Indirect Midterm (copy)
1/287
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
288 Terms
principles of tooth preparation
preservation of remaining sound tooth structure
tooth reduction to provide necessary space for bulk of restorative material
geometry of preparation to provide retention and resistance
margins of tooth and restoration must maintain their integrity
periodontal health after restoration must be maintained
path of insertion (poi)
allows for restoration to be placed/removed in the long axis of the tooth
proper poi and planes of reduction provides space for material
occlusal reduction
should follow cuspal inclines for tooth preservation while providing space for the material
retention
prevents removal of the restoration along the poi or long axis of the tooth preparation
resistance
prevents dislodgment of the restoration by forces directed in an apical or oblique direction and prevents any movement of the restoration under occlusal forces
the essential element of retention is….
two opposing vertical surfaces on the same tooth
can be external (extracoronal restoration walls) or internal (walls of proximal box)
the two opposing external (extracoronal) walls in a prep must gradually _____ in an occlusal direction
converge
the two opposing internal (intracoronal) walls must gradually ______ in an occlusal direction
diverge
the inclination of each wall of 3-5 degrees will result in a taper of the preparation of ____ degrees
6-10
the _____ the surface area, the greater the retention
greater
preparation margins must be well supported at how many degrees?
greater than or equal to 90 degrees
bur for breaking interproximal
859 010
chamfer bur
856 014
rounded shoulder bur
856 016
sharp 90 internal bur (also used for occlusal reduction)
6847 014
end cutting bur
10839 014
tooth areas reduction for crowns
cvc cast metal dimensions
buccal gingival axial: 0.65 mm (0.5-1.0)
mid axial reduction: 1.0 (0.8-1.3)
lingual gingival axial: 0.65 (0.5-1.0)
occlusal reduction: 1.5 (1.0-1.75)
all ceramic monolithic zirconia
buccal gingival axial: 0.65 mm (0.5-1.0)
mid axial reduction: 1.0 mm (0.8-1.3)
lingual gingival axial: 0.65 (0.5-1.0)
occlusal reduction: 1.5(1.0-1.75)
all ceramic layered zirconia (pfz)
buccal gingival axial: 1.0 mm (0.5-1.0)
mid axial reduction: 1.3 mm (1.0-1.4)
lingual gingival axial: 1.0 (0.8-1.1)
occlusal reduction: 2.0 mm (1.5-2.5)
metal ceramic (pfm)
buccal gingival axial: 1.3 mm (1.0-1.5)
mid axial reduction: 1.5 mm (1.3-2.0)
lingual gingival axial: 0.65 (0.5-1.0)
occlusal reduction: 2.0 mm (1.5-2.5)
most conservative crown prep is…
cvc cast metal
outline requirements
supragingival margin placement
including caries and defects
separation from adjacent teeth
preservation of adjacent teeth and peridontium
internal requirements
removing caries
buildup when necessary
path of insertion and draw
preservation of tooth structure planes of reduction
remove enough tooth structure based on restorative type of material
retention requirements
height of the vertical axial walls of the preparation
proper taper convergence angle
free of undercuts
marginal finish
margins configuration and angulation for the type of material
margins well supported terminate on sound tooth structure
finish line identifiable, continuous, clear, regular
free of debris
outline should terminate…
supragingival at 0.65 mm (range 0.1-1.0)
clinical outline determining factors
Caries, Access, Defects, Existing resorations, margins Terminate on sound tooth structure
preparation wall height
esthetic factors
biological width considerations
proper separation from adjacent teeth
separation from adjacent tooth should be…
greater than or equal to 0.5mm at the gingival margin
POI usually follows the…
long axis of the tooth and parallel to the adjacent proximal contacts
poi of the maxillary teeth is…
slightly buccal
axis of the bur should be ____ to the long axis of the poi
parallel
on mandibular posterior teeth, the side of the bur touches at the height of contour which is the ______ of the lingual surface
middle third
connecting grooves should be at the ____ poi & the _____ of the bur should not be changed
same; angulation
at the correct poi, the mid axial reduction will be ________ the gingivial axial reduction
more than
breaking interproximal contact
follow the same poi
follow the gingival scallop, curve around the papilla
protect adjacent teeth
maintain a thin layer in contact with adjacent to avoid damage
look for supragingival margin and gingival separation
proximal axial wall reduction
do not change angulation of the bur
only half, no more than 2/3 of the bur diameter
gingiva axial reduction of 0.65
pay attention to line angles for proper reduction and taper
marginal finish for a cast metal crown (cvc)
chamfer (1.3 diameter at the tip)
marginal finish for a monolithic zirconia crown
shoulder 90 with round internal
mandibular molar occlusal reduction
gauging grooves follow the b/l inclination at the proper depth
remove tooth structure between the grooves
removal of tooth structure should be uniform
functional cusps (stamp cusps
buccal cusps of mandibular posterior teeth
lingual (palatal) cusps of maxillary posterior teeth
non-functional cusps
lingual cusps of mandibular posterior teeth
buccal cusps of maxillary posterior teeth
for functional cusps, which planes are part of the occlusion?
2nd and 3rd planes
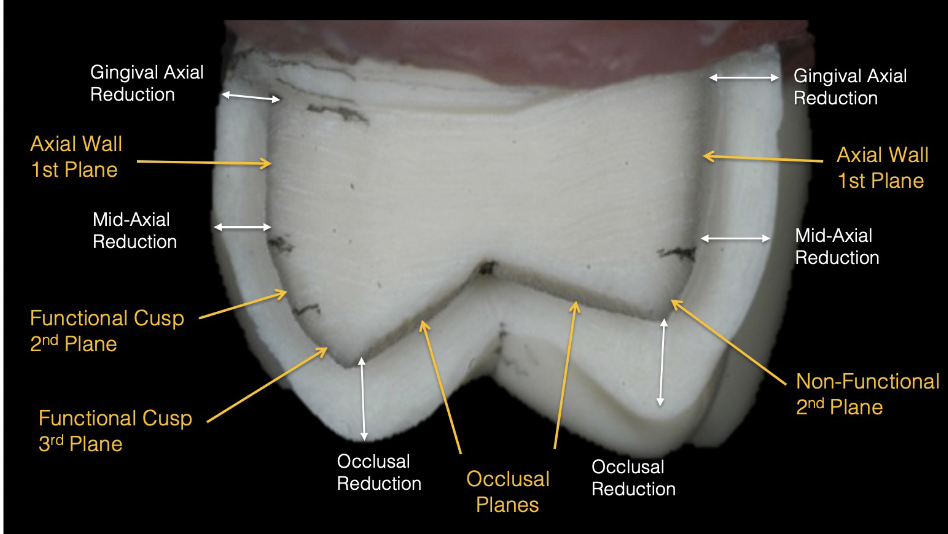
functional cusp 2nd and 3rd planes
must preserve at least 3.0mm of 1st axial wall height
2nd plane should be a gradual transition from the 1st plane
3rd plane should be a gradual transition from the 2nd plane
place 2nd and 3rd from line angle to line angle ONLY
purpose of 2nd and 3rd planes
provide space for restorative materjal and will move back the cusp tips in line with the adjacent teeth and the opposing fossa
non-functional cusp 2nd plane
must preserve at least 3.0-4.0 mm of 1st axial wall height
2nd plane should be a gradual transition from the 1st lpane to bring the cusp tips in line with the adjacent teeth
place 2nd plane from line angle to line angle only
non-functional cusps have how many planes?
2 planes
if the walls are overtapered, do you still need cusp planes?
no
rounding off sharp occlusal line angles is _____ as 2nd or 3rd cusp planes
not the same
occlusal clearance
the space measured against the opposing teeth (measuring instrument must follow the angulation of the cusp)
how do you measure occlusal clearance on lingual cusps?
bite registration
retention prevents…
removal of the restoration along the poi or the long axis of the tooth preparation
resistance prevents…
dislodgement of the restoration by forces directed in an apical or oblique direction and prevents any movement of the restoration under occlusal forces
indirect cemented restorations ____ have proper retention and resistance form
MUST
luting cement will not add retention to the crown
CAD/CAM indirect bonded restorations _____ need retention form
DO NOT
only need proper resistance form to ensure the onlay will stay in position during try-in and bonding
the longer the wall, the ____ the retention
better
ideal taper is?
6 degrees convergance
larger teeth have _____ surface area
more
______ finish is better than _______
diamond; carbide
secondary retentive features include…
grooves, boxes, countersink
when do you place secondary retentive grooves?
on a wall 90 degrees to the shortest or overtapered wall
on a wall with proper hright, poi, and taper
on the longest part of the wall
finish line
the peripheral extension of a tooth preparation
the terminal portion of the prepared tooth
should be clear, continuous, and free of irregularities
margin
the outer edge of a restoration
should be well supported and terminates on sound tooth structure
margin angulation is based on the type of preparation
shoulder bevel
indicated for metal margins only
pfm porcelain margin
shoulder 90 degrees with sharp internal (“butt joint”)
knife edge
usually contraindicated because it is not good for gingival health
limited indications for metal margins
provisional
fixed or removable prosthesis
designed to enhance esthetics, stabilization, and/or function for a limited period of time, after which is to be replaced by a definitive prosthesis
assist in determining the therapeutic effectiveness, form, and function of the planned definitive prosthesis
when do we need a provisional
transitional restoration
if missing teeth
evaluation of proposed treatment plan
do provisionals influence the final result?
yes, it must have the exact same parameters as the final restoration
functions of a provisional
occlusal function
pulpal function
maintain periodontal health
positional stability
esthetics
template for a final restoration
occlusal function
fixes poor esthetics
reestablish function
mastication
speece
pulpal protection
replaces removal of tooth structure
exposure of dentin
exposure of dentinal tubules
contamination of tubules by bacteria
increased sensitivity
intra arch stability
includes the variation in tooth position within an arch
inter arch stability
includes the variation in tooth position within 2 different arches
a hyper occluded provisional causes…
patient discomfort
occlusal trauma
tmj issues
tooth movement
extrusion of adjacent teeth
intrusion of prepared tooth (rarely)
a hypo occluded provisional causes…
tooth movement
extrusion of antagonist teeth
extrusion of prepared tooth
open proximal contact causes…
food impaction
patient discomfort
tooth movement
of the prepared tooth
of the adjacent tooth
tight proximal contact causes…
tooth movement
of either the prepared tooth or adjacent teeth
then creates an open contact with definitive restoration
the provisional allows us to…
evaluate multiple aspects of the proposed design
can change and modify before we move to the final restoration
how long should a provisional last for?
2 weeks
for long term provisionals, what do we need to look out for?
wear of the provisional resulting in tooth movement
discoloration of the restorations
breakage of the restorations
marginal leakage, leading to caries, sensitivity, pulpal problems
provisionals should be evaluated at least ONCE every month
spend ____ time on provisional and ____ time on the final restoration
more; less
modifications of the provisional are easy, reversible, and low cost
phonetics & their relationship with provisionals
phonetics affect speech due to the relationship of the teeth to soft tissues
characteristics of a provisional material
high strength and wear resistance
ease of manipulation
dimension stability
polishability
color stability
non-irritating
poor thermal conductivity
easy to modify/repair
cost
biocompatability
types of prefabricated provisionals
aluminum shells
acrylic shells
celluloid crown forms
polycarbonate crowns
stainless steel crowns
iso-form crowns
types of custom made crowns
composite resins
acrylic resins
composition of acrylic resins
liquid
(mma) monomer
hydroquinonenone; tertiary amine (initiator)
powder
(pmma) polymer
benzoyl peroxide (activator)
advantages of acrylic resins
good physical properties
good esthetics
ease of manipulation
easily repaired
low cost
disadvantages of acrylic resins
exothermic reaction
polymerization shrinkage
setting time: 6-9 min
excessive free monomer
can cause allergy
unpleasant odor
conventional acrylic resins are…
powder/liquid “jet”
acrylic resins for cad/cam
pmma is industrially processed
higher polymerization
fewer voids
filler particles
milled
can be monochromatic or multilayered
to increase the strength of long term provisionals we can…
cure in a pressure pot to decrease porosity (crack propagation)
reinforce with fiber
reinforce with metal
to avoid discoloration for long term provisionals we can…
cure in a pressure pot to decrease porosity (crack propagation)
high polish
use surface sealing materials like BisCover LV
types of composite resins are…
bisacryl
light cure resin
composition of bisacryl
resin
dimethylacrylate polymer
bisGMA
filler
zirconia silica
fumed silica
silane
pigments
advantages of bisacryl
low heat
minimal pulp irritation
low polymerization shrinkage
high tensile strength
color stability
minimal odor
polishability
disadvantages of bisacryl
brittle
thick oxygen inhibited layer
limited shades
no possibility of layering
difficult to repair
“one time” provisional
expensive
light cure resin composition
triad vlc
pmma, urethane dimethacrylate
microfine silica
camphorquinone
amine
fermit, fermit n, telio
polyester urethane dimethylacrylate
silica
ethilriglycomethacrylate
advantages of light cure resin
direct technique
low curing heat
low polymerization shrinkage
no mixing
ease of use and repair
low odor
no cement required
disadvantages of light cure resin
low strength and wear resistance
plastic after setting
cannot be polished
radiolucent
does not prevent movement of teeth
water absorption
not long term
high cost