2. Postmortem Changes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Are postmortem changes considered lesions?
- No
What is the difference between somatic death and cellular death?
- Somatic death is the death of the body while cellular death is the death of cells which occurs at different rates (ex. neurons die first)
How can one minimize. postmortem changes?
- Rapid cooling (Do not freeze)
What is autolysis?
- Enzymatic and bacterial breakdown of dead tissue following somatic death (aka decomposition)
What does the progression of autolysis depend on?
- Depends on environment and host factors (size, environmental temp., presence of fever or infection, wool, etc.)
Is there such a thing as a fresh dead sheep?
- Not really because their wool prevents rapid cooling of the body to prevent postmortem changes
What changes are involved in autolysis?
- Changes in tissue color, texture, smell, gas production by bacteria, bloating, sloughing of mucosa
Differentiating autolysis from ___________ can be challenging.
- Lesions
What is rigor mortis?
- Temporary (1-2 days) postmortem contraction of muscles resulting in stiffness of the carcass
What is particular about ventricular rigor?
- It is difficult to differentiate from cardiac hypertrophy
What causes rigor mortis?
- Loss of calcium homeostasis and ATP depletion (Can't release actin and myosin until proteins break down)
What is livor mortis also known as? What is it?
- Hypostatic congestion
- Gravitational pooling of blood on "down" side of body
In what organs is livor mortis most common? What does it result in?
- Skin and paired viscera (lungs and kidneys)
- Results in purple-red "bruising" on dependent skin/organs
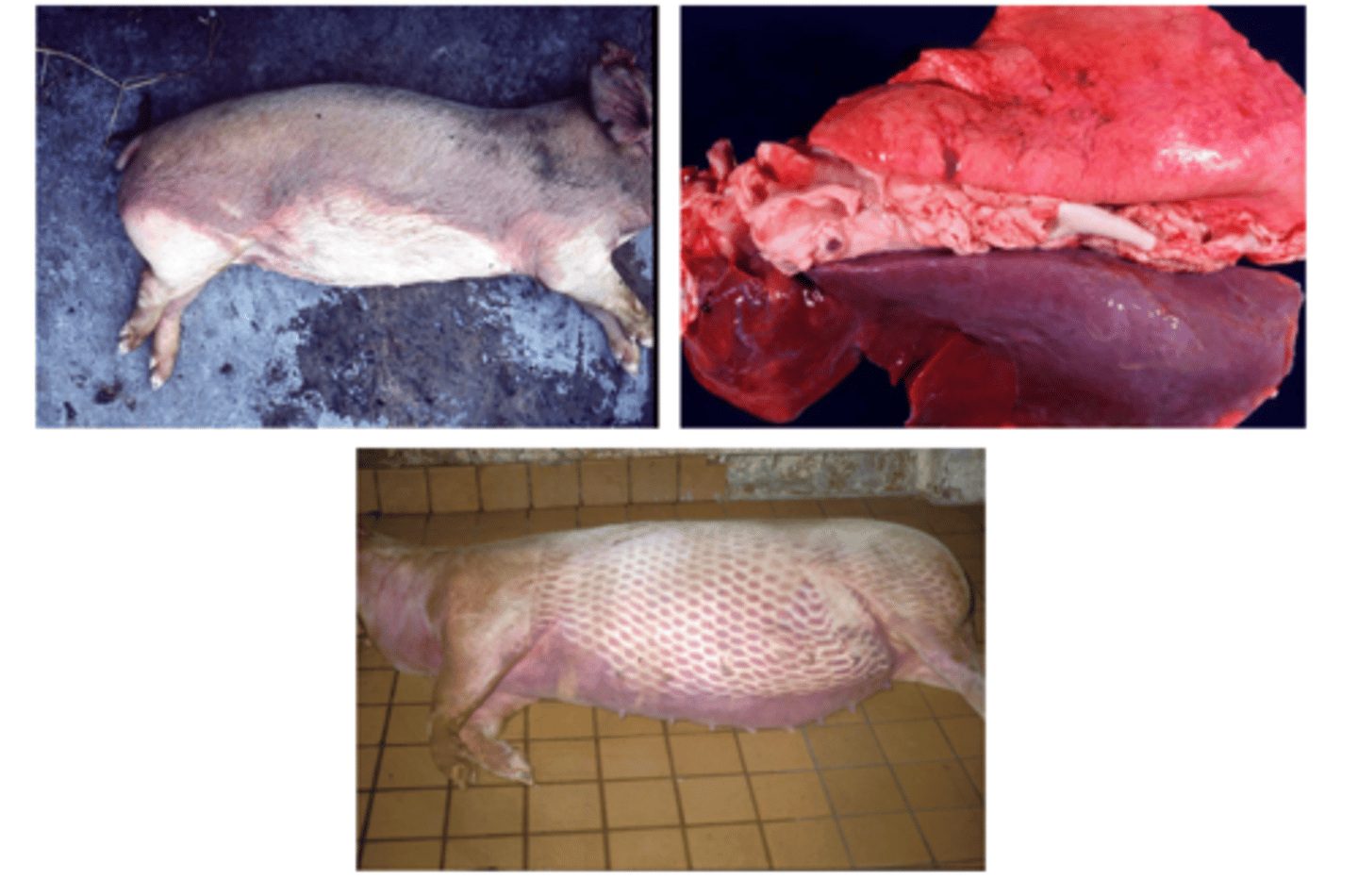
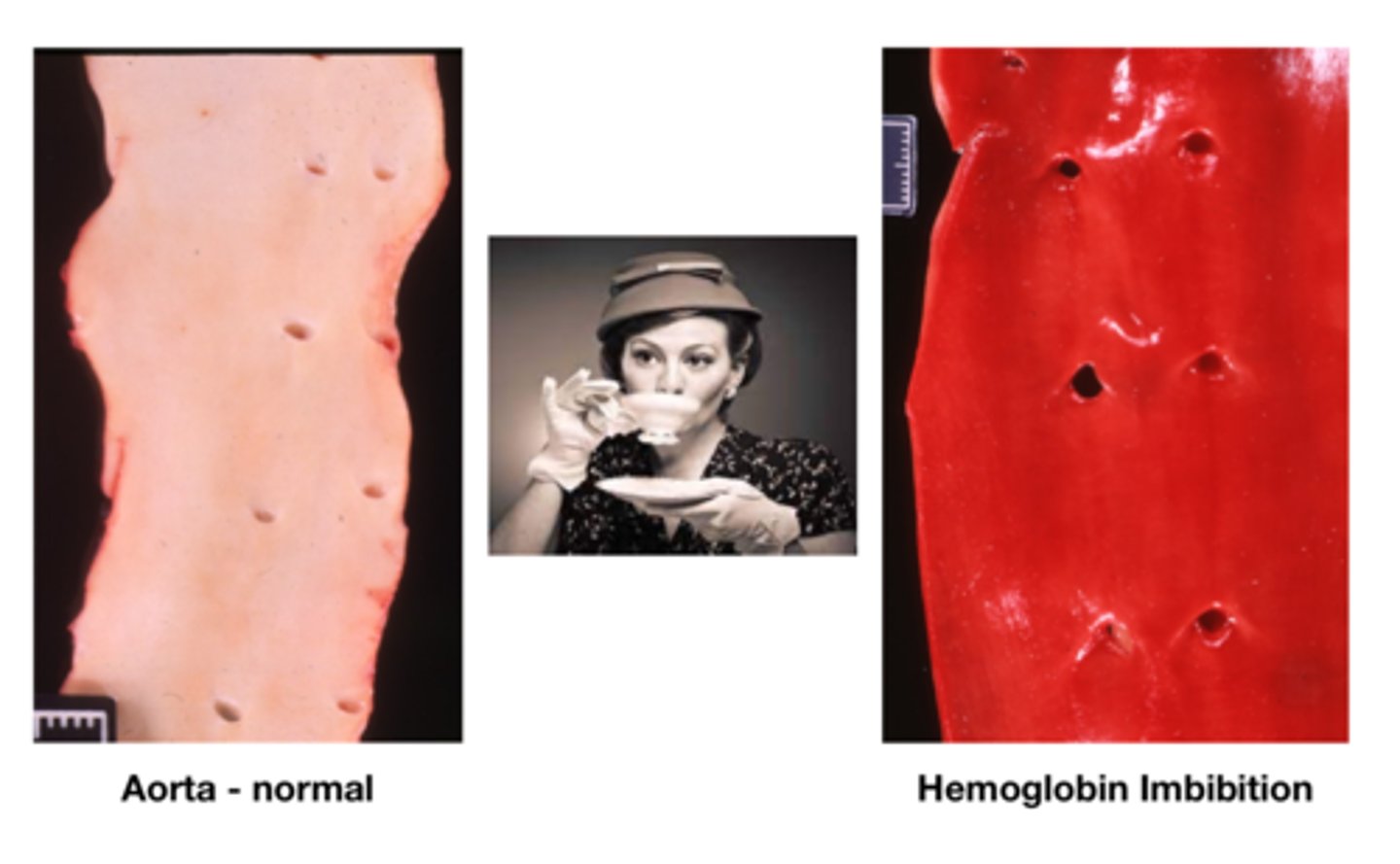
What does "postmortem imbibition" mean?
- Postmortem staining of tissues with endogenous pigments
What are the three primary types of imbibition?
- Hemoglobin imbibition
- Bile imbibition
- Pseudomelanosis
What is hemoglobin imbibition?
- Red staining of tissues due to RBC lysis and hemoglobin breakdown
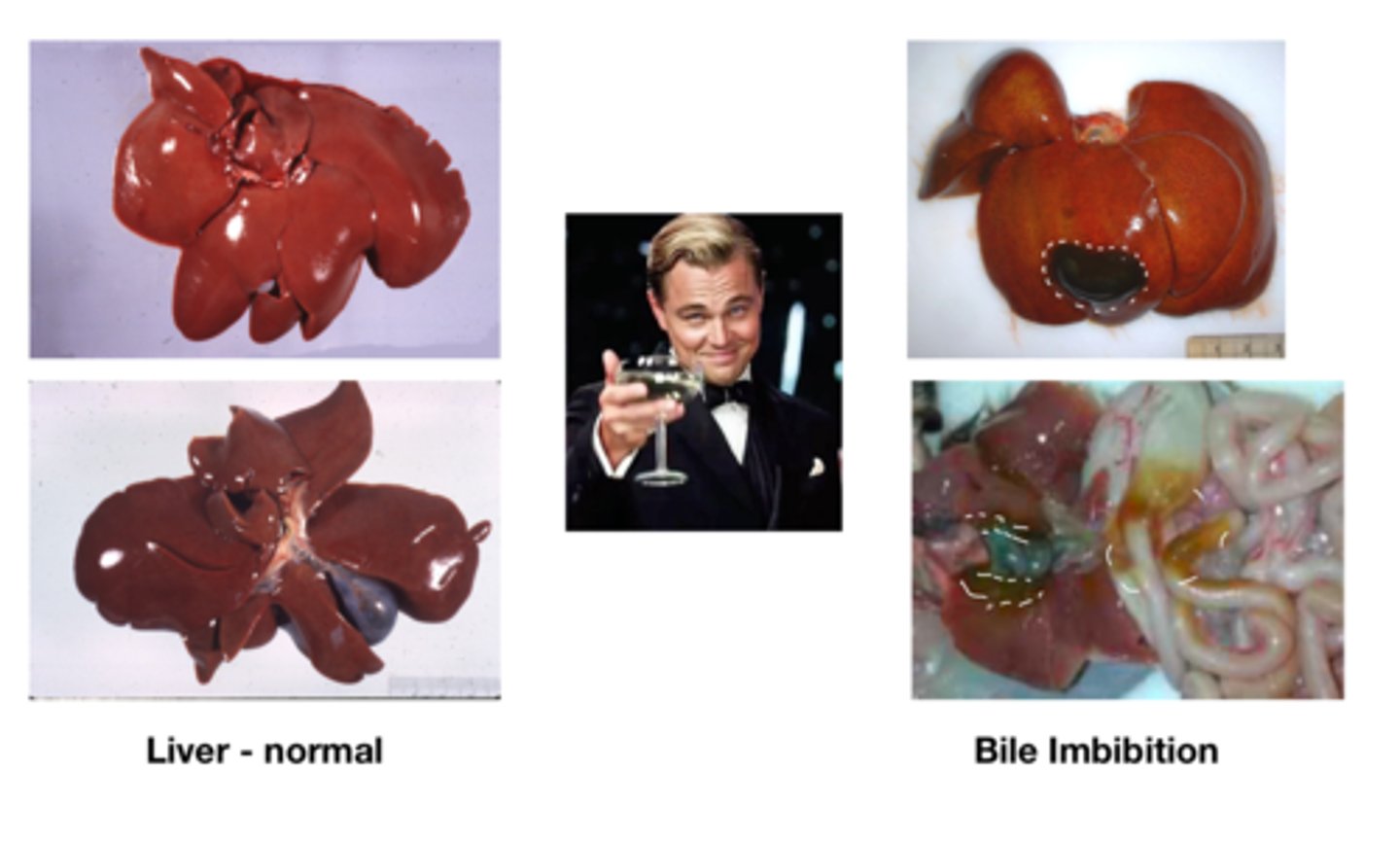
What is bile imbibition?
- Dark green staining of tissues due to breakdown of gallbladder and release of bile, usually affects tissues directly surrounding the gall bladder
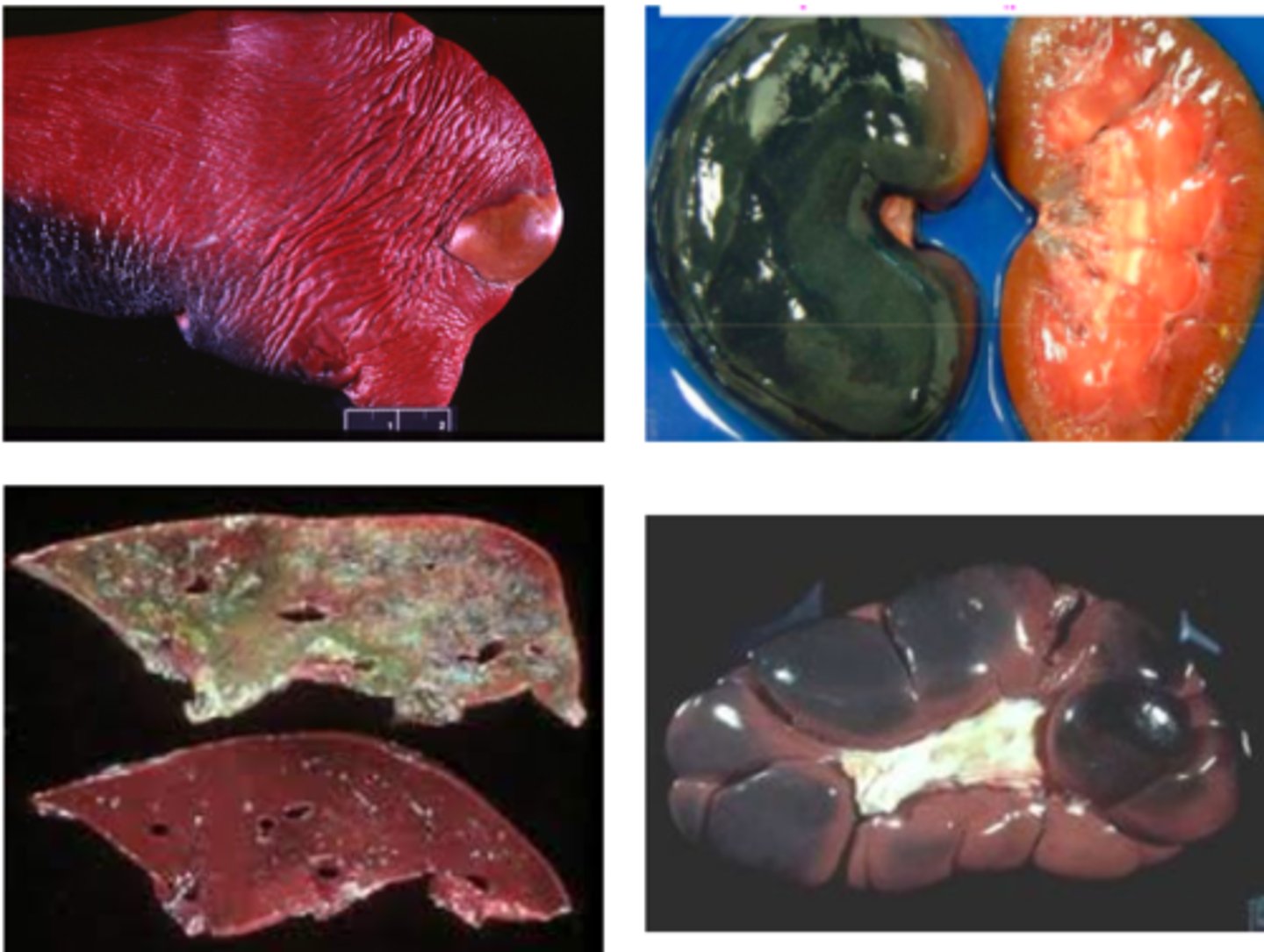
What is pseudomelanosis? Where is it most commonly seen at first?
- Blue-green staining of tissues due to Iron Sulfide (H2S + Fe) as a result of bacteria acting on blood breakdown products
- Frequent on the liver, and is different from bile imbibition because it is located where the liver touches the GI tract
Does blood clot rapidly or slowly following somatic death?
- Rapidly
What eventually happens to postmortem clots?
- Postmortem clots eventually break down with autolysis
What does the presence or absence of clots during necropsy indicate?
- Does not imply OR exclude coagulopathy
What should one do if coagulopathy is suspected in a patient?
- Sample antemortem blood if suspected
Are postmortem blood samples acceptable for any sort of tests?
- No
Antemortem clotting is referred to as _______________.
- Thrombosis
How can one tell the difference between postmortem and antemortem clots?
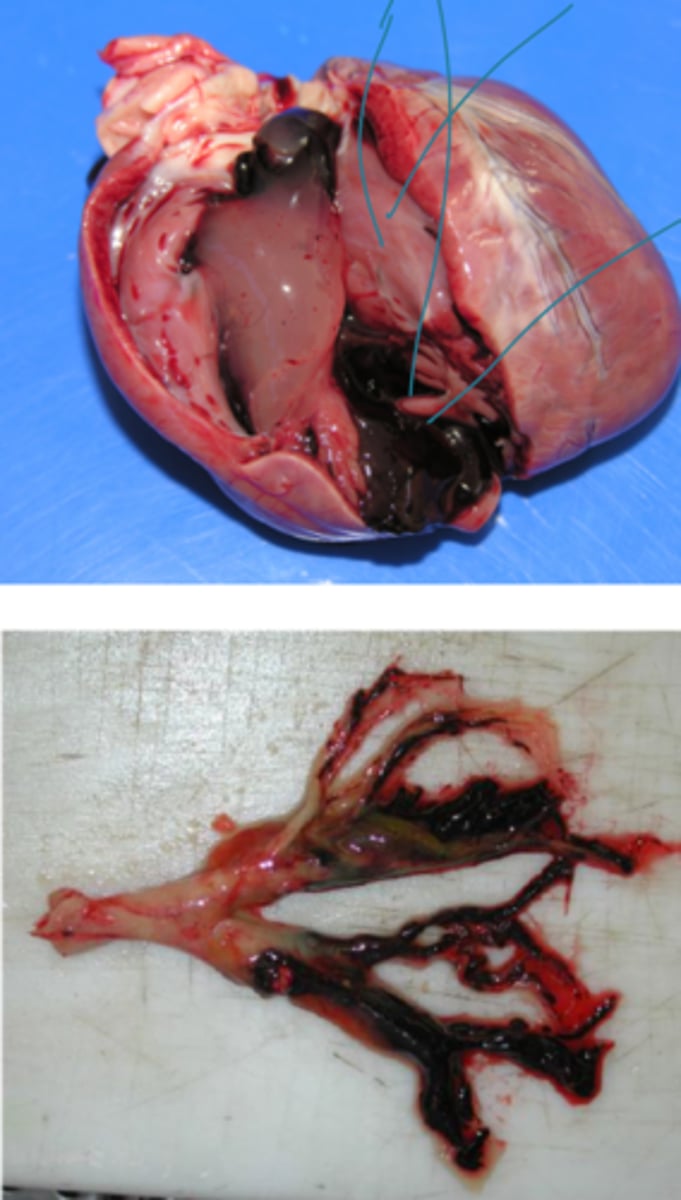
- Postmortem clots may separate into RBC and serum components ("chicken fat" especially in the heart and great vessels)
- Postmortem clots form a perfect cast of the vessel lumen while antemortem clots may have a tail
- Postmortem clots are rubbery or gelatinous texture, glistening, soft
- Postmortem clots are easily removed, not adhered to vessel walls, and friable
What does euthanasia solution do (chemically) in the body?
- Forms salts with blood components which precipitate out in tissues
Barbiturate artifact is more common with what types of euthanasias?
- More common with intracardiac euthanasia, large barbiturate:body weight ratio (smaller animals)
What does barbiturate artifact present as?
- Gritty opaque tan-white plaques on endo/epicardial surface, lungs, pleura, diaphragm
- Brown discoloration of parenchymal tissue surrounding large blood vessels (liver, kidney, lung)
- Dark red-black "gritty" or "coffee ground" texture to blood, especially heart blood
What is mucosal sloughing? What must it be differentiated from? How can it be prevented?
- Separation of mucosa from submucosa, especially GI
- Differentiate from ulceration
- Minimize handling of mucosa prior to sampling
What is lens opacity? What must it be differentiated from?
- A reversible change that results from cooling/freezing
- Differentiate from cataract
List some other postmortem changes.
- Corneal opacity (dust sticks to cornea due to lack of blinking)
- Bloating, gas production (due to bacteria released from the guts producing gases)
- Organ displacement
- Gradual cooling (algor mortis)
- Predation
What is a bubble in a tissue referred to as?
- Emphysema