WBC Profiles
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
plasma -- most plentiful component
--> water, proteins, antibodies, hormones
RBCs
Buffy coat (platelets/WBCs)
components of blood
Innate immunity
nonspecific defense mechanisms that are present at birth, and come into play immediately or within hours of an antigen's appearance in the body; does not require prior exposure
epithelial barrier
HCl
lysozyme (breast milk, saliva, tears)
mucous membranes (GI, respiratory tract)
what are some examples of the non-cell mediated components of innate immunity?
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes/macrophages
what are some components of the cell-mediated innate immune response?
Granulocytes
a group of leukocytes with granules present in the cytoplasm; they often have a multi-lobed nucleus and originate in the bone marrow; major players in innate immunity
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
examples of granulocytes
adenoids, tonsils, thymus, spleen, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes
organs/body structures involved in the immune system
Adaptive immunity
immunity that is constantly being refined throughout a person's life; it is not present at birth; and is characterized by a slower, antigen-specific response to pathogens; provides "memory" of response for future exposures
B cells and T cells
monocytes also play a role
cell-mediated components of adaptive immunity
Agranulocytes
leukocytes with non-lobular nuclei; no granules in the cytoplasm; originate in the lymphoid tissue; they are major players in adaptive immunity that arrive later, have a greater capacity to consume more foreign pathogens, and live a LONGER LIFE!
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factors
what is responsible for stimulating maturation of leukocytes?
Complement
series of 60+ plasma and surface proteins that are produced by the liver; first line of defense against invading pathogens; enhances other WBCs; can be activated independently
to "complement" the other WBCs
function of complement
Alternative pathway
complement pathway responsible for attracting other leukocytes and encouraging phagocytosis
Lectin pathway
complement pathway responsible for triggering inflammation
Classic pathway
complement pathway responsible for damaging the cell membrane of the pathogen via "pores" (MAC)
phagocytes start to arrive to the area and consume foreign material until they themselves die (pus)
once complement is activated, what occurs next?
pyogenic infections
neutrophils are responsible for responding to what kind of stimuli?
allergic disorders, parasites
eosinophils are responsible for responding to what kind of stimuli?
parasitic
basophils are responsible for responding to what kind of stimuli?
Neutrophil
most plentiful phagocytic granulocyte; produced by bone marrow, circulate for about 8 hrs, then proceed to tissues; first cells to arrive at site of infection/inflammation; responsible for phagocytosis of extracellular pathogens
bacterial infections
neutrophilic can be seen in what conditions?
Band neutrophils
immature neutrophils
Eosinophil
phagocytic granulocyte that is elevated to play a role in the allergic response along with mast cells; can also elevate in response to parasites; they are produced by the bone marrow, circulate for about 18hrs, then move to thymus and GI tract
segmented neutrophils
mature neutrophils
parasitic infxns
allergic reaction
asthma
atopic dermatitis
eosinophilic esophagitis
eosinophilia can be seen with what conditions?
Basophil
least numerous of all the NON-phagocytic granulocytes that are increased in parasitic infections; they are produced by the bone marrow and circulate the blood treatment; this cell type contains granules secrete many potent immune modulators (histamine, interleukins, heparin)
parasites (helminths)
malignancy (AML, CML, myeloproliferative disorders, polycythemia vera)
inflammation (IBD, RA, UC)
allergy (asthma, allergic rhinitis, food allergy)
basophils are increased in what conditions?
Mast cells
NON-phagocytic granulocyte that resides in large number sin peripheral tissues (not present in blood); contains IgE receptors; releases histamine, serotonin, heparin, leukotrienes, platelet-activating factor; activates basophils/eosinophils; interacts with B/T cells, dendritic cells, via MHC proteins.
vasodilation and bronchoconstriction
the substances secreted by mast cells cause what physiologic effects?
Monocyte
agranulocyte that originates in the bone marrow and circulates for 5-8 days before entering the tissues; these cells are capable of processing foreign antigens and presenting them to the immunocompetent lymphocytes
enter the tissue where it is transformed into a macrophage
remain in circulation as monocytes
acted upon by cytokines to turn them into dendritic cells
*can change back into monocytes if leaves tissues
what are the 3 potential fates of a monocyte once it develops?
Dendritic cells
major antigen presenting cell that is the key link between the innate and adaptive immune system; functions in capturing, processing, and presenting antigens to T-cells; start as innate cells but as they mature begin to develop specificity for antigens
viral
lymphocytes respond to what kind of infections?
B cells, T cells, NK cells
types of lymphocytes
B-lymphocyte
major players in humoral immunity that are made in the bone marrow; they have antigen-specific receptors but they cannot directly attract infected cells, they work instead of creating antibodies; when it meets its receptor's match, it secretes Abs
Plasma B-cells
short lived cells that disappear once immune response is finished; not normally present in blood; can be seen with some disease processes
Multiple myeloma, cancers, arthritis, lupus
plasma cells can be seen in the blood in what immune processes?
Memory B-cells
Produced during a B cell response, but are not involved in antibody producing during the initial infection; are held in reserve for the rest of your life in case you encounter that pathogen again.
T-lymphocyte
lymphocyte that is made in the bone marrow but matures in the thymus; only recognizes "processed" antigens by APCs
Helper T cells
T cells that secrete cytokines that attract macrophages, neutrophils, activate B cells; also directs the cells once they arrive
Cytotoxic/Killer T cells
T cells that destroy infected cells, tumor cells, or any other cells which show signs of damage
Memory T cells
T cells that persist post-infection; liver longer than memory B cells and rapidly proliferate if re-exposure occurs.
Natural killer cells
lymphoid cells that do not have antigen specific receptors making them part of the innate immune system; can alter their behavior based on prior exposure to particular antigens; contain granules that released, damage the cell membranes of its target and induce apoptosis; relies on MHCs to avoid targeting healthy cells
CBC w/o diff
measure of mature cells; does NOT tell you if you have more of one specific type of WBC or if you have immature WBCs called bands
the body recognizes infection but cannot produce enough mature cells to effectively fight the infection
release immature cells to do a mature cells job
the presence of bands on bloodwork indicates...
CBC with differential
total number of WBCs that provides the percentage of each cell type present; normal ranges are 2 standard deviations above/below the mean
Leukocytosis
WBC > 11,000 that is usually caused by an increase of only one type of leukocyte
N -- bacterial infxn
E -- allergy, parasite
B -- parasite, malignancy, allergy
L -- viral infxn
what do increases in neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes indicate?
hemoconcentration -- look for dehydration
if there is an increase in all cell types in a CBC with differential, what could be the cause?
any stressful or infectious process
what can cause a leukocytosis?
Trauma or tissue injury (surgery)
Med side effect -- glucocorticoids
Leukemia/myeloproliferative disorder
what are ones non-infectious causes of a leukocytosis?
stress, excitement, pregnancy, pain, anesthesia
if one has a leukocytosis without evidence of clinical disease, think...
Neutrophilia
Neutrophils >7700/microL
infection
inflammation
medictions
asplenia
smoking
stress/exercise
obesity
endocrine causes
causes of neutrophilia
clumped platelets
what lab error can result in a falsely high neutrophil count?
6%
up to __ bands is normal
Regenerative left shift
neutrophilia with some bands; commonly seen with acute bacterial infections; GOOD prognosis!
Degenerative left shift
neutroPENIA with bandemia; POOR prognosis :(
Right shift
few bands, more mature cells; increased segmented neutrophils (hyperhsegmented neutrophils)
megaloblastic anemia, liver disease, cancer, drugs, allergies
resolving infection
causes of a right shift
Leukemoid reaction
WBC count >50,000; can be myeloid or lymphoid; excess of MATURE WBCS; because of similar presentations, ALL/AML needs to be RULED OUT!
stress/infection
--> infection (TB, Cdiff, pertussis, mono)
--> drugs (steroids, all-trans retinoic acid)
--> asplenia
by definition, leukemoid reactions are due to...
Leukopenia
total WBCs <4000
Viral or overwhelming bacterial infection
Leukopenia is TYPICALLY caused by...
Problem with bone marrow (disease, nutritional deficiency, medications)
other causes of leukopenia other than infection
avoid fresh fruits/veggies due to possible food contamination
avoid IM injections, rectal temps, enemas/suppositories, or razor blades
what are some clinical tips for leukopenia?
Neutropenia
low neutrophil count; <1500 ANC
infection -- EBV, HIV, hepatitis, bacterial/parasitic infections
Medications -- rituximab
Nutritional -- B12, folate, copper deficiency
Malignancy
Rheumatologic
Autoimmune
causes of neutropenia
observe with repeat lab in a few weeks
education on neutropenic precautions
--> monitor for infxn, good hygiene, avoid crowded areas, avoid unwashed raw fruits/veggies, unpasteurized foods, identify possible causes
treatment for neutropenia if the pt is asymptomatic and ANC >1000
admission for abx
neutropenic precautions
evaluation for underlying etiology
consult with heme
Severe -- <500/microL
treatment for neutropenia if the pt is symptomatic
Atypical lymphocytes
irregularly shaped and/or have irregular amounts of granules in their cytoplasm
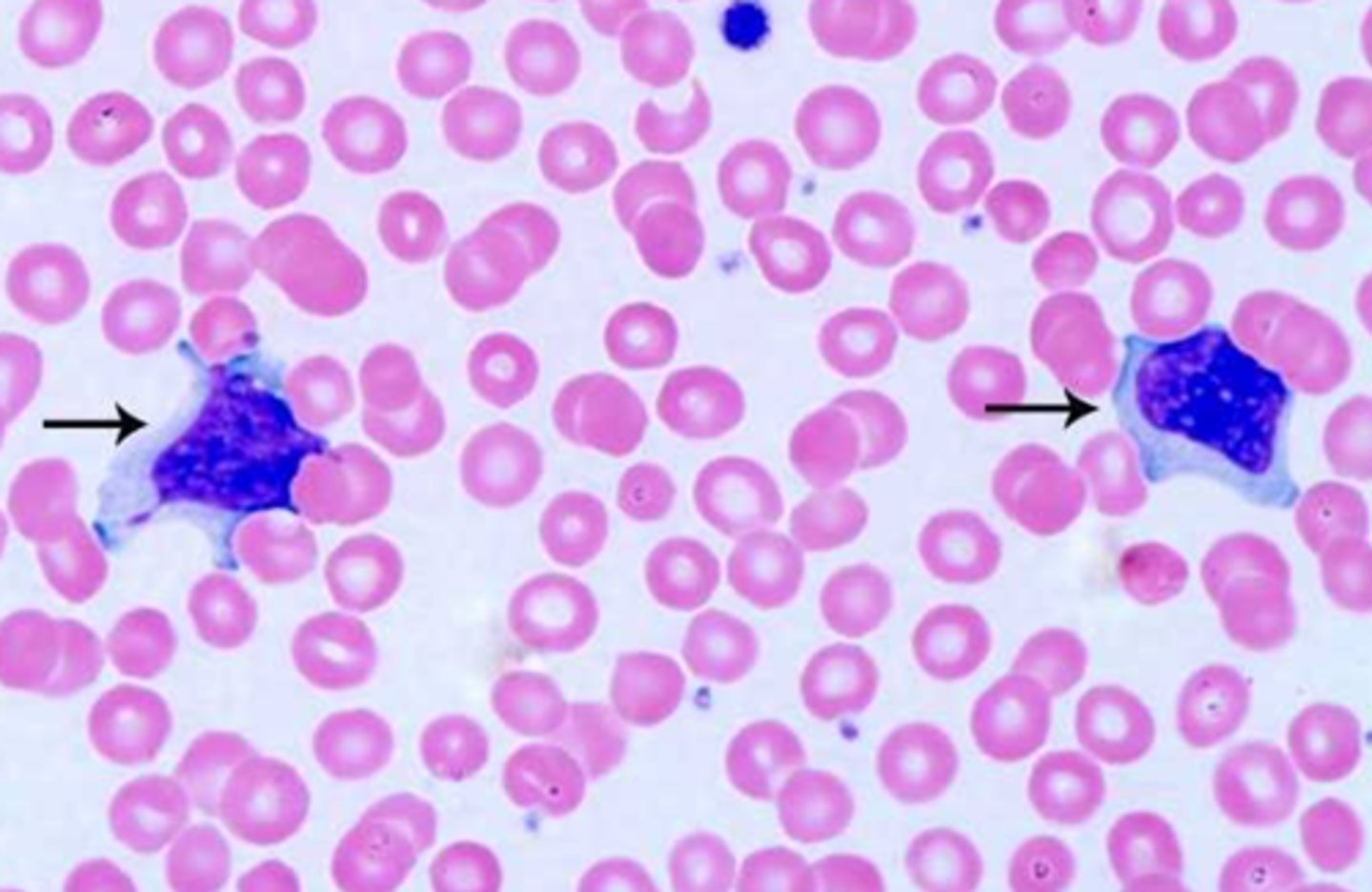
INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS -- DOWNEY CELLS
can also be caused by CMV, hepatitis, tuberculosis
causes of atypical lymphocytes
Dohle bodies
small blue cytoplasmic inclusions in neutrophils; presence can be normal in small numbers; increased numbers can indicate disruption in WBC production
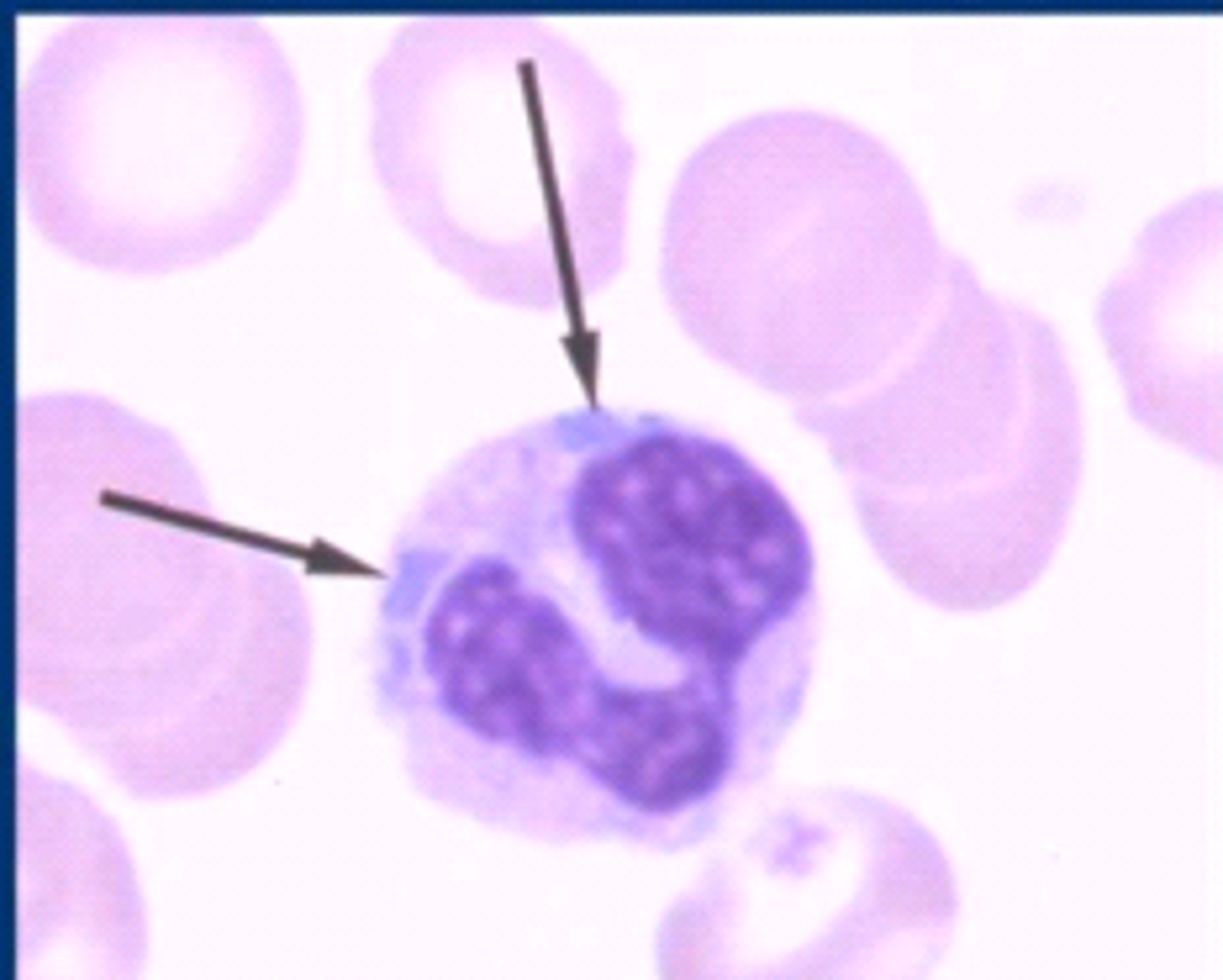
infections
inflammation
leukemia
myeloproliferative diseases
causes of Dohle bodies
LE cells
red-purple inclusions distending from the cytoplasm; a neutrophil/macrophage that has phagocytize denatured material from another cell; NOT NATURALLY OCCURRING!!!
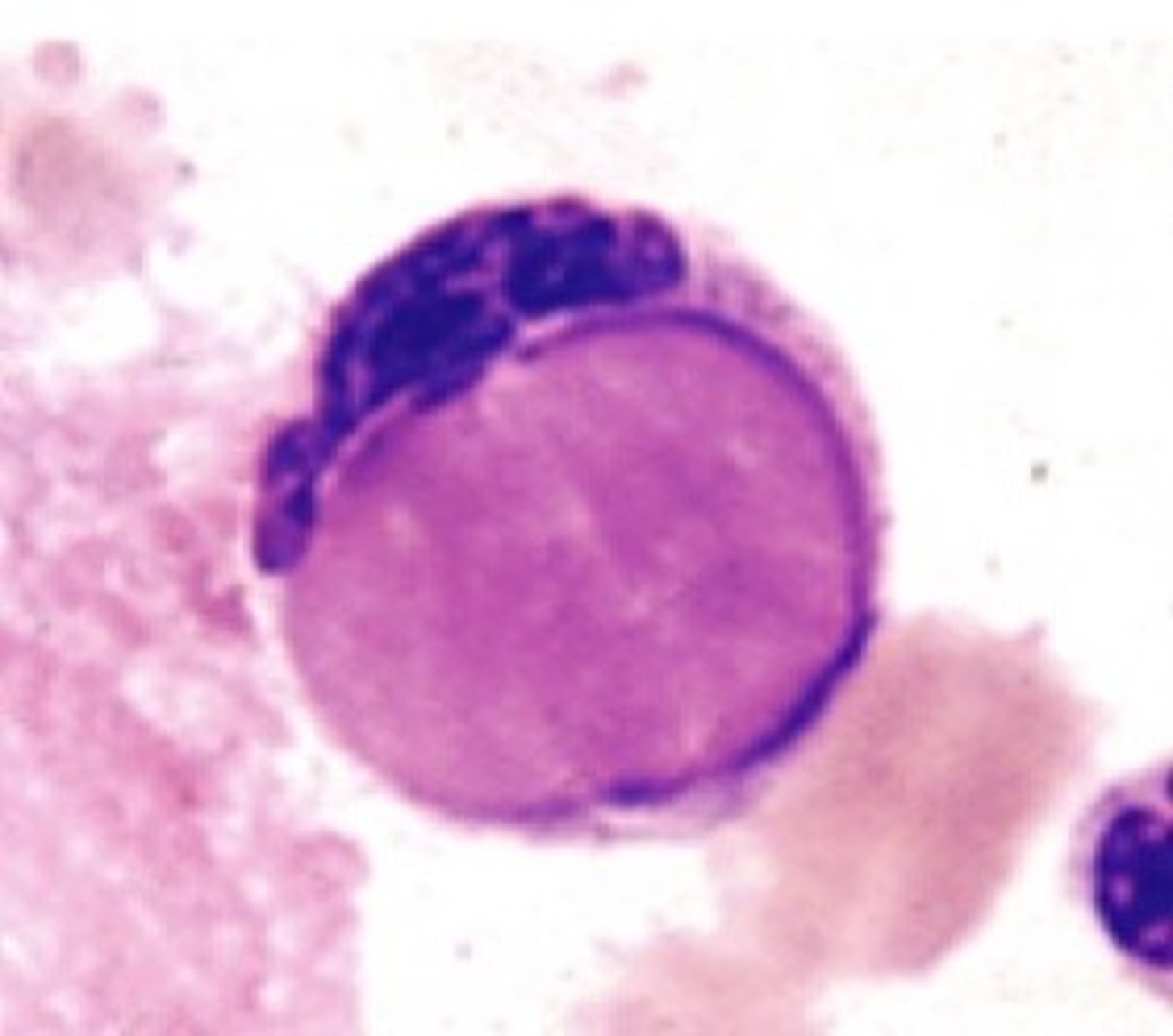
SLE or other autoimmune disease
chronic hepatitis, drug reactions
causes of LE cells
Hypersegmented neutrophils
mature neutrophil that has more than 5 distinct lobes
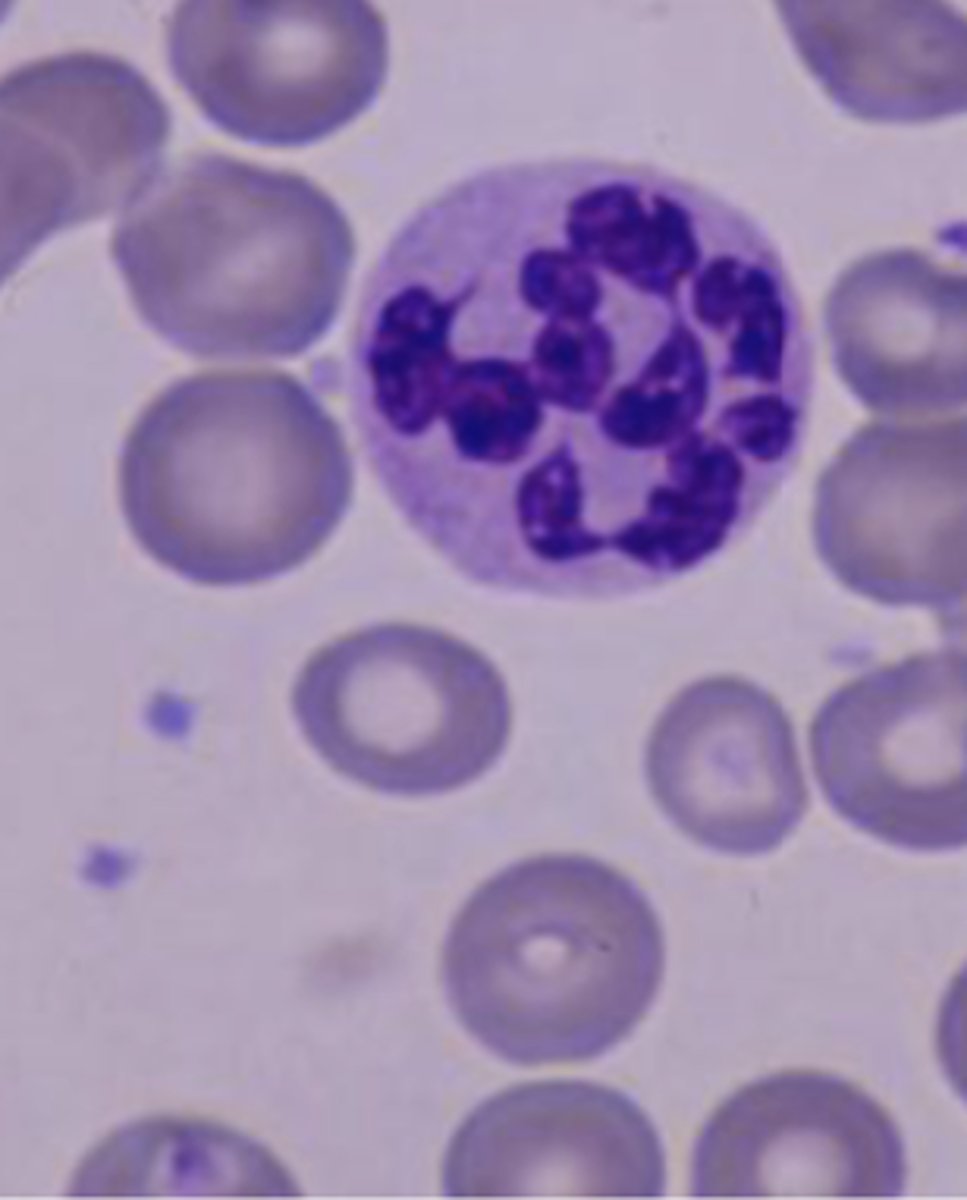
megaloblastic anemia
can indicate long term chronic infection
causes of hyperhsegmented neutrophils
Auer bodies
rod-like structure in the neutrophil; composed of fused lysosomes; can be seen in myeloid blast cell phase
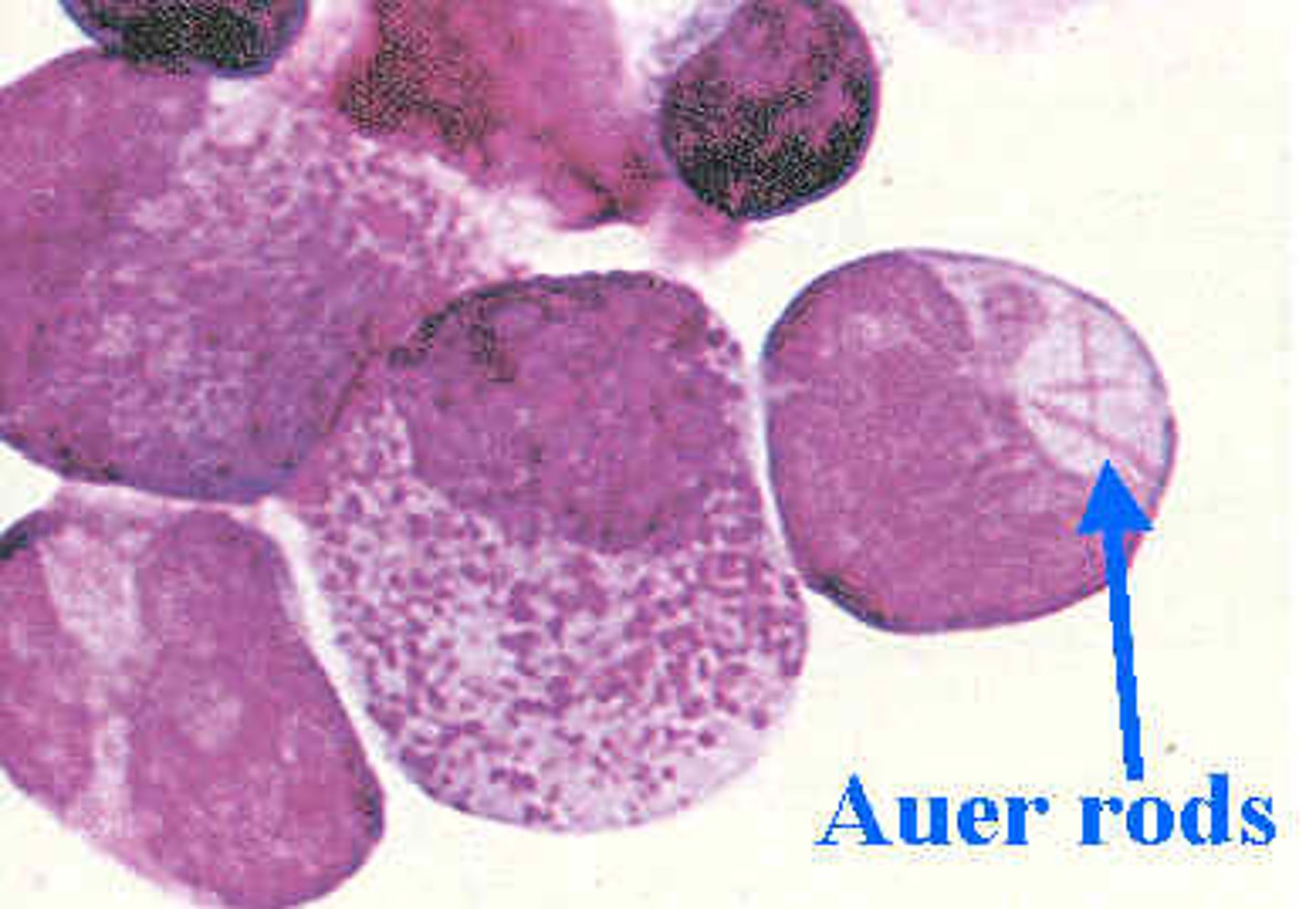
AML
causes of Auer bodies
Pelger Huet anomaly
neutrophils develop with dumbbell shaped nucleus
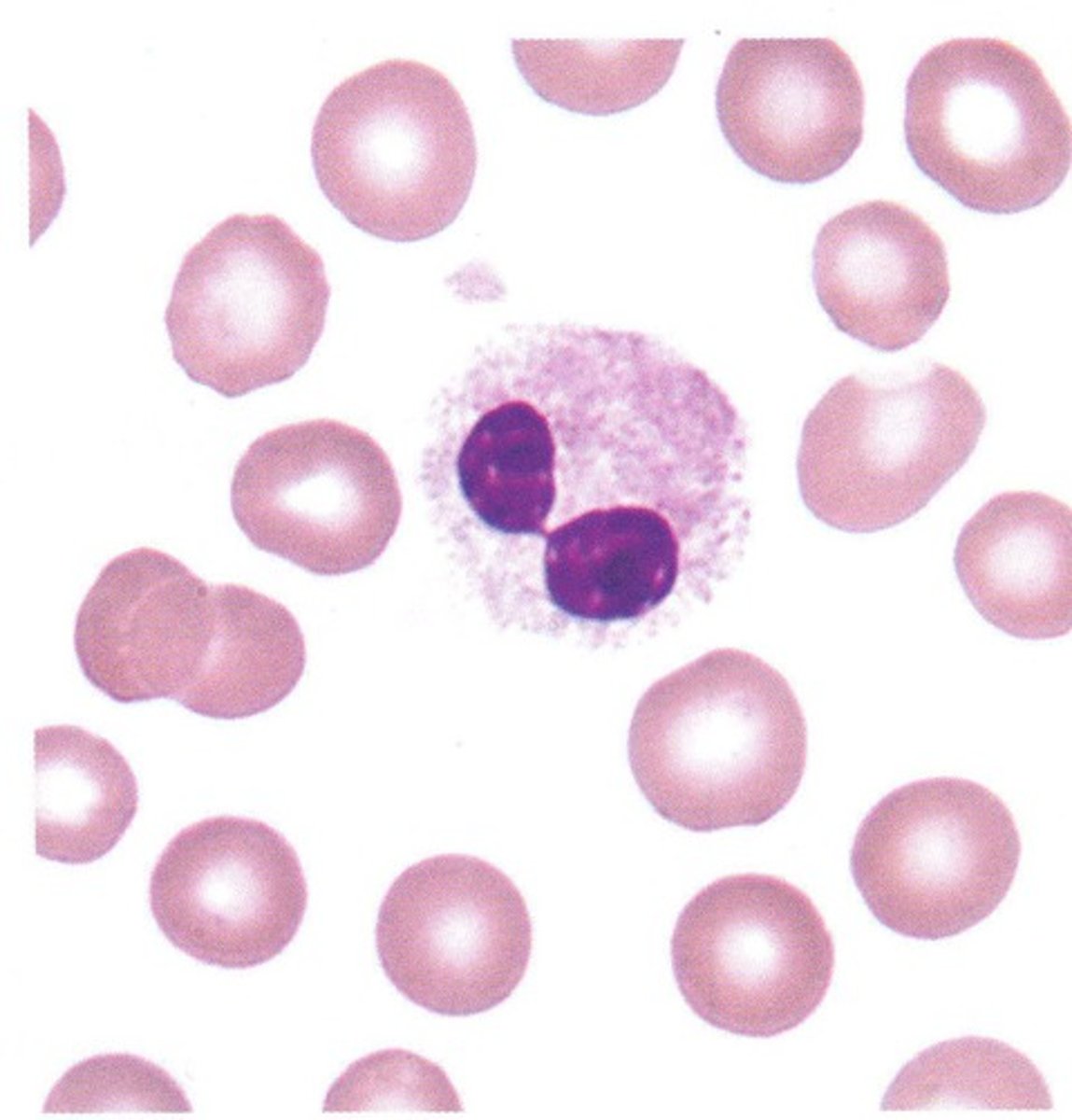
myelodysplastic syndroems
Acute/chronic leukemias
causes of Pelger Huet anomaly
Smudge cells
lymphocytes that look flattened/smudged when a peripheral smear is obtained; these cells are fragile and are easily distorted when cover slide is placed on the sample
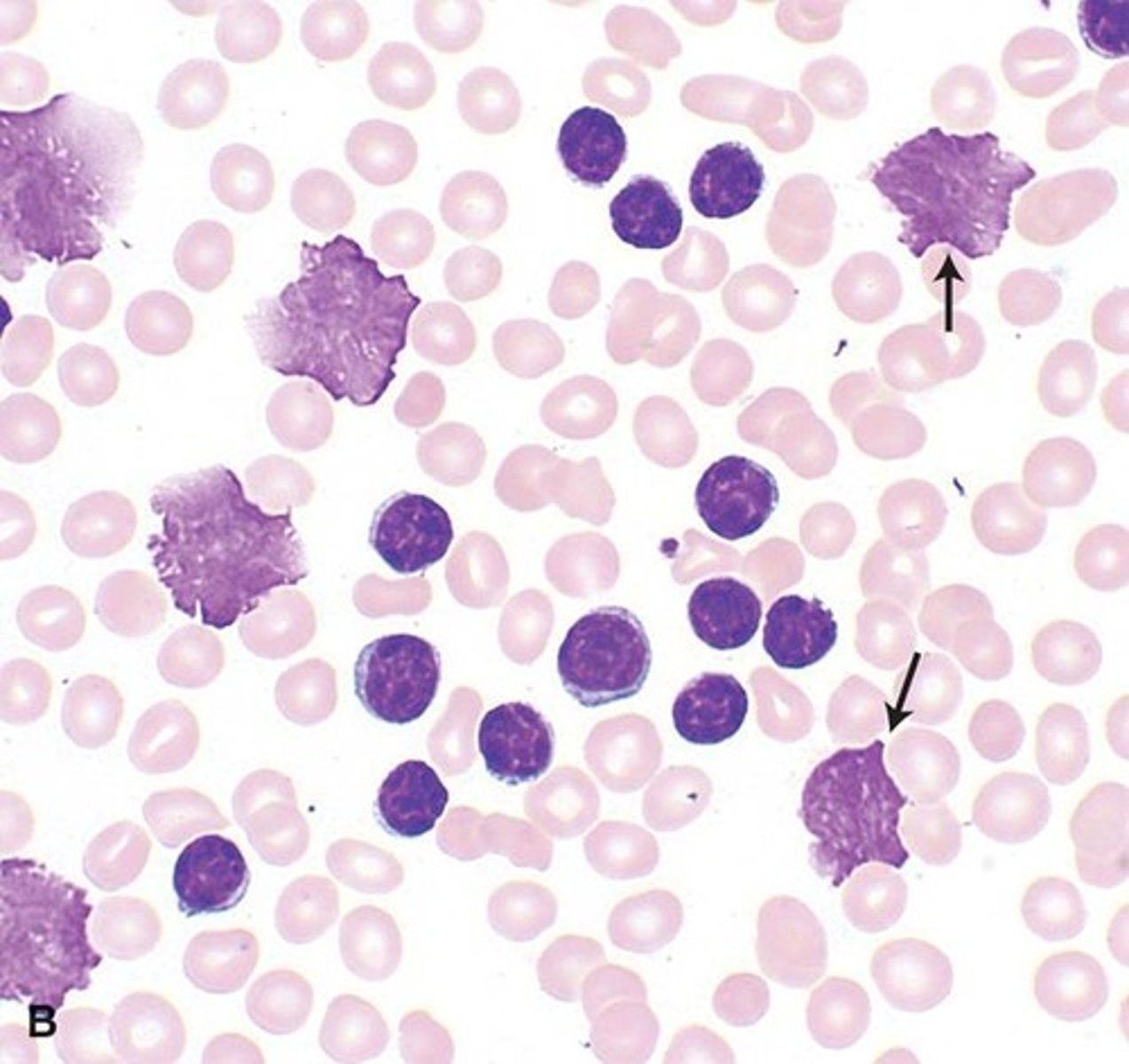
CLL
causes of smudge cells