Individual & Family Nutrition - Mississippi State University Test 3 (Amy Weiskopf)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
water soluble
travel freely, not stored excreted in urine. needed more often
Fat soluble
require fat, stored in liver/adipose tissue. can lead to more toxicity
B vitamins
coenzymes in energy metabolism

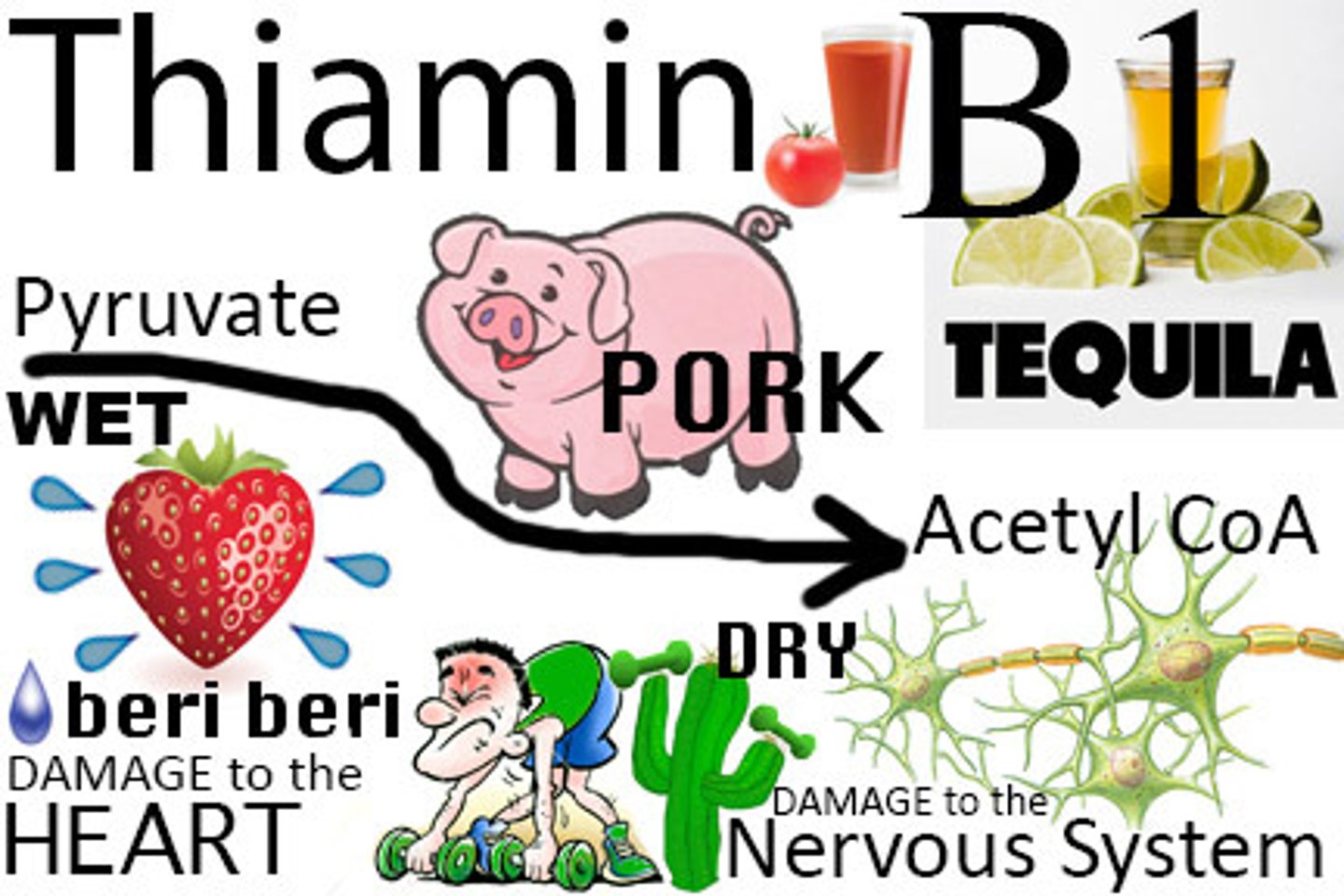
Thiamin (B1)
deficiency = Beriberi; Sources = pork, grains, legumes
Riboflavin (B2)
Light sensitive; milk in opaque containers

Niacin (B3)
Deficiency = Pellagra; Toxicity = Flush

B6
Stored in muscles
Folate
prevents neural tube defects; Sources = greens, legumes; Can mask B12 deficiency
B12
Needs intrinsic factor; Deficiency = pernicious anemia; Sources = animal foods
Vitamin C
Deficiency = Scurvy; RDA 90mg (men), 75mg (women), +35mg smokers; Sources = CITRUS FRUITS, peppers.

Vitamin A
Retinoids (animal) vs Carotenoids (plants); Deficiency = night blindness
Vitamin D
Deficiency = Rickets/Osteomalacia; Synthesized via sunlight.

Vitamin E
Sources= oils, nuts; Deficiency = nerve damage. children: erythrocytes. hemolysis- red blood cells split open and can lead to hemorrhage.

Vitamin K
Blood clotting & bone health; Toxicity rare; Caution with anticoagulants.

Body ~60% water
regulates temperature, transport, solvent; makes up majority of our body weight
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
regulates blood pressure (BP) & fluid balance
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
low sodium, high potassium/calcium for hypertension

Sodium
Fluid balance; excess -> hypertension
Potassium
Heartbeat & muscle; low = irregular rhythm. Sources: fresh fruits
Chloride
Fluid balance; part of stomach acid
Calcium
Bones, blood clotting; low = osteoporosis
Phosphorus
Bones, ATP; excess = calcium loss
Magnesium
Muscle & enzyme function; low = cramps
Trace minerals
minerals essential in nutrition, needed in small quantities daily. iron and zinc are examples
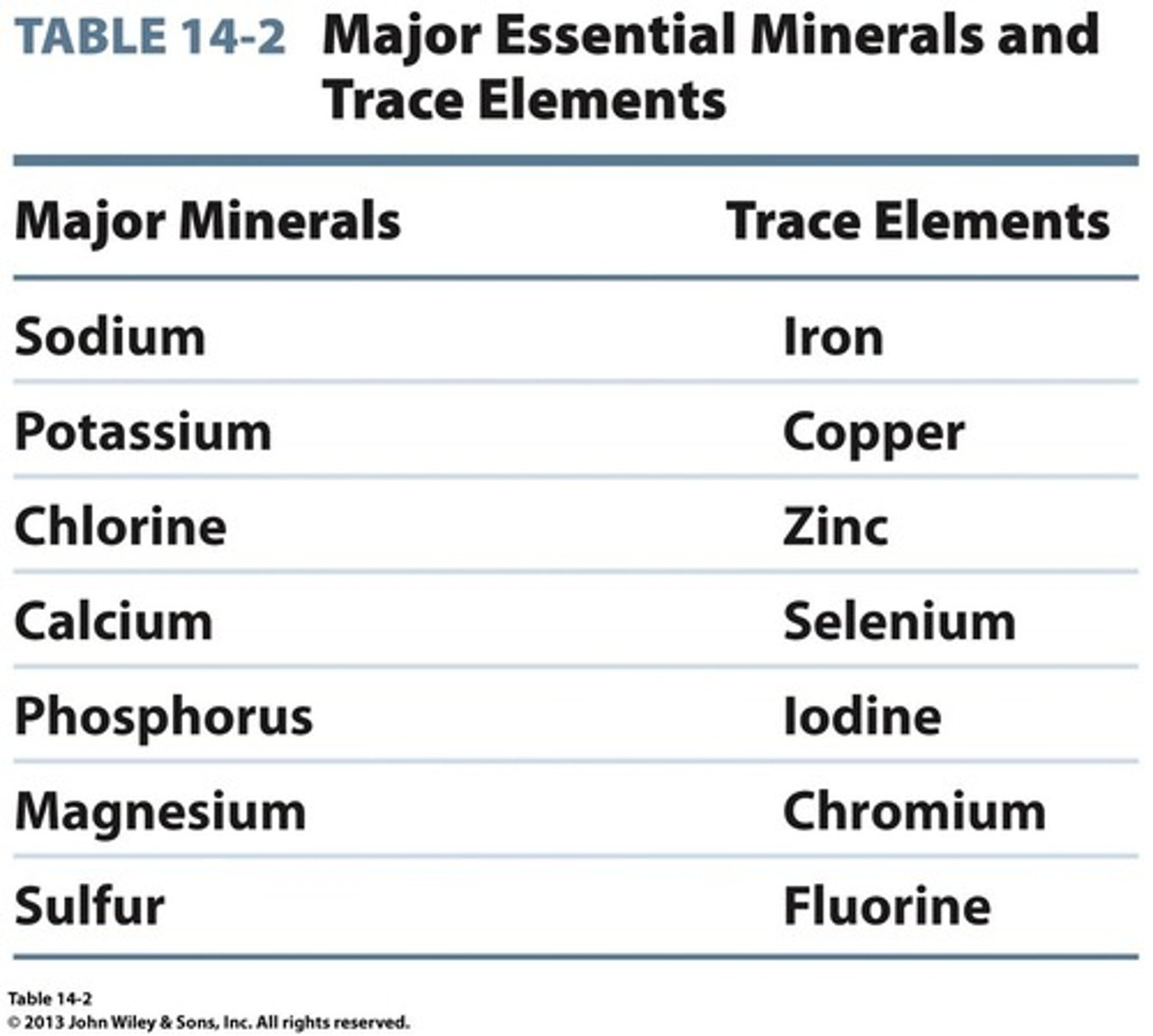
Iron
Heme (animal) vs Nonheme (plant); deficiency = anemia
Zinc
Growth, wound healing, immune health
Copper
Deficiency= Menkes; toxicity = Wilsons disease
Iodine
Thyroid hormones ; deficiency = goiter
Fluoride
Strengthens teeth; water & seafood
what is the name of the niacin-deficiency disease? ( 4 D's: diarrhea, dementia, dementia, and death)
pellagra
Chromium
Aids insulin in glucose metabolism
Physical activity
Benefits: stronger heart, muscles, mind, longevity
Anaerobic
short bursts-that does not require oxygen
aerobic
long duration (uses fat & glucose)
what is the function of water in the body fluids?
Carries nutrients and waste products
participates in metabolic reactions
aids in temperature regulation
maintains structure of proteins and glycogen
Pregame meal
high-carb, low-fat; between 300-800 kcals
post-activity meal
fluids + proteins + carbs
Hydration
Water for normal activity; sports drinks >60 min

which is a symptom of a zinc deficiency
Stunted growth
impaired immune response
poor wound healing
after how long does energy from the phosphagen system diminish?
10 seconds
which dietary nutrient is most effective at raising muscle glycogen concentrations
Carbohydrates