Prelim 3- Schizophrenia and Psychosis pt.2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Brief Psychotic Disorder
one symptom for less than one month
Schizophrenia form disorder
2 symptoms lasting between 1 and 6 months
schizophrenia
2 symptoms lasting more than 6 months + declines in functioning
delusional disorder
1 or more delusions, lasting more than one month, no disorganized speech, no hallucinations or not prominent hallucinations
Schizoaffective Disorder
full symptoms of schizophrenia + symptoms of major mood disorder
Psychosis Treatment
first line: antipsychotic medications
relative to other disorder, higher rate of inpatient hospital admission with psychosis
involuntary hospitalization\
duration varies by state and each has regular legal hearing to determine i hospitalization
involuntary hospitalization
person is deemed legally incapable of taking care of themselves and presents immediate threat of harm to self or others
hospitalization
around 80% of young adults with schizophrenia will be hospitalized involuntary, generally in the first 2 years of onset
often perceived by patients as traumatic and frightening and associated with avoidance of mental health support in future
Does Hospitalization Help?
can provide short term benefits in stabilizing symptoms or accessing new or different treatments
minimal evidence that provides long term changes in functioning or symptoms
minimal evidence that is is associated with prevention of relapse
expressed emotion (ee)
pattern of family interaction associated with high rates of relapse rehospitalization, more severe delusional thinking, and longer episodes of severe symptoms in people with schizophrenia
risk of rehospitlalization following discharge in high EE families is more than double than that in low EE families
3 components of expressed emotion
criticism
hostility
emotional overinvolvement
criticism
negative comments about person and their behavior
hostility
family members believe symptoms are within person’s control and the patient could choose to less affected
emotional overinvolvement
family members blame themselves for illness; any problems or setbacks are perceived as their fault and not due to schizophrenia itself
What fosters EE?
relatives high in EE tend to be more conscientious, and higher locus of control, and feel more burdened and distressed in their caregiver roles
people with schizophrenia from high EE families tended to have higher premorbid functioning
interventions to reduce expressed emotion
reducing expressed emotion in family members reduces relapse and symptom severity in people with schizophrenia
intervention is conducted primarily with family members and not people with schizophrenia themselves
focuses on education about schizophrenia, effective communication skills and problem solving
what declines as people with schizophrenia show improvement?
EE
suggest it may not worsen symptoms, but emerge in family members as a response to their loved one’s symptoms
Is CBT a treatment for Psychosis?
CBTp: goal is not to reduce or re-evaluate hallucinations or delusions, but to adjust their impact
examine behavior and feelings that are linked with hallucinations and delusions
targets negative symptoms
reduces distress and effects of symptoms by 20-65%, depending on study
improves reasoning skills, daily functioning, and beliefs about self and others
What is the situation —> automatic thoughts —> emotional response for psychosis?
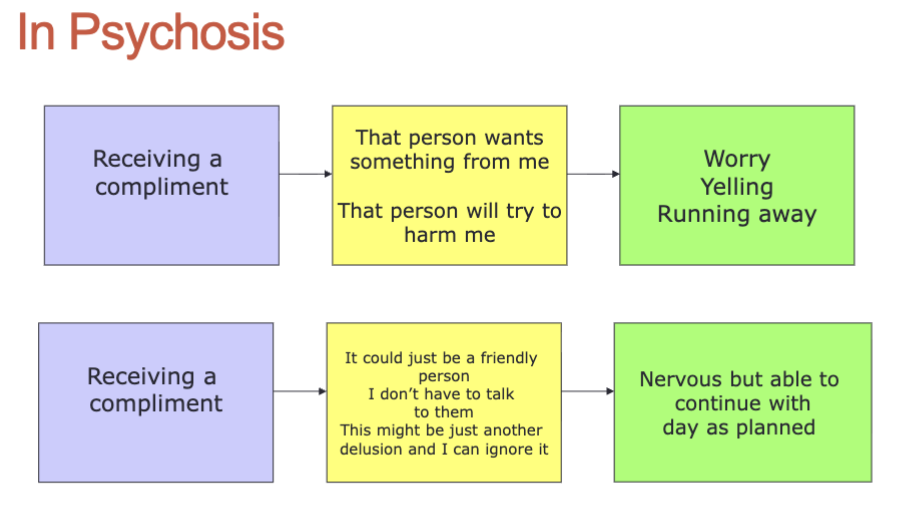
what is the relationship between client and therapist in CBTp
therapist avoids confronting patient about reality, gaps or contradictions in their accounts
approach: patient’s perception of events is logical
normalizes cognitive processes
therapist conveys that a delusion is a reasonable reaction to a puzzle or threatening experience (hearing voice or panic)
works to change response to psychotic symptoms
Are there many CBTp therapists?
few trained and limited availability
Hearing Voices Movement
shift public and professional perceptions of psychosis
challenges assumption that hearing voices are necessarily a sign of severe mental illness
emphases that may people hear voices
voices viewed as reflection of or reaction to life experiences, stressors, culture, relationships
promotes empowerment and self determination by emphasizing that people should work with their voices on their own terms
Are voices a sign of mental illness?
no, but more particularly, what the person is the person’s relationship with their voices
if causes distress, someone can learn how to cope with the voices and the past experiences that shape their response to the voices
voice cessation is not considered a sign of success or progress
hearing voices self help groups
user led organization present in 31 countries globally
attendance is informal and not time-limited
few outcome studies with small (-), but promising results
less distressed about hearing voices
gives support for hearing voices that they would not otherwise have
helps people make sense of hearing voices
greater confidence in employment and work situations, family relationships, health care system and health seeking