external surface of the brain (3)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
term for the grooves
Sulcus/Sulci
left brain hemisphere is responsiblr for?
language
hand dominance
right brain hemisphere is responsiblr for?
spatial awareness
Frontal Lobe
•Motor
•Executive Functions
Premotor Cortex (Area 6)

(sensory-guided movement)
Plans and prepares movements
Uses external sensory cues (visual, auditory) to guide movement
Organizes and sequences movements
Prepares posture before movement
See it, plan it
Supplementary Motor Cortex (Area 8)

(self-initiated movement)
Plans and initiates movements
Controls internally generated movements
Coordinates bilateral movements
Involved in movement timing and sequencing
Think it, do it
Brocas Area
Responsible for speech production
Controls motor planning for speech
Involved in expressive language
Brodmann’s Areas
Regions of the cerebral cortex classified by cell structure
Used to link brain anatomy with function
ex:Area 4: Primary motor cortex
Area 6: Premotor cortex
Area 8: Supplementary motor area
Area 4 – Primary Motor Cortex
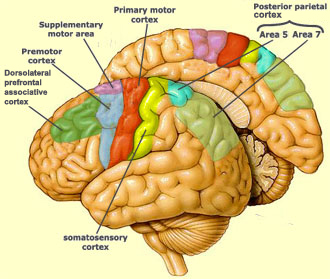
Executes voluntary skeletal muscle movement
Controls force, direction, and precision of movement
Example:
Voluntarily moving your hand to pick up a pencil
Areas 44 & 45 – Broca’s Area
Motor planning and production of speech
Expressive language
Example:
Forming words to answer a question out loud
Areas 3, 1, 2 – Primary Somatosensory Cortex

Receives and processes tactile, proprioceptive, pain, and temperature input
Example:
Feeling the texture of a coin in your hand without looking
Areas 5 & 7 – Superior Parietal Lobule
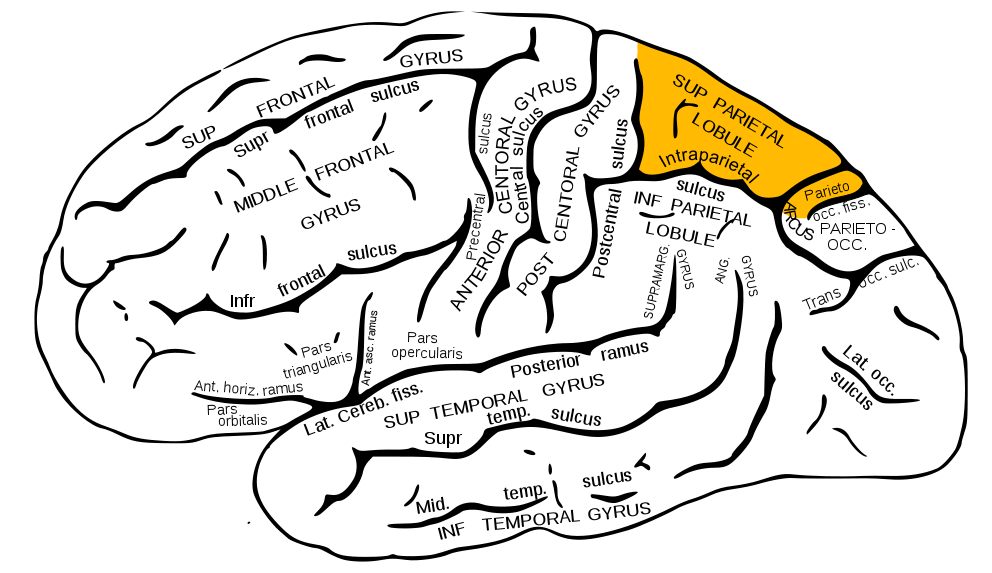
Integrates sensory information
Supports spatial awareness and body position in space
Example:
Reaching for an object while accurately judging where your arm is in space
Area 41 – Primary Auditory Cortex
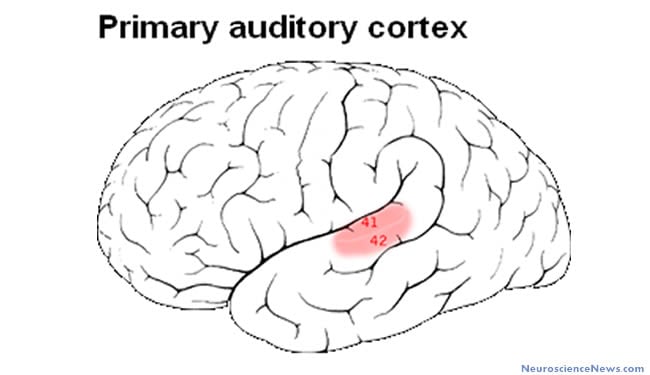
Receives and processes auditory input
Detects sound pitch, volume, and location
Example:
Hearing a doorbell ring and recognizing the sound
Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex

Executive functions
Working memory
Planning, problem solving, and organization
Attention and Language swtiching
Example:
Remembering instructions and organizing steps to complete a school assignment
Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex

Inhibitory control
Emotional regulation
Language processing and response selection
Decision-making based on rules
Example:
Stopping yourself from blurting out an answer and waiting your turn to speak
Ventromedial & Dorsomedial Prefrontal Cortex
Emotional processing
Social behavior and judgment
Self-awareness and insight
Decision-making based on emotions and values
Example:
Understanding how your actions affect others and choosing an appropriate response
Orbitofrontal Cortex & the Frontal Pole
Primarily related to loss of inhibitory and emotional control and an inability to function socially
Damage to the Frontal Pole is subtle but seems to affect decision making, creativity and metacognition.
Parietal Lobe
•Sensory
•Perceptual
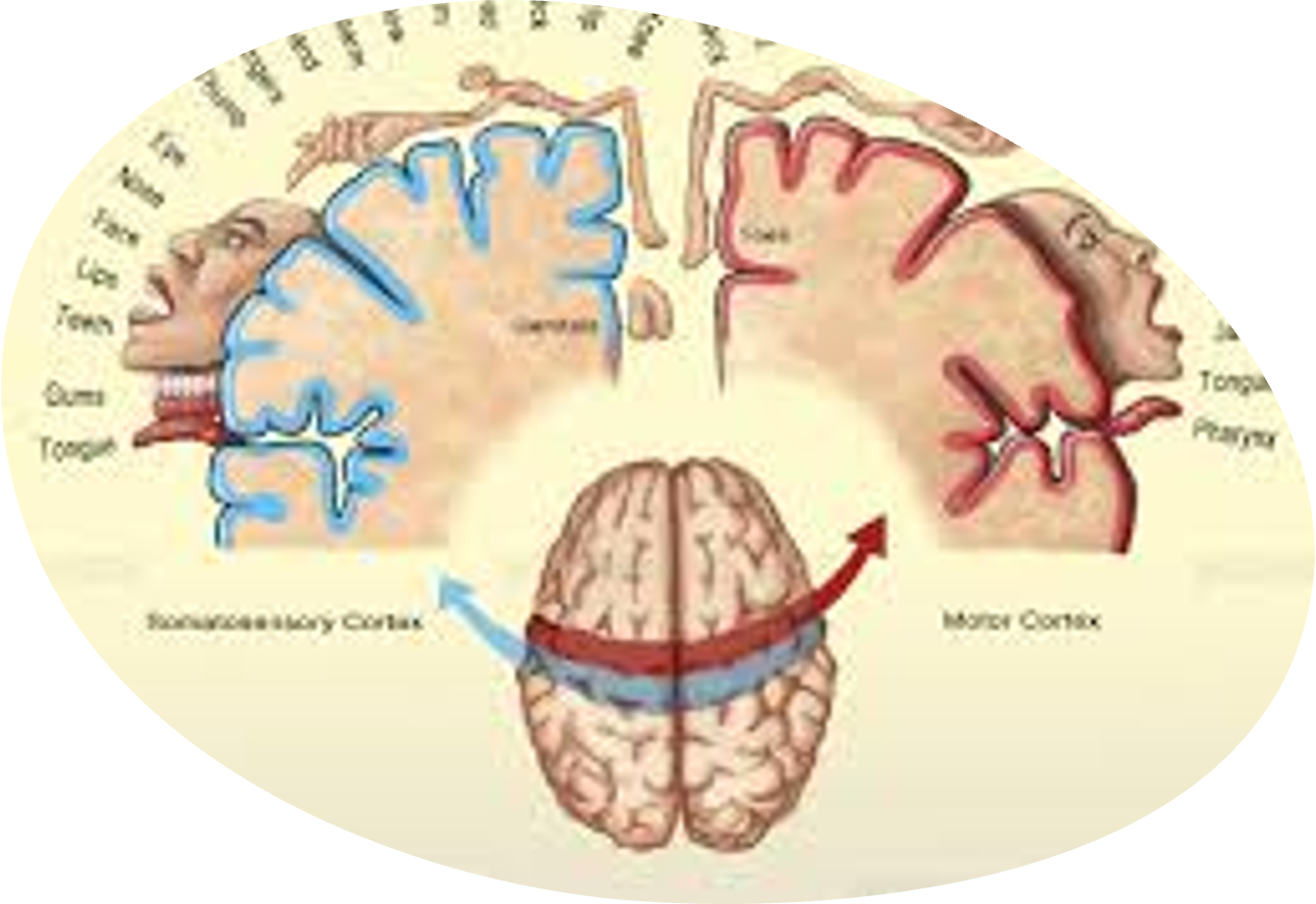
Homunculus
most goes to your face and hands
Temporal Lobe
•Hearing/Auditory Processing
•Memory
Hippocampus
primary memory area
The Temporal Lobe for Clinicians
•Primary auditory Cortex
•Wernicke’s Area
•Hippocampus/AD (under-surface)
•Seizure Disorders
parahippocampal gyrus
primary short term memory
first place to decrease with age
UNCUS (overlies Amygdala or Amygdaloid Nucleus)
Processes smells (part of olfactory cortex)
Links smells to emotions and memories (via amygdala): Smelling cookies triggers recognition and happy memories
Example:Smelling cookies triggers recognition and happy memories
Amygdaloid Nucleus
Processes emotions, especially fear and aggression
ex: Seeing a snake triggers fear and a memory of danger
Fusiform Gyrus
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/fusiform-gyrus/rEBNATOG81n5R88MicA_Fusiform-gyrus.png)
Recognizes faces
Helps identify objects and words
Plays a role in visual processing and recognition
example: Seeing a friend’s face and immediately recognizing them