LATIN III GRAMMAR (FINAL)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
ut noun clause
"substantive clause"
- ut + subjunctive
- translate 'ut' as 'that' and the subjunctive verb as though it were indicative (regular)
- also translated as 'to'
syncopated perfect
1st conjugation (āre) verbs, perfect pp often ends in 'vī'
- shortening the verb and dropping the v + vowel
-- ex: superāverit = superārit
passive periphrastic
future passive participle ending in -ndus/a/um + form of 'sum/esse' (to be)
- shows necessity- translated with "must" or "should"
-- Carthage must be destroyed
imperfect subjunctive
present infinitive + endings (re + endings)
- shows action at same time/after action in main clause
-- translated as regular past tense
- ex: she asked where I lived (past tense verb occurs present)
pluperfect subjunctive
perfect infinitive + endings
- isse + endings (ex: parāvissem)
- shows action before main clause action
-- ex: she asked where I had lived (more past tense with had)
- "lived" is before the main clause action "she asked"
contrary-to-fact imperfect subjunctive
something that cannot happen in present
- if I where you, I would apply for that job
-- imperfect because the action isn't complete
contrary-to-fact pluperfect subjunctive
something that cannot have happened in the past
- "if you had applied for that job, you would have gotten it"
temporal cum clause
cum + indicative
- "when"
circumstantial cum clause
cum + subjunctive
- "when"
causal cum clause
cum + subjunctive
- "since"
consessive cum clause
cum + subjunctive
- "although"
relative clause
quī/quae/quod, gives more information about a noun/its antecedent
- the tree on which there are white berries
relative clause of characteristic (rel clause + subjunctive)
generalizes about the antecedent
- abored in quā sint poma alba
- the kind of tree on which there are white berries
relative purpose, result, circumstantial, causal, concessive clauses
replace ut or cum with relative pronoun
- context tells us which type of clause
apposition
noun followed by another noun with the same function
- George Washington, our first president... (both subject)
gerund
verbal noun- verb acts as a noun
- future passive participle (-ndus/a/um) in latin
-- studeō nandō (I am interested in swimming)
present subjunctive
present stem with changed last vowel for each declension (we fear a giant liar)
- jussive "may" "let"
-- shows action at same time/after main action
- let him live here
perfect active subjunctive
perfect active stem + eri + endings
- shows action before the action in the main clause
- "she is asking where I lived"
perfect passive subjunctive
4th pp + sim/sis/sit/simus/sitis/sint (present subjunctive of esse)
- shows action before action in main clause
- he suggested the project had been completed today
ablative absolute
noun/pronoun and its participle (tense/voice) are both in ablative case- verb looks different, formed in same case # gender as noun
-- provides more information about conditions under which main event occurs (time, reason..)
- verbs usually 2-1-2
- domo ruina
-- ruina also ablative, elaborates on the house/that its collapsing
purpose ut clause
ut = to, so that
- states reasoning why
- tell me so that I may know
result ut clause
ut = that
- shows what comes of it
-- its so hot that I'm sweating
negative fear clause
ut + neg adverb = that...not
- that he will not fight
negative purpose, neg ut noun, positive fear
all use nē
- np: don't tell me so I may not know
- un: I beg you not to leave
- pf: I fear that he will leave
future conditional clause
shows possible action in the future
- uses sī + indicative verb "if"
-- if you come
future perfect conditional clause
most likely action in future, uses sī + future perfect
- if you come (which is most likely)
present subjunctive conditional clause
shows unlikely action in future, sī + subjunctive
- if you should come (but not likely)
aliquis/quis/quid rule
aliquis/quis/quid = some(one/thing)
- ali-'s fall away after sī, nisī, num, nē
-- ex: sī quid (= aliquid)...
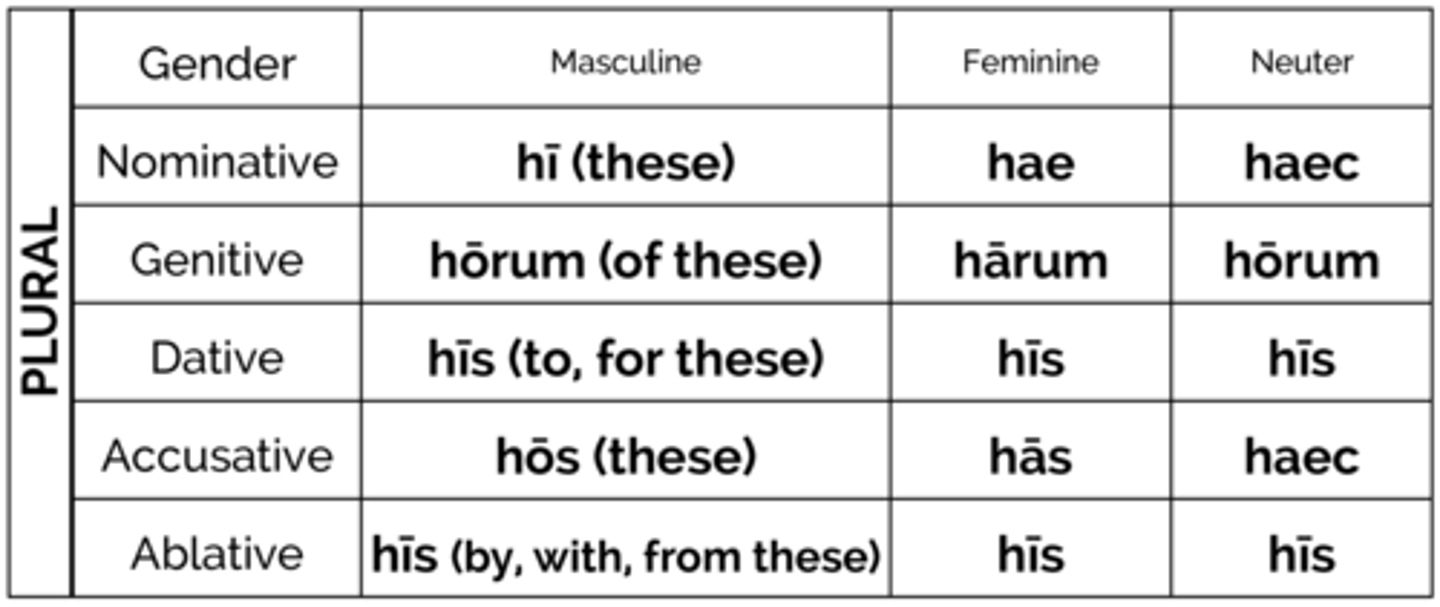
hic,haec, hoc demonstrative pronoun
this(sg)/these(pl)
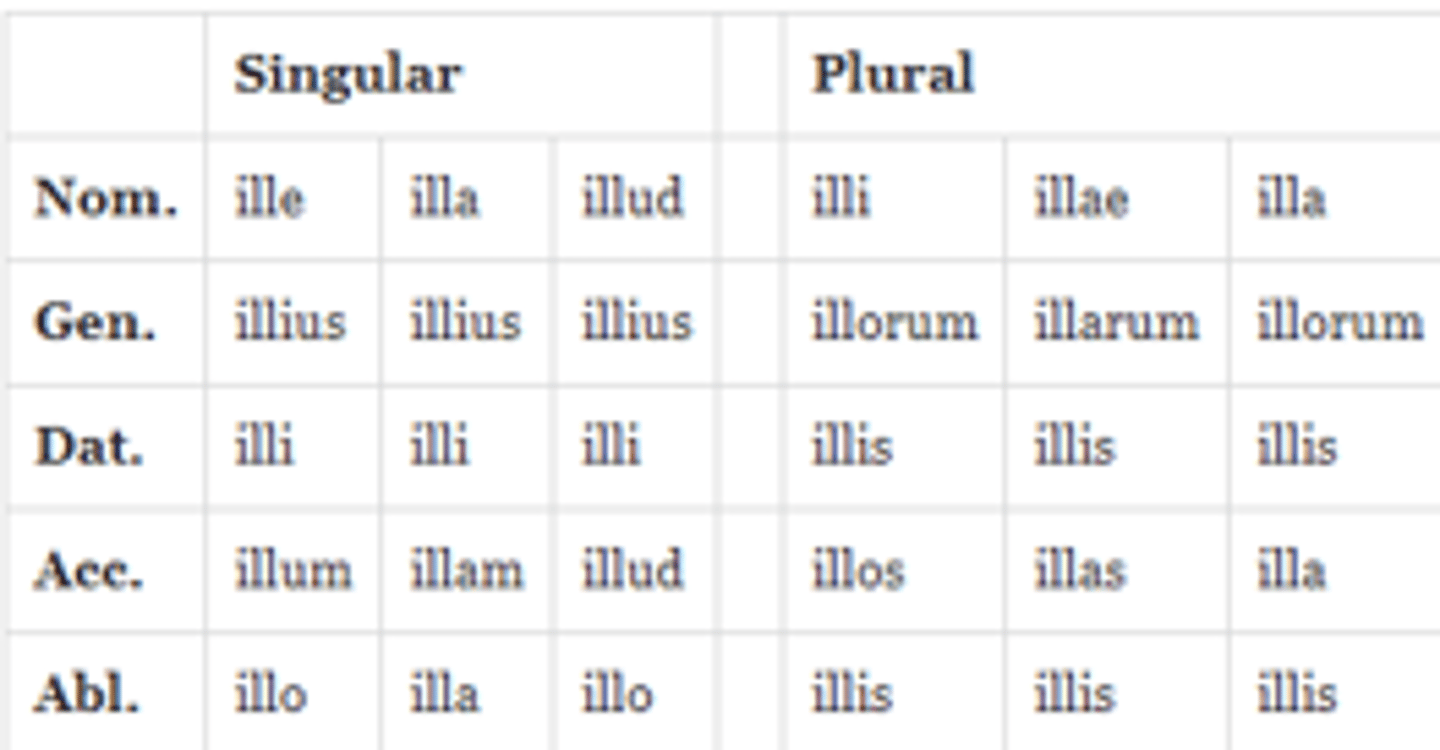
ille, illa, illud demonstrative pronoun
that (sg)/those (pl)
- 'that' when talking about possession can also be iste/a/ud
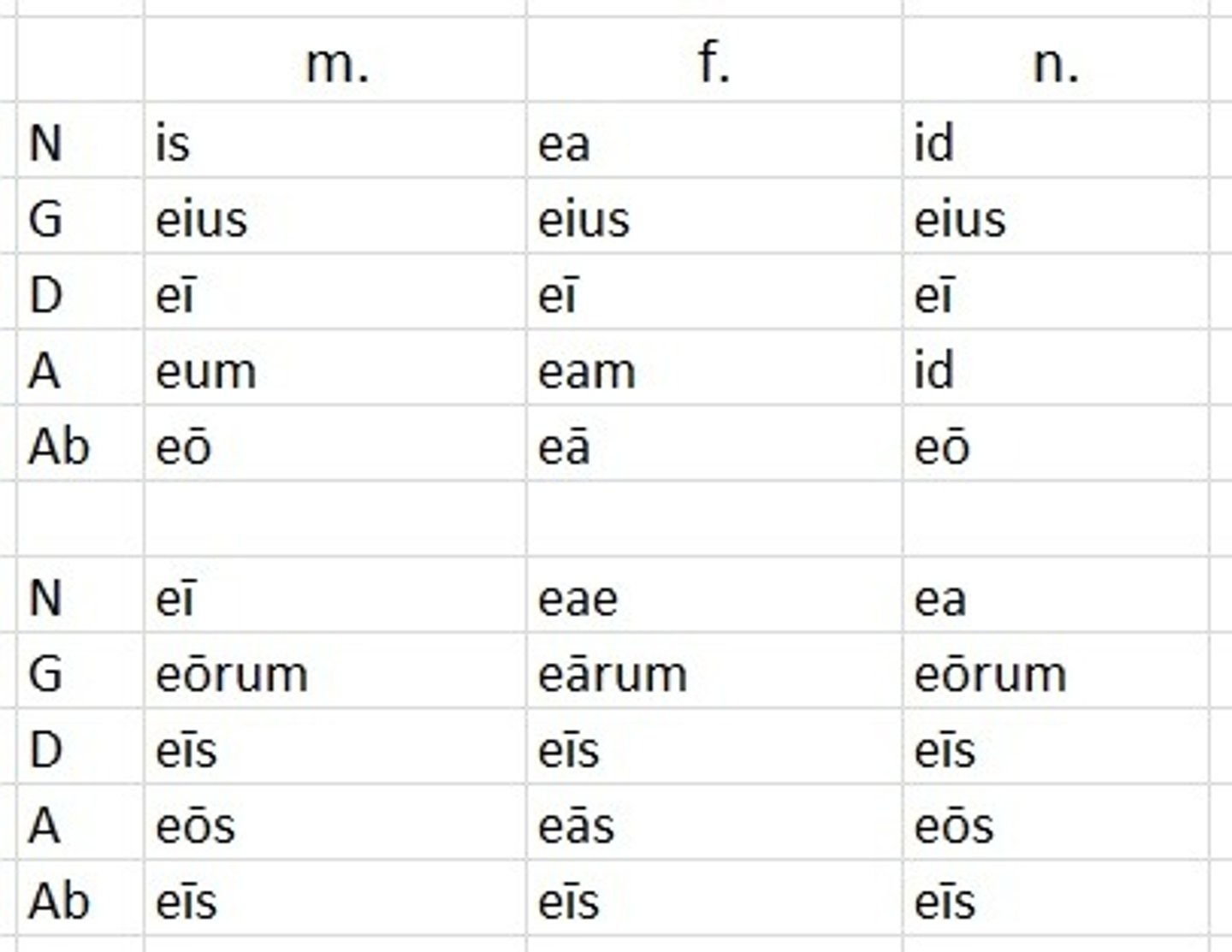
is, ea, id
he/she/it
- can also be used to say this/that
suus, sua, suum
shows possession
- his/hers/its
ablative with cardinal numbers
shows the whole part from which a part comes from
- ex/de + ablative
-- out of these three armies, he sent one into africa (1/3)
genitive of the whole
shows whole from which a part comes
- whole in genitive form with no preposition
- part of the army