W8 - Health as an Economic Commodity and Market Equilibrium
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is market equilibrium in economics?
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in no pressure for price changes.
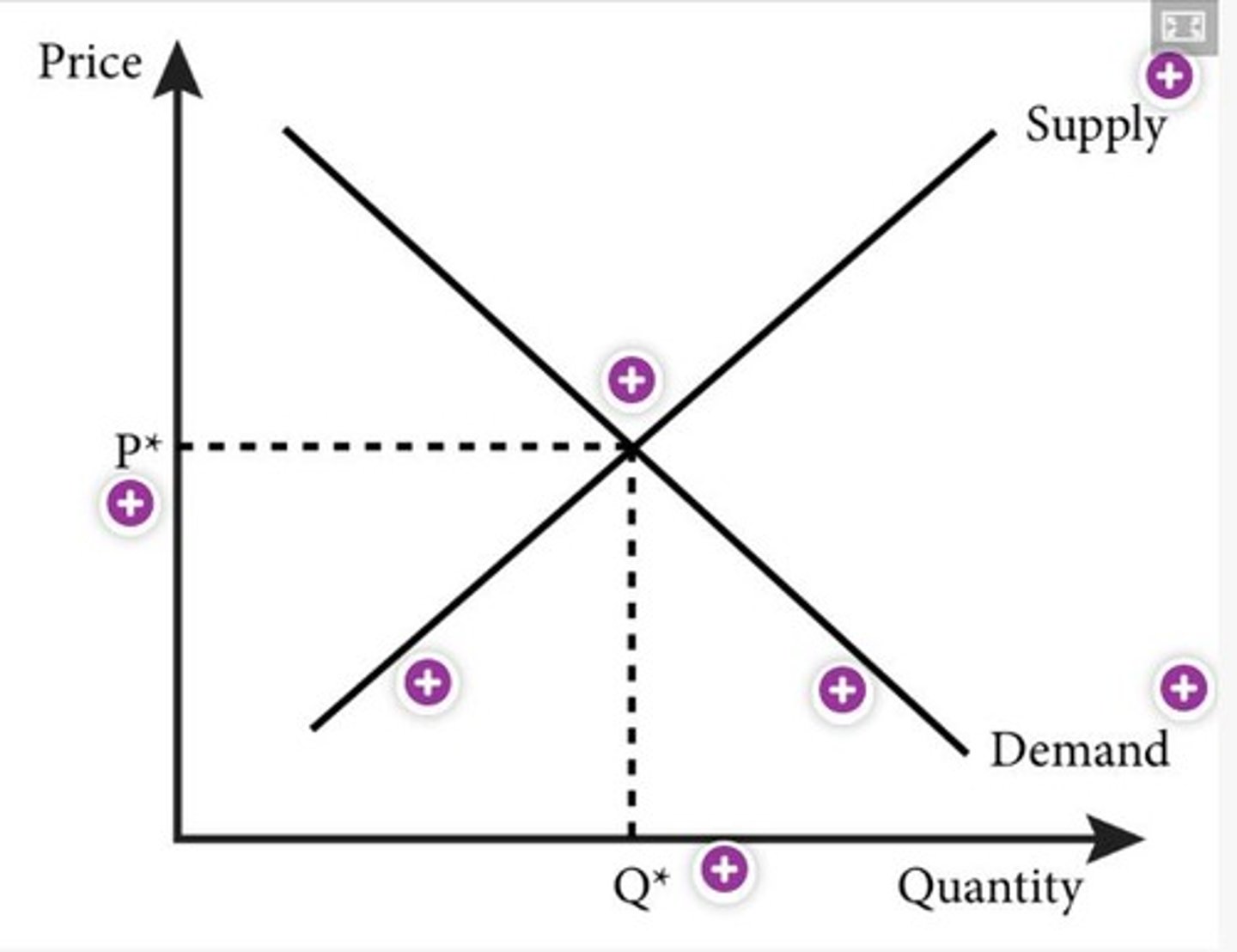
What is the equilibrium price (P*)?
The equilibrium price is the price at which supply and demand are equal, with no market pressure to change.
What happens to supply when prices are low?
Producers tend to supply smaller quantities when prices are low.
What is the equilibrium quantity (Q*)?
The equilibrium quantity is the quantity that is both supplied and demanded at the equilibrium price.
How does health function as a commodity?
Health can be viewed as a stock that loses value over time and requires investment to maintain.
What factors influence the benefits derived from health capital?
The benefits from health capital depend on market and non-market factors such as age, income, and education.
What information do health economists need to assess cost-effectiveness?
Health economists need outcome data from treatments, resource usage data, cost per unit of effect, and the impact of illnesses on patients and the economy.
What is disinvestment in healthcare?
Disinvestment is the process of removing investment from inefficient, ineffective, or unnecessary healthcare products or services.
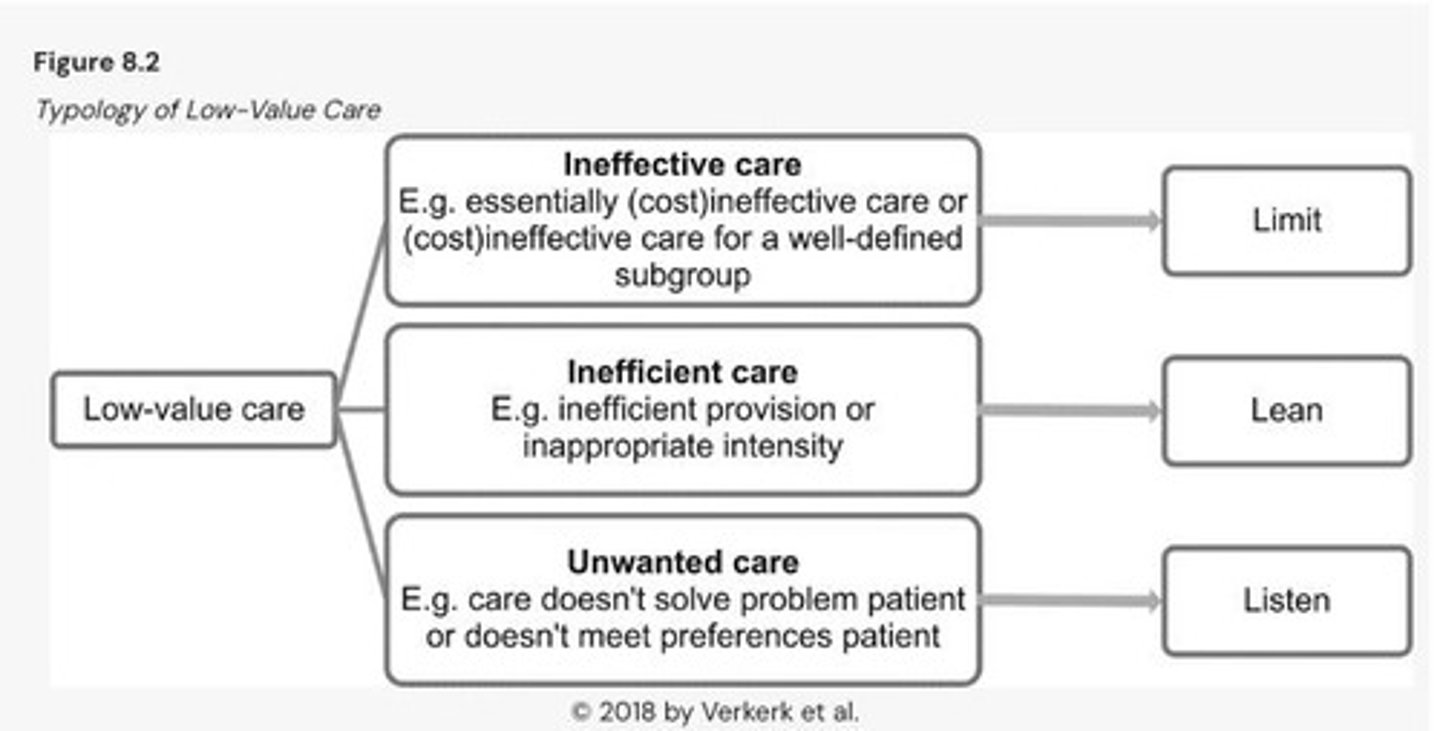
What is the purpose of the typology of low-value care framework?
The framework aims to limit funding and use of ineffective care, focusing on improving societal value in healthcare.
What is asymmetric information in healthcare?
Asymmetric information occurs when one party has access to more complete information than another, often seen between healthcare providers and patients.
Why is government participation necessary in the health sector?
Government participation is essential for financing and delivering health-related goods and services, such as disease surveillance and preventative health programs.
What is the impact of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) on the economy?
NCDs can significantly impact both microeconomic (individual level) and macroeconomic (overall economy) factors, affecting workforce productivity and healthcare costs.
What are the consequences of disinvesting in low-value care?
Disinvesting in low-value care can lead to better allocation of resources towards more effective healthcare interventions.
How does aging affect the benefits derived from health capital?
As people age, the benefits from health capital may decrease, making it more expensive to maintain the same level of health.
What is the importance of public health data in evaluating health programs?
Public health data is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of health programs and their broader health benefits.