Kinematics
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Define speed, its equation and SI base unit
The rate of change of distance
v = d / t
v = speed, ms^-1
d = distance, m
t = time, s
How is average speed measured?
Work out the speed over a specific time interval
Define distance
The total length covered
Define velocity, its equation and its SI base unit
The rate of change of displacement
v = s / t
v = velocity, ms^-1
s = displacement, m
t = time, s
Define displacement
The distance covered in a given direction
Define acceleration, its equation and SI base unit
The rate of change of velocity
a = v / t
a = acceleration, ms^-2
v = velocity, ms^-1
t = time, s
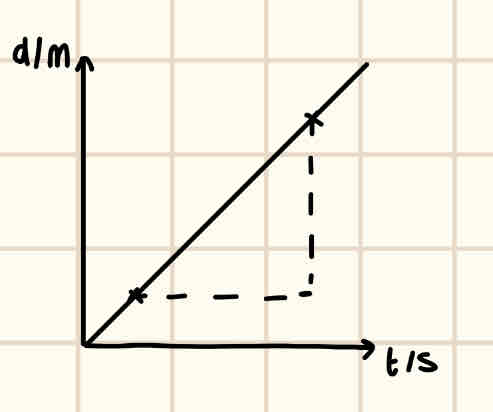
Describe a distance time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = distance/m
m = speed, ms^-1
The gradient cannot be negative because direction isn’t accounted for.
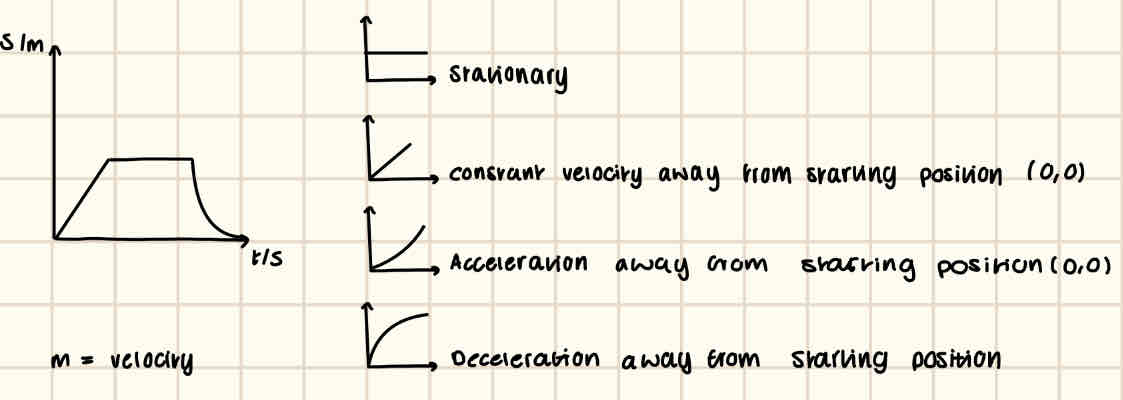
Describe a displacement time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = displacement/m
m = velocity, ms^-1
The y intercept determines the starting position.
When the gradient becomes positive or negative, it determines whether the object is moving away from/towards the starting position. NOT whether its accelerating or decelerating.
When the gradient increases rapidly then slows down the object is decelerating, when the gradient increases slowly but speeds up rapidly , the object is accelerating.
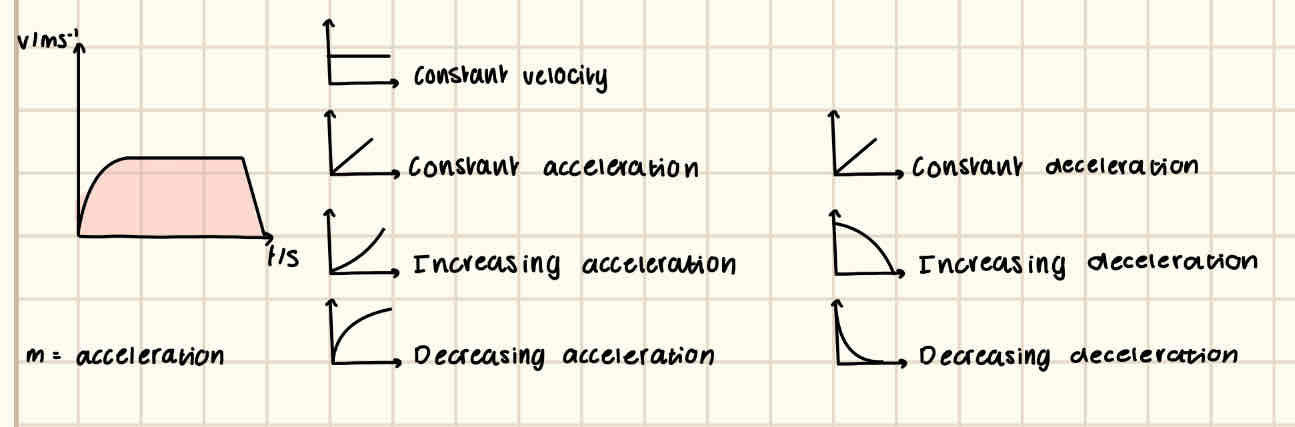
Describe a velocity time graph with notes
x axis = time/s
y axis = velocity/ms^-1
m = acceleration, ms^-2
area under graph = displacement, m
The y intercept determines the stating velocity.
When the gradient becomes positive or negative, it determines whether the object is accelerating or decelerating.
Define instantaneous speed/velocity/acceleration
The speed/velocity/acceleration measured over a very short period of time