4. carbohydrates
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
carbohydrates
the most abundant class of bioorganic molecules on Earth
75%
carbohydrates constitute this percentage by mass of dry plant materials
photosynthesis
green plants produce carbohydrates via this
carbon dioxide from the air, water from the soil
reactants in photosynthesis
sunlight
energy source in photosynthesis
in the form of cellulose, in the form of starch
2 main uses of plants for the carbohydrates they produce
structural elements
carbohydrates serve as ___________ in the form of cellulose
energy reserves
carbohydrates serve as __________ for the plants in the form of starch
plant materials
the major carbohydrate source for humans and animals
2/3
the average human diet should ideally be about _________ carbohydrate by mass
oxidation
carbohydrate __________ provides energy
glycogen
carbohydrate storage, in the form of _______, provides a short-term energy resreve
carbon atoms
carbohydrates supply ___________ for the synthesis of other biochemical substances
dna and rna molecules
carbohydrates form part of the structural framework of ______________
cell membranes
carbohydrates linked to lipids are structural components of _____________
cell-cell and cell-molecule recognition processes
carbohydrates linked to proteins function in a variety of ______________
CnH2nOn
most simple carbohydrates have empirical formulas that fit this general formula
Cn(H2O)n
an early observation by scientists was that the general formula can be written like this
hydrate of carbon
the basis for the term "carbohydrate"
not correct
the hydrate viewpoint is (correct/not correct)
carbohydrate
used to refer to an entire family of compounds, only some of which have the formula CnH2nOn
carbohydrate
is a polyhydroxy aldehyde, a polyhydroxy ketone, or a compound that yields polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones upon hydrolysis
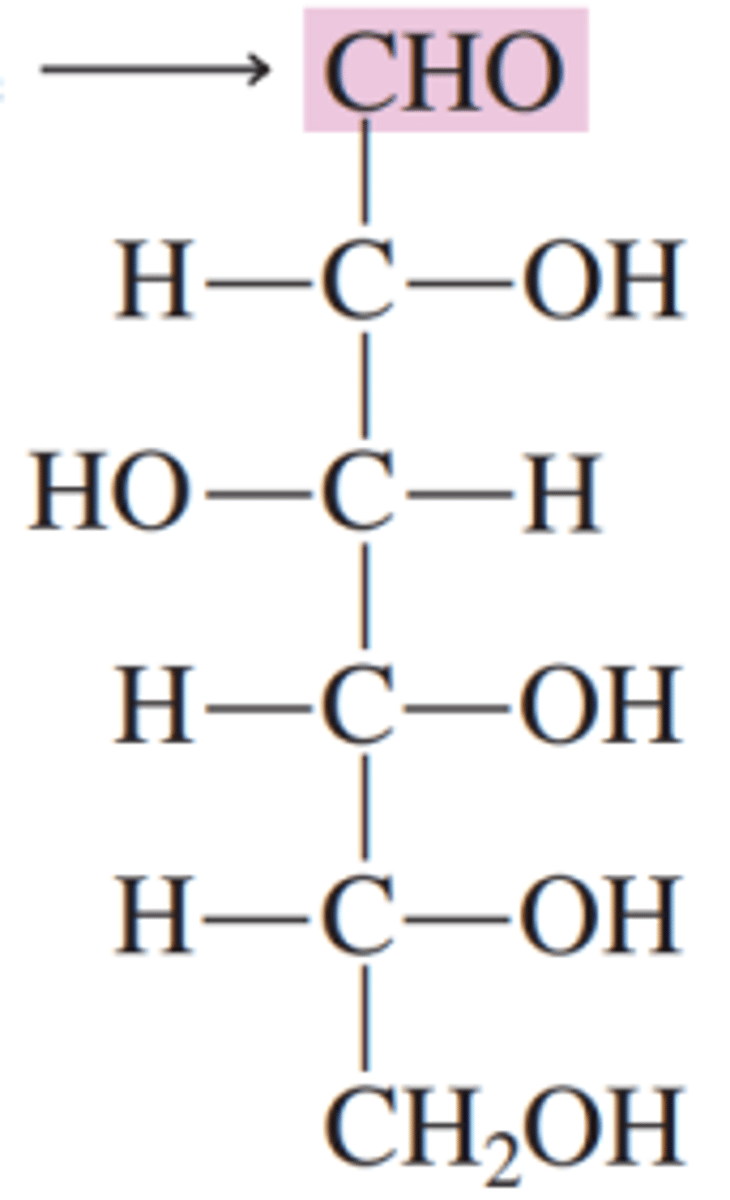
glucose
this carbohydrate is a polyhydroxy aldehyde
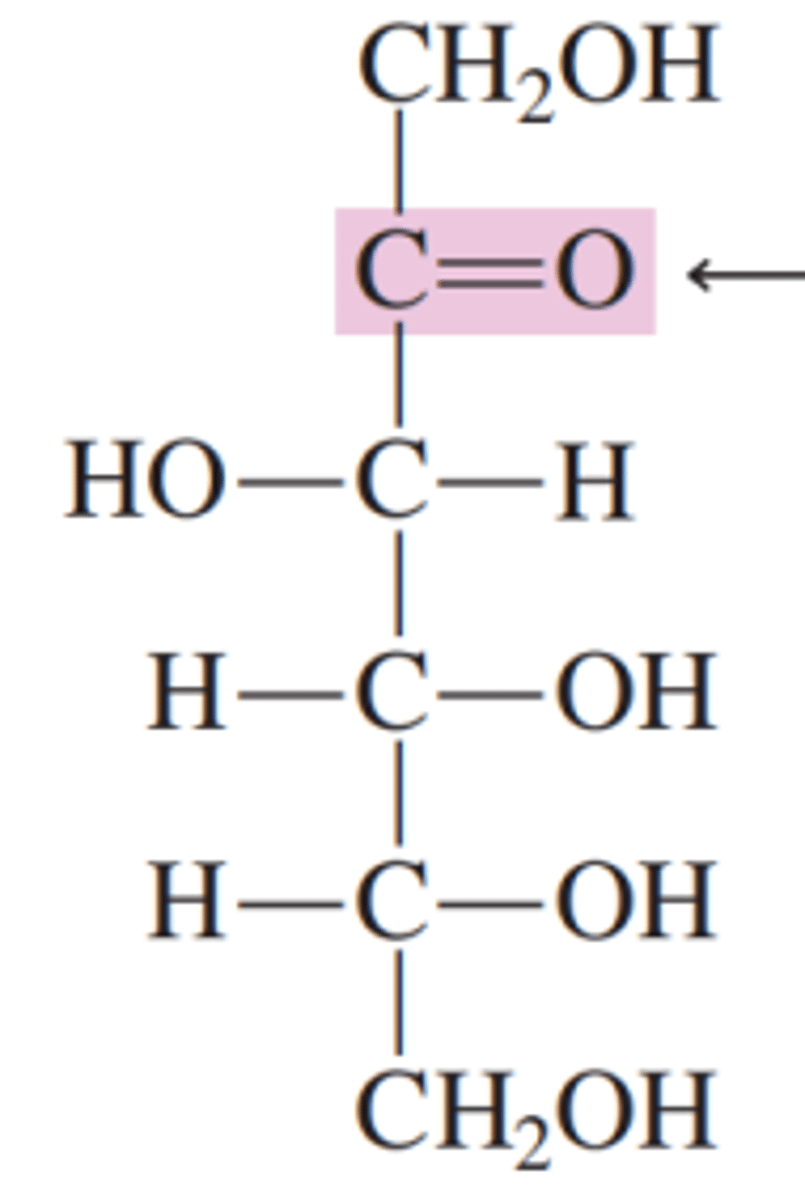
fructose
this carbohydrate is a polyhydroxy ketone
glucose
fructose
large number of functional groups present
striking structural feature of carbohydrates
each
in glucose and fructose, a functional group is attached to ________ carbon atom
monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides
carbohydrates are classified on the basis of molecular size as these 4:
monosaccharide
is a carbohydrate that contains a single polyhydroxy aldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone unit
monosaccharide
this cannot be broken down into simpler units by hydrolysis reactions
monosaccharide
classification of both glucose and fructose
3-7 carbon atoms
number of carbon atoms of naturally occurring monosaccharides
5 and 6 carbon species
number of carbon atoms of naturally occurring monosaccharides that are especially common
pure monosaccharides
are water-soluble, white, crystalline solids
disaccharide
is a carbohydrate that contains 2 monosaccharide units covalently bonded to each other
sucrose, lactose
2 examples of disaccharides
table sugar
sucrose other name
milk sugar
lactose other name
disaccharide
hydrolysis of this produces 2 monosaccharide units
oligosaccharide
is a carbohydrate that contains 3 to 10 monosaccharide units covalently bonded to each other
free oligosaccharides
these oligosaccharides are seldom encountered in biochemical systems
oligosaccharides
are usually found associated with proteins and lipids in complex molecules that have both structural and regulatory functions
oligosaccharide
complete hydrolysis of ___________ produces several monosaccharide molecules
trisaccharide
produces three monosaccharide units
hexasachharide
produces six monosaccharide units
polysaccharide
is a polymeric carbohydrate that contains many monosaccharide units covalently bonded to each other
few hundred units to more than a million units
the number of monosaccharide units present in a polysaccharide varies from a _____________________
polysaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides
these 3 undergo hydrolysis under appropriate conditions to produce monosaccharides
cellulose, starch
2 naturally occurring polysaccharides that are very prevalent in the world of plants
cellulose
paper in textbooks is usually this polysaccharide
cellulose
polysaccharide in cotton in clothing
cellulose
polysaccharide in wood used in home construction
starch
is a component of many types of foods, including bread, pasta, potatoes, rice, corn, beans, and peas
left-handed form, right-handed form
molecules that possess handedness exist in these 2 forms
mirror images
handedness in molecules
mirror image
the reflection of an object in a mirror
all
_______ objects have mirror images
objects with superimposable mirror images, objects with nonsuperimposable mirror images
2 classes of objects on the basis of their mirror images
superimposable mirror images
are images that coincide at all points when the images are laid upon each other
superimposable mirror images
a dinner plate with no design features have these mirror images
nonsuperimposable mirror images
are images where not all points coincide when the images are laid upon each other
nonsuperimposable mirror images
human hands are these mirror images
4
the structural requirement for handedness is the presence of a carbon atom that has ___________ different groups
tetrahedral
the structural requirement for handedness is the presence of a carbon atom that has 4 different groups bonded to it in a ________ orientation
single bonds
the tetrahedral orientation requirement is met only if the bonds to the four different groups are all ____________
chiral center
the handedness-generating carbon atom
chiral center
an atom in a molecule that has four different groups bonded to it in a tetrahedral orientation
chiral
a molecule that contains a chiral center
chiral molecule
is a molecule whose mirror images are not superimposable
chiral molecule
this molecule has handedness
achiral molecule
is a molecule whose mirror images are superimposable
achiral molecule
this molecule does not possess handedness
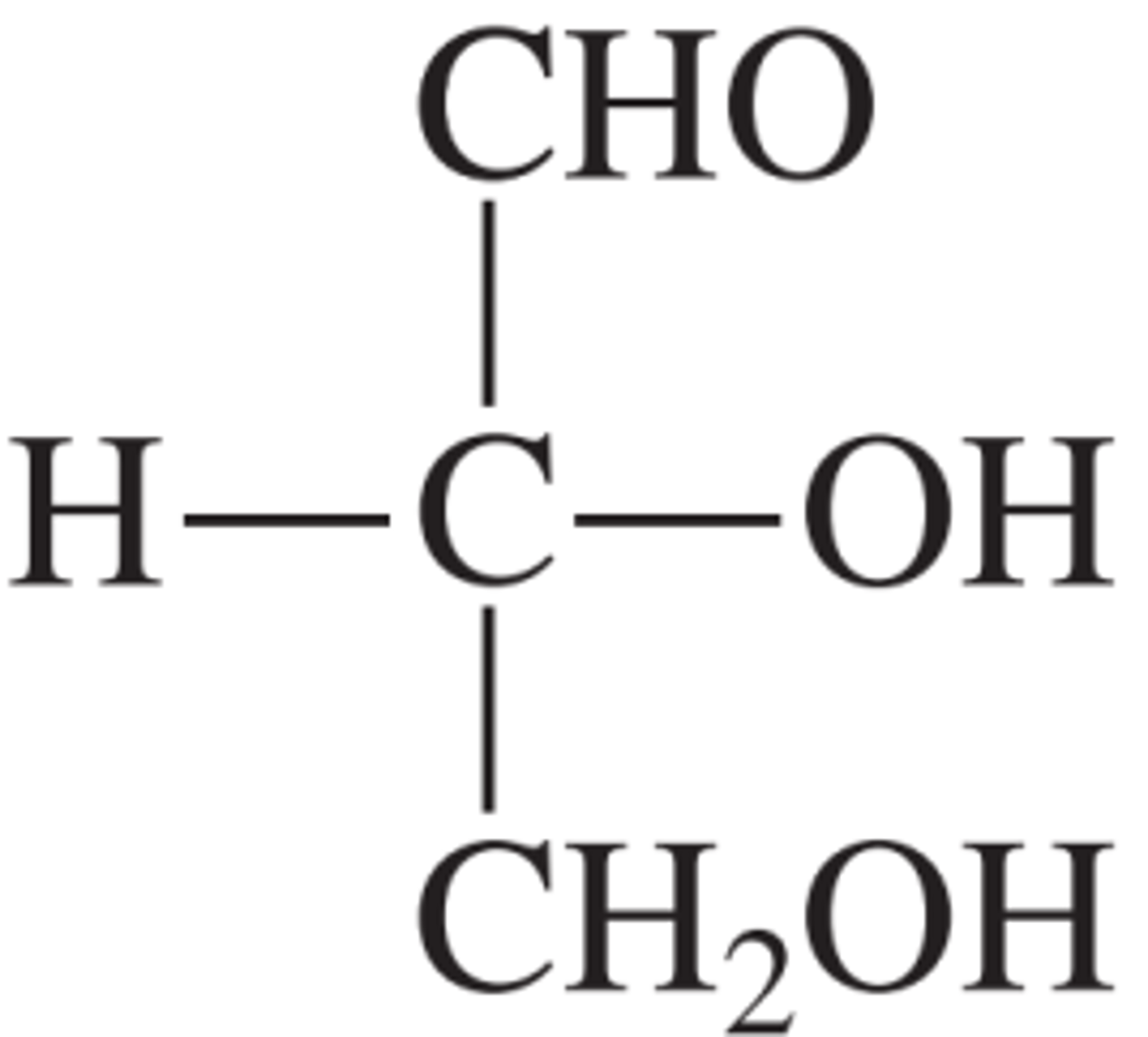
bromochloroiodomethane
the simplest example of a chiral organic molecule
never
carbons with double bonds are _______ chiral
chiral
chiral/achiral
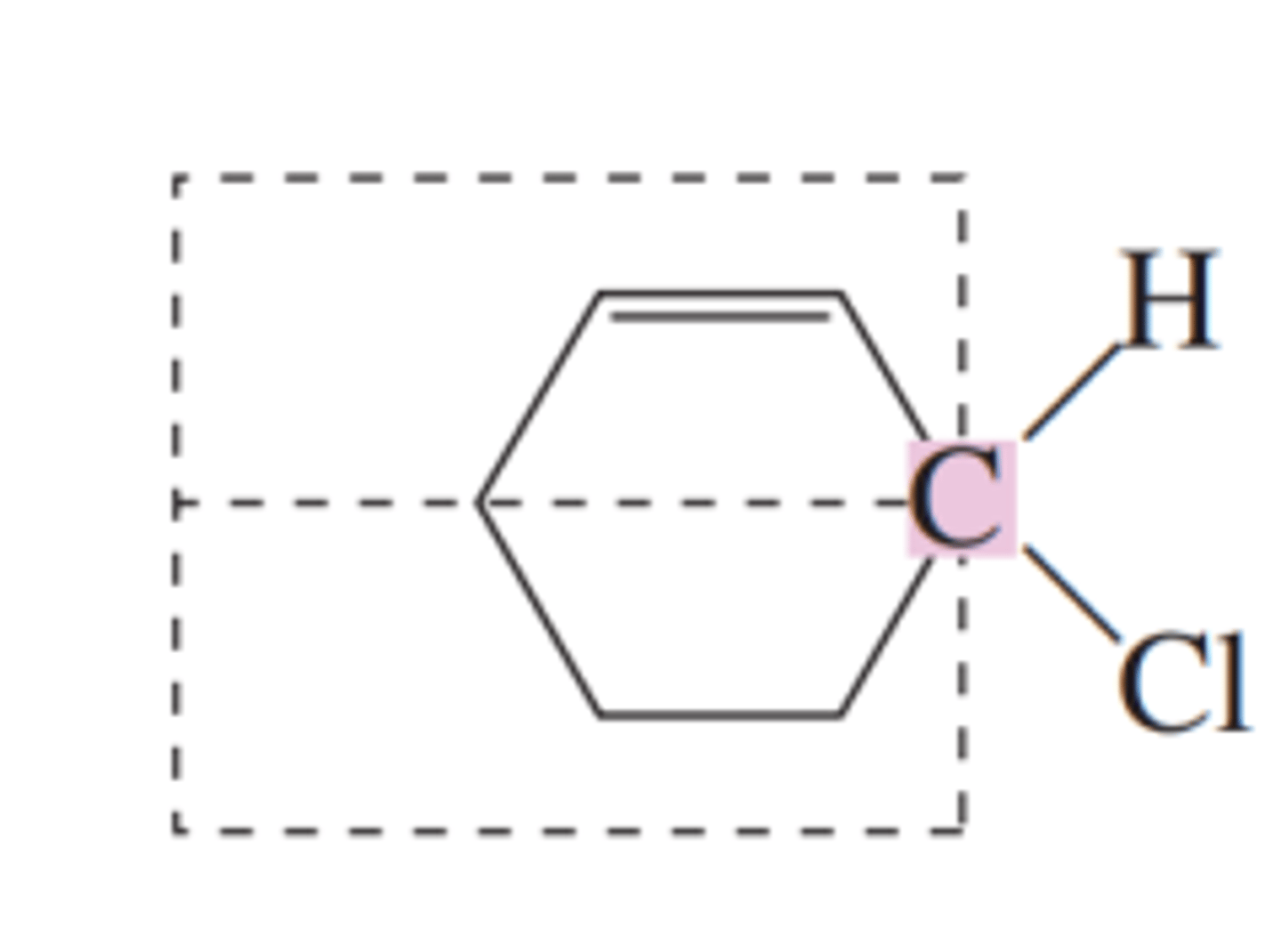
multiple bond
a carbon atom involved in a __________ cannot be a chiral center since it has fewer than four groups bonded to it
single bonds
to have four groups present, all bonds about the chiral center must be _____________
like groups
a carbon atom that has two ____________ bonded to it cannot be a chiral center since it does not meet the requirement of four different groups
can be
carbon atoms in a ring system, if not involved in multiple bonding, (can be/cannot be) chiral centers
two substituents are different, two halves of the ring from the chiral center are different
chirality in a ring system occurs when these 2 conditions are met
chiral
chiral/achiral
achiral
chiral/achiral
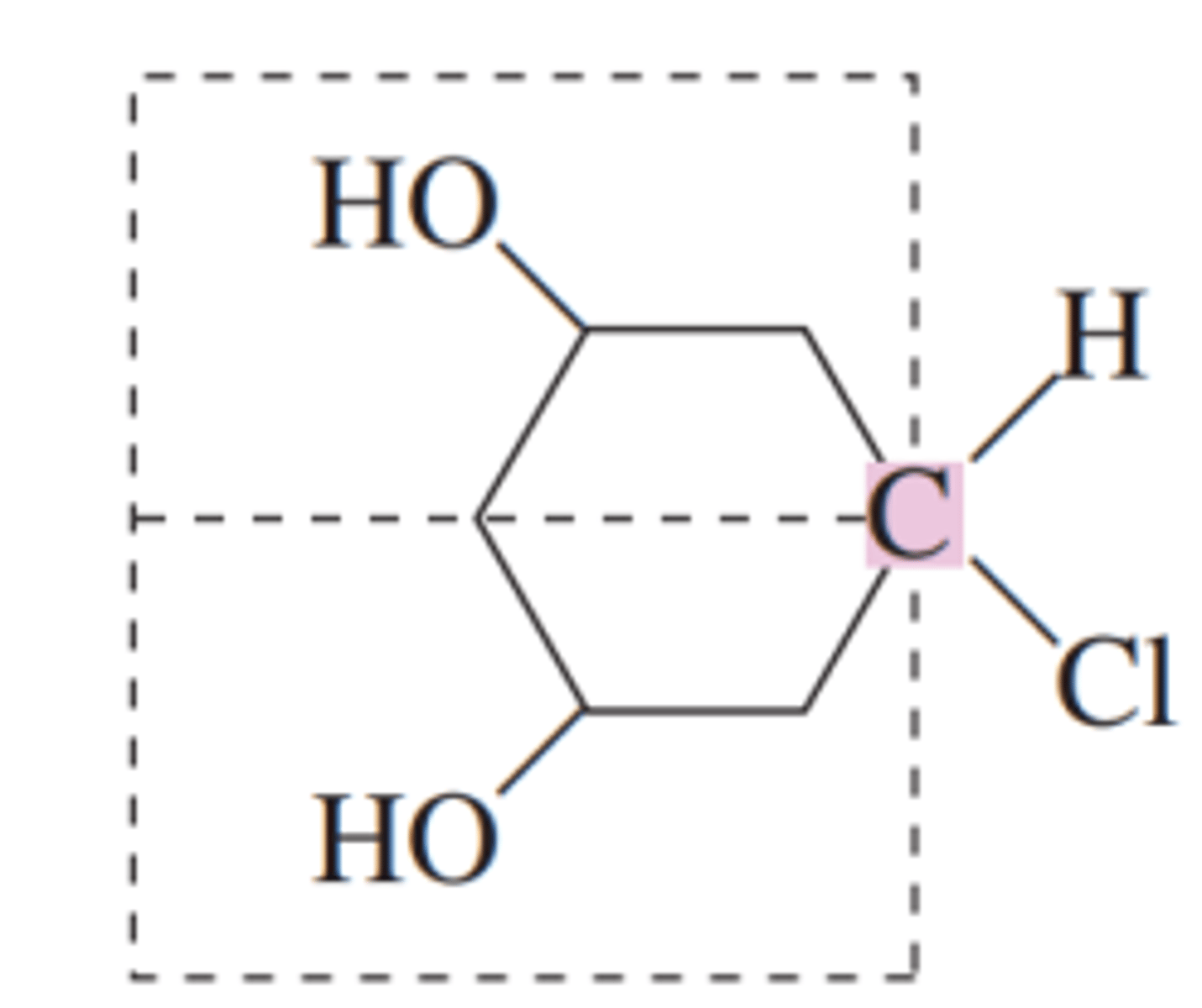
more than one
organic molecules may contain _____________ chiral center
different responses
in human body chemistry, right-handed and left-handed forms of a molecule often elicit _____________ within the body
r-thalidomide
sleep inducing thalidomide
s-thalidomide
teratogenic thalidomide
biologically active
sometimes both chiral forms are ________, each giving a different response
greater
sometimes both chiral forms elicit the same response, but one form's response is many times __________ than that of the other
biochemically active
sometimes, only one of the two chiral forms is _____________
right-handed form
the body's response of this form of epinephrine is 20 times greater than its response to the other
monosaccharides
these are the simplest type of carbohydrate and the building block for more complex types of carbohydrates
right-handed
monosaccharides are almost always (left-handed/right-handed)
right-handed
plants produce only (left-handed/right-handed) monosaccharides
amino acids
are the building blocks of proteins
left-handed
amino acids are always (left-handed/right-handed)
phocomelia
side effect of thalidomide
phocomelia
extremities resemble those of a seal
phocomelia
hands and feet are present but the intervening arms and legs are absent