Blood Supply to the Brain
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
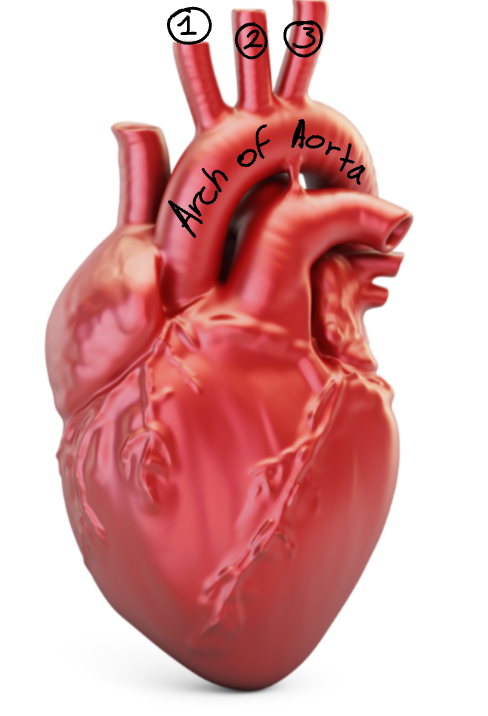
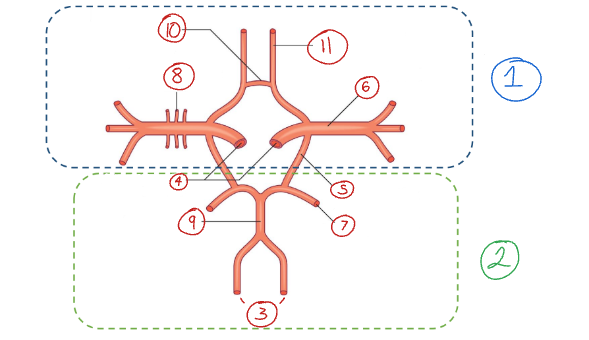
Label this diagram of the aortic arch.
Brachiocephalic trunk
Left common carotid a.
Right subclavian a.
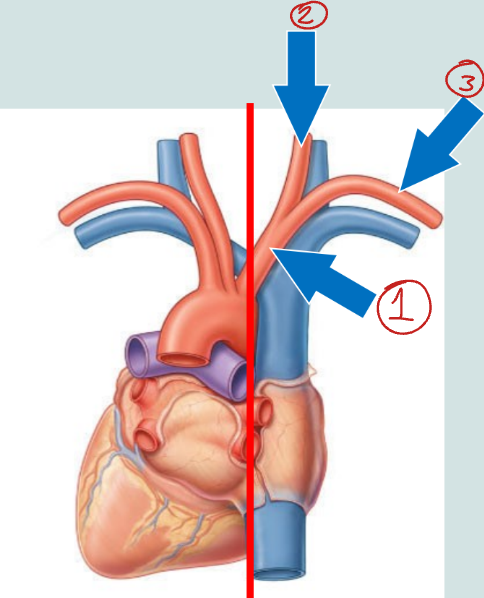
Label this diagram.
Brachiocephalic trunk
Right common carotid a.
Right subclavian a.
What are the branches on the aortic arch called?
Brachiocephalic trunk
Left common carotid a.
Right subclavian a.
What does the brachiocephalic trunk bifurcate into?
Right common carotid a.
Right subclavian a.
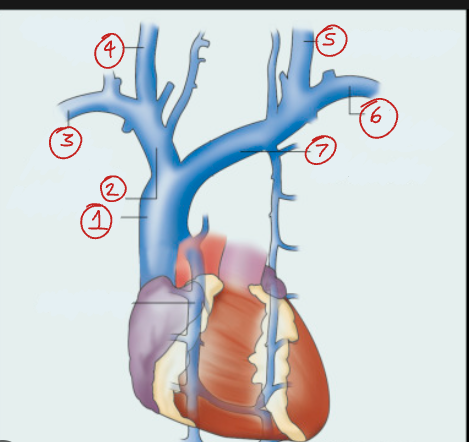
Label this diagram of the venous supply to the heart.
Superior vena cava
Right brachiocephalic v.
Right subclavian v.
Right internal jugular v.
Left internal jugular v.
Left subclavian v.
Left brachiocephalic v.
What is another name for the brachiocephalic vs.?
Innominate vs.
What are the names of the veins that join to form the superior vena cava?
Right brachiocephalic v.
Left brachiocephalic v.
What veins join together to form the brachiocephalic vs.?
Internal jugular vs.
Subclavian vs.
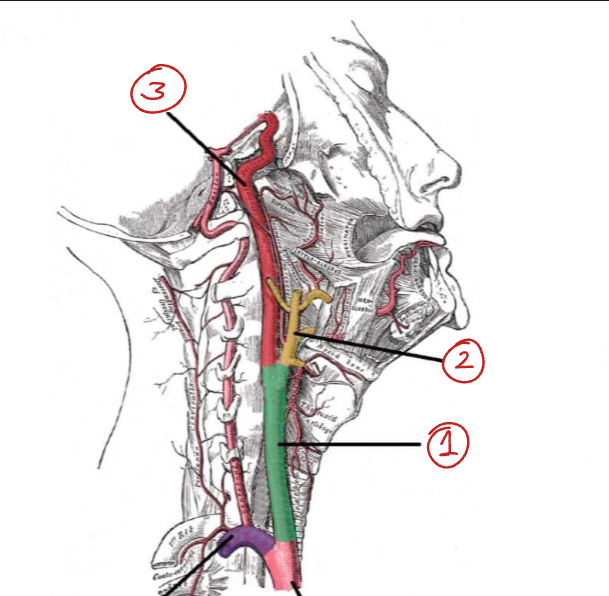
Label this diagram of the important structure that runs from the arch of the aorta to the base of the skull.
Carotid sheath (connective tissue)
Common carotid a.
Internal jugular v.
Vagus nerve
Which muscle is located anterior to the carotid sheath?
The sternocleidomastoid.
What does the common carotid a. bifurcate into?
Internal and external carotid as.
Common carotid a.
External carotid a.
Internal carotid a.
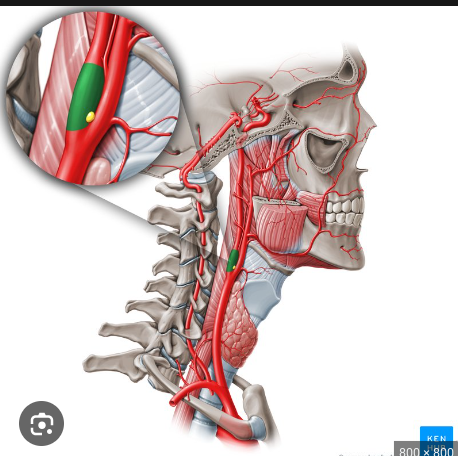
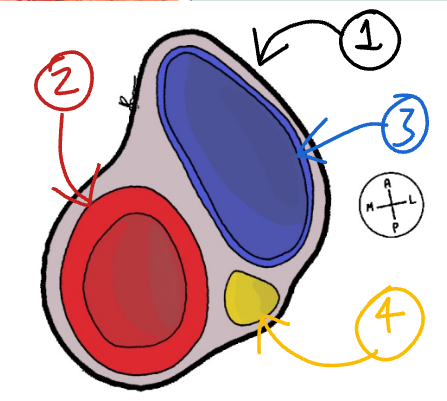
What are the structures labelled in green and yellow called?
Green - carotid sinus
Yellow - carotid body
Carotid body function
The carotid bodies can detect changes in the quality in the composition of arterial blood flow, such as pH, CO2, temperature, and partial pressure of arterial oxygen.
Where does the internal carotid a. enter the skull?
The carotid canal.
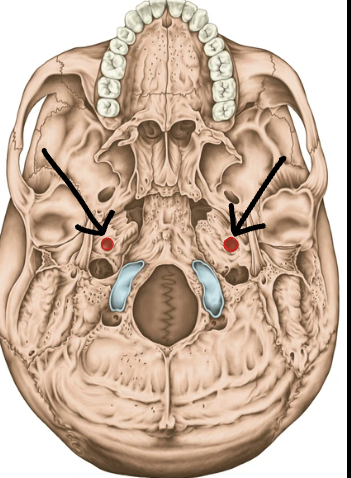
What are these structures called?
The carotid canals.
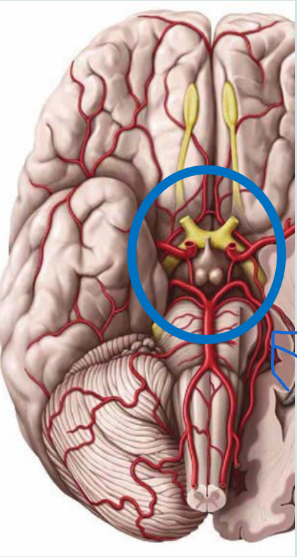
What is this structure called?
The cerebral arterial circle / circle of Willis
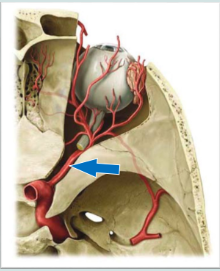
What is the name of this blood vessel, and what artery does it branch off of?
It is called the opthalmic artery, and it branches off of the internal carotid artery.
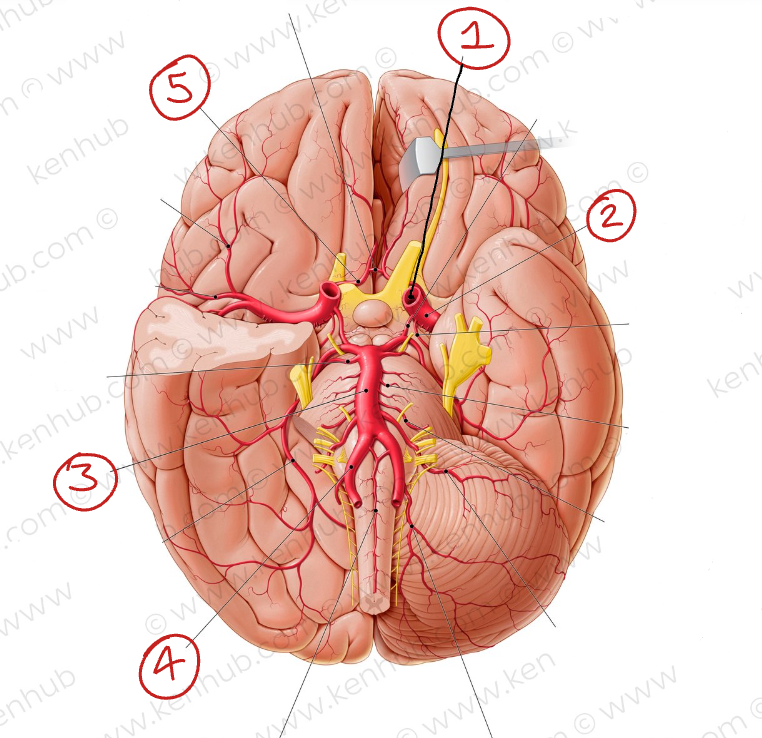
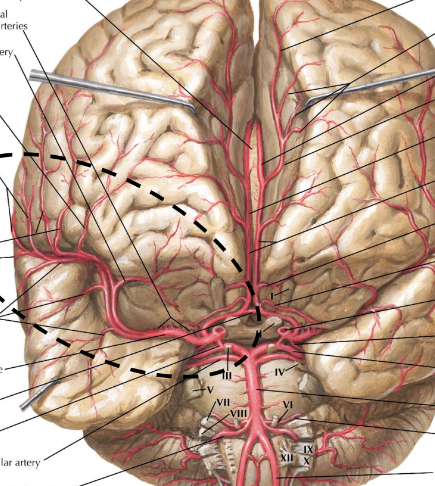
Label these blood vessels
Internal carotid a.
Middle cerebral a.
Basilar a.
Vertebral a.
Anterior cerebral a.
What does the internal carotid a. bifurcate into?
Middle cerebral a.
Anterior cerebral a.
What is the venous drainage for the brain and meninges called?
Dural venous sinuses.
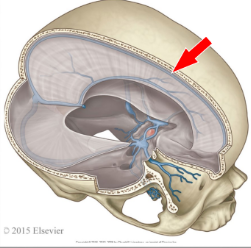
What are these structures called?
The dural venous sinuses
What are the three main jugular vs. called?
Internal jugular v.
External jugular v.
Anterior jugular v.
What veins join together to form the subclavian v.?
Retromandibular v.
Posterior auricular v.
Occipital v.
Facial v.
External jugular v.
Internal jugular v.
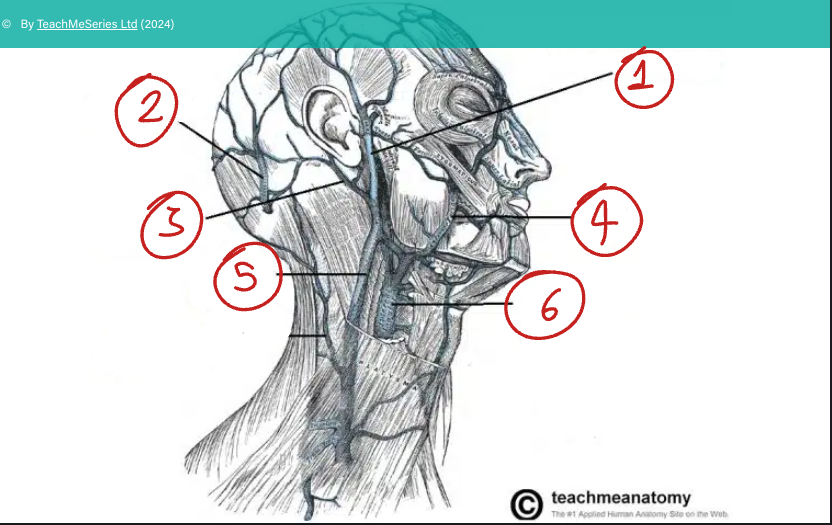
Where do the external and anterior jugular veins drain into?
The subclavian v.
Where do the dural venous sinuses drain into?
The internal jugular vein.
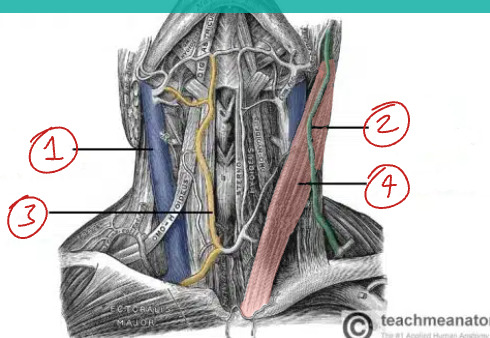
Label this diagram of the veins in the neck.
Internal jugular v.
External jugular v.
Anterior jugular v.
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Which vein is deep to the sternocleidomastoid?
The internal jugular v.
Which vein is superficial to the sternocleidomastoid?
The external jugular v.
What are the 2 main arteries that supply the brain that travel up the neck from the aorta?
The internal carotid a. and the vertebral a.
What doe the vertebral arteries branch off of?
The subclavian arteries
What does the vertebral a. travel up the neck within?
It travels within the bony foramina of the cervical spine
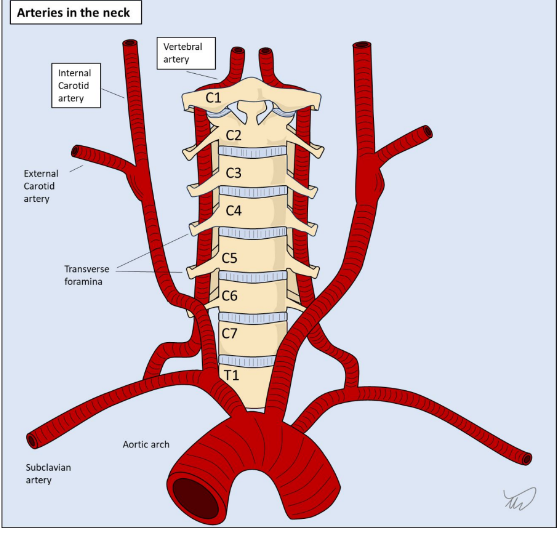
The vertebral arteries connect to which artery?
The basilar a.
Is there a connection between the carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries?
They anastomose.
The circulation of the brain can be split into 2 sections called what?
Anterior and posterior.
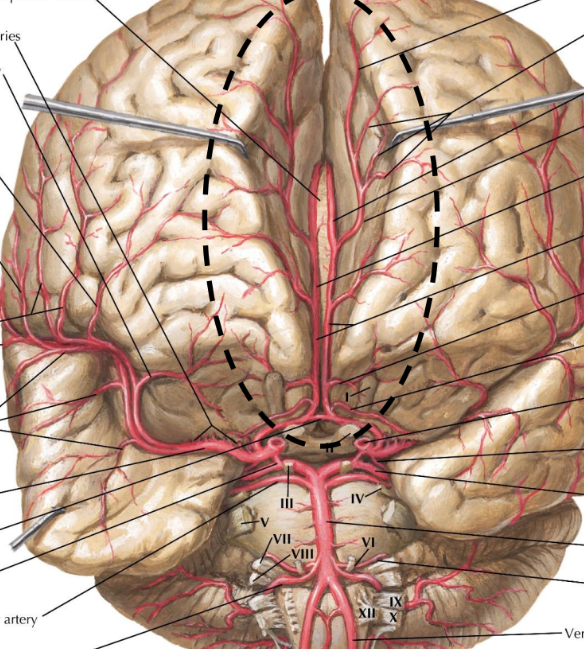
Label this diagram of the circle of Willis
Anterior circulation
Posterior circulation
Vertebral arteries
Internal carotid arteries
Posterior communicating artery
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Small perforating vessels
Basilar artery
Anterior communicating artery
Anterior cerebral artery
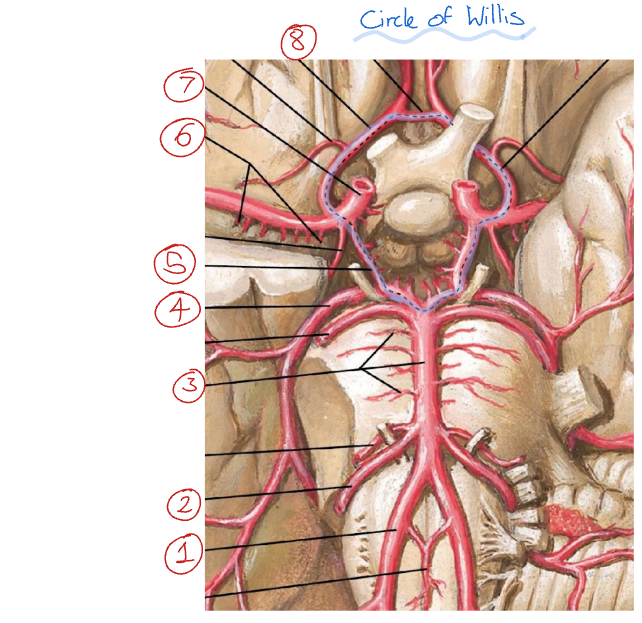
Label this diagram
Vertebral a.
Anterior inferior cerebellar a.
Basilar a.
Posterior cerebral a.
Posterior communicating a.
Middle cerebral a.
Internal carotid a.
Anterior cerebral a.
What is the name of the circled artery?
Middle cerebral artery
What is the name of the circled artery?
Anterior cerebral artery
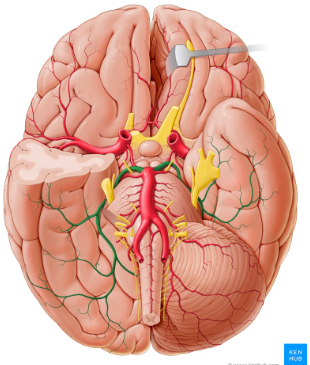
What is the name of the highlighted artery?
The posterior cerebral artery
What parts of the brain does the posterior cerebral artery supply?
The posterior and inferior parts of the brain, including the basal temporal lobe, occipital lobe and posterior aspects of the parietal lobe.
What parts of the brain does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
The anterior medial partes of the brain, including most of the frontal lobe, parietal lobe and corpus callosum.
What parts of the brain does the middle cerebral artery supply?
It supplies the majority of the lateral surface of the brain, including the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes.
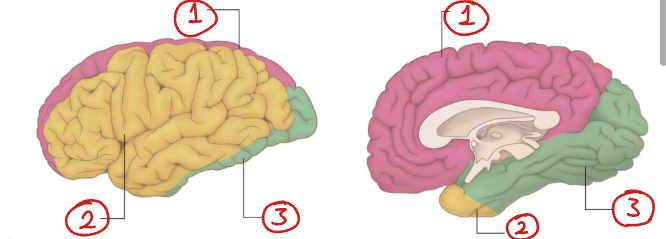
What arteries supply each of these regions of the brain?
Anterior cerebral a.
Middle cerebral a.
Posterior cerebral a.
What part of the circulation supplies the brainstem + cerebellum: the anterior or posterior circulation?
Posterior
What radiological technique is used to image arteries?
Angiography
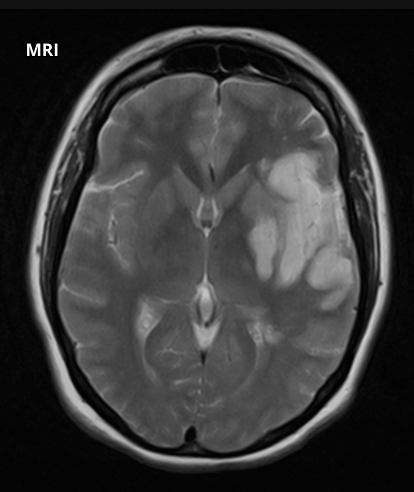
What does this image show?
Ischaemic stroke - There has been ischaemia and infarction of this patient’s left hemisphere.
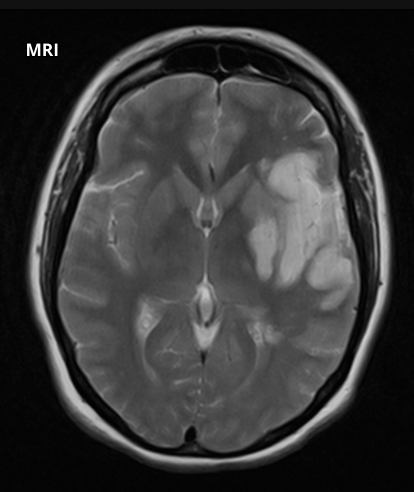
This ischaemic stroke has been caused by blockage of what artery?
Left middle cerebral artery
What are the symptoms of an MCA ischaemic stroke?
Unilateral contralateral motor weakness
Sudden worsening or loss of senses
Dysarthria
Aphasia
Neglect
Ataxia
What are the symptoms of an ACA ischaemic stroke?
Dysarthria
Aphasia
Unilateral contralateral motor weakness
Left limb apraxia
Urinary incontinence
Minimal sensory changes

This ischaemic stroke has been caused by blockage of what artery?
Right anterior cerebral artery
This ischaemic stroke has been caused by blockage of what artery?
The left posterior cerebral artery
What are the symptoms of an PCA ischaemic stroke?
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
Hemisensory loss
Hemi-body pain
If bilateral, loss of visual-motor coordination may be present.
What is the most commonly occluded artery in the brain?
The MCA. The PCA is also more commonly occluded than the ACA.
What are the symptoms of a cerebellar stroke?
Ataxia
Vertigo
Headaches
Double vision
Tremors
Nausea
Unconsciousness
Blood drains into the venous sinuses from where?
Smaller draining veins called cortical veins.
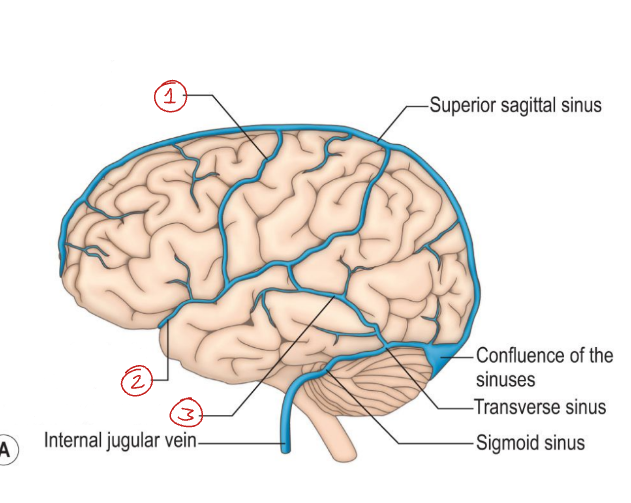
What are the names of the venous sinuses?
Sagittal
Transverse
Sigmoid
What structure do the sagittal sinuses travel with?
The falx cerebri (along the midline of the brain)
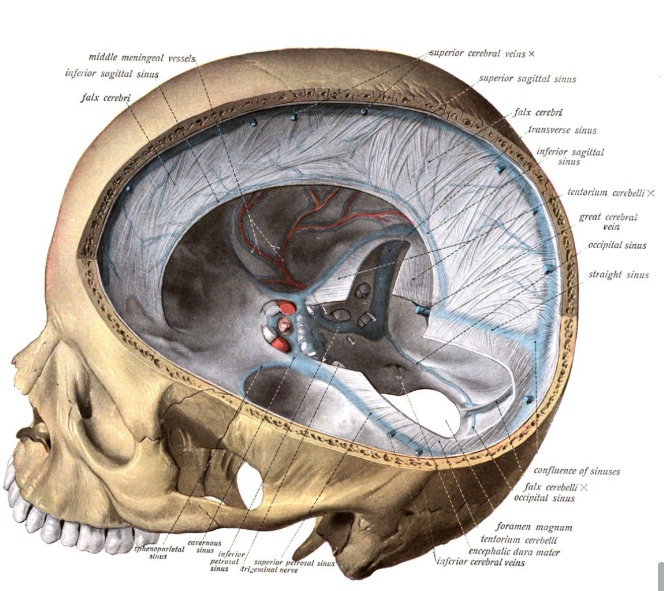
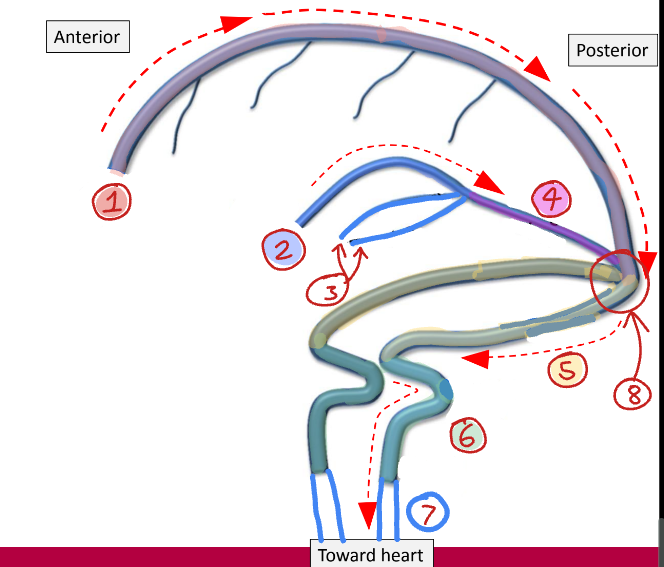
Label this diagram of the venous sinuses
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Internal cerebral veins
Straight sinus
Transverse sinus
Sigmoid sinus
Internal jugular vein
Confluence of sinuses
Are their valves in the veins that drain the brain?
No
Label these cortical veins
Superior anastomotic vein
Superficial middle cerebral vein
Inferior anastomotic vein
What radiological technique is used to image veins?
Venography
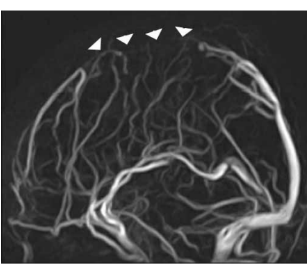
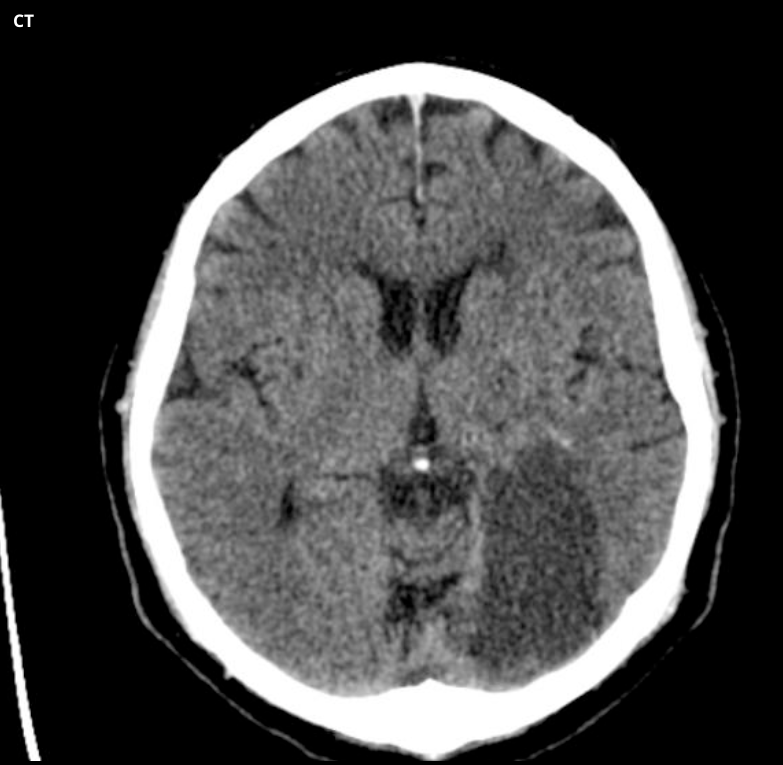
What is wrong with this patient?
The venography shows interrupted flow of the sagittal sinus - so they likely have a venous sinus thrombosis.
What are the symptoms of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)?
Worsening headache
Seizures
Altered mental status
It may cause a stroke
Can lead to a coma
Is a CVST common?
No, they are very rare. If a patient has one, it is very likely they had one or more risk factors for it - like pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives, cancer etc.
What are the main diseases of the brain’s vascular system?
Ischaemic stroke
Haemorrhagic stroke
Venous sinus thrombosis
Aneurysm
Ischaemic stroke
Blockage of an artery in the brain
Haemorrhagic stroke
Bursting of an artery in the brain
Venous sinus thrombosis
Blood clot in a vein in the brain
Brain aneurysm
Abnormal growth in a portion of a brain artery.
How can aneurysms damage the brain?
If it ruptures, it causes a subarachnoid heamorrhage
It can compress nearby structures