Foundations of Nutrition: Exam 1 Material
1/289
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
290 Terms
Health vs Wellness
Health = optimum physical, mental, and social well-being — absence of disease
Wellness = development of full potential for each individual within their given environment
Functions of Nutrients in Foods (3)
(1) Provide energy
(2) Build tissue
(3) Regulation and control of metabolism
Which nutrients are important for tissue building?*
Macros: amino acids and phospholipids
Micros: vitamins C, D, K, calcium, phosphorus, iron
Which nutrients are important for metabolism?*
B vitamins, iron, copper, water, and fiber
Carbohydrates provide how much energy?
4 kcal/g
Lipids provide how much energy?
9 kcal/g
Protein provides how much energy?
4 kcal/g
What is 1 kcal?*
1 kcal = 1 Calorie
Heat necessary to increase 1 kg of water by 1 degree Celsius
Optimal Nutrition
Person consumes a diet with adequate and balanced macro and micronutrients
Essential nutrient production should be enough to provide some reserves without unnecessary excess
Undernutrition*
Reserves are depleted and intake is not enough to meet needs
Occurs in food insecure or hospitalized patients
Overnutrition*
Excessive nutrient intake (but not the quality, so missing nutrients)
Due to overeating or over supplementation
Deficiency vs Insufficiency*
Deficiency = very low level of nutrient found in the blood that causes a specific disease (Ex: Pellagra, Beriberi, and Scurvy)
Insufficiency = subclinical or deficient nutrient pools due to chronic poor intake
Standards of Nutritional Requirements
Set by the Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) of the Institute of Medicine (IOM), National Academy of Sciences
First published in 1941 and revised every 5-10 years
New recommendations are called dietary reference intakes (DRI)
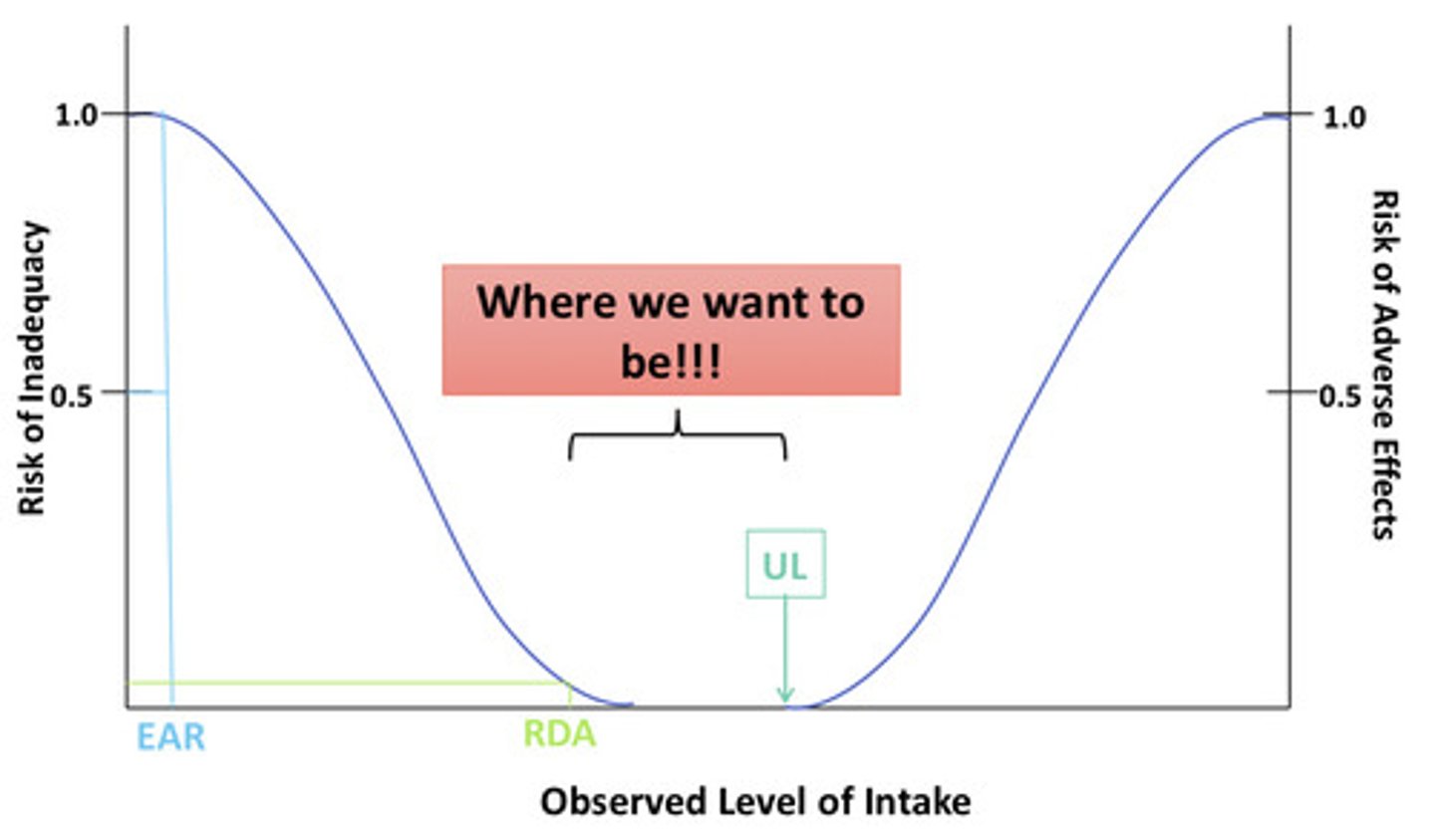
What does EAR stand for? What is it?*
Estimated average intake
Amount of nutrient that prevents deficiency in 50% of the population
Needs to use clinical assessment data (RCT studies)
What does RDA stand for? What is it?*
Recommended dietary allowance
Amount of nutrient that prevents deficiency in 97.5% of the population
Also uses RCT data
What does AI stand for? What is it?*
Adequate intake
Used as a guide, when clinical data is not available
Determined by observational data and used for individuals, NOT populations
What does UL stand for? What is it?*
Tolerable upper intake level
Maximum intake unlikely to cause adverse effects
Combined dosage of diet and supplement intake
Where is the optimum level of intake that we want to be?*
Between the RDA and UL
What is the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR)?*
Carbohydrates = 45-65% Calories (130g needed)
— Fiber = 25g (women) and 38g (men)
Total Fat = 20-35% Calories
Protein = 10-35% Calories (0.8 g/kg body weight)
Adult Nutrient Recommendations for N-6 and N-3?
N-6 = 11-17g
N-3 = 1.1-1.6g
What is the calculation for sedentary protein requirements?*
0.8 g/kg of body weight
Lbs / 2.2 = kg then multiple that by 0.8
Dietary Planning: generally how much of the plate should be plants?*
75% (fruits, vegetables, and grains)
Over half should be fruits/veggies + protein source, whole grains, and a source of dairy
What is the top source of added sugar?*
Sugar sweetened beverages
What is the top source of saturated fats?*
Sandwiches
What is the top source of sodium?*
Sandwiches
Influences of Food Habits (Individual Approach)
(1) Social (symbolizes warmth and acceptance, memories and interactions, etc.)
(2) Psychologic (habits, preferences, emotions, and cravings; positive or negative experiences)
(3) Physical (food availability, food tech, geography, season, climate, storage, etc.)
(4) Physiologic (allergies, disability, health & diseases, nutrient and energy needs)
What is the responsibility of the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA)?*
Main governing body over the U.S. food supply (except for meat, poultry, and eggs)
— also governs dietary supplements, bottled water, food additives, and infant formulas
What is the responsibility of the Food Safety and Inspection Service of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)?*
Regulates domestic and imported meats, poultry, and egg products
What is the responsibility of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Seafood Inspection Program?*
Regulates safety of seafood and fisheries
What is the responsibility of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)?*
Regulates pesticide usage and monitors water safety
What is the responsibility of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)?*
Regulates advertising and truthful marketing of foods and supplements
What is the responsibility of the CDC?*
Monitors and investigates cases of food-borne illness
History of food labels
(1) 1960's — 'Truth in packaging' regulation dealt with standards of identity
(2) 1973 — FDA developed a nutrition labeling system
(3) 1994 — Required to be used on foods sold in the U.S.*
Every 5ish years the label is updated
WHO, AHA, FAO, IOM, etc. all recommend that which percent of daily energy comes from added sugars?
Less than 10% of daily energy
What is an added sugar?
Anything added to a product that sweetens it
Ex: syrups, nectars, honey, granulated sugar, concentrated fruit and vegetable juices
Interpreting percent daily value*
If %DV < or equal to 5% = low
If %DV > or equal to 20% = high
Overall base off of a extremely generic diet...not good to use for much other interpretation
How do you calculate the percent calories from saturated fat?**
Use this same calculation for total fat, protein, sugar, etc.
For 9 Cal/g — just modify that to how much energy you get from each gram of that specific macro (Ex: carbs and protein = 4 Cal/g; lipids = 9 Cal/g)

What is the serving size for cheese?*
1.5 ounces = pointer finger
What is the serving size for milk?*
8 ounce cup = one fist
What is the serving size for veggies?*
1 cup = one fist
What is the serving size for a salad?*
2 cups = 2 fists
What is the serving size for raw fruit?*
1 medium size = one fist
What is the serving size for cut or canned fruit?
1/2 cup = 1/2 baseball
What is the serving size for noodles, rice, or oatmeal?*
1/2 cup = handful
What is the serving size of chicken, fish, beef, or pork (meat)?*
3 ounces = palm of hand or deck of cards
What is the serving size of peanut/nut butters?*
2 Tablespoons = thumb)
Who regulates gluten free labels?*
FDA
Must contain less than 20 parts per million (ppm) of gluten per serving

The "Gluten-free Opportunity"*
Take gluten out, and charge more —> make money off the gluten free foods
BUT usually worse nutritional value (higher in saturated fat, sodium, starch, and other processed carbohydrates)
What does the "organic" label mean? Who regulates it?*
GMO-free (NOT pesticide or fertilizer free)
Known as a "process verification" label
Regulated by USDA

What is not allowed for organic farming?*
(1) No synthetic fertilizers
(2) Transgenic modification
(3) Ionizing radiation
(4) Antibiotics
(5) Growth hormones
What is allowed for organic farming?
Some synthetic pesticides IF structurally identical to natural
Nutrition: organic vs conventional
Vitamin and mineral contents are similar in organic vs conventional foods
Organic foods do have more phenolic compounds (antioxidants) and less cadmium, but less phosphorus and potassium
Organic Farming —> increased price of organic foods
— may be better for agricultural workers and provide a more diverse soil ecosystem
— organic farming has lower yields, requires more land, and hands-on work
— more expensive to produce
— current premium in the U.S. is about 30% price increase over conventional
Hazard vs Risk*
Hazard: anything that can cause harm
Risk: the chance that someone will be harmed by the hazard (takes into account the dose and other factors)
How do you remove pesticides from fruit and veggies?
Wash them under cold running water
Labels
Who regulates the "cage free" egg labels?*
Certified Humane (NOT government)
Chicken Production
(1) Conventional (minimum of 0.5 ft squared)
(2) Cage-free (minimum of 1 ft squared, not required to let birds outside
(3) Free-range (minimum of 2 ft squared, allowed outside for at least 6 hours/day
(4) Pasture-raised (minimum of 108 ft squared, outside year-round with housing available)
Who regulates the irradiation label?*
FDA

Who regulates the Whole Grain Label?*
Whole Grain Council (non-profit)

Who regulates the bioengineered label?*
USDA

Who regulates the Non-GMO label*
Non-GMO Project (non-profit)
Carbon Neutral Label is regulated by who? What does it mean?*
Climate Neutral (non-profit)
Company's emissions are measured
— company develops and implements plan to reduce carbon emissions
— purchase carbon credits to offset emissions (1 credit = 1 ton carbon emissions)

What are health claims?*
Describe a food, ingredient, or supplement that has been shown to decrease the risk of some type of disease
— specific to a food/component and health benefit
*CANNOT be used on foods that contain >20% DV for fat, saturated fat, cholesterol, or sodium
Nutrient Content Claims*
Must meet specific quantity of a specific nutrient in food
*"Reduced" = 25% less calories/fat/etc. than the reference product
Structure/Function Claims*
Describe the role of a nutrient or ingredient intended to affect normal structure or function in humans
Ex:
— calcium builds strong bones
— fiber maintains bowel regularity
— antioxidants support cell integrity
Food industry labeling: moving away from "natural" and toward _______
Simple
How are transgenic crops different from hybrids?*
Transgenics = addition of 1-4 genes from another genome and safety testing is required
Hybrids = tweak, but do not add genes (don't need testing)
Benefits of transgenic crops?*
— resistance to insect damage
— resistance to droughts
— use of less pesticides
— decreased cost of food with increased shelf-life
— faster growing and more produced
Unprocessed or minimally processed foods*
Not touched or slightly altered for preservation
Cleaning, peeling, refrigeration, pasteurization, fermentation, freezing, vacuum packaging
Processed culinary ingredients
Ingredients derived from minimal processing
Pressing, refining, grinding, milling, etc.
Processed foods*
Foods with added salt, sugar, or fats
Canned fruits/veggies, canned fish, cheese, freshly made bread
Ultra-processed foods*
Aka "highly processed foods"
Foods that include artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives
Typically low in fiber and nutrients
Food Additives*
Chemicals added to foods to prevent spoilage and extend shelf-life
Most Common = sugar and salt
Generally Recognized as safe = GRAS
Which type of food additive prevents spoilage, changes, in color, flavor, or texture and delay rancidity? Examples?
Preservative
Ex: ascorbic acid, citric acid, sodium benzoate, calcium propionate, potassium sorbate, BHA, BHT, EDTA, tocopherols
Which type food additive adds sweetness with or without added calories? Examples?
Sweeteners
Ex: sucrose, glucose, fructose, sorbitol, mannitol, corn syrup, HFCS, aspartame, sucralose, neotame
Which type of food additive offsets color loss due to exposure to air, light, temperature, or moisture and corrects the natural color variation? Examples?
Color additives
Ex: FD&C Blue No. 1 & 2, Green No. 3, Red No. 3 & 40, Yellow No. 5 & 6; annatto; grape skin; paprika; beta carotene; fruit and veggie juices
Which type of additive adds natural or synthetic flavors? Example?
Flavors and spices
Ex: natural flavoring, artificial flavor, spices
Which type of food additive enhances flavors without adding their own flavor? Examples?
Flavor enhancers
Ex: MSG, hydrolyzed soy protein, yeast extract, inosinate
Which type of food additives provide texture in reduced-fat foods? Examples?
Fat replacers
Ex: olestra, cellulose, carrageenan, polydextrose, modified food starch, guar and xanthan gum, whey protein concentrateW
Which type of food additive replaces vitamins and minerals lost during processing or add nutrients that may be lacking?
Nutrients
Which type of food additives prevent separation, reduce stickiness, and help products dissolve more easily? Examples?
Emulsifiers
Ex: soy lecithin, mono and diglycerides, egg yolks, polysorbates, sorbitan nonstearate
Which type of food additives produce uniform texture and improve mouthfeel? Examples?
Stabilizers, thickeners, binders
Ex: gelatin, pectin, gums
Which type of food additive controls the acidity and alkalinity and prevent spoilage? Examples?
pH control agents
Ex: lactic acid, citric acid, ammonium hydroxide, sodium carbonate
Which type of food additives promote rising? Examples?
Leavening agent
Ex: baking soda, monocalcium phosphate, calcium carbonate
Which type of food additive prevents moisture absorption to keep powdered foods free-flowing? Examples?
Anti-caking
Calcium silicate, silicon dioxide, iron ammonium citrateW
Which type of food additives retain moisture? Examples?
Humectants
Ex: glycerin, sorbitol
Which type of food additive produces more stable dough? Examples?
Dough conditioners
Ex: ammonium sulfate, azodicarbonamide
Which type of food additive maintains crisp and firm foods? Examples?
Firming agents
Ex: calcium chloride, calcium lactate
Types of Plant Breeding
(1) Conventional Crossbreeding
(2) Mutagenesis
(3) Transgenics
(4) Gene editing
Conventional Crossbreeding
Hybrids ("natural mutations")
No safety testing and regulation
Mutagenesis
Use of chemicals or ionizing radiation to mix up genome
No safety testing, no regulation
Transgenics*
Addition of 1-4 genes from another genome
Safety testing required and needs FDA approval for use in food
Gene Editing
Tweaking of the plant genome (often using CRISPR)
No safety testing and no regulation
DNA Intake*
We eat over 100 trillion genes per day
Most of it is degraded (very small percent of small genetic material gets through the gut, but never full genes
Most of the transgenic DNA we eat is destroyed by processing or GI conditions
What are some currently approved modified foods?
Alfalfa, pink pineapple, apples, potatoes, canola, soybeans, corn, summer squash, cotton, sugar beets, papaya, and cotton
What is the safe minimum internal cooking temperature of beef, pork, veal, and lamb cuts (steak, chops, roasts)?*
145 degrees F (62.8 C) and allow to rest for at least 3 minutes
What is the safe minimum internal cooking temperature of ground meats?*
160 F (71.1 C)
What is the safe minimum internal cooking temperature of ham, fresh, or smoked meats?*
145 F (62,8 C) and allow to rest for at least 3 minutes
What is the safe minimum internal cooking temperature of all poultry?*
165 F (73.9 C)