ANSC 221 Lecture #18: Lipid catabolism
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the primary signaling molecule that initiates lipolysis?
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
What enzyme cleaves fatty acids from glycerol during lipolysis?
Triacylglycerol lipase
Where does fatty acid activation occur in the cell?
In the cytosol
What is the energy investment required for fatty acid activation?
1 ATP is converted to AMP
What is the role of CoA in fatty acid activation?
CoA forms a high-energy thioester bond with the fatty acid
What is the function of Carnitine acyltransferase 1 (CPT-1)?
It facilitates the transport of acyl-CoA across the outer mitochondrial membrane
What are the products of one cycle of beta-oxidation of palmitate (16C)?
8 Acetyl-CoA, 7 FADH2, and 7 NADH
What is the net ATP yield from the complete oxidation of one palmitate molecule?
106 ATP
What happens to odd-chain fatty acids during beta-oxidation?
They produce propionyl-CoA, which enters the TCA cycle at Succinyl-CoA
What triggers ketogenesis?
High levels of acetyl-CoA and low circulating glucose
What is the first step in the formation of ketone bodies?
Condensation of two acetyl-CoA molecules to form acetoacetyl-CoA
What enzyme links beta-oxidation and ketogenesis?
Thiolase
What is the final product of acetoacetate metabolism?
β-hydroxybutyrate or acetone
How do fatty acids enter the mitochondria for beta-oxidation?
They are transported as acyl-CoA via carnitine shuttle mechanisms
What is the role of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase in beta-oxidation?
It oxidizes the α-β bond of the fatty acid, producing FADH2
What does the term 'lipolysis' refer to?
The breakdown of triacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol
What is the significance of reduced equivalents produced in beta-oxidation?
They are used to generate ATP in the electron transport chain
What occurs during the hydroxylation step of beta-oxidation?
Enol-CoA hydratase adds water to the beta carbon
What is the fate of glycerol produced from lipolysis?
It enters glycolysis for energy production
What is the overall purpose of lipid catabolism?
To convert stored fats into usable energy in the form of ATP
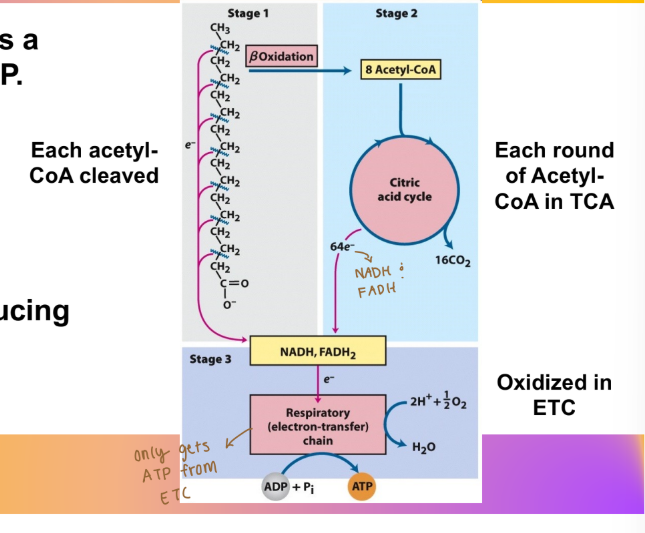
Core Concept: fatty acid oxidation yields a very high amount of ATP by what equivalents?
In the form of reduced reducing equivalents
Lipid anabolism (organismal energy high)
Utilizing acetyl-CoA and glycerol to ultimately form triglycerides (TAG) for energy storage
Lipid catabolism (organismal energy low)
1) Cells receive signal to initiate lipolysis
2) Triacylglycerol lipase cleaves fatty acids from glycerol in the cytosol
3) Fatty acids are activated in the cytosol
4) “Fatty acids” are transported into the mitochondria
5) “Fatty acids” are oxidized in the mitochondria (beta oxidation) to capture
energy as reduced reducing equivalents
What do we use to form Fatty acids?
NADPH
When does lipolysis occurs?
In response to low energy
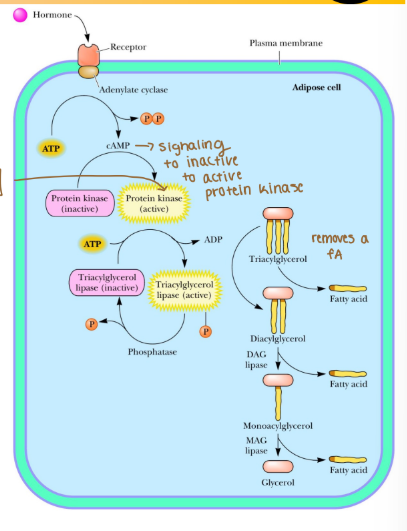
Lipid catabolism: activation of lipase
1) Hormones activate adenylate cyclase, which forms cyclic AMP (cAMP), a signaling molecule
2) cAMP activates Protein Kinase
3) Protein Kinase phosphorylates TAG Lipase to the active form of the enzyme
4) TAG/DAG/MAG Lipases cleave fatty acids (Tri-, Di-, and Monoacylglyceride lipase)
5) FAs continue to activation, glycerol to glycolysis
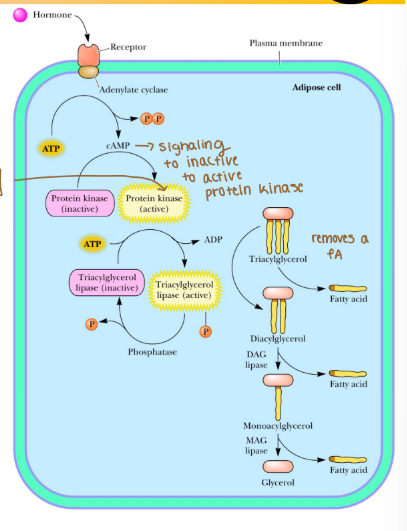
When hormones activate adenylate cyclase what does it form?
It forms cyclinc AMP (cAMP), a signaling molecule
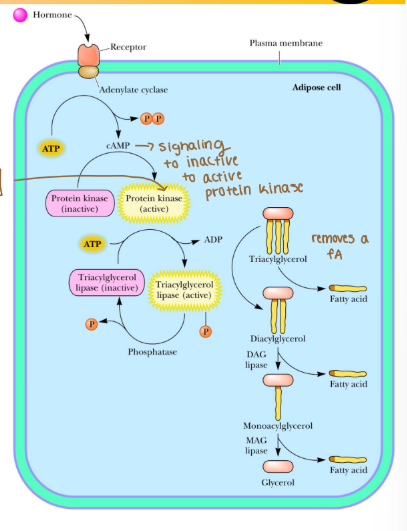
What does cAMP activate?
Activates Protein kinase
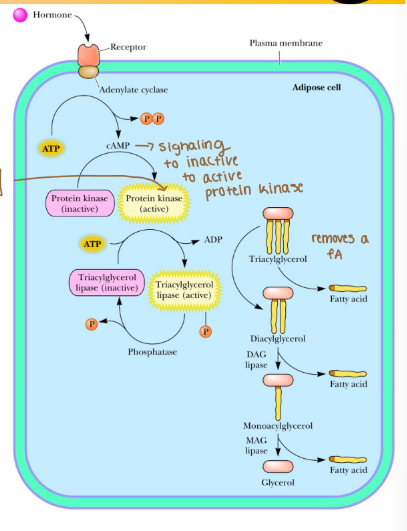
What does protein kinase phosphorylate?
TAG lipase to the active form of the enzyme
What type of molecule signals to adipose tissue to begin lipolysis?
Hormones
Where does lipolysis occur?
Cytosol
Where does Beta-oxidation occur?
In the mitochondria the very center
Which molecule is complexed with fatty acids to allow them to
utilize VDAC to pass the outer mitochondrial membrane?
CoA
How many of each energy holding compounds are produced in one cycle of beta-oxidation?
1 FADH
1 NAD
0 ATP
Which enzyme links beta-oxidation and ketogenesis?
Thiolase
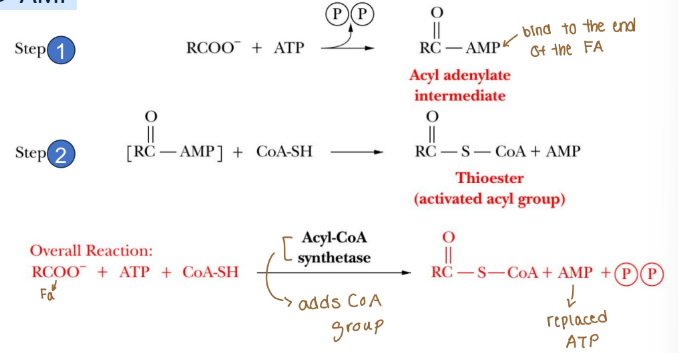
Lipid catabolism-fatty acid activation
Fatty acids cleaved from triacylglycerol are activated in the cytosol
Activation occurs via covalent bonding with CoA (high energy thioester bond)
Energy provided by ATP -> AMP
AMP bonds to fatty acid
AMP is displaced by CoA
Acyl-CoA is now ready to move into the mitochondria for beta-oxidation
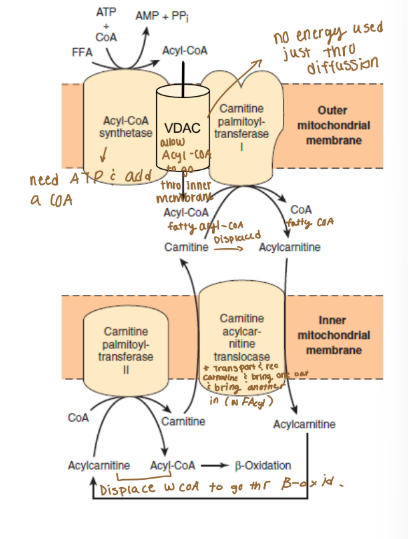
Fatty acids have to be what in order to pass the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes?
They have to be modified
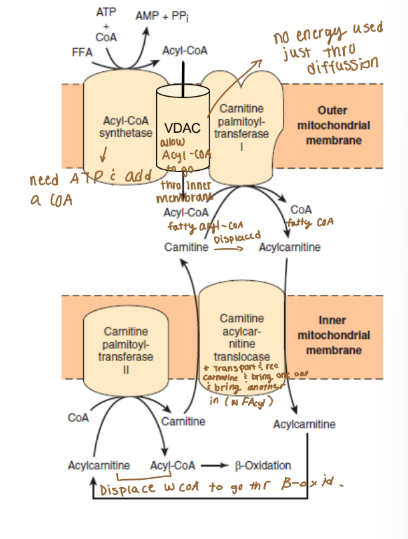
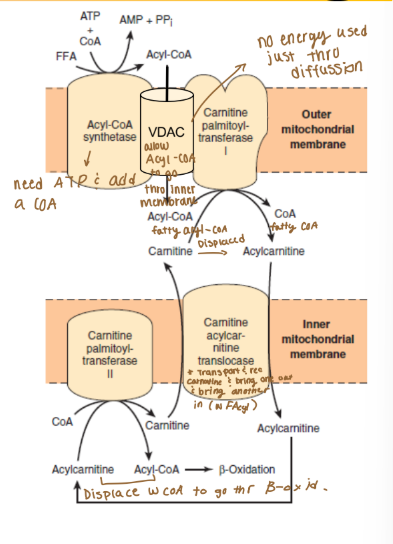
Lipid catabolism: lipid transport
Fatty acyl-CoAs must cross the outer and inner
mitochondrial membranes to enter β-oxidation
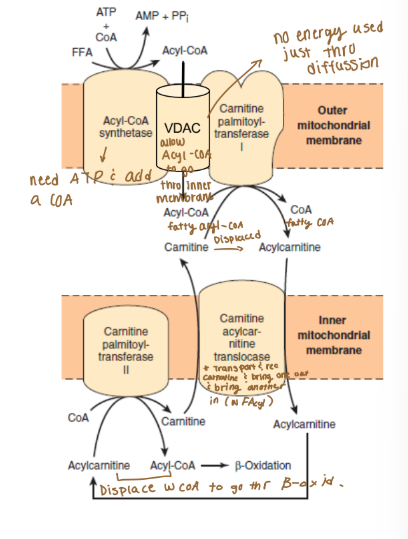
What do fatty acyl-CoAs must do to enter beta-oxidation?
They have to cross the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes
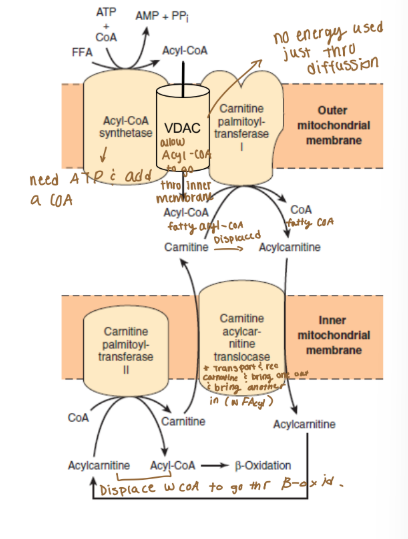
Outer Membrane (lipid catabolism, lipid transport)
Acyl-CoA Synthetase (ATP to AMP)
Voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC)
Carnitine acyltransferase 1 (CPT-1)
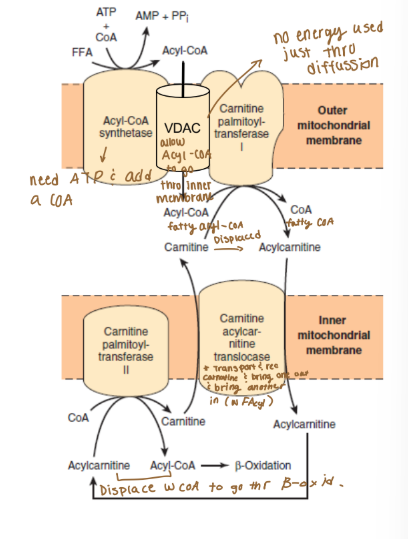
Inner membrane (lipid catabolism, lipid transport)
Carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase (CACT)
Carnitine acyltransferase 2 (CPT-2)
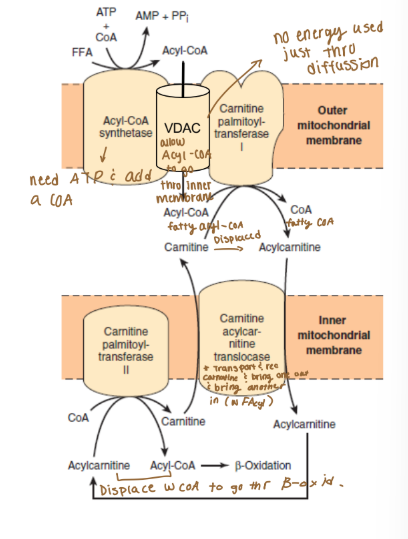
How can CoA diffuse back across the outer membrane?
VSAC allows CoA to diffuse across the outer membrane
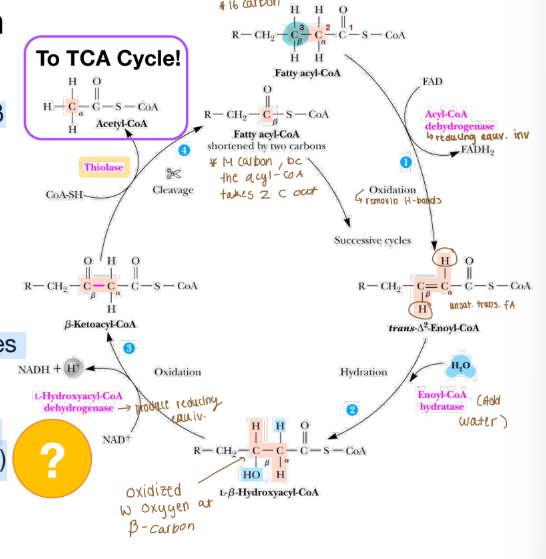
Beta oxidation
1) Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase oxidizes the ⍺-β
bond (between fatty acid carbons 2 & 3)
Results in unsaturated, trans FA
Reduces FAD to FADH2
2) Enol-CoA hydratase hydroxylates the beta carbon (beta oxidation!) using water
3) L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase oxidizes the beta carbon; reduces NAD+ to NADH
4) Thiolase cleaves acetyl-CoA from the fatty acid, and a new acyl-CoA is formed (CoA-dpt)
Why is it called beta oxidation?
It occurs at the beta carbon
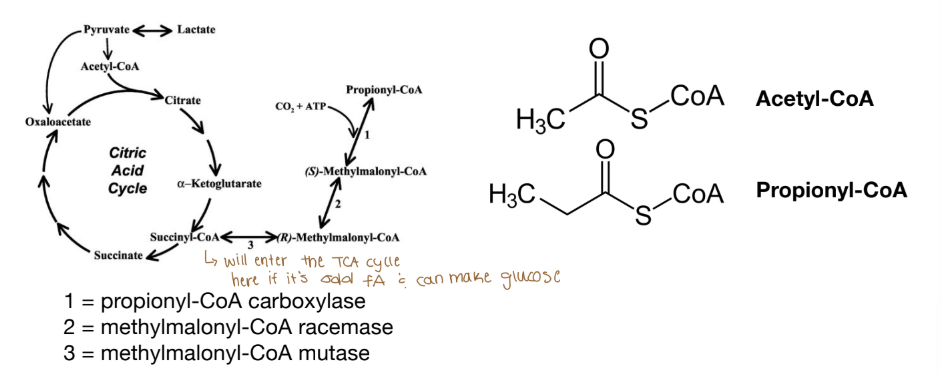
Where do odd-chain fatty acids enter the TCA?
They enter at Succinyl CoA
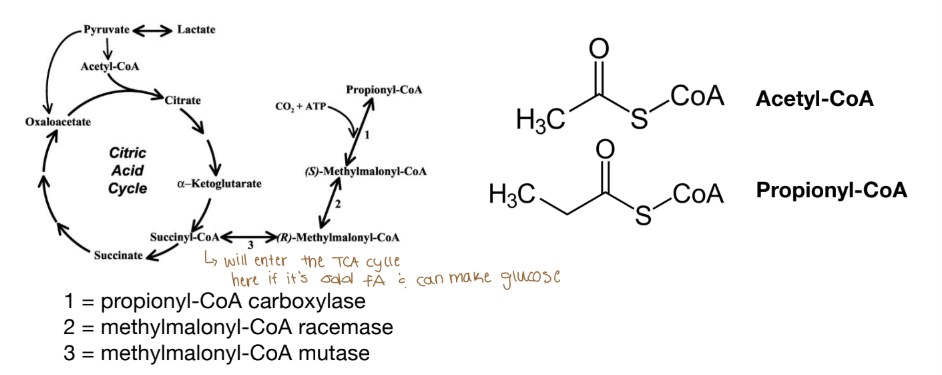
Odd-numbered Fatty Acids
Final cycle of beta-oxidation results in propionyl-CoA (instead of acetyl-CoA)
Propionyl-CoA enters TCA at Succinyl-CoA