Exam 4
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
immunology, digestive, renal, urinary
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Specific defenses
target specific antigens
initially slower, faster on next exposure
memory involved
Non specific defenses
body’s first line of defenses
rapid and immediate
no memory
inflammation
immediate response, body’s way of telling you that the healing process has begun
serves to contain damage, remove harmful agents, and initiate tissue repair
fever
body temp. increase as body’s defense mechanism against infection or injury
function of the immune system
protect the body from harmful agents and maintain internal homeostasis
b-cells
made in bone marrow (RBC)
clonal expansion
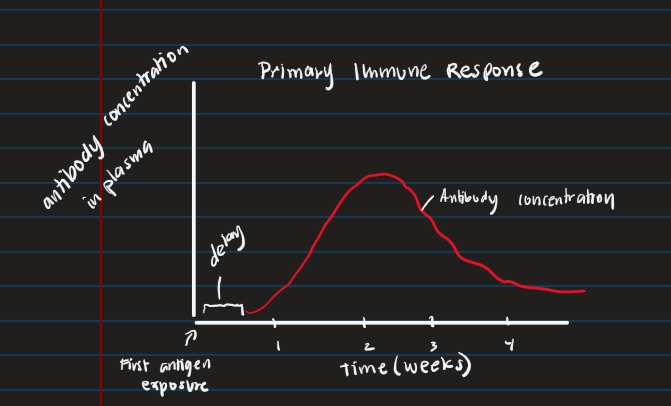
primary immune response
why do b cells make clones of itself when exposed to a pathogen?
creating a more powerful immune response to fight the infection and develop long-lasting immunity
why do b cells need memory cells?
to respond more quickly and more strongly with long term immunity
t-cells
matures in the thymus
physically attacking foreign or diseased cells directly.
double recognition
secondary immune response
antigens
capable of triggering an immune response when recognizes a foreign or “non-self”
antibodies
produced by b-cells that specifically recognize and bind to antigens
immunocompetence
capability of recognizing a particular antigen
“sensitization”
what are the advantages of having a one-way gut?
Efficient in digesting food molecules, proteins, carbs, and fats
why is the lumen of the gut not inside the body?
gut microbes that live in the tube help with digesting food
function of the digestive system
break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body
challenges to the digestive system
prevent autodigestion
match input with output
process of digestion
ingestion, propulsion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion, absorption, defacation
immunodeficiency
when the immune system is too weak to attack pathogens
autoimmune disease
when the immune system is too aggressive and attacks its own cells, healthy and foreign
how does antigenic stability relate to the difficulty of finding a HIV vaccine?
HIV mutates too quickly for a vaccine to be able work
vaccine
designed to recognize and remember what a specific germ is
active immunity
passive immunity