Variation
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Which source of variation includes new alleles that could be introduced to the population with genetic mutations?
mutation
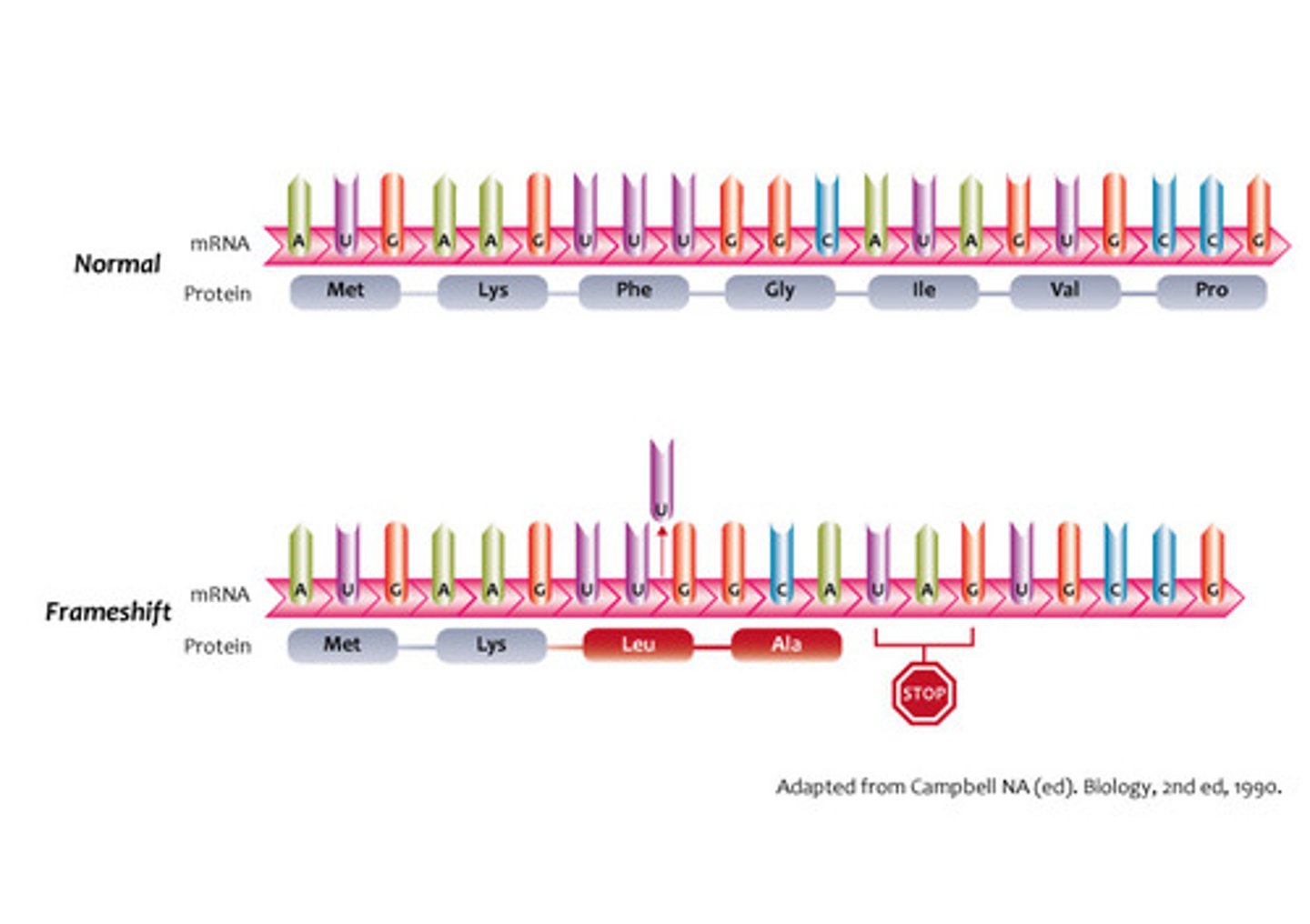
Which source of variation includes crossing over, independent assortment, and random joining of gametes in sexual reproduction?
sexual reproduction
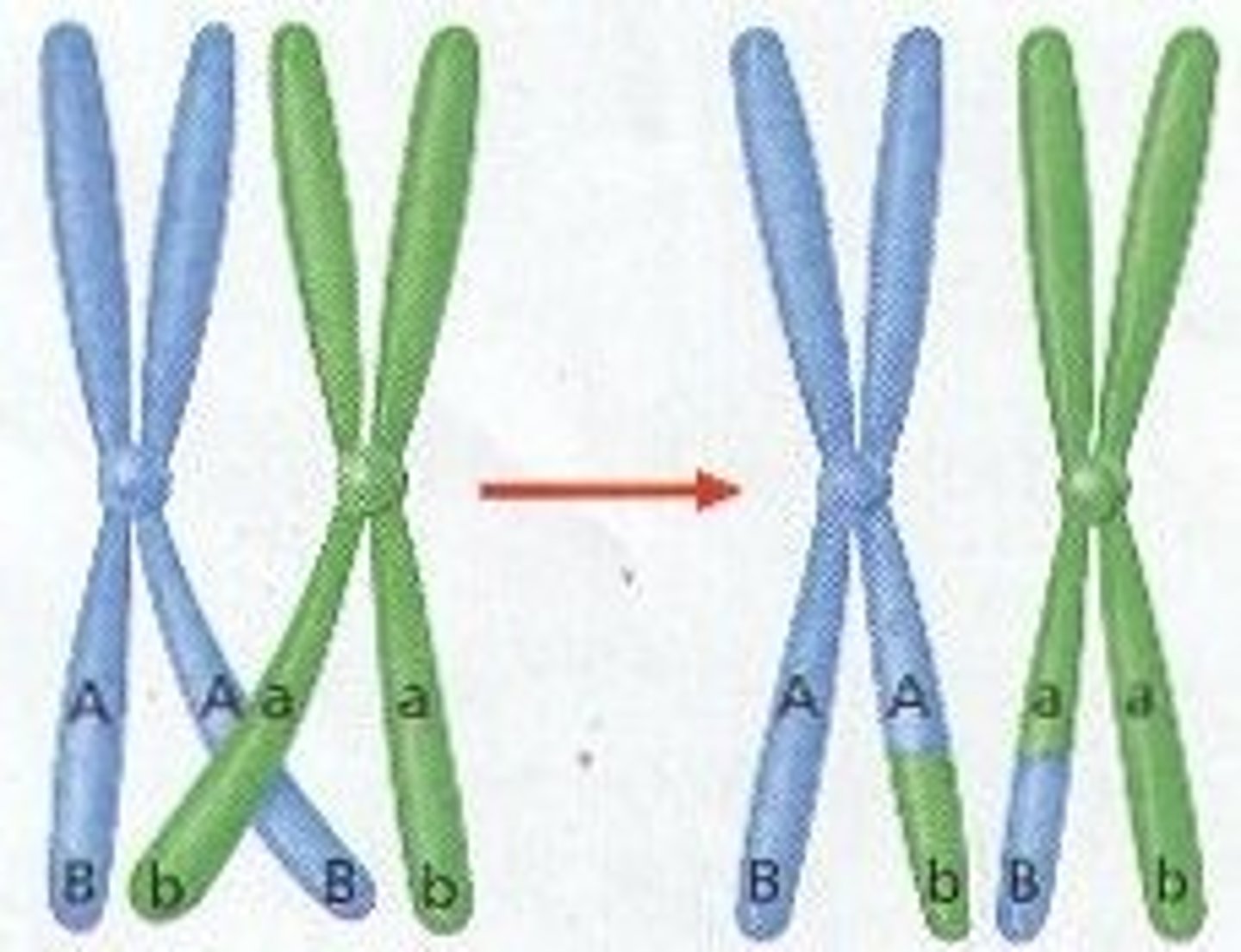
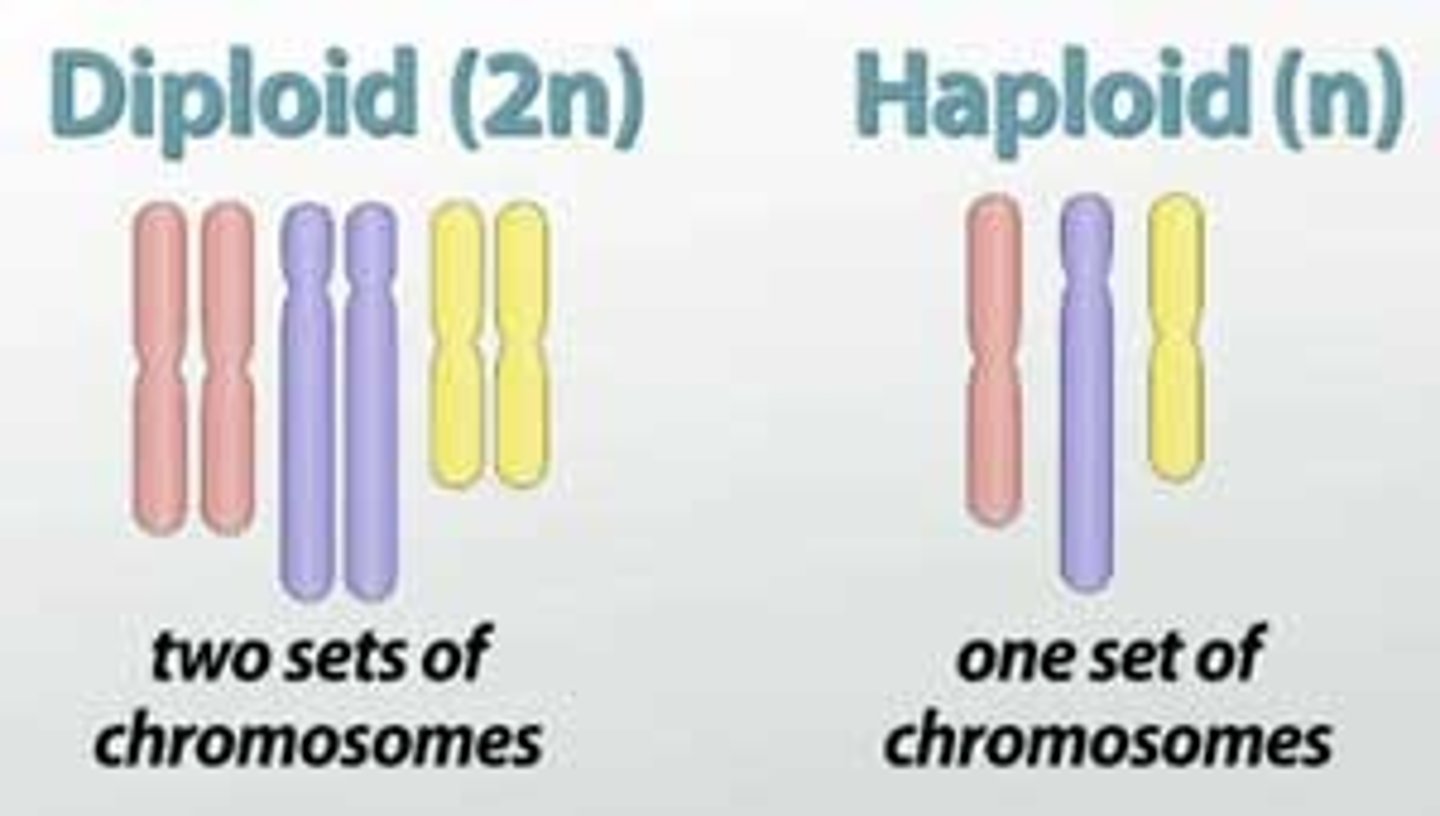
Which source of variation includes diploid organisms that have two copies of each chromosome?
diploidy
How are more variations maintained in the gene pool in heterozygous conditions?
recessive allele is stored
for later generations
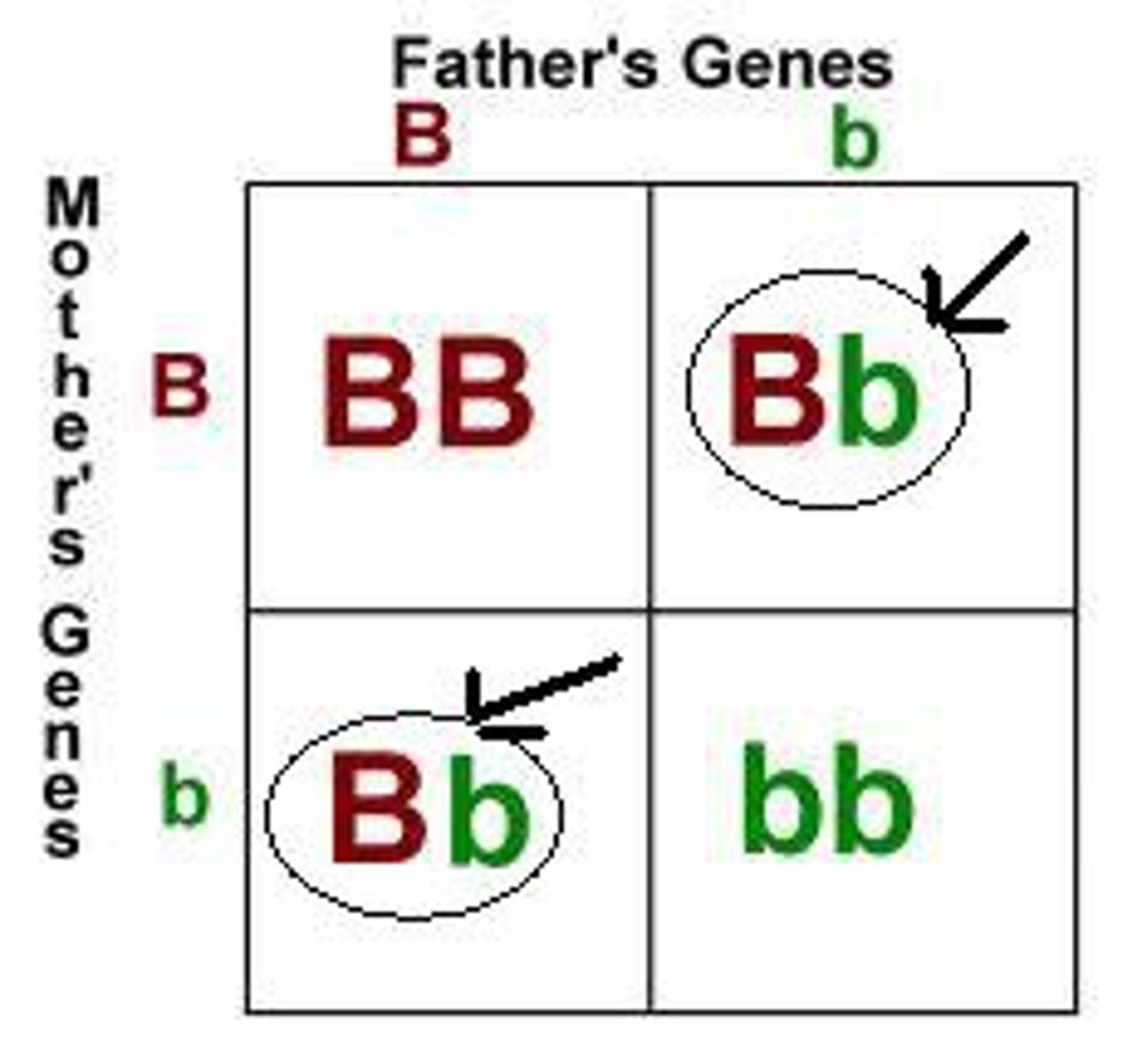
Which source of variation includes mating with unrelated partners results in mixing alleles and creating new allele combinations?
outbreeding
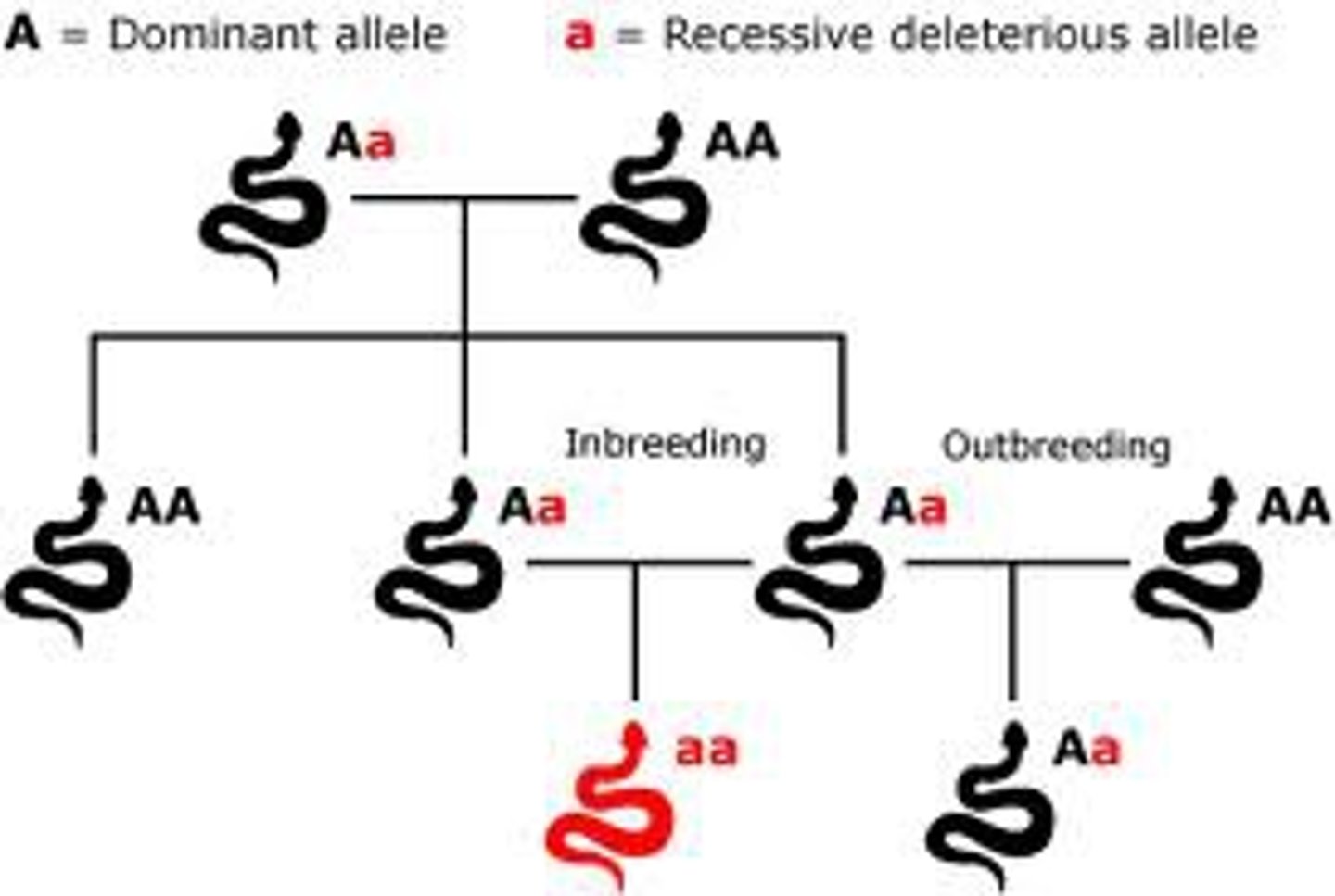
Which source of variation involves the maintenance of different phenotypes in a population?
balanced polymorphism
(Note: usually one phenotype is best, but in polymorphism, two or more can exist)
What source of variation occurs when a heterozygote condition bears greater advantage than either homozygous condition?
heterozygote advantage
(Note: sickle cell anemia
is homozygous recessive,
but heterozygotes have
resistance against malaria)
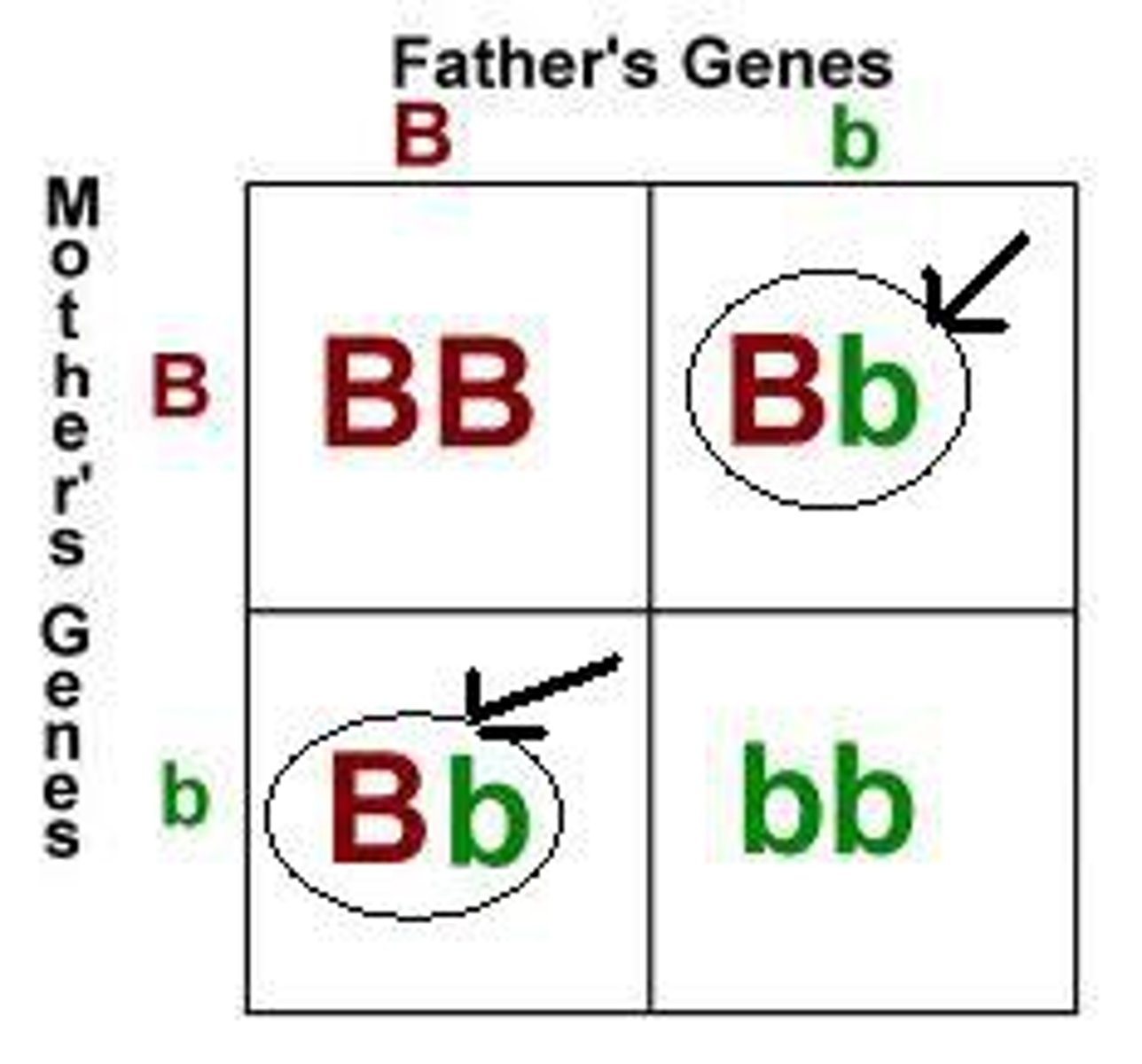
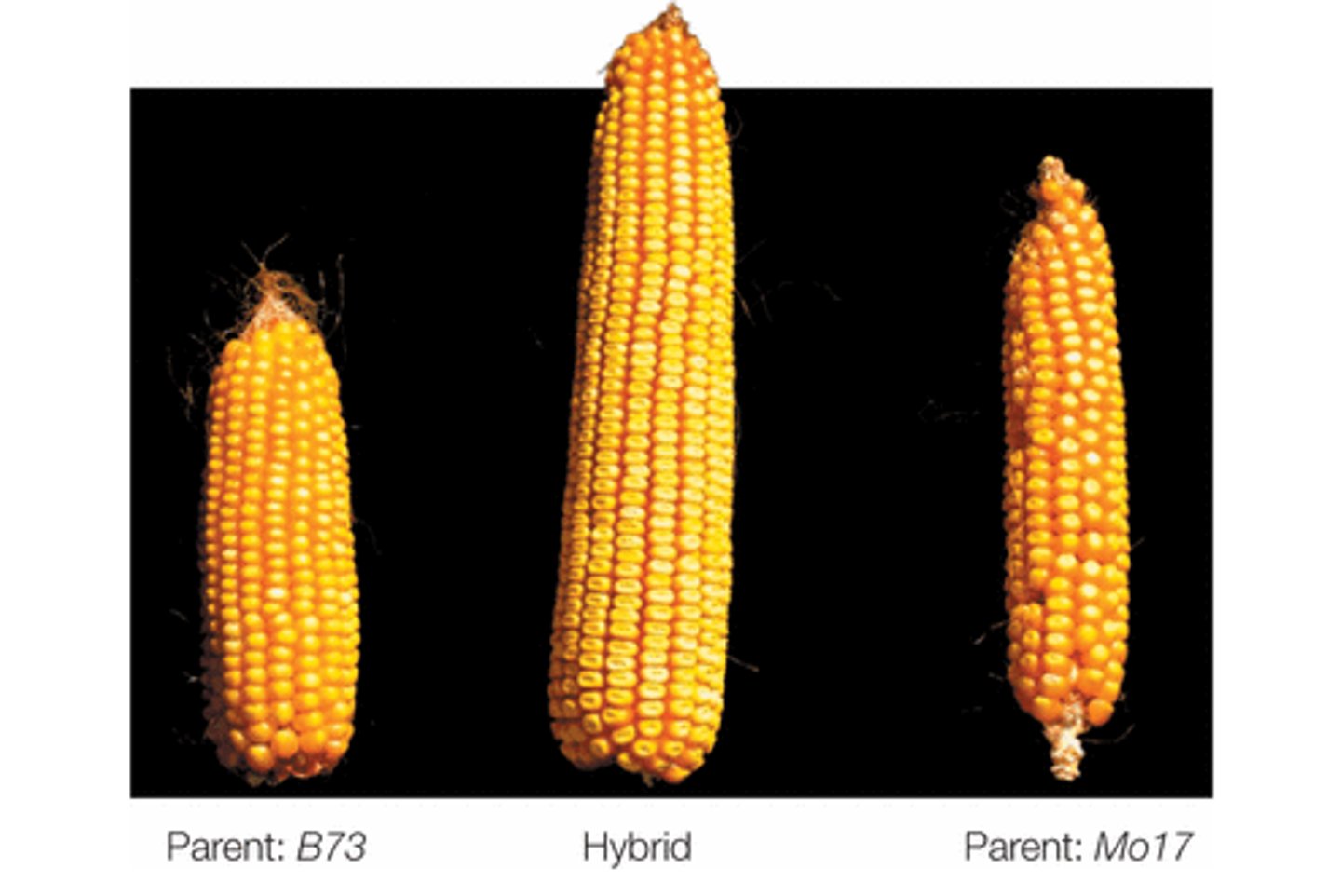
Which source of variation involves the superior quality of offspring resulting from crosses between two different inbred organisms?
hybrid vigor (heterosis)
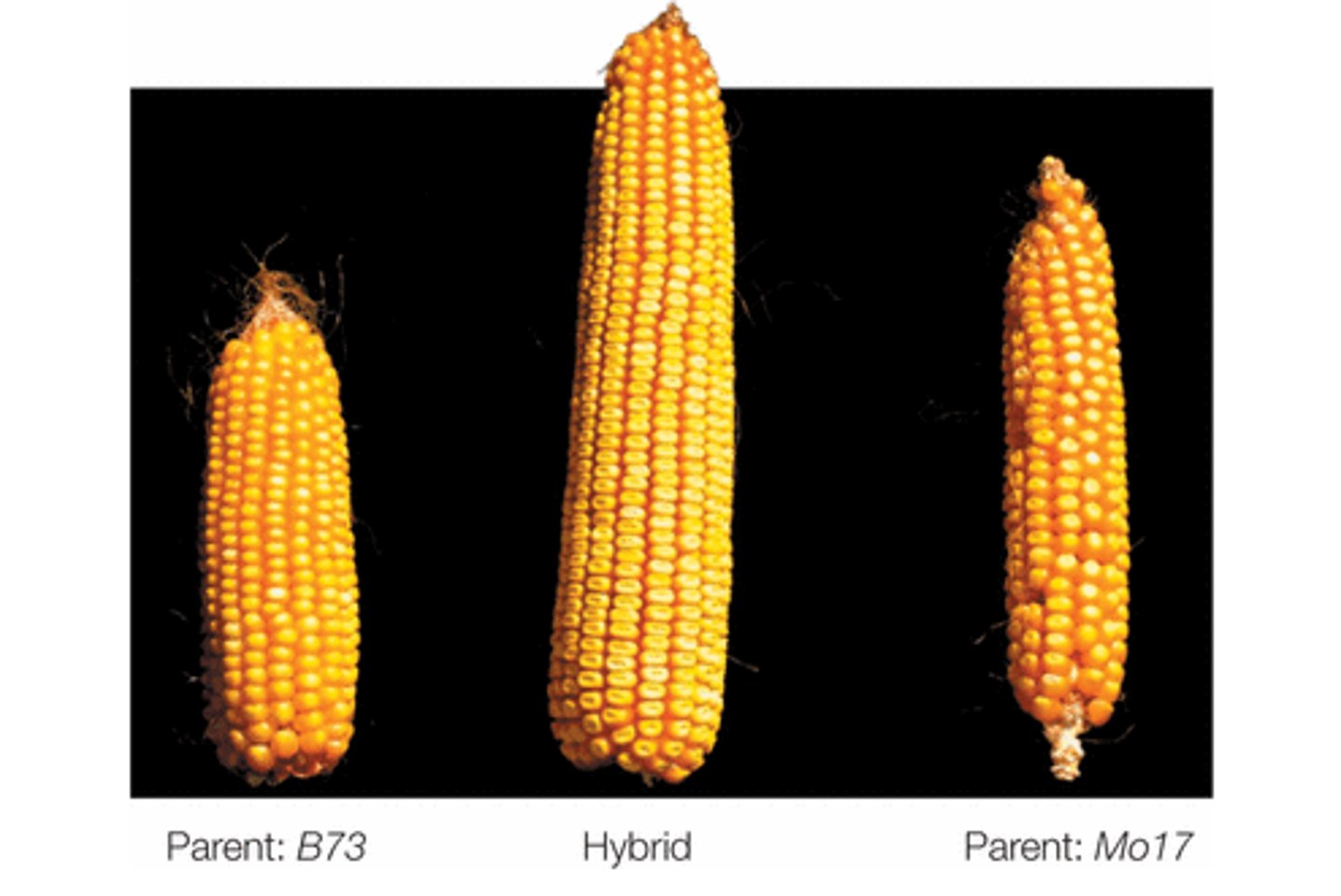

What results from reducing deleterious recessive homozygous conditions and increasing heterozygous advantage in hybrids?
hybrid superior quality

What source of variation occurs when the least common phenotypes have a selective advantage
frequency-dependent
selection (minority advantage)
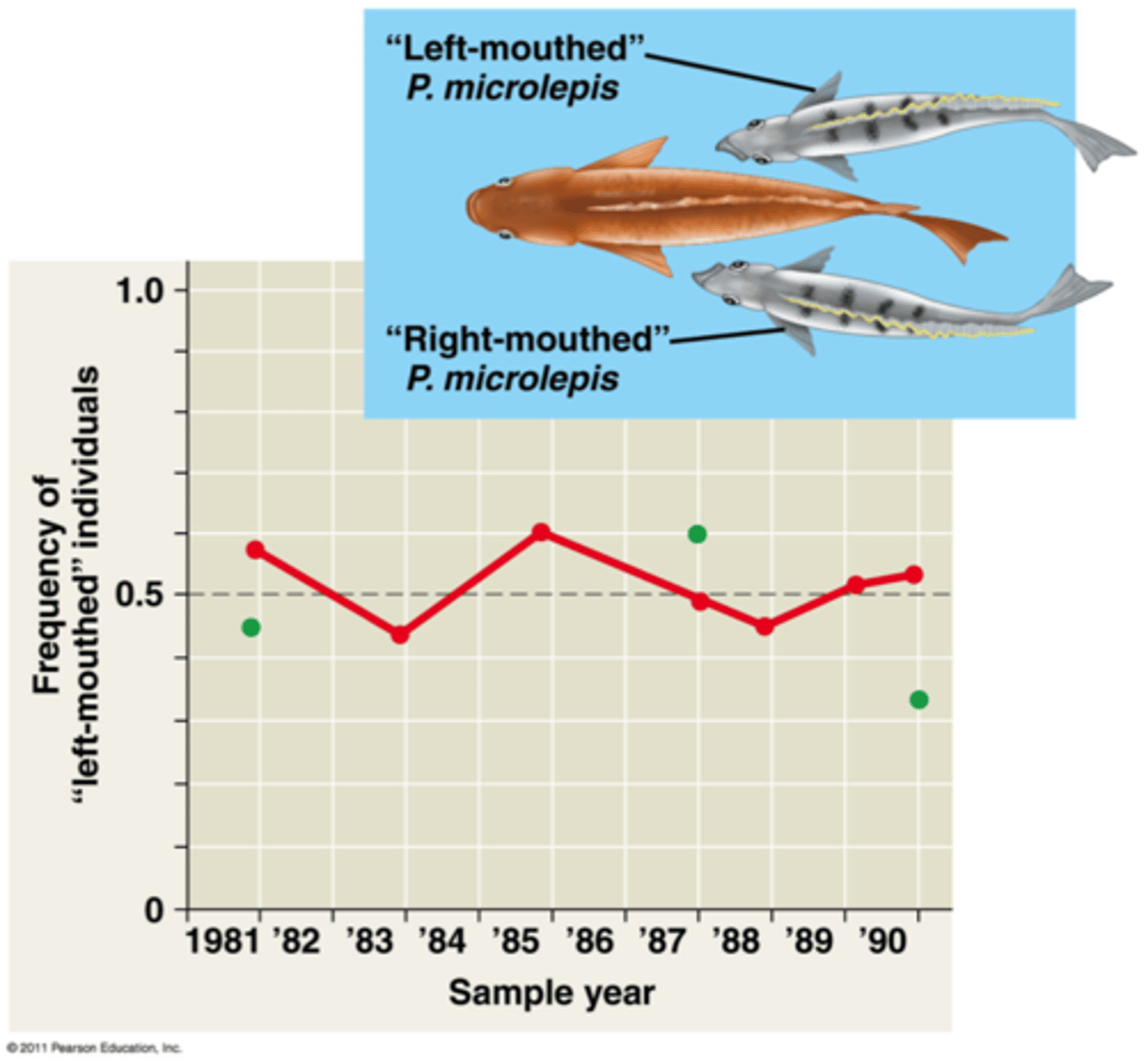
How does frequency-dependent selection happen in a cycle?
Rare phenotypes will increase in frequency and will then be selected against, repeating the cycle
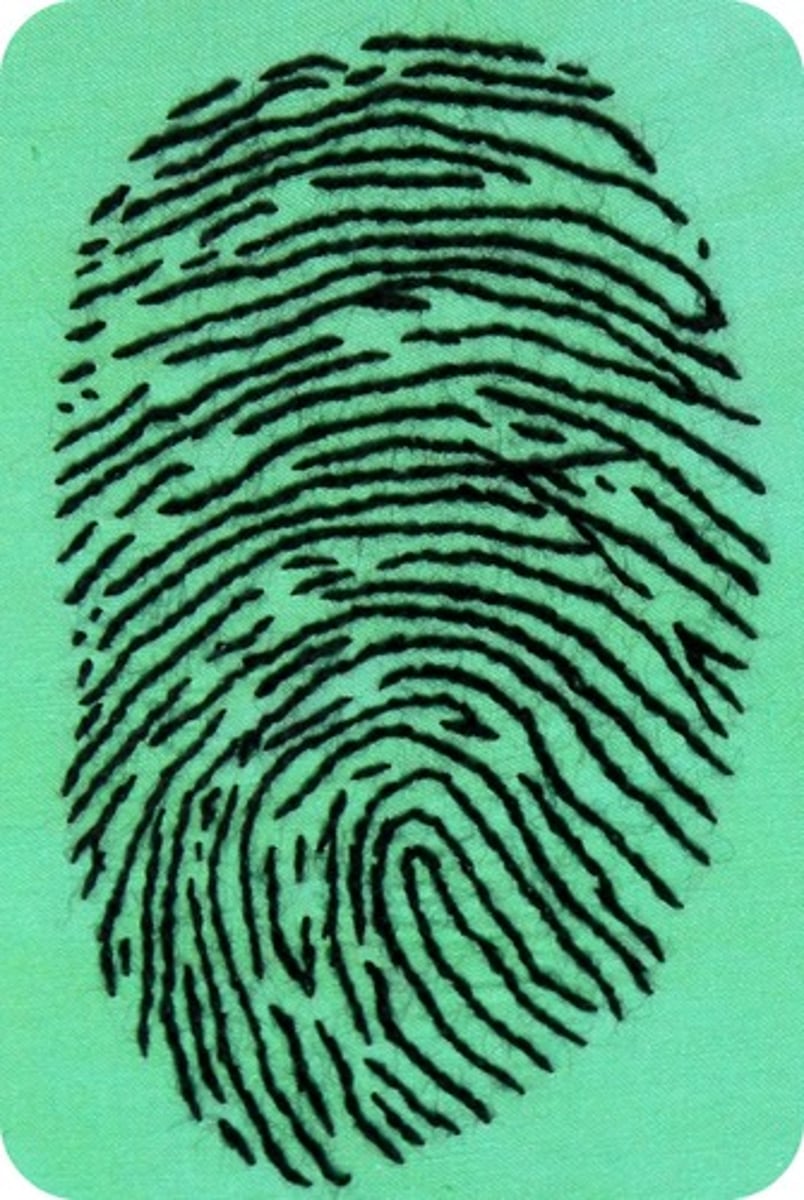
What source of variation involves variations that are passed down without any selective value, such as fingerprints in humans?
neutral variation

What source of variation occurs when variation of a species is dependent on climate or geographic conditions?
geographic variation
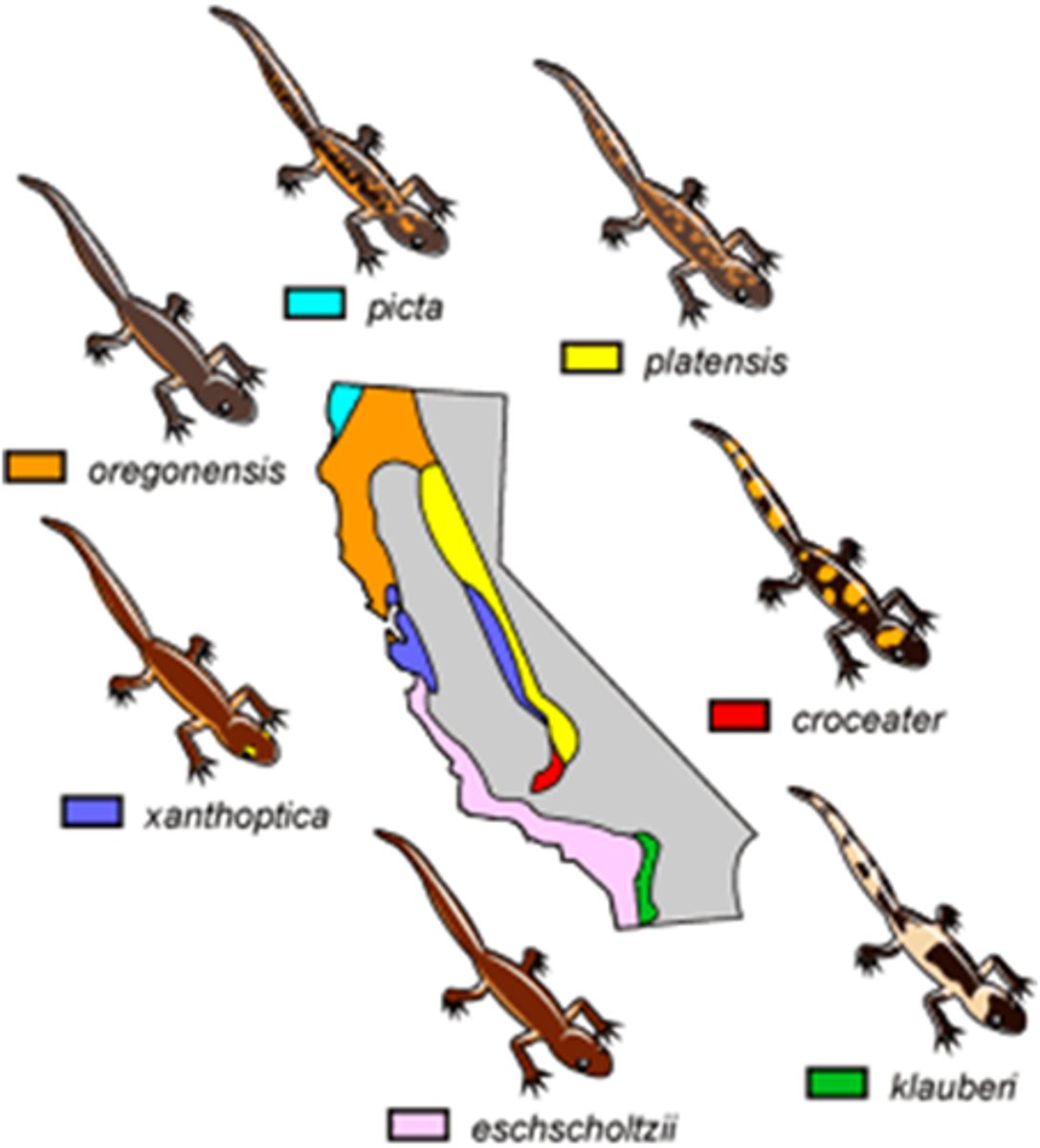
What is a graded variation of a phenotype due to geographic variation?
cline
(Note: such as a
north-south cline)
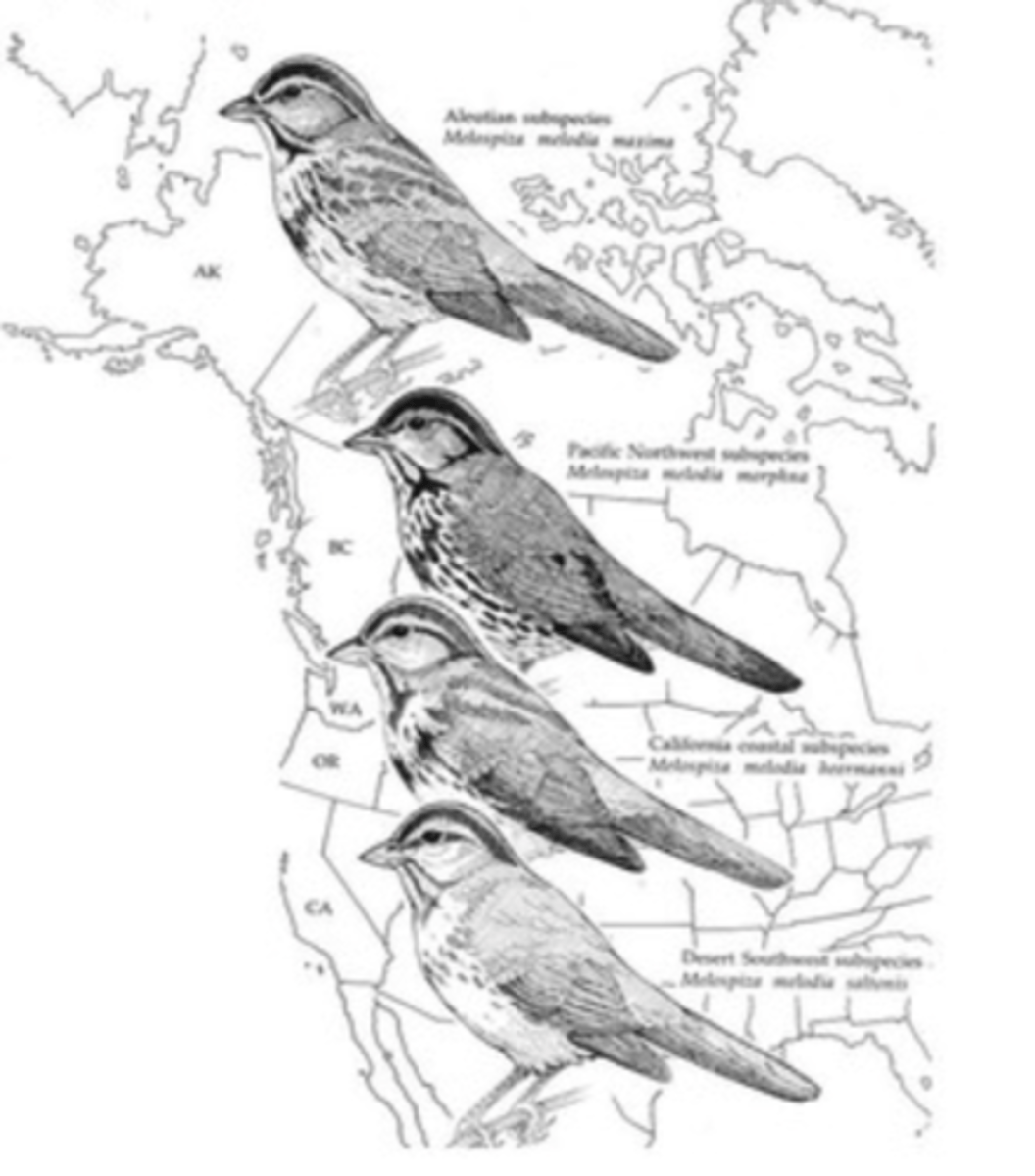
Which cause of change in allele frequency is due to adaptations to the environment?
natural selection
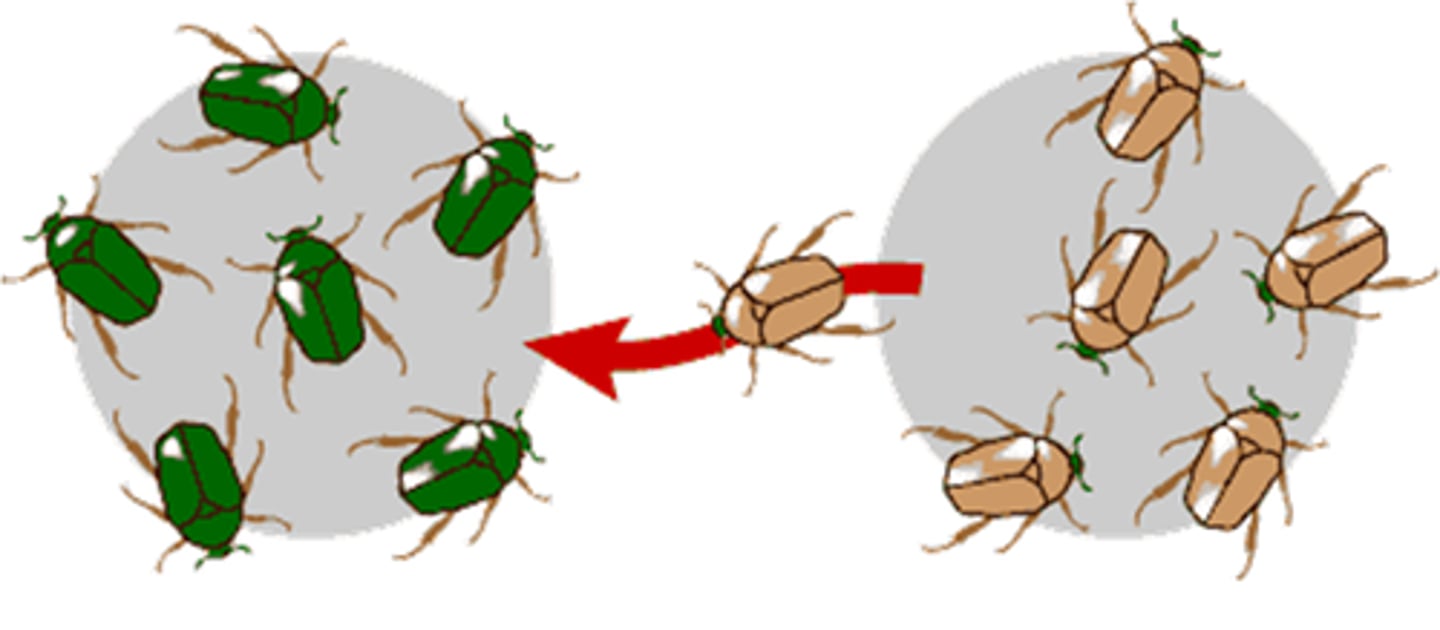
Which cause of change in allele frequency involves the introduction and removal of alleles from the population?
gene flow
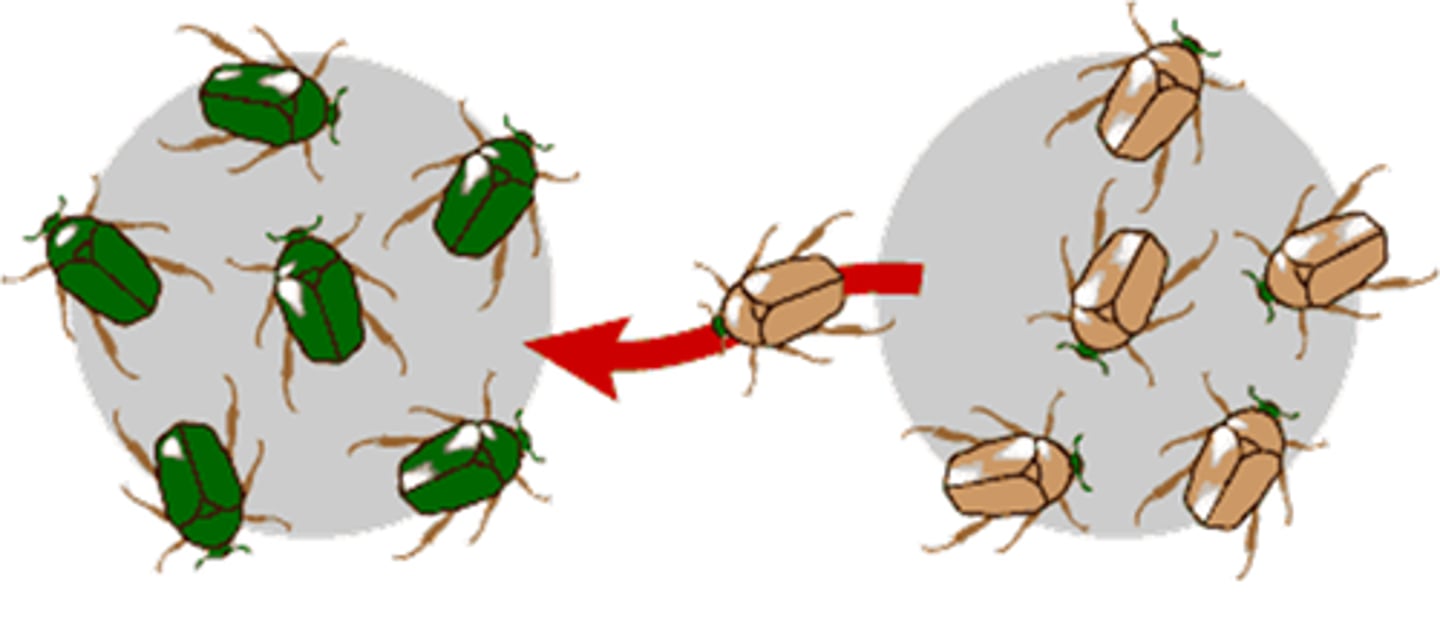
How does gene flow occur?
individuals leave (emigration)
or enter the population
Which cause of change in allele frequency involves the random increase and decrease of an allele by chance?
genetic drift

In which populations does genetic drift have a larger effect?
small populations

Which cause of change in allele frequency involves the reduction of a gene pool when a small group of individuals migrate to a new location?
founder effect
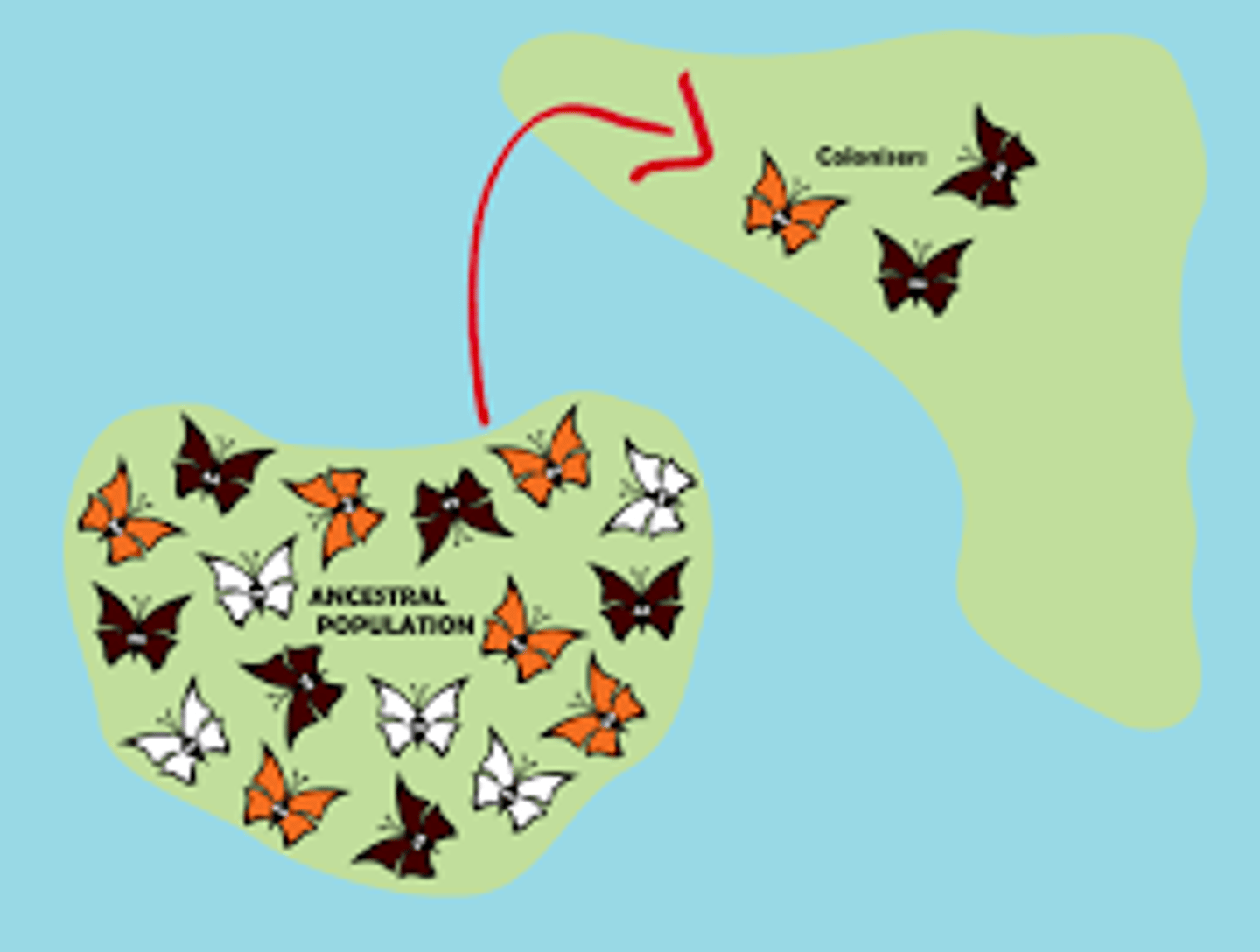
In the founder effect, how will the genetic makeup of the new population compare to the original after many generations?
it will be unique

Which cause of change in allele frequency occurs when the population decreases size due to natural catastrophes or other events?
bottleneck effect
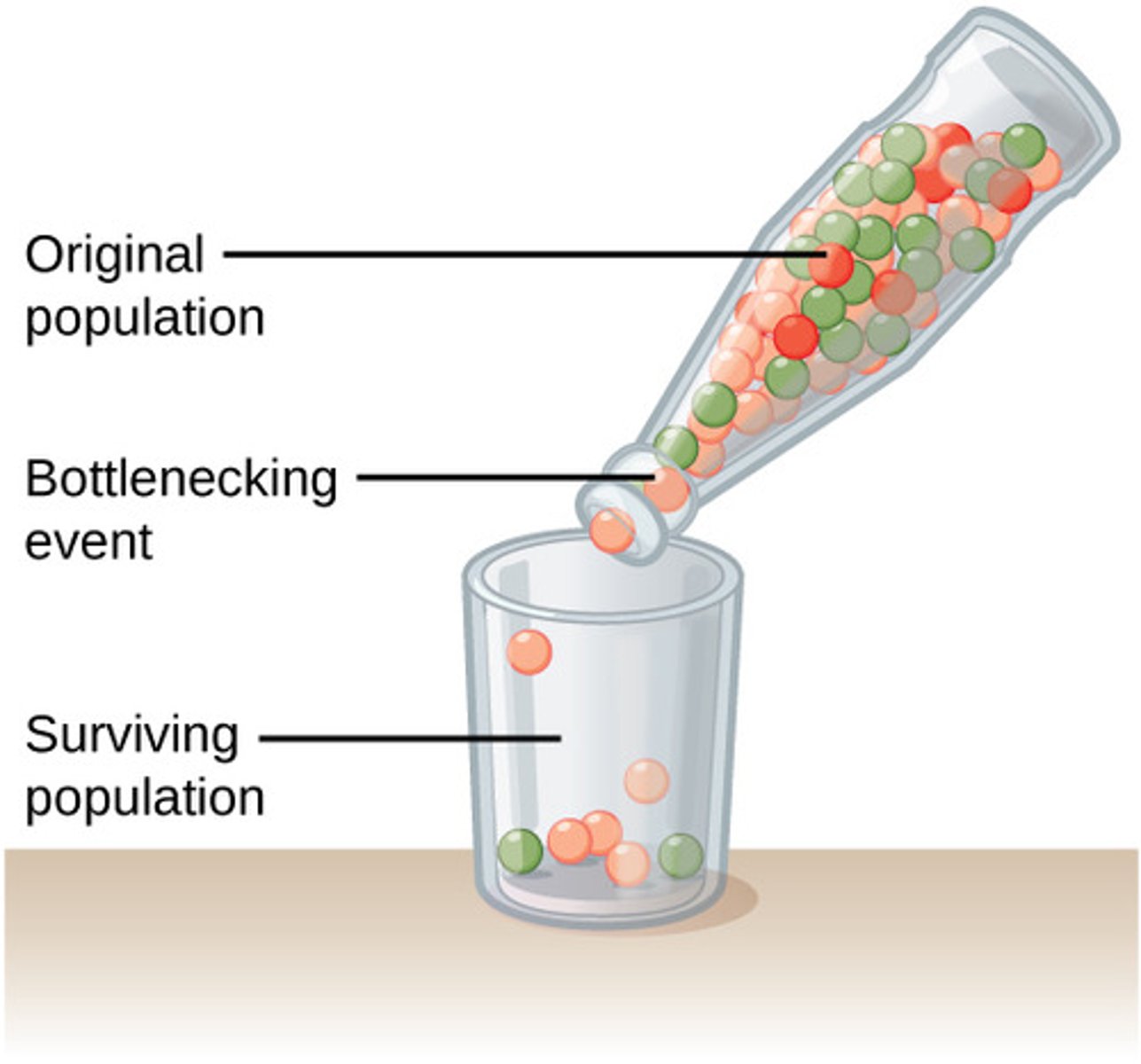
What process is a population vulnerable to following the bottleneck effect?
genetic drift
Which cause of change in allele frequency occurs when individuals choose mates based upon their particular traits?
nonrandom mating
Which cause of change in allele frequency occurs when individuals mate with relatives?
inbreeding
(Note: changes genotype proportions but not allele frequencies)
Which cause of change in allele frequency occurs when females choose males based on superior traits?
sexual selection

Which cause of change in allele frequency occurs when new alleles are introduced through random genetic anomalies?
mutations
If allele frequencies remain constant from generation to generation, what process is not occurring?
evolution
In the situation of constant allele frequencies, what equation can be used to determine the allele frequencies for a population?
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
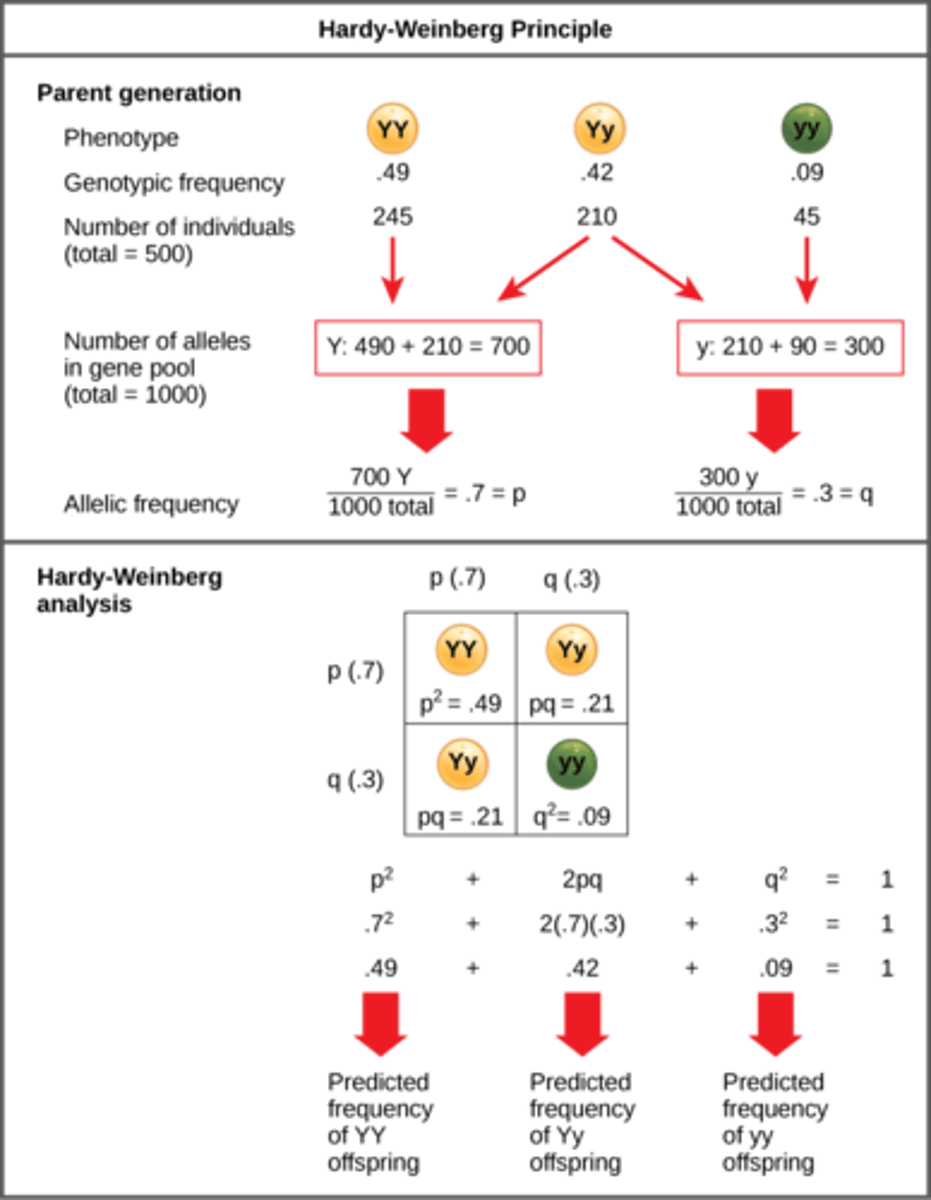
What phenomenon in a population does p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 represent?
all individuals sum to 100%
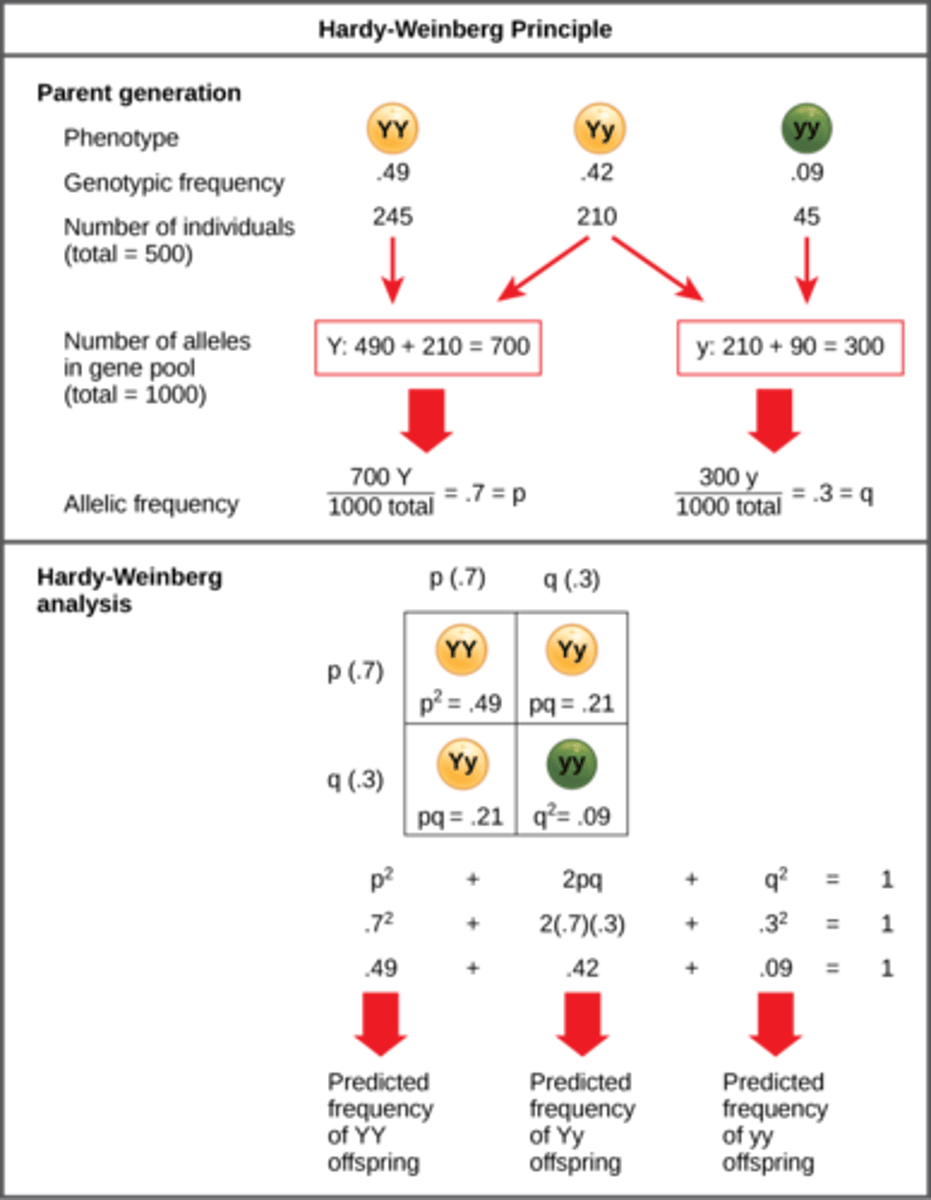
What phenomenon in a population does p + q = 1 represent?
all alleles sum to 100%
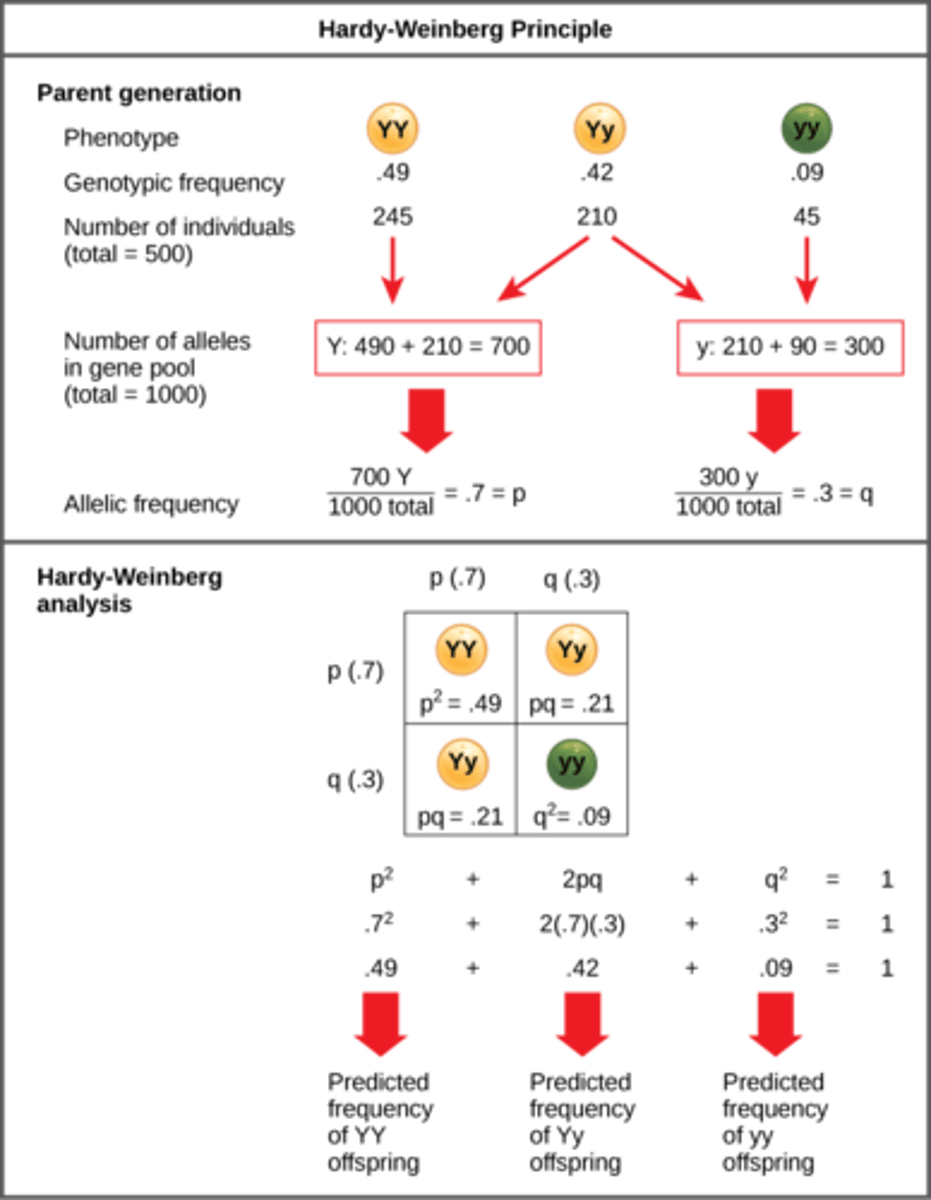
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
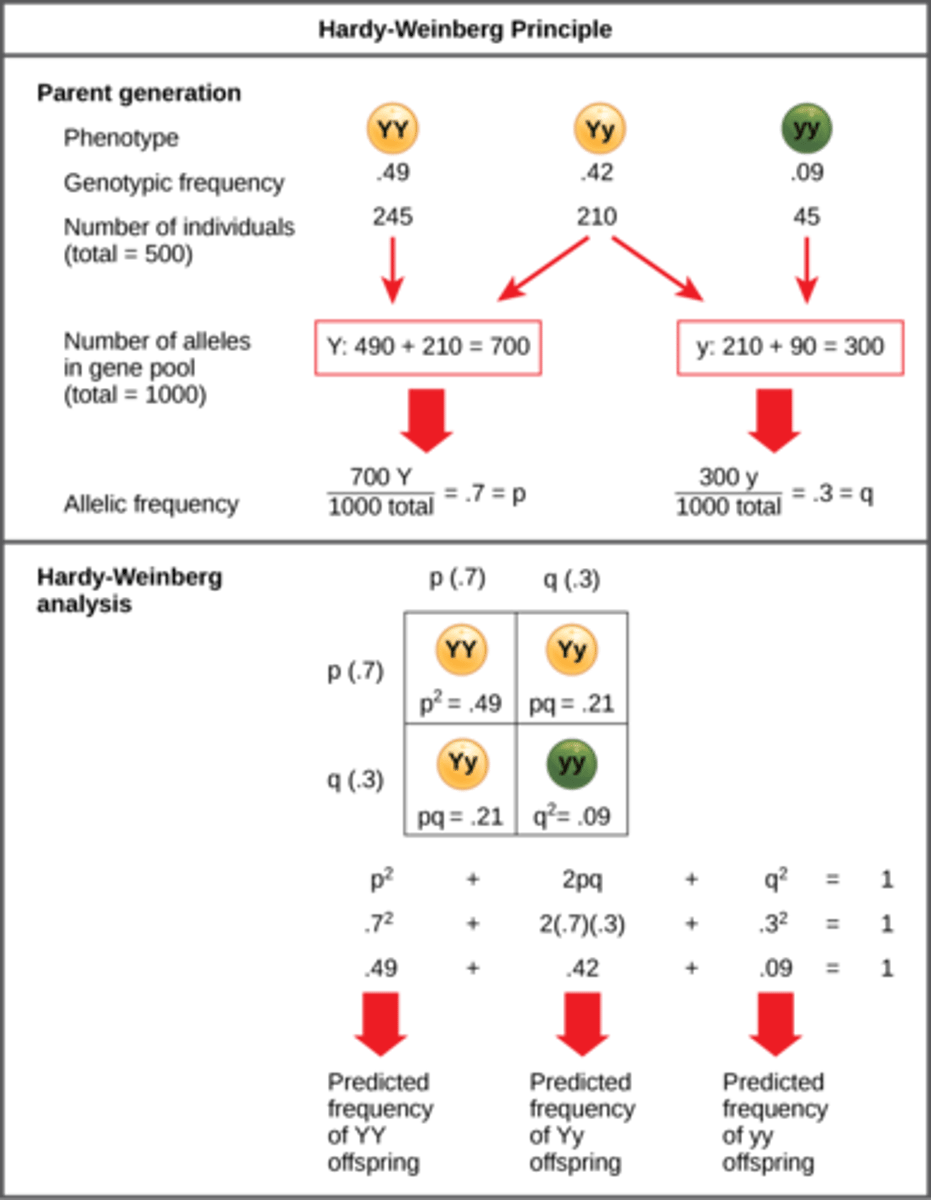
What is p in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
frequency of dominant allele
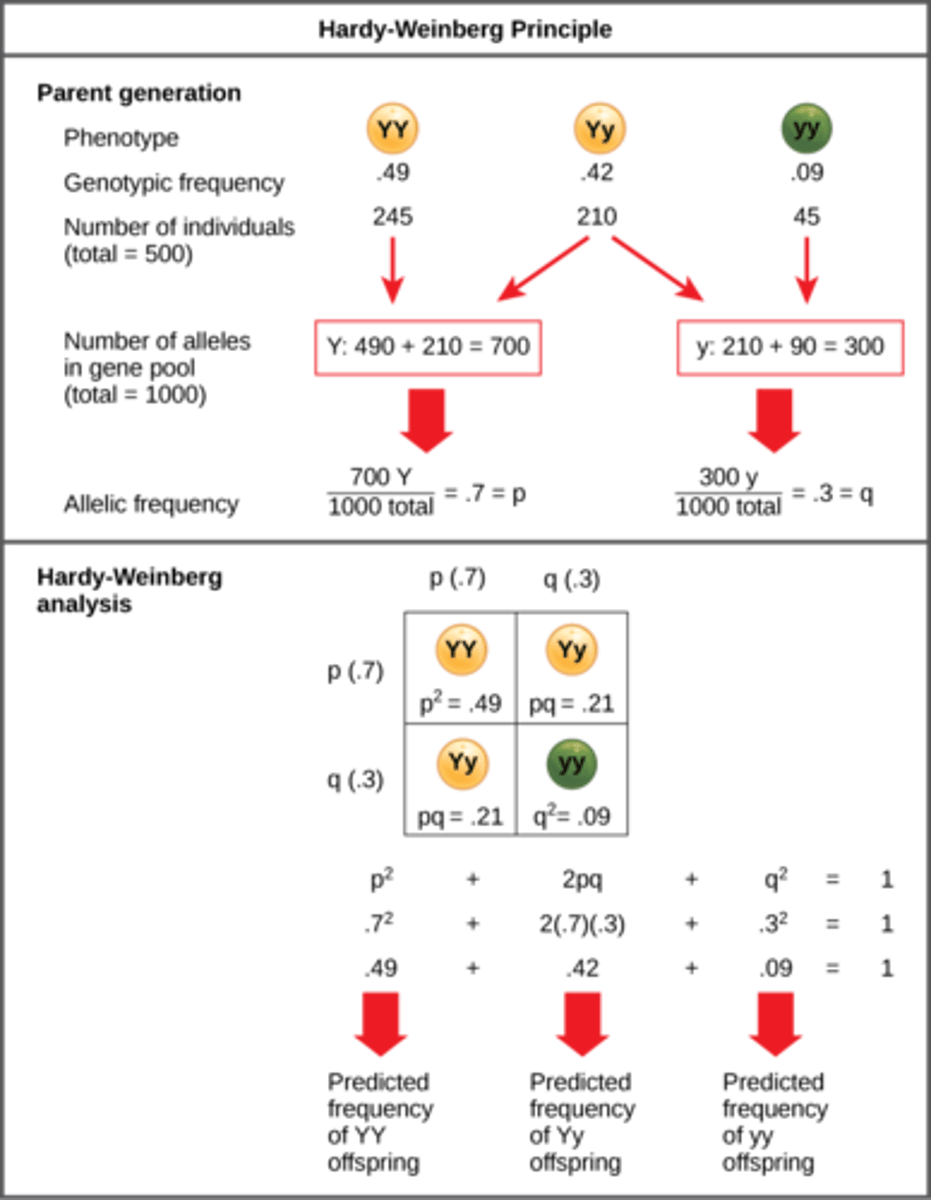
What is q in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
frequency of the
recessive allele
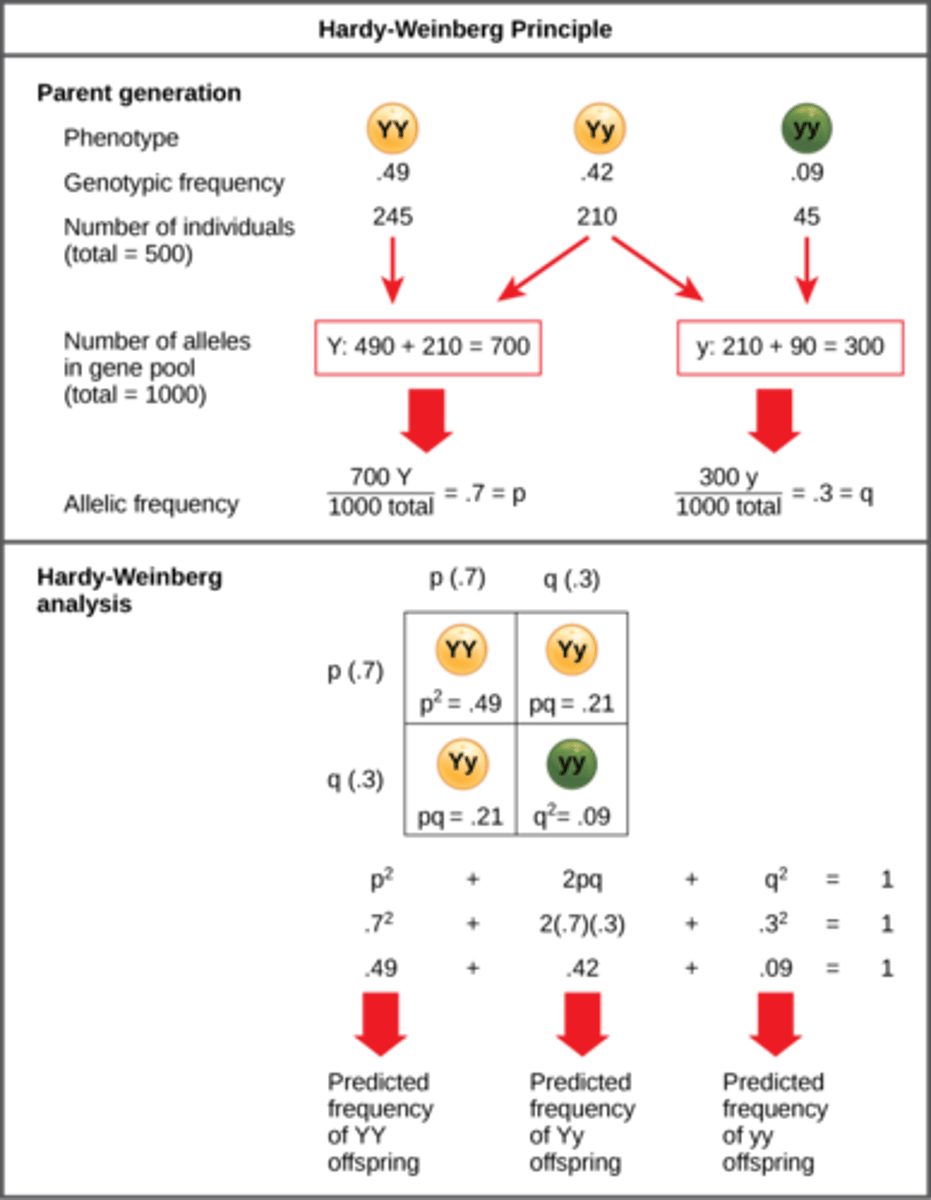
What is p^2 in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
frequency of homozygous
dominant individuals
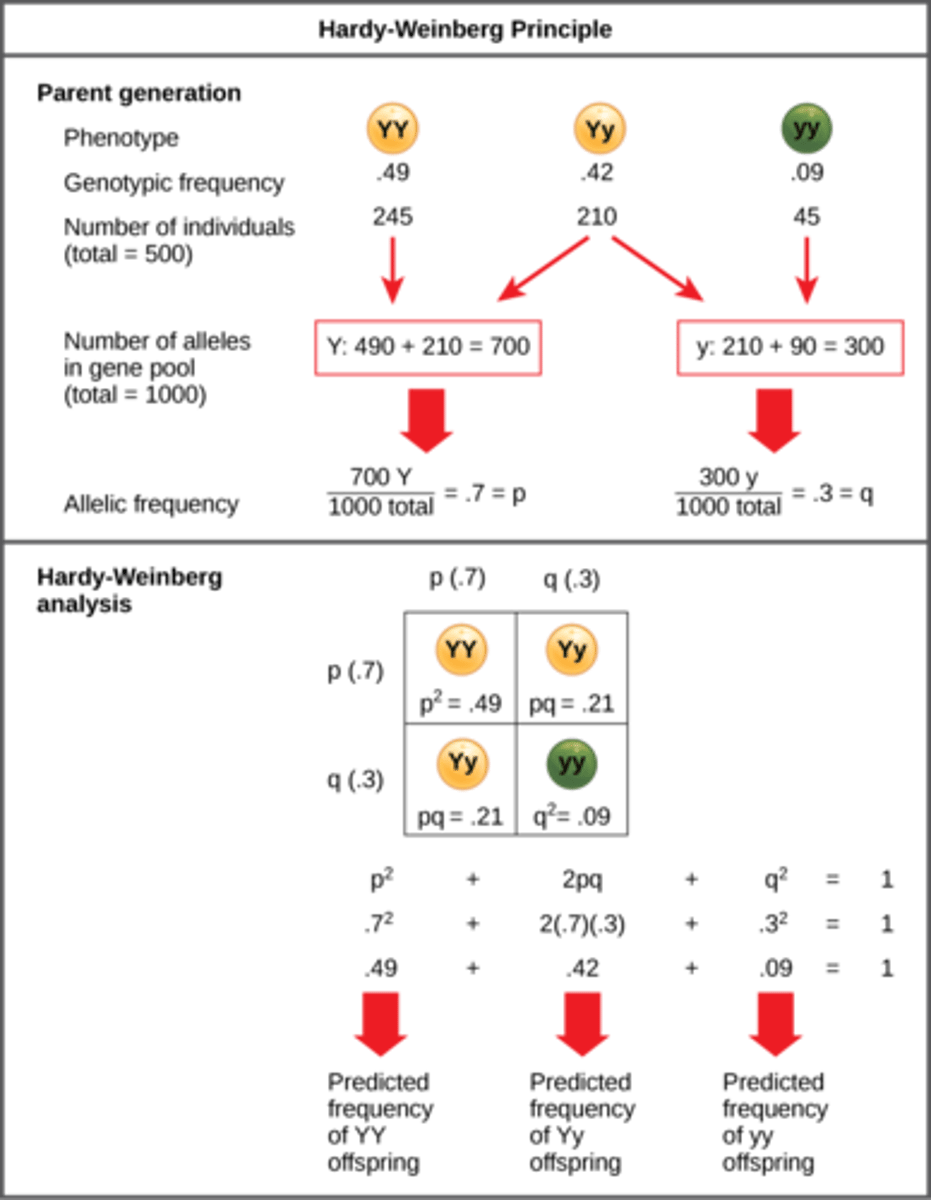
What is q^2 in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
frequency of homozygous
recessive individuals
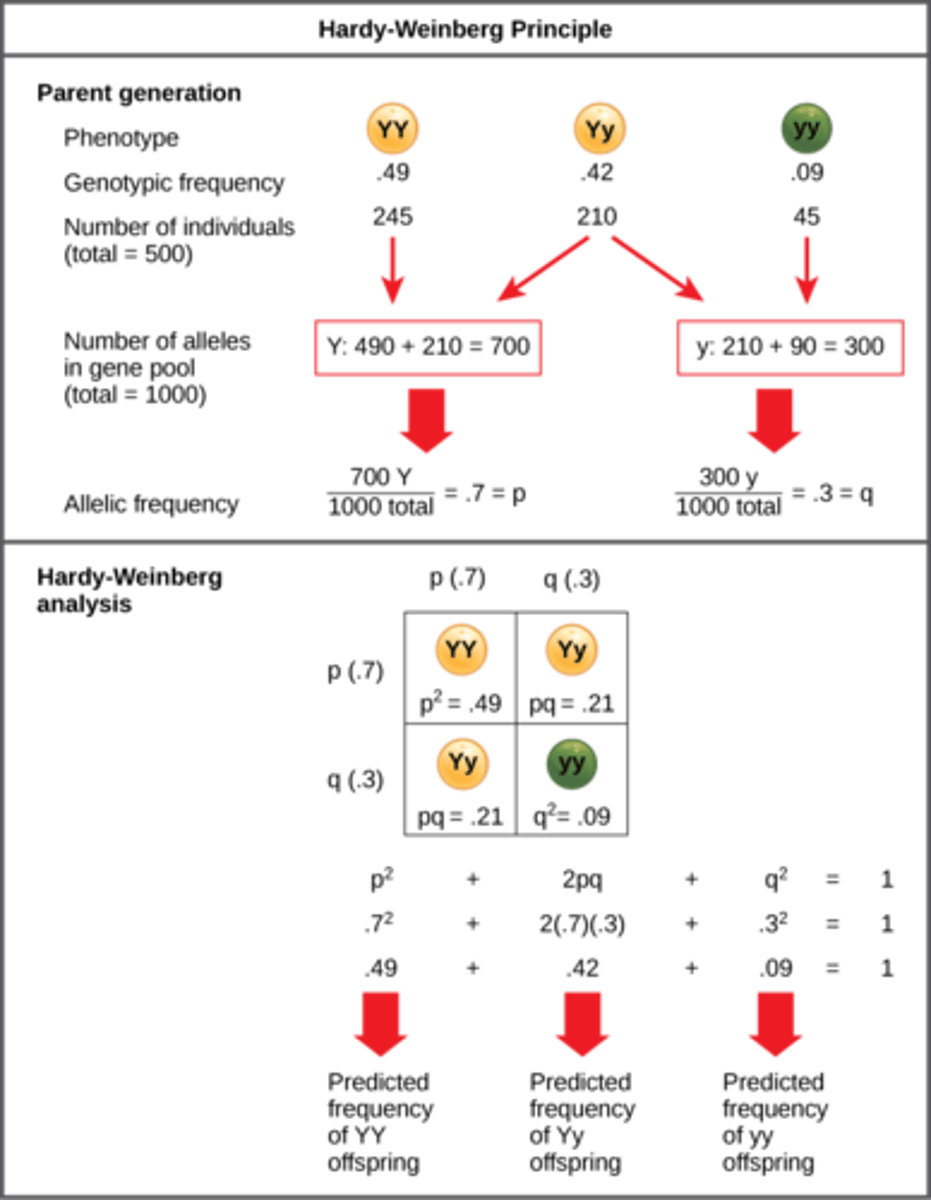
What is 2pq in the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
frequency of
heterozygous individuals
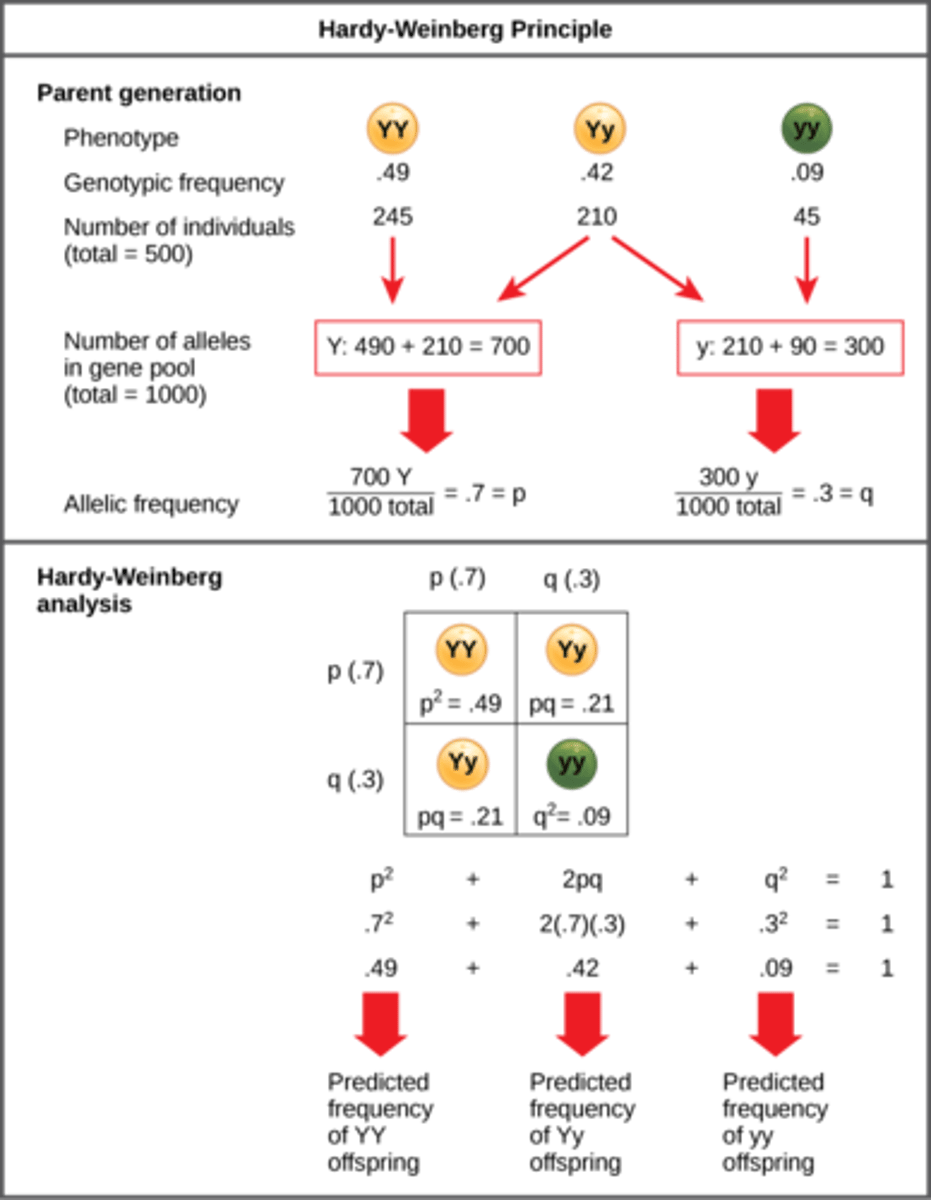
Which equations must sum to 1 in order for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 and p + q = 1
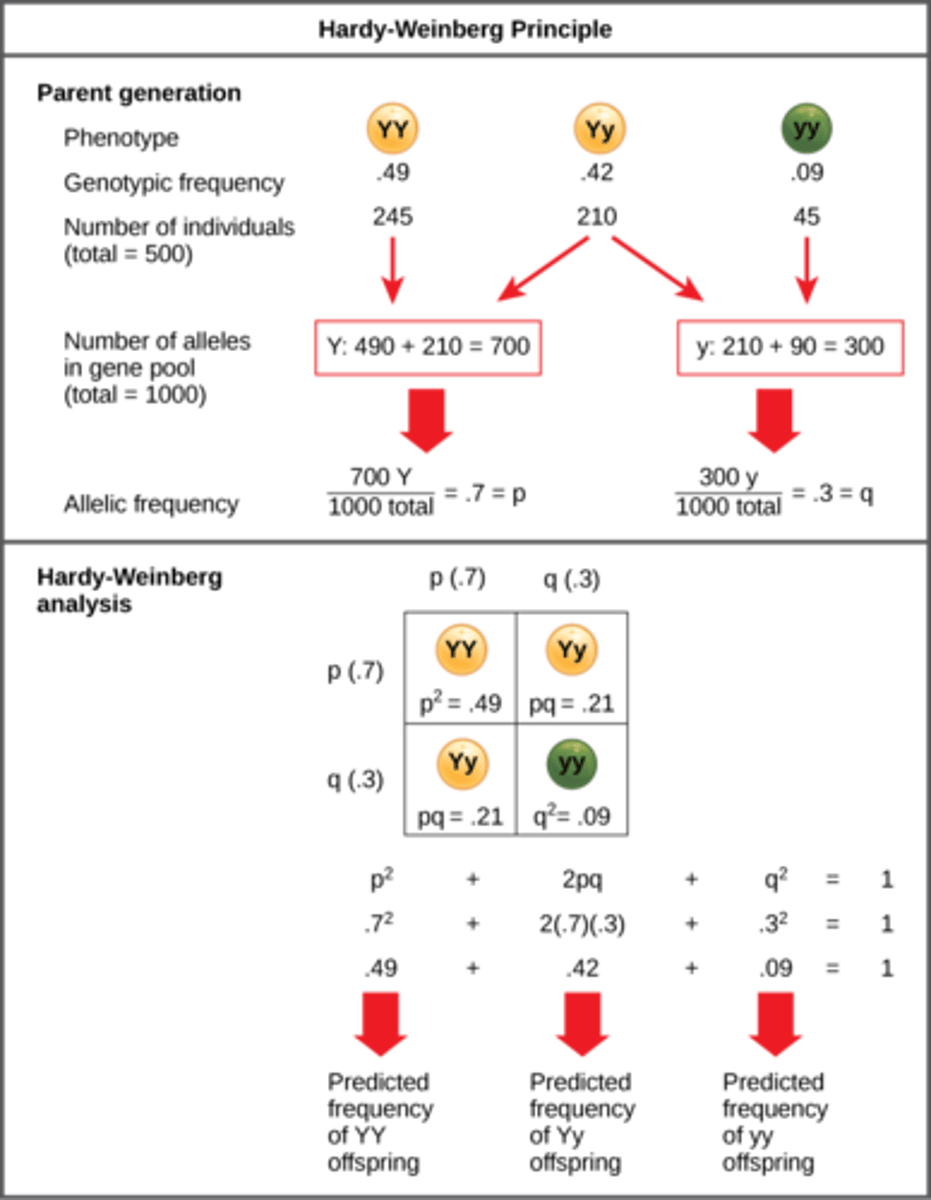
What are the requirements for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
1. no mutations
2. no natural selection
3. no gene flow
4. large population
5. random mating
Why must there be no mutations for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
no new alleles can be introduced to the population
Why must there be no natural selection for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
the environment is not impacting allele frequencies, and so traits are neutral
Why must there be no gene flow for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
an isolated population will have no gene flow
Why must there be a large population for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
decreases the effects of genetic drift
Why must there be random mating in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
decreases the chance of any allele from changing in frequency