Zool 250 lec 1-13
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Why study? (6)
application: can be eaten as food, be pests, or used as biocontrol agents
Testing evolutionary theory + genetics: bc they quickly develop and reproduce a lot
Practical discovery: biomimicry like making a nicer needle from learning from mosquitos
Aesthetics + decor
Cultural importance: stingless bee in Peru given human rights to protect them
Cool
Systematics
Theory/practice of classifying organisms
Systema naturae for animals: what is is, who made it, and when
Book that argued for a binomial naming system with a genus and specific epithet, and used nested categories/ranks
Linnaeus
1758 → valid scientific names for ANIMALS start now
What organization has the rules for naming animals, and what ranks does it fall in (acryomn)
ICZN international code for zoological nomenclature
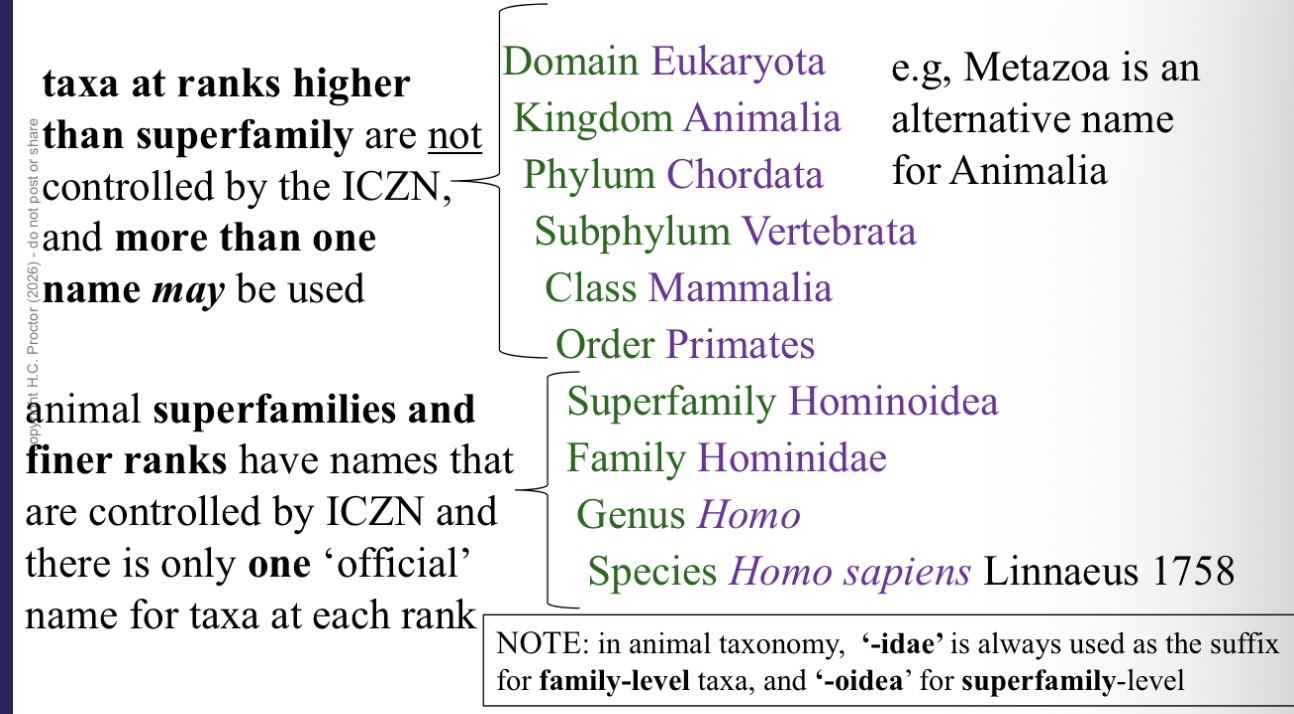
Domain, kingdom, phylum, subphylum, class, order, , super family, family, genus, species

Naming conventions of ICZN (2)
Taxa at ranks higher than super family may have more than one name not controlled by ICZN
Idae is always used for family, and oidea for superfamily
How do you name a new spp (2)
If the species in question is already distinctly different from defined spp, then taxonomists must describe it
Measurements, drawings/photos, differences between other species like using barcode sequencing
Then publish in a scientific journal
Species are often reclassified into different genera, why and how?

Why is it ok for homonymys (same bionomial names) to exist?
Bc they probably come from different codes (ICZN for animals vs ICBN for plants vs ICNB bacteria)
What did Linnaeus later suggest on the origin of new species
Many diff spp in a genus might have arisen after the creation of the world (bc he believed in god) through hybridization
Who was the first genetic tree published by? Who popularized the tree and decided to use real taxa rather than hypothetical examples?
Darwin
Haeckel
Who began determining the phylogenetic relationships ? How was this done? What was his approach called to making trees?
Willi Hennig
Relationships based on ad authoritatum arguments (cause i said so for non dna/molecular data) → common for palenotologists
Cladistics
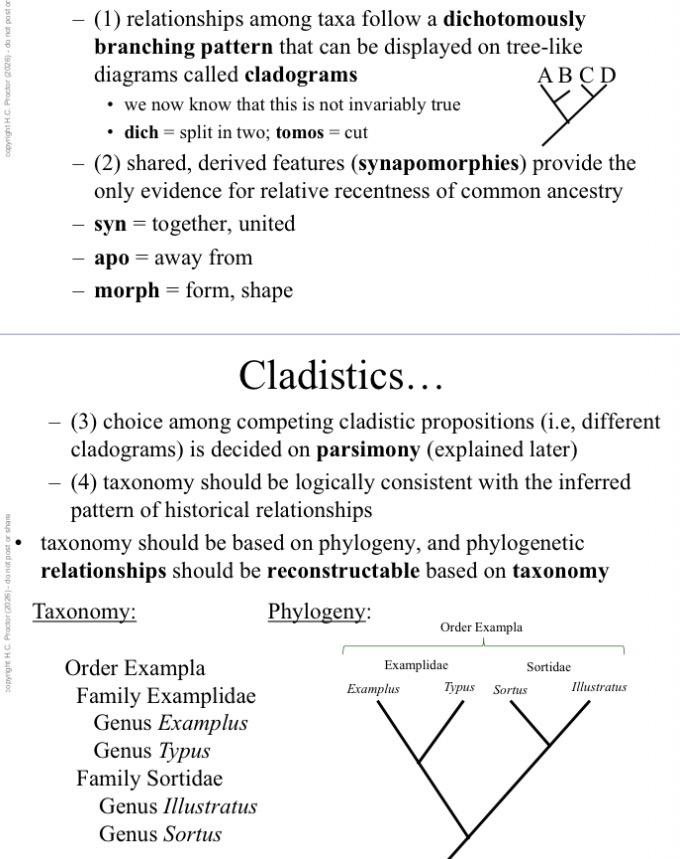
4 main points to cladisitcs:
Taxa whose relationships you wish to untangle are called ____ and you choose another group that are known to split off prior to the taxa of interest diversification is called the ___.
And then you compare using 0 or 1; what does this mean?
In group
Outgroup

Why is the outgroup necessary for creating a tree?
To initially start and root it
Clade vs taxa
Clade: contains ALL descendants of a common ancestor and no others
If a Clade is named, it’s called a taxon. If the Clade is not, it might not be a true Clade