L12-nucleophilic substitution
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what is a nucleophile
a region of high electron densisty,from a lone pair or from negative charge
what is an electrophile
a region of low electron density, for example an atom next to an electronegative atom or a carbocation would be electron deficient
what makes a good leaving group
its able to stabilise a negative charge so its is more likely to be formed
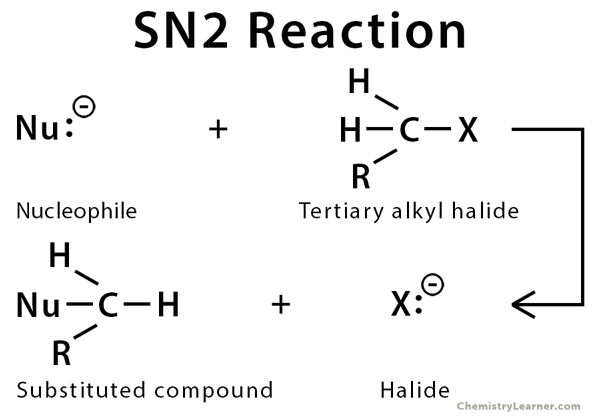
explain the SN2 mechanism
substitution nucleophilic bimolecular
the nucleophile attacks ( 180 attack ) the electrophile to make a bond and then a bond is broken
a high energy transition state is made which shows the nucleophile joining and the leaving group leaving
the product is formed containing the nucleophile is made which has a stereochemical centre that is inverted
what things are required/ encourgae SN2
a good nucleophile-one that is able to displace the leaving group
primary substrates
explain the SN1 mechanism
substitution nucleophilic unimolecular
due to steric hinderance initially the nucleophile cant attack
first the leaving group needs to leave
once its left the nucleophile is able to attack the carbocation produced - it has an equal chance of attaching at either position racemic
what are the features of a SN1 reaction and what can cause it to occur
only one molecule is involved at the start
the first step ( waiting for the leaving group to leave ) is the rate determining step and the slowest
what causes it:
weak nucleophiles
large nucleophiles
stabilised carbocation
a very good leaving group
explain E1
first the the leaving group leaves in the slowest rate determining step
this forms a carbocation intermediate to be formed which the base can take a proton from to form a molecule with a double bond
explain E2
elimination bimolecular
the base attacks the proton ( attacks the proton which allows maximum orbital overlap ) making a bond and a bond between the leaving group is broken
it goes through the transition state
finally forms the molecule with the double bond