role of blood vessels & platelets
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
hemostasis
the process by which the body stops bleeding, prevents spontaneous bleeding, and maintains blood in fluid state (bleeding vs. clotting)
triad of hemostasis
vasculature (blood vessels), platelets, & coagulation proteins. all 3 must function normally or one will bleed or clot
tunica adventitia (tunica externa)
fibrous connective tissue. strength & support. provides strength to resist damage
tunica media
smooth muscle, elastic fibers. contraction/dilation
tunica intima (tunica interna)
endothelium
what are the 3 primary roles in hemostasis?
vascular integrity, reduce blood loss upon vascular injury, activate platelets (2nd arm) & clotting proteins (3rd)
role of vascular integrity
prevent blood loss from intact vessels. tunica externa provides strength to resist damage. clotting initiated upon vascular damage. platelets nurture endothelium: natural endothelial death & sloughing of dead endothelial cells, platelets replace lost endothelial cells, release PDGF to produce new endothelial cells
role of blood loss upon vascular injury
vasoconstriction. diversion of blood flow around damaged vessel
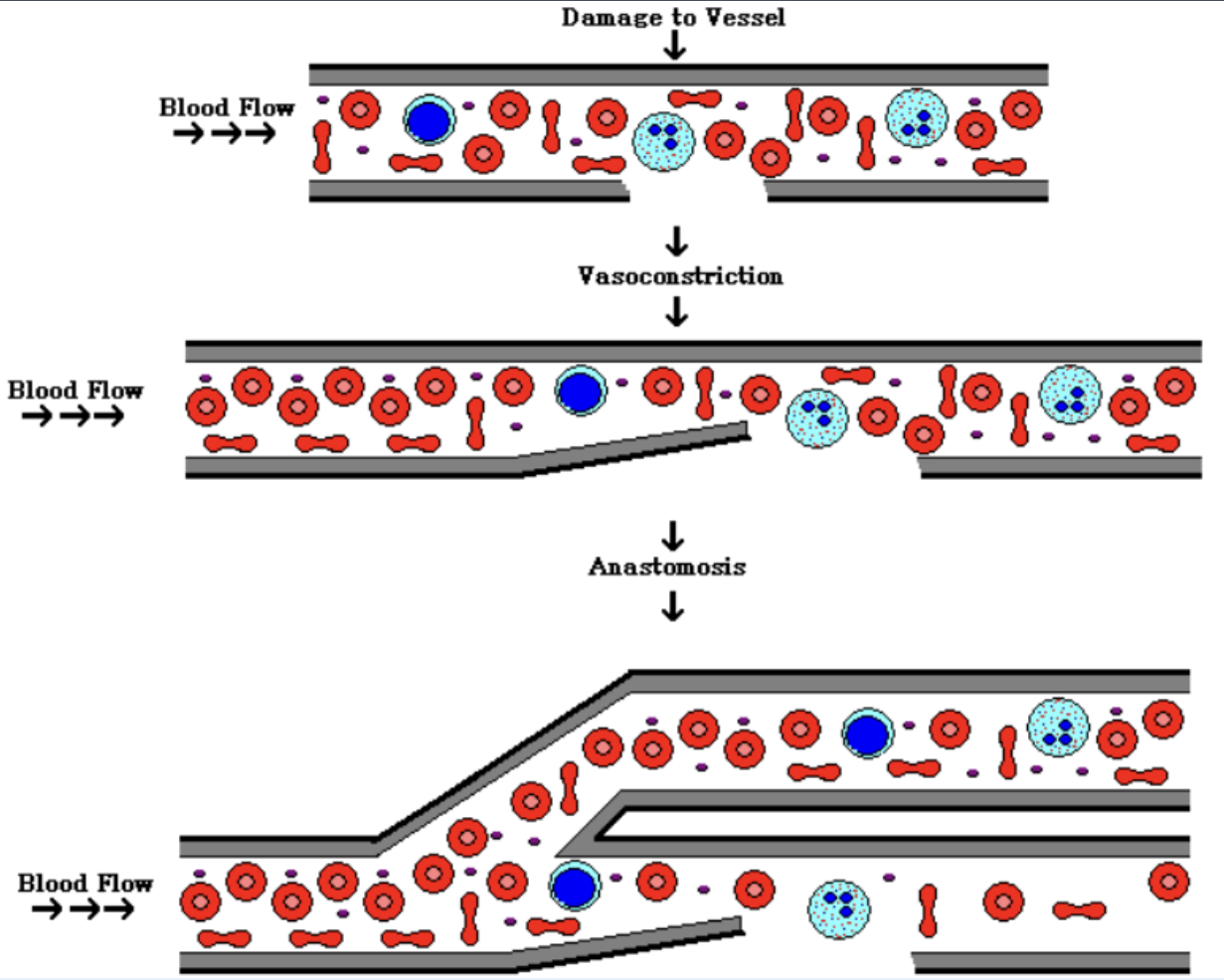
role of activating platelets (2nd arm) & clotting proteins (3rd)
initiation of platelet plug formation. activation of the coagulation factors (cascade)
peripheral zone (external surface)
one of the 3 layers of platelet ultrastructure. consists of glycocalyx, plasma membrane, and open canalicular system (OCS).
glycocalyx
outer membrane (glycolipids & glucoproteins). holds surface antigens (ABO) & receptors
plasma membrane
provides containment for the cytoplasm
open canalicular system (OCS)
tubular invaginations of the plasma membrane
sol-gel zone (sub-membranous)
one of the 3 layers of platelet ultrastructure. consists of circumferential microtubules & microfilaments
circumferential microtubules
organized bundles of contractile proteins (actin/myosin). maintains discoid shape & changes shape upon aggregation. circumferentially located
microfilaments
unorganized contractile proteins. connects ends of plasma membrane
organelle zone (cytoplasmic)
one of the 3 layers of platelet ultrastructure. consists of mitochondria, dense tubular system (DTS), granules, peroxisomes, & lysosomes
dense tubular system (DTS)
stores calcium. site for protein synthesis (like ER). prostglandin synthesis
alpha granules
20-200/platelets.
coagulation factors: V, XIII, fibrinogen, XII.
coagulation inhibitors: PAI-1 (inhibits TPA), protein S (inhibits clotting).
heparin inhibitors: platelet factor 4.
platelet effectors: von willebrand factor (platelet adhesion).
vessel repair: thrombospondin (anti-angiogenic).
fibroblast effectors: beta-thromboglobulin (fibroblast chemokine), platelet derived growth factor (fibroblast growth factor).
albumin: abundant blood protein (carrier).
dense granules
2-10/platelets. platelet activation: ADP, calcium, serotonin, epinephrine. energy source: ATP.