biology final exam prep
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Write the complementary strand of DNA : ACTACGGT
TGATGCCA
What stores genetic information in a cell?
DNA
What must occur before mitosis in order for each daughter cell to revive a complete copy of DNA
DNA replication
Is this molecule RNA OR DNA?: AUGAACUCU
RNA because it has Uracil
What’s is the type of DNA that contains a copy of DNAs instructions for protein synthesis?
mRNA
What would be the complementary DNA sequence for the MRNA?- AUGGCUUGUUGU
TACCGAACAACA
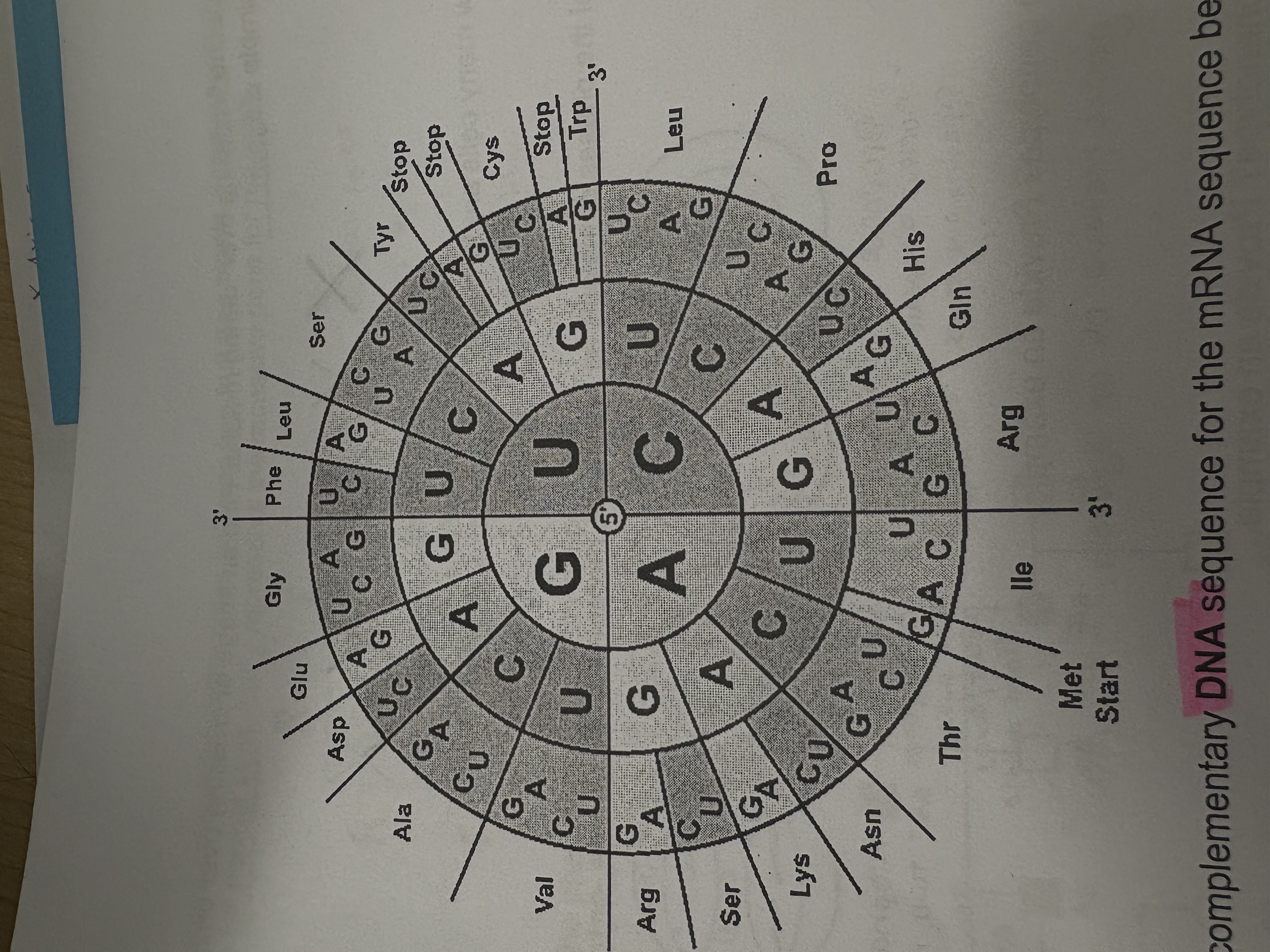
Using a codon chart determine what UAU codes for?
TYR
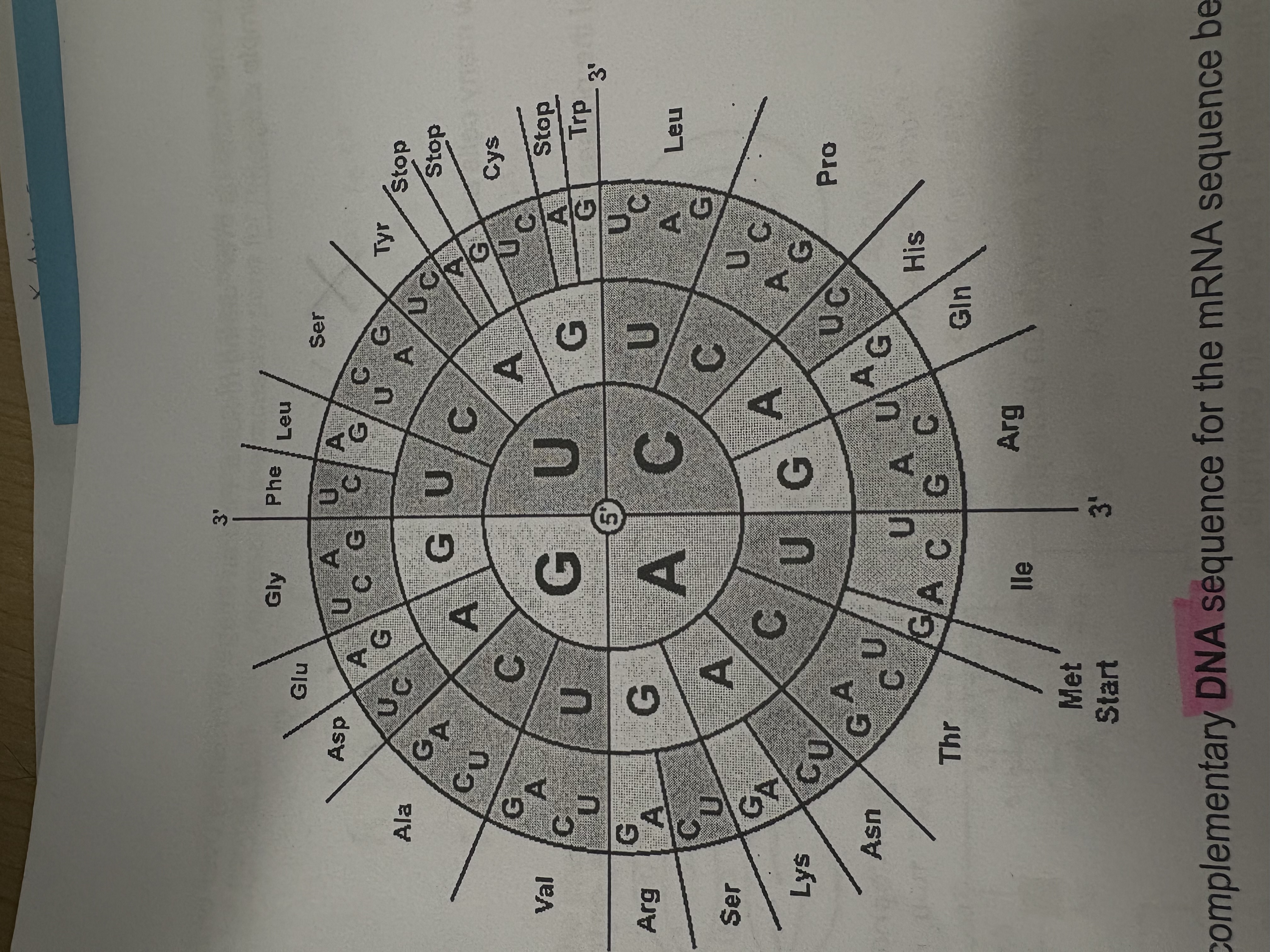
Using a codon chart determine what GCU codes for?
ALA
What are gametes?
Gametes are sex cells
What is the process of forming gametes called?
Meiosis
How many cells are formed at the end of meiosis?
4 haploid cells
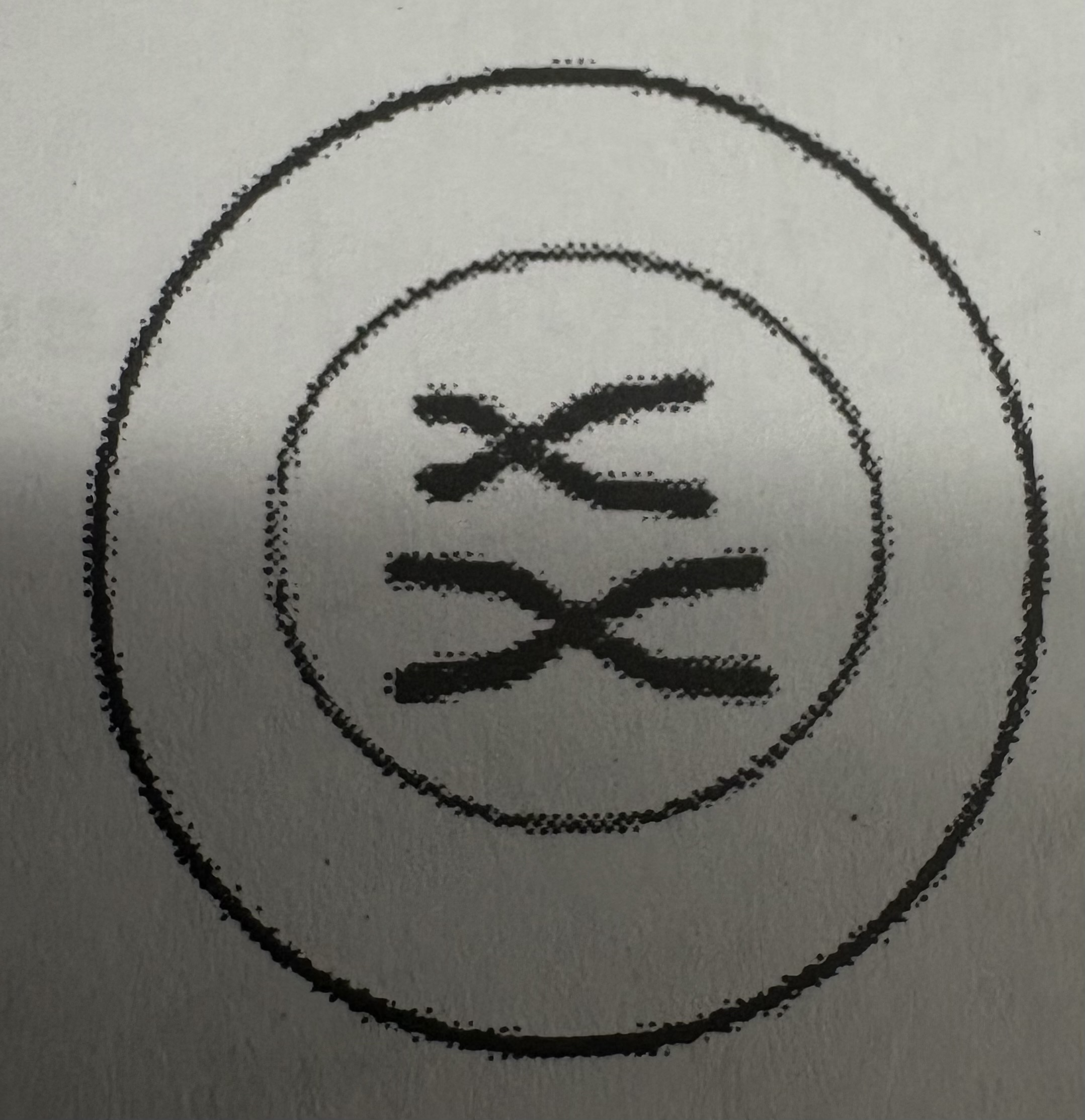
What phase of meiosis is this?
Prophase
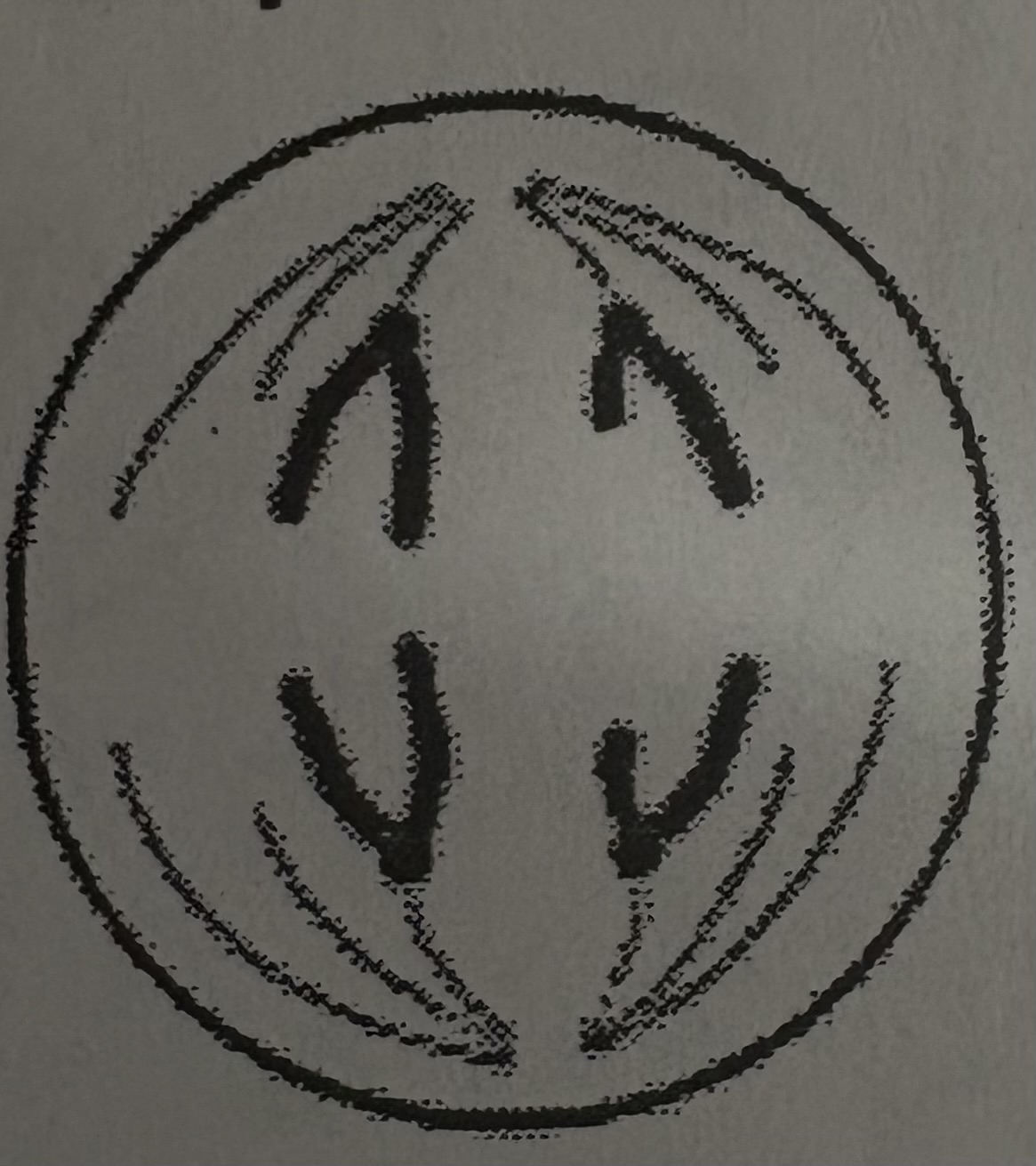

What phase of meiosis is this?
Anaphase
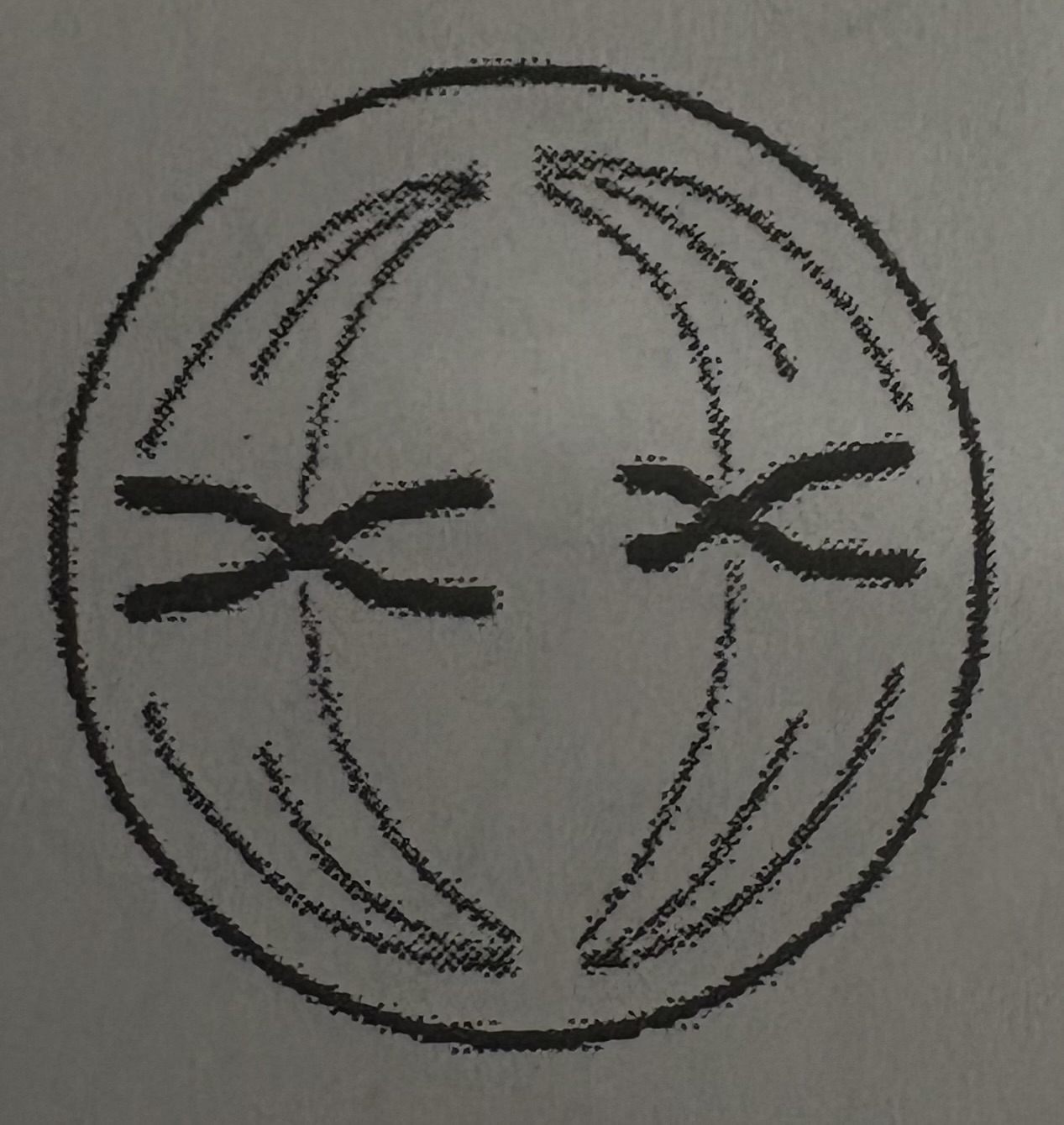
What phase of meiosis is this?
Metaphase
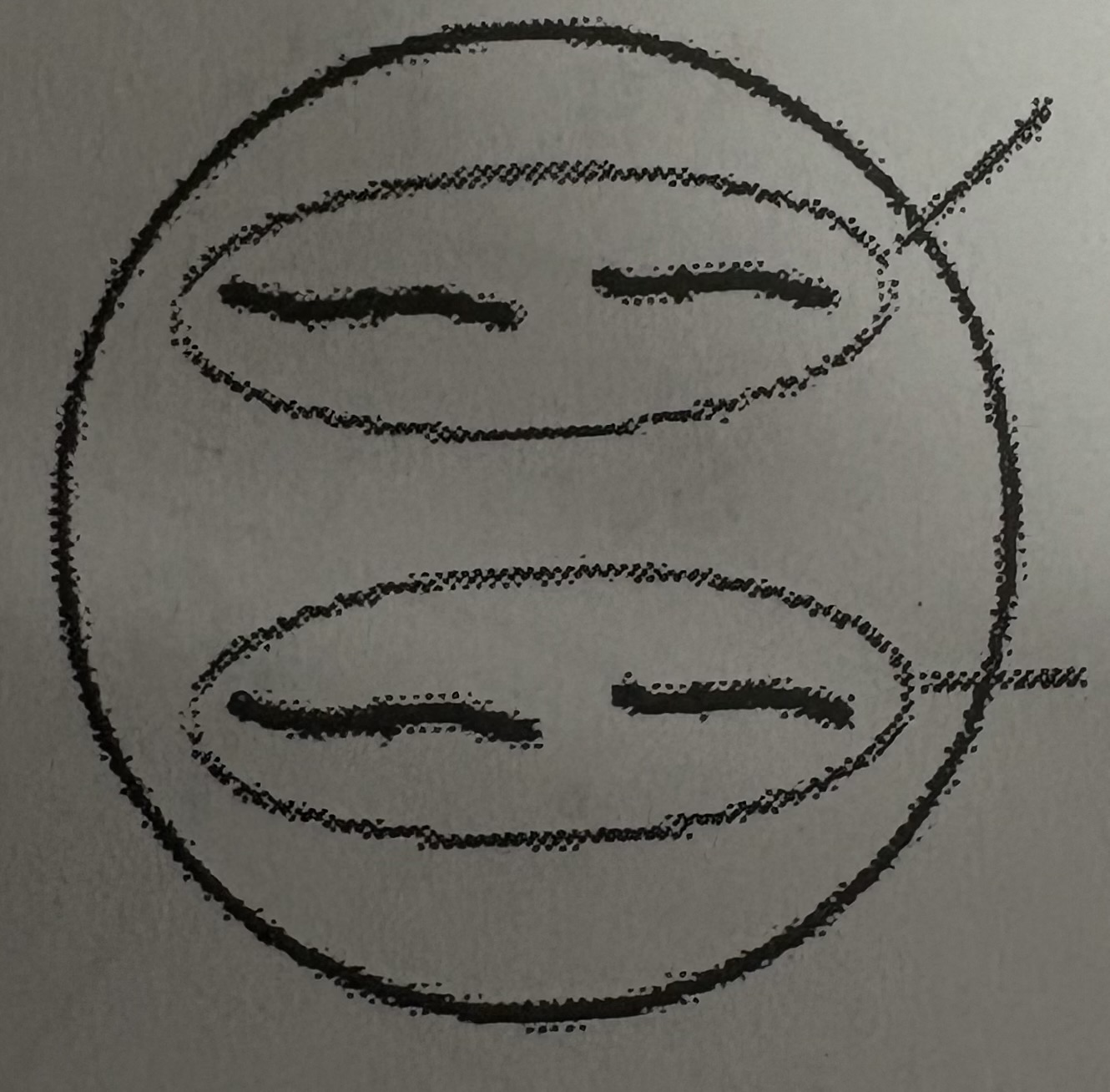

What phase of meiosis is this?
Telophase
What is a genotype? Provide an example
A genetic makeup of an organism
if an organism genotype is “aa” what does that mean
It’s homozygous recessive
An organism genotype is “aa” what does that mean?
It received an “a” from both of its parents
The genotype Aa is..?
Heterozygous

What is this bacteria shape?
Bacilla
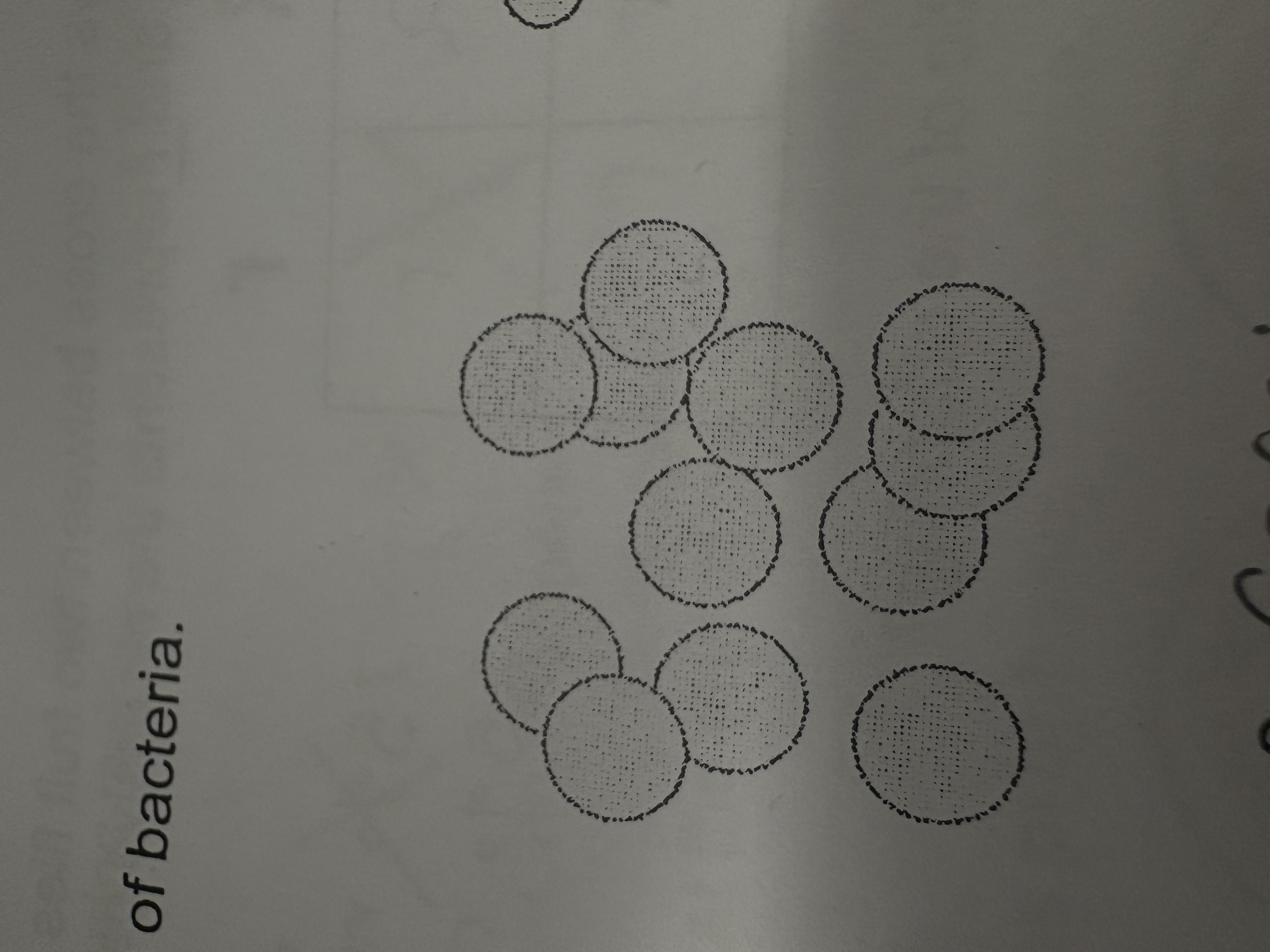
What is this bacteria shape?
Cocci
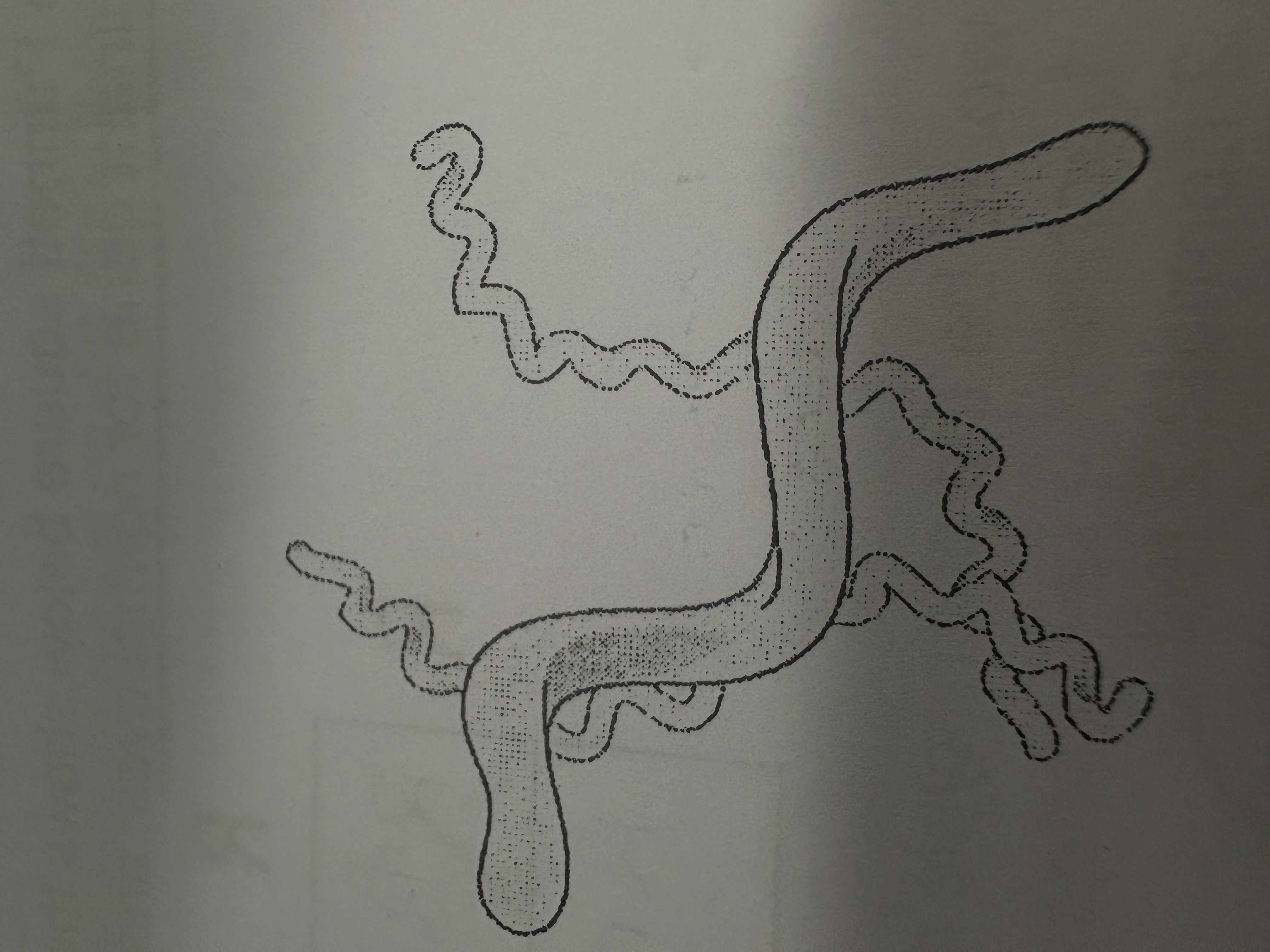
What is this bacteria shape?
Spirilla
What are the 5 benefits that bacteria play in our environment?
Nitrogen fixation
Decomposition
Digestion
Food production
Biotechnology (medicine)
What is a pathogen?
A bacteria that cause disease
How are viruses prevented?
hygiene
Vaccines
Washing hands
How are bacterial infections treated?
Antibiotics
In the correct order from largest to smallest?
Animal cell -largest
Bacteria - middle
Virus - smallest
List at least 3 diseases caused by bacterial infections
tuberculosis
Strep throat
Lyme disease
3 diseases caused by pathogenic viruses?
flu
Smallpox
COVID 19
Who was Charles Darwin and what was his idea?
He discovered the organisms evolve through natural selection
What is fitness in terms of natural selection?
Surviving it’s best in it’s environment
Explain natural selection. Provide and example
Organisms with best traits survive and reproduce offspring while until organisms die.the best traits become more common.EX: giraffe necks
Explain artificial selection. Provide an example
When humans decide what traits get passed on a farmer breeding its best animals. Ex:domestication to wolves and dogs.
What’s is an adaptation?
A beneficial trait
What did darwin noticed on his voyage to the Galapagos island?
The different beaks.the beaks was adapted for the food on the island
What are the evidences for evolution?
Biogeography - distribution of animals and plants
Fossils -preserved remains of ancient organisms
Biochemistry - molecule of heredity that codes for trait
What’s is homologous structures?
Same structure, different function
What is Analogous structure
Similar functions but different structure.
What is Vestigial structures ?
Features that have lost much or all of their original function.
What is speciation?
A new species is formed from a preexisting species.
what is coevolution?
Two species evolve and mutually affect each other
what is convergent evolution?
Unrealated organisms evolve similar traits because they live in a similar environment.
Define ecology
Ecology is the study of organisms and their environment
What does abiotic mean ? Ex: water
A non-living organism
What does biotic mean? Ex- animals
Living organisms
What are producers?
They make their own energy from the sun
Why are consumers?
Consumers eat other organisms for energy
How much energy is lost as you move up the tropic level?
90%
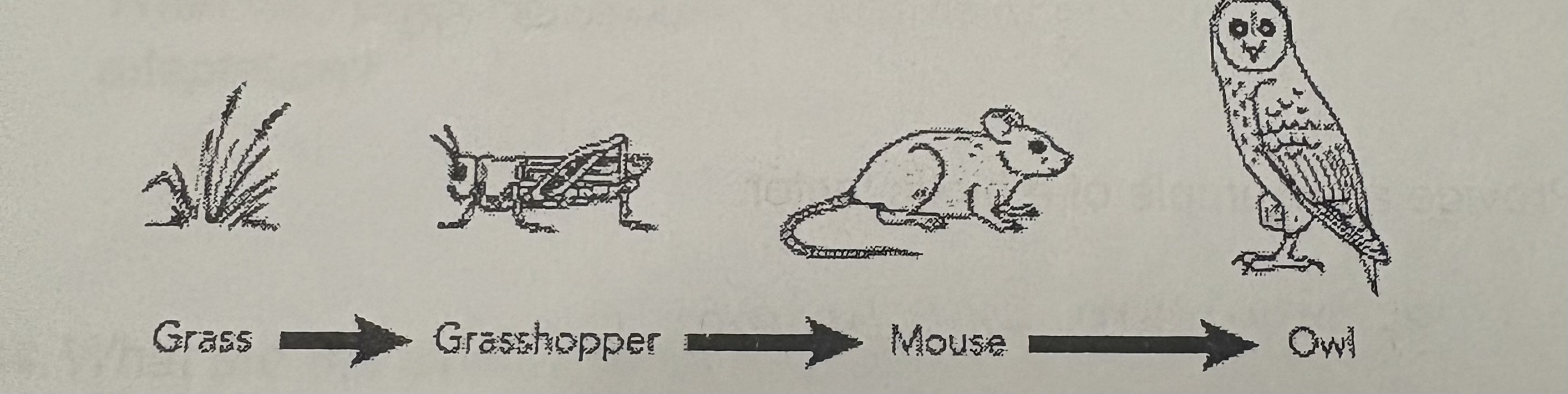
What is the trophies level is the grasshopper?
Primary consumer
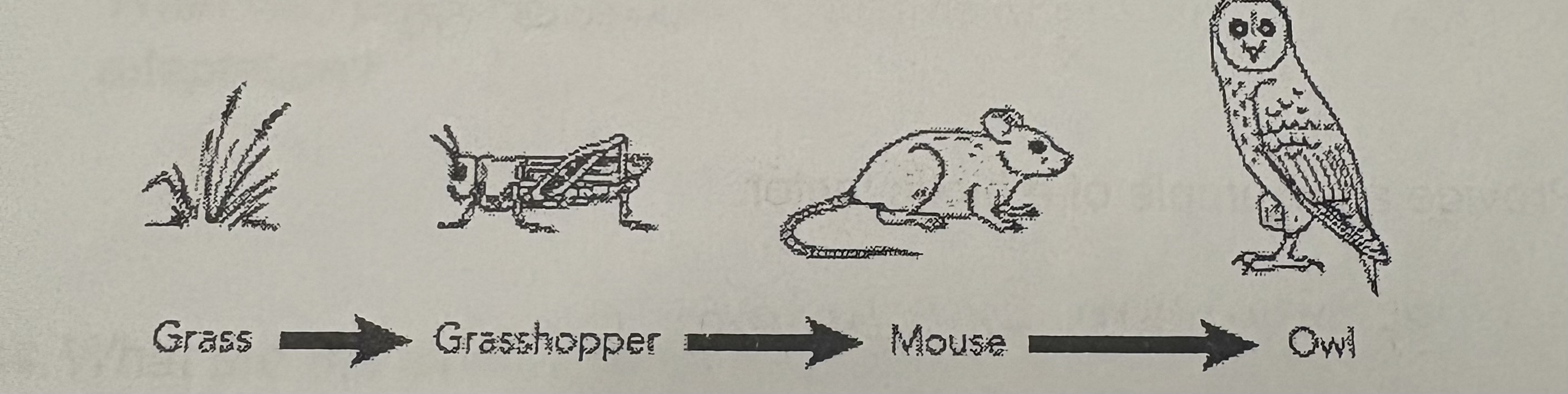
What trophies level is the owl?
Tertiary consumer
What is Mutualism
Both organisms benefit ex: bees and flowers
What is commensalism?
One benefits,other unaffected
What is parasitism?
One benefits, one harms
What is Competition?
Organisms interact when they both need the same limited resources
What is Predator prey?
Relationships between organisms where one,the predator consumes the other,the prey.
Two factors that determine a biome?
Temperate
Precipitation
Influences organism survival
What’s is a phenotype? Provide an example
A physical feature EX: blue eyes