Welding
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is welding?
The process of joining multiple parts through melting
Done because it is hard to make a whole thing out of a single piece
How to weld
Parts heated at high temps, parts cool, they fuse together
Early Welding
Iron, silver and gold were welded for jewelry and weapons
Simple terms
welding is melting a filler metal to deposit onto or join a work peice.
Electric current between a workpiece and filler metal cause a temp gradient
filler metal melts to form a bead that is deposited on the workpiece or joins multiple parts
shielding gas surrounds the weld pool to prevent oxidation of the cooled metal
Common types
Arc, MIG (metal inert gas), Tungsten (tungsten inert gas), Automated laser beam
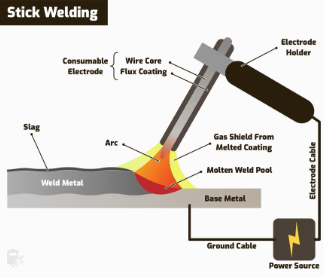
How it works - Arc Welding
uses a power source, torch and electrode.
Power source is connected to the torch and workpiece and provides an electric current between them
Torch is loaded with an electrode
The electrode has a wire made off the desired filler material and a flux coating providing a gas shield for the weld pool.
When the power source is applied, heat between the torch and workpiece melts the electrode.
Flux melts to provide a gas shield for the weld pool
flux cools to form slag (non ferrous by product of weld pool that must be removed
Arc Welding
Advantage - easiest cheapest welding process, can be applied to contaminated materials, almost anything can be arc welded
Disadvantages - poor weld quality, post processing is required to remove slag, heat also causes distortion and problems with thin materials
Applications - construction, ship building, general fabrication
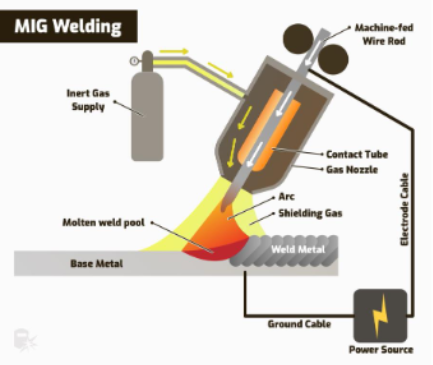
MIG (metal inert gas) welding How it works
Power source is connected to the torch and workpiece and provides an electric current between them
Torch now contains a machine-fed wire rod that is electrically charged by the power source
The torch has an gas around it fed by bottle of inert gas
When the power source is applied heat between the torch and workpiece melts the rod
continous supply of inert gas provides a gas sheild for the weld pool
MIG Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages- easy process, provides clean welds (no slag), continous wire feed meaning no electrode replacement
Disadvantages - wind or air can easily impact gas, materials cannot have contaminants
TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding
Power source connected to the torch and workpeice to provide electric current
Torch now contains a fixed tungsten electrode that is electrically charged
torch has an outer housing fed by pressurized bottle of inert gas
Welder must now hand feed the welding rod into the weld pool (lots of skill)
When the power source is applied, heat between then torch and workpeice melts the hand fed rod
Contunous supplu of inert gas provides gas sheild
TIG Pros and Cons
Pros: Highest quality, precision of the welding process, better heat control meaning less distortion and ability to weld thinner materials, provides prettiest and cleanest welds
Cons: High operator skill required, expensive equipment and electrodes
Automated Welding
Laser beam provides a concentrated heat source
Filler metal is applied through a powder or wire feeder
Robotic head containg laser and material supply is moved over the workpiece in patterns (coded)
Weld material is deposited along the weld path to form the desired geometry
Vision systems are often used to customize weld paths to individual components
Automated Welding advantages and disadvantages
Advantages- ultimate control over size, shape and heat input of welds, computerized control can consistently achieve complex geometries
Disadvantages- very expensive process requiring specialized equipment and software, variations in input must be accounted for by vision systems or programs
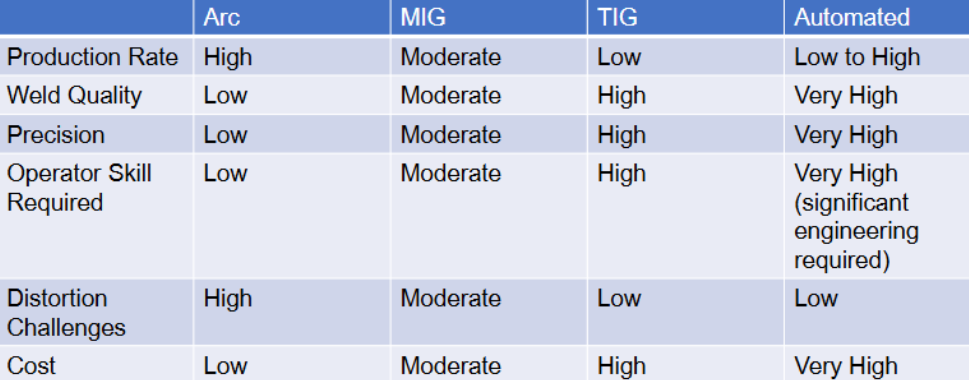
Welding comparison
Welding Materials
Certain materials are easy to weld (mild steel) and others are very difficult (superalloys)
Weldability is related to carbon content, more carbon means more strength, less ductility, less weldability.
Nickle based super alloys are difficult to weld w/o cracking
General rule: Stronger materials, harder to weld
Techniques for Weldability
Heat treat the components before welding, to get rid of stresses and soften
Head during welding to reduce the thermal gradient between base and welding region
Use special filler wires with ductility- increasing compounds (boron and silicone)
Reduce heat input or size of welds.
Welding Distortion
This happens when the workpiece changes shape or size during welding, can be cause by heat input or cooling after,
Distortion affects dimensional requirements and is a major downside to welding design
Techniques for minimizing distortion
Jigs or fixtures- constrain the part during welding
Order of welds- choose weld sequence appropriately
Heat treatment- Relieve welding stresses before unclamping parts
Straightening- Use jigs or fixtures to reshape the parts after welding
Welding Alternatives - Brazing
A method fusing pieces together using another material
Advantages- low temp, doesnt distort, dissimilar materials can be joined
Disadvantages- produces a much weaker joint then welding, can contaminate
Welding Alternatives- Adhesives
Substance applied to seperate surfaces to join them togerther firmly
Advantages: no heat, no distortion or cracking
Disadvantages: Limited temp range, delamination voids the bond, health and saftey concerns.