleeding occurs into the subarachnoid space, where CSF circulates, usually caused by trauma or rupture of an aneurysm’
Sudden severe headache, and as ICP increases, decreased LOC, pupil changes, vomiting, seizures. If people survive, often have permanent neurologic impairment.
Intracerebral hematoma:
bleeding w/in the brain from a penetrating injury or rapid deceleration. High mortality.
• All cause ICP:
symptoms are Cushing reflex: triad of increased systolic BP, decreased heart rate and irregular respirations that signifies increased ICP
What are the most common mechanisms of blunt trauma?
Motor vehicle crashes and falls are the 2 most common MOIs for blunt trauma. During assessment, maintain a high index of suspicion for hidden internal injuries.
When treating gunshot wounds, does the speed or size of the bullet have a greater impact on injury?
The energy available for a bullet to cause damage is more a function of its speed than its weight. If the mass of the bullet id doubled, the energy that is available to cause injury is double, but if the speed of the bullet is doubled, the energy that is available to cause injury is quadrupled.
What happens in the body when tissue is injured? (5 steps)
Wounds heal in a natural process that involves several overlapping stages, all directed toward the larger goal of maintaining homeostasis.
To stop the flow of blood, the vessels, platelets and clotting cascade begins working
Next, comes inflammation where WBCs migrate to the area to combat pathogens. Histamine is released which dilates BVs, increasing blood flow to the injured area resulting in a reddened area immediately around the site.
A new layer of cells will be created to replace damaged cell layers
New BVs form as the body attempts to bring O2 & nutrients to the injured tissue. New capillaries bud from intact adjacent capillaries
Collagen is created in the last stage of wound healing to provide stability to the damaged tissue and join wound borders thereby closing the open tissue
How are burns classified and know how to use the rule of nines and how to measure burns.
Superficial burns (1st degree): involve only the top layer of skin (sunburn is an example), no blisters, skin is red and painful
Partial-thickness burns (2nd degree): involve the epidermis and some portion of the dermis, skin is moist, mottled and white to red. Blisters are present, intense pain
Full-thickness (3rd degree): extend through all skin layers and may involve subcutaneous layers, muscle, bone or internal organs. Burned area is dry, leathery, and may appear charred.
When calculating the extent of burns, only include partial and full-thickness burns.
Can also use the rule of palm: size of patient’s palm, including fingers, is roughly 1% of the patient’s TBSA
Describe and fill it out. (We are gonna suggest that the kid is actually a baby)
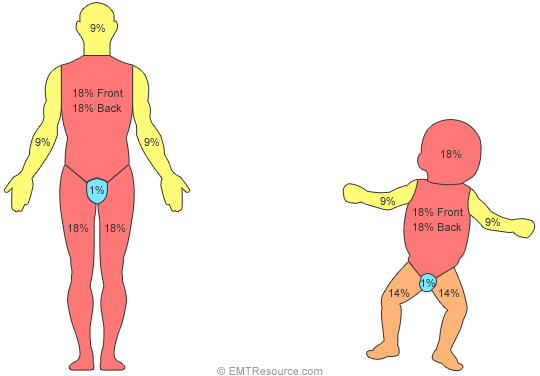
The rule of 9s!
The back consists of 18% (including the thoracic and lumbar regions) and abdomen which are both 9%) the front of the trunk is 18% (chest and abdomen)
Each leg is 18% (front and back are each 9%)
Each arm is 9% (4.5% each side)
The head is 9%
genitalia: 1%
The baby is:
(same) The back consists of 18% (including the thoracic and lumbar regions) and abdomen which are both 9%) the front of the trunk is 18% (chest and abdomen)
(same) Each arm is 9% (4.5% each side)
(same) genitalia: 1%
(different) Each leg is 14% (front and back are each 7%)
(different) The head is 18%
Why do we check pupils?
The diameter and reactivity to light can reflect the status of the brain’s perfusion, oxygenation and condition. Presume abnormal pupillary response indicates altered brain function as a result of CNS depression or injury.
Possible causes of unequal pupils include (6):
Use of over-the-counter eye drops
Certain asthma inhalers (if inadvertently sprayed into the eye)
Brain injury
Nerve disease
Glaucoma
Meningitis
What should your priority treatment be when there is any type of fluid in the mouth?
Ensure a clear airway and prevent aspiration. This involves suctioning the airway to remove the fluid and preventing it from entering the lungs. If the patient is unconscious or has difficulty breathing, advanced airway maneuvers like intubation may be necessary
What can cause a lack of pulse after a direct blow to the chest?
Commotio cordis: blunt chest injury caused by a sudden, direct blow to the chest over the heart that occurs during a critical portion of a person’s heartbeat that causes a lethal vfib. Most often sports related and often immediate cardiac arrest
Other potential causes include cardiac tamponade (fluid buildup around the heart) or a rupture of a heart chamber
What are the signs of a cardiac tamponade? (3)
1) Pericardial sac fills w/ blood or fluid, so the heart is less able to fill w/ blood during each relaxation period, so it can’t pump adequate amounts of blood. LOW BP!
2) Beck triad: distended/engorged jugular veins on both sides, narrowing pulse pressure and muffled heart sounds
3) Decreased mental status due to decreased blood flow to brain, also chest pain, shortness of breath
Explain what needs to be done for a sealed chest would if the patient complains of increased discomfort, change in vitals or difficulty breathing?
“Burp” the wound: briefly lift the flap to allow air to escape
If a patient has a C7 injury what would that most likely result in?
A C7 spinal cord injury most likely results in some degree of paralysis affecting the upper and lower extremities, along with potential bowel and bladder dysfunction. While some individuals with C7 injuries may retain some degree of arm and hand function, it's crucial to understand that the specific functional outcomes can vary depending on the severity and type of injury
For C1-C5, describe the type of injury to each 7
C1-C3: Difficulty breathing (C1 completely gets rid of this, C2 impairs and paralyzes from the neck down)
C3: Difficulty breathing and potential paralysis
C4: Reduced Diaphragm function
C5; paralysis and reduced lung capcity
How much blood can be lost w/ a femur fracture?
As much as 500-1000 mL (1 L or 2 units).
At what temperature does the body lose its ability to shiver?
When the core temp of the body is less than 90 degrees F (32.2 degrees C)
Know the types of pit vipers (3)
Rattlesnakes: can grow to 6 ft, often have a diamond pattern, rattle on tail, most common in US
Cottonmouths: approx. 4ft, aka water moccasins, olive or brown w/ black cross-bands and yellow undersurface. Fatalities are rare, but tissue destruction is severe.
Copperheads: 2-3 ft long w/ red-copper color crossed w/ brown or red bands. Live in wood piles/abandoned dwellings. Account for most venomous snake bites in eastern US, but almost never fatal
Swelling & ecchymosis appear in ______ min. Venom destroys tissues and can interfere with clotting, affects entire nervous system.
Swelling & ecchymosis appear in 5-10 min. Venom destroys tissues and can interfere with clotting, affects entire nervous system.
Signs following pit viper bites
Weakness, nausea, vomiting, sweating, seizures, fainting, vision problems, change in LOC, shock.
What is the difference between Lyme & Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
Lyme Disease: first symptoms are usually fever/flulike, bulls eye rash that may spread. After a few days/weeks, get painful swelling of joints (esp knees). Often confused w/ rheumatoid arthritis. If not recognized and treated promptly w/ antibiotics, pt may never recover completely.
Rocky Mtn Spotted Fever: occurs w/in 7-10 days after a bite. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, headache, weakness, paralysis and possible CV collapse
What does a brown recluse and a black widow spider look like?
Black widows are glossy black w/ bright red-orange hourglass marking on abdomen
Bite is neurotoxic: dizziness, sweating, nausea, vomiting and rashes. Tightness in chest and difficulty breathing can develop within 24 hrs, as well as cramping and board like rigidity of ab muscles
Brown recluse: dull brown and have dark violin-shaped mark on the back
Bite is cytotoxic, causing severe local tissue damage. Rarely causes systemic S/S, but cause a scab of dead skin, fate and debris and digs down into skin producing a large ulcer
How do you officially transfer a patient from EMT to the hospital?
Initiate eye contact, manage the environment, ensure the ABCs, provide a structured report & provide documentation
What is the treatment for Anaphylactic reaction?
Manage the airway, assist with ventilations, administer high-low O2, determine cause, assist w/ Epi, transport promptly and consider ALS
What is Psychogenic shock, what are the main signs, and
Sudden reaction of the nervous system that produces a temporary generalized vasodilation, resulting in syncope (temporary). Syncope occurs when blood pools in dilated vessels, reducing blood supply to the brain, causing the brain to suddenly stop functioning normally. After pt faints, normal function is restored.
Pt will have a rapid pulse and normal/low BP
Can significantly worsen other types of shock – do not assume the fainting was caused by psychogenic shock alone
Treatment is to determine the duration of unconsciousness, place the pt supine, record initial vitals and LOC, suspect head injury if pt is confused or slow to regain consciousness, transport promptly
What is the treatment for Spinal Injury?
Be aware of any unnecessary movement and assess pt in position found. After correcting any life-threatening injuries (XABCs), manually hold spinal stabilization and determine whether a cervical collar needs to be applied, and apply appropriate sized collar. Apply high-flow O2 and assess LOC, rapid assessment to identify DCAP-BTLS, PMS, etc. Use appropriate moving device (backboard, vacuum mattress, KED, scoop to lift patient to stretcher.
For an unconscious patient with a suspected spinal injury, the primary treatment involves immediate stabilization of the spine and airway management
What is the treatment for Nosebleed(3 steps)?
Position the pt sitting, leaning forward and apply direct pressure, pinching the fleshy part of the nostrils together
• Alternative method is to apply pressure w/ a rolled gauze bandage between the upper lip and the gum. Calm the pt.
• Apply ice over the nose and maintain pressure until bleeding is controlled. Initiate prompt transport while you or pt continues to apply pressure. Assess/treat for shock, including O2, as needed.
What is the treatment for severe bleeding from the groin area (both men and women)?
The area is highly vascular so control XABCs, monitor for tachycardia, tachypnea, low BP, weak pulse, cool, moist, pale skin = shock. The area also has a rich nerve supply, so injuries will be painful.
• Men: Injuries are very painful, but rarely a life threat. Local direct pressure with a moist, sterile dressing. Bring any amputated or avulsed parts with you to the ED wrapped in a moist, sterile dressing in a plastic bag, kept cool.
• Women: Local compression, moist sterile dressings. Do not pack vagina and leave any foreign bodies in place. You can use a sanitary pad to absorb blood also. Wrap a diaper style gauze bandage to hold compression dressings in place.
o If pregnant, rich blood supply to uterus, and it is enlarged so subject to both penetrating and blunt injuries. Place pt on left side to relieve pressure on vena cava and treat for shock.
What signs of shock should you monitor for when treating severe bleeding to groin
tachycardia, tachypnea, low BP, weak pulse, cool, moist, pale skin = shock.
What is the treatment for abdominal evisceration?
• Place sterile dressing moistened w/ normal saline over the wound, apply a bandage (sometimes an occlusive bandage) and rapid transport. Never attempt to push tissue/organs back into the abdominal cavity.
• Pt will experience loss of body heat, so keep affected areas warm. Pt will also lose fluid rapidly, so keep area moist.
• Avoid using adherent materials
What is the treatment for avulsions?
Injury that separates various layers of soft tissue so they become completely detached or hang as a flap
• Replace the flap in its original position as long as it isn’t visibly contaminated w/ dirt/foreign material. Never remove the flap
• If it is completely detached, wrap the separated tissue in steril gauze and take it with you to the ED.
What is the treatment for eye injuries – chemical?
Hold the eyelid open w/out applying pressure over the globe of the eye and flood w/ a gentle stream of water. Flush from the inside corners to the outside to prevent cross contamination. If only 1 eye has been affected, turn the pt’s head to that side and flush. If both eyes have been affected, consider hooking up a nasal cannula to a bag of saline to flush both eyes simultaneously
• Continue flushing en route to the hospital
What are the symptoms of kidney injury?
May or may not see bruises or lacerations, blood in the urine (hematuria). Treat for shock and provide rapid transport
• Can also see changes in urination (like decreased output or frequent urination at night), swelling in the legs and feet, high blood pressure, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes blood in the urine. In severe cases, symptoms may include difficulty breathing, confusion, and seizures
What are the symptoms of frostbite?
When exposed body parts become frozen, permanently damaging cells
o Superficial frostbite, only the skin becomes frozen
o Deep frostbite, deeper tissue can become frozen as well
• Signs/Symptoms make take several days to develop and it may be hard to distinguish between superficial and deep
• Affected tissues will have a hard, waxy feel, and will feel firm to frozen
• Necrosis or gangrene
• In most cases, move pt from cold environment, do not allow pt to walk to prevent further injury to feet, remove wet clothing, place dry blankets over and under pt, remove jewelry from affected part, and cover w/ loose, soft, dry sterile dressing, do not rub or break blisters
What are the symptoms of labored breathing?

Define Septic Shock:
occurs because of severe infections (usually toxins from bacteria). Toxins damage vessel walls increasing cellular permeability = widespread dilation of vessels in combination w/ plasma loss
• s/s include warm/fever, tachycardia, low BP
• Treatment is prompt transport, administer high-flow O2 or assist ventilations, keep pt warm and consider ALS
Define Obstructive shock
Define the revised trauma scale
A score using gsc, rr, and systolic bp
Define arterioles
• The smallest branches of arteries leading to the vast network of capillaries, the site of gas and nutrient exchange.
• Arterioles are crucial for regulating blood flow and blood pressure by adjusting their diameter, acting as the primary source of systemic vascular resistance in the circulatory system. They control how much blood reaches specific tissues and organs, ensuring adequate delivery of oxygen and nutrients
• Arterioles play a critical role in maintaining overall bodily homeostasis by ensuring adequate tissue perfusion and regulating blood pressure
Hypertension, winding pulse pressure, bradycardia
Visclera pluera vs. porietal
Lines the organs vs. lines the cavity
unresponsive with snoring respirations + amputated arm jest below the elbow. HWat do you do?
apply tourniquet to the amputated limb to control bleeding.
treatment for full thickness burns
dry, sterile dressings, keep patient warm
a 40-year-old ma has burns to the entire head, anterior chest, and both anterior upper extremities. What is his percentage?
27%
An adult patient opens his eyes in response to a painful stimulus, moans when you ask him questions, and pulls his arm away when you palpate it. What is his GCS?
8
2 for pain response
4 for withdrawing
and 2 for verbal
A Scuba Diver complaints of shortness of breaths, severe muscle and joint pain after ascending from a dive. He is cyanotic and is coughing bloody froth. What is it? A) Air embolism, B) Decompression sickness C) Tension Pneumothorax, D) Diving Reflex
Air embolism: a serious condition caused by air bubbles entering the bloodstream after rapid ascent, leading to potential obstruction of blood vessels.
Define hemophilia
Define hemophilia
• Blood lacks one or more clotting factors, most forms are hereditary and some are severe.
• Pt can sometimes occur spontaneously
• Because blood does not clot effectively, all injuries, no matter how trivial, are potentially serious. Transport immediately
Define abrasion (aka road rash)
Define abrasion (aka road rash)
• A wound of the superficial layer of the skin, caused by friction when a body part rubs or scrapes across a rough or hard surface.
• Usually doesn’t penetrate completely through the dermis, but blood may ooze from the injured capillaries in the dermis
• Painful because lots of nerve endings are exposed
Define laceration
• A jagged cut in the skin caused by a sharp object or a blunt force that tears the tissues
Define retrograde amnesia
A pt w/ a concussion who can remember everything but the events leading up to the injury. YOU CANT REMEMBER BEFORE THE EVENT
Define reflex arc
• In connecting sensory & motor nerves of limbs, the connecting nerves in the spinal cord form the reflex arc. If a sensory nerve in this arc detects an irritation stimulus, it will bypass the brain and send a message directly to a motor nerve, causing a response
You bypass your brain since the stimuli is recognized by a nerve in your spine
Define Intracerebral hematoma and what are the signs?
• Intracerebral hematoma: bleeding w/in the brain from a penetrating injury or rapid deceleration. High mortality.
• ICP, Sudden, severe headaches, neurological defects(weakness/numbness, esp on 1 side of the body, slurred speech, vision problems) , changes in LOC, nausea/vomiting, seizures,
Define autonomic nervous system
Define autonomic nervous system
• Controls involuntary activities
• divided into sympathetic (fight or flight, pupils dilate, smooth muscle in lungs dilate, heart rate increases, BP rises) and parasympathetic (rest & digest: BVs dilate, heart rate slows) nervous systems
Define pleural fluid
• a thin, serous fluid found in the pleural space, which is the space between the lungs and the inner chest wall. It acts as a lubricant, allowing the lungs and chest wall to slide smoothly during breathing. A buildup of this fluid, calledpleural effusion, can occur due to various reasons, including infections, cancer, or heart failure
Define colles fracture
Fracture of the distal radius, esp common in older pts w/ osteoporosis.
• Aka silver fork deformity due to the distinctive appearance of pt’s arm
Define direct injury
• an injury caused by an external force, where the impact or force is directly applied to the injured area. Examples include being hit by a ball in sports, a collision during a tackle, or being struck by an object. These injuries often involve bruising, broken bones, or dislocations
Define mobile integrated healthcare (MIH) model
Define mobile integrated healthcare (MIH) model
A type of preventive care
• Method of delivering health care that utilizes the prehospital spectrum of care resources. Goal is to facilitate improved access to health care at an affordable price.
• Health care is provided w/in the community rather than at a physician’s office/hospital. Integrated team of health care professionals (incl. EMS) delivers health care services in the community, connects pts w/ other valuable resources.
• Advantage is that if offers access to care for pts w/in communities who may have limited medical resources, and better service to those who are homebound or disabled.
Distal
• Farther from the trunk or nearer to the free end of the extremity
Define medial
• Closer to the midline
Define lateral
• Farther from the midline