Human Geography AP- Unit 4: Chapter 10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Last updated 12:00 PM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
1
New cards
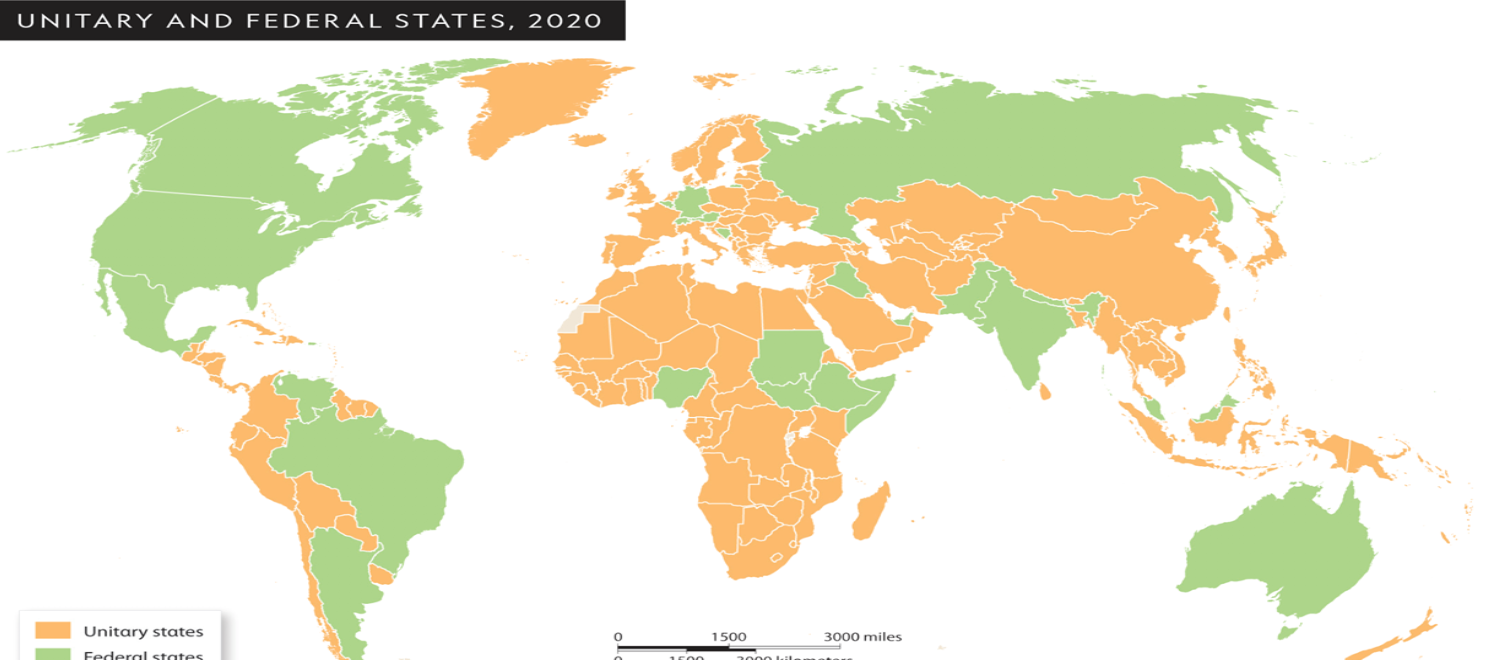
Unitary State
power is held by a central government that maintains authority over all the state’s territory, its regional units, and its people.
2
New cards
Advantages of a Unitary state:
* fewer government agencies, especially those dealing with taxation
* less corruption at local levels
* laws are implemented quickly, evenly, and fairly
* regional districts/assemblies can better care for local citizens
* less corruption at local levels
* laws are implemented quickly, evenly, and fairly
* regional districts/assemblies can better care for local citizens
3
New cards
Disadvantages of a Unitary state:
* highly centralized governments can become disconnected from local areas and the concerns of people living there
* policies tend to serve the needs of the region adjacent to the capital or where the ruling elites reside
* may fail to equitably distribute goods and services to peripheral areas
* policies tend to serve the needs of the region adjacent to the capital or where the ruling elites reside
* may fail to equitably distribute goods and services to peripheral areas
4
New cards
Federal state
power is more broadly shared between a federal government and its regional units
5
New cards
Examples of Federal states
* Mexico, The US, Germany, India
6
New cards
Advantages of Federal states:
* a regional unit can pass a law that applies to it and not to the rest of the country
* allows for more diversity
* multiple political parties can be in power in different areas of the country, which helps keep oppression by one authority at bay
* attention to local issues within a federal system boosts political participation by citizens
* allows for more diversity
* multiple political parties can be in power in different areas of the country, which helps keep oppression by one authority at bay
* attention to local issues within a federal system boosts political participation by citizens
7
New cards
Disadvantages of Federal state:
* regional and local leaders may prevent progress on issues that may impact the whole country
* the costs and benefits of federal policy and aid are often distributed unevenly among the country’s regional or local governments
* the federal government can experience conflict within the regional authorites
* the costs and benefits of federal policy and aid are often distributed unevenly among the country’s regional or local governments
* the federal government can experience conflict within the regional authorites
8
New cards
Gerrymandering
the process by which the party in control of the state legislature redraws legislative maps to favor their party
9
New cards
Packing
when local population is used to draw a district that is full of the opposing party’s voters
10
New cards
Cracking
the practice of splitting up the opposition party’s voters across many districts, thereby diluting their electoral strength
11
New cards
at-large election
the entire population of geographical area elects someone to represent them as a whole
12
New cards
Advantage of at-large election:
* representatives keep the interests of the entire community in mind and tend to be less partisan
13
New cards
Disadvantages of at-large election:
* minority groups are underrepresented because those groups tend to be concentrated in certain areas
14
New cards
District election
a single individual is elected to represent the population of a smaller geographical area