DNA Replication
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Nucleoside
Includes a sugar and a nitrogenous base
Function in cell signaling and a precursor for genetic material
Nucleoside Bases
Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine, and Thymidine
What base pair needs more energy to break and why?
C to G pair because it has 3 hydrogen bonds instead of 2
Major Groove
The wide, prominent indentation in the double helix
Minor Groove
The small, narrow indentation in the double helix
What type of bonds connect the base pairs?
Hydrogen Bonds
What bonds connect the base pairs to the sugar-phosphate backbone?
Phosphodiester bonds
Phosphodiester bonds
The bonds that connect the nucleotides to the backbone; Formed by condensation reactions between the phosphate and sugar-hydroxyl groups
Polarity
The way in which nucleotide strands line together gives them biological polarity which means they run in antiparallel to each other
Purines
The double ringed bases of DNA
What bases are purines?
Guanine and Adenine
Pyrimidines
The single ringed bases of DNA
What bases are pyrimidines?
cytosine and thymine
What type of reaction links the nucleotides together?
Dehydration reaction which is catalyzed by DNA polymerase
What type of polymerase is used in replication?
DNA polymerase
What type of polymerase is used in transcription?
RNA polymerase
What is the main organelle used in translation?
ribosomes
Replication machine
clusters of proteins that include replisomes that help copy DNA
Semiconservative Model
Each parental strand serves as the template for one new strand. Each daughter DNA double helix is composed of one of the original strands plus one strand that is completely new.
The Centrifugation in what compound allowed what process to occur?
the centrifugation in a cesium chloride gradient allows the separation of heavy and light DNA
Meselson-Stahl Experiment Part 1
Bacteria grown in 2 mediums (N15 and N14) loaded and isolated into different tubes to centrifuge. Based on the density, DNA separates in different ways.
Describe the pattern of separation for more dense DNA.
Heavy N15-DNA forms a high density band, closer to the BOTTOM of the tube
Describe the pattern of separation for less dense DNA.
Light N14-DNA forms a low-density band, closer to the TOP of the tube
What did scientists find after the first part of the experiment?
They found that the marker was in the middle, which meant that DNA was either made from the dispersive model or the semiconservative model
How did they differentiate between the dispersive model and the semiconservative model?
They denatured the DNA from each type of sample which makes the DNA split. When it splits, the markers from the bacteria show up.
What was the final result of the experiment?
It showed 2 bands (1 of each type of density) instead of a single thick band with the same density which demonstrated a semiconservative model of DNA
Replication Initiator Proteins
They recognize sequences of DNA at the replication origins and locally pry apart the two strands of the double helix
The exposed single strands during replication serve as what?
Templates for copying the DNA
What type of base pair connections do the replication origins have?
usually have more A-T connections since they are easier to open due to less bonds
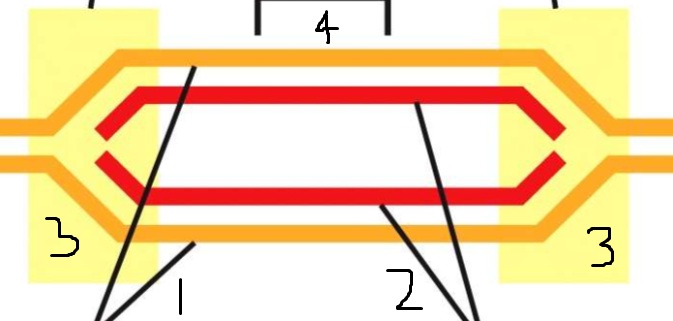
1?
Template DNA
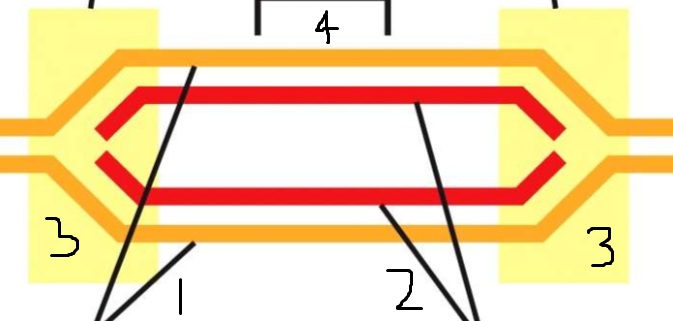
2?
Newly synthesized DNA
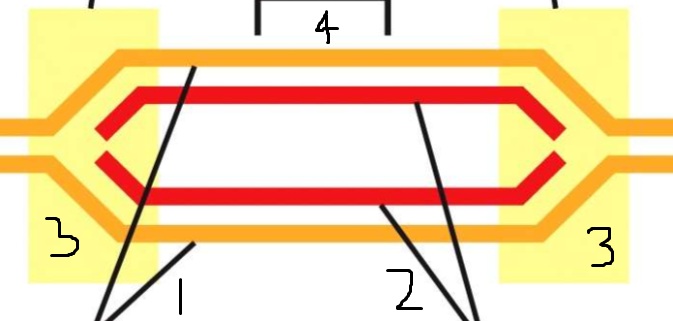
3?
Replication forks
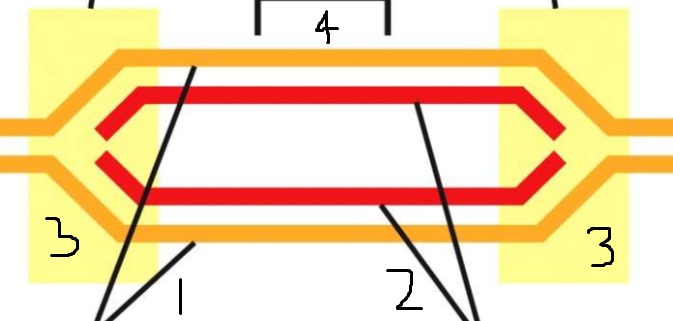
4?
Replication origin
How many replication origins are there in bacteria?
1
Replication happens in ____directions from the origin
both
Nucleosomes
Structures made of DNA and the protein complexes around which the DNA is wrapped
Chromatin
a mixture of DNA and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms
Histones
package the massive amount of DNA in a genome into a highly compact form that can fir in the cell nucleus
Chromatin packaging method is found in what type of cells?
Eukaryotic cells
What direction does DNA synthesis occur?
5’ → 3’
What end is each nucleotide added to on the growing new strand?
3’ end due to the free hydroxyl group
DNA Polymerase
a multiple protein sub-unit complex that adds a deoxyribonucleotide to the 3’ end of a growing DNA chain
What happens to the triphosphate group on the incoming nucleotide when added to the chain?
broken into pyrophosphate and then further into 2 single inorganic phosphates
What is the purpose of breaking the pyrophosphate?
it prevents a reversible reaction meaning it prevents it from gaining back the third phosphate so that the nucleotide can stay in place
When you break down the phosphates what is actually happening?
energy is being released
Why is DNA polymerase also a catalyst?
it catalyzes covalent linkage of nucleotides into the growing new strand
Polymerization reaction
involves the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3’ end of the growing DNA chain and the 5’-phosphate group of the incoming nucleotide
The nucleotide incoming to the polymerization reaction in the formation of DNA enters the reaction as what molecule?
deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
The energy for polymerization comes from where?
the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate; hydrolysis of the high-energy phosphate bonds fuels the reaction that links the nucleotide monomer to the releasing pyrophosphate
Does DNA polymerase dissociate?
No, it stays associated with the DNA and moves along the template strand stepwise for many cycles of the polymerization reaction
At the _____ _____, the newly synthesized DNA strands are of ____ ____
replication fork, opposite polarities
Okazaki Fragments
Since both strands are synthesized in the 5’→3’ direction, the lagging strand of dNA must be made initially in a series of short DNA strands
What mechanism does DNA polymerase use to replicate the lagging strand?
backstitching
Describe the movement of DNA polymerase as it synthesizes the lagging strand
synthesizes the Okazaki fragments in the 5’→3’ direction and then moves back along the template strand (toward the fork) before synthesizing the next fragment
What strand takes longer to synthesize and why?
The lagging strand takes longer because there are more steps and it takes more time
In what direction is the leading strand copied?
towards the origin of replication
What happens if an incorrect nucleotide is added to a growing strand?
the DNA polymerase will cleave it from the strand and replace it with the correct nucleotide before continuing
Proofreading
correcting a rare mistake; carried out by a nuclease that cleaves the phosphodiester backbone
The proof-reading nuclease works on what end of the DNA strand?
the free end
Exo-nuclease activity
when the nuclease works on the free end of the DNA strand
Endo-nuclease activity
works on the middle end of the strand
What direction does proofreading occur?
3’→5’
DNA polymerase contains _____ ____ for synthesis and proofreading
separate sites
What does the p side do?
polymerization activity
What does the E side do?
proofreading activity (editing)
What happens when the polymerase adds the incorrect nucleotide?
the newly synthesized DNA strand transiently unpairs from the template strand and its growing 3’ end moves to the error-correcting catalytic site (E) to be removed
What would happen in terms of proofreading if DNA was copied 3’→5’ instead of 5’→3’?
Polymerization can’t proceed because there is no high energy bond (phosphate) available to drive the reaction
What are RNA primers synthesized by?
primase (a type of RNA polymerase)
What is a key difference between DNA polymerase and primase?
unlike DNAP, primase can start a new polynucleotide chain by joining together two nucleoside triphosphates without the need for a base paired 3’ end as a starting point
DNA polymerase is _____ dependent
primer
the short length of RNA base pairs from the primer serve as a ____ for DNAP
starting point
What would happen if there wasn’t a primase?
there would be no initiation of DNA synthesis on either strand and no Okazaki fragments would be made
How are primers removed?
by nucleases that recognize an RNA strand in an RNA/DNA helix and degrade it
What happens when the RNA primers are removed?
it leaves a gaps that are filled in by a repair DNA polymerase that can proofread as it fills in the gaps
What is the final step after removing the primers?
the Okazaki fragments are finally joined together by an enzyme called DNA ligase
How exactly does DNA ligase connect the fragments?
DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3’-OH end of one fragment and the 5’-phosphate end of the next, thus linking up the sugar-phosphate backbones
What energy molecule is required for the linking of the backbone through ligase?
ATP
On what strands do you need ligase for?
both strands
Protein clamps
DNA polymerases are held on the leading and lagging strands by these that allow the polymerases to slide
When does the clamp detach and on what strand?
detaches each time the polymerase completes an Okazaki fragment on the lagging-strand template
Clamp loader
required to attach a sliding clamp each time a new Okazaki fragment is begun
DNA helicase
At the head of the fork, it unwinds the strands of the parental DNA double helix
Single-strand DNA binding proetins
they keep the DNA strands apart to provide access for the primase and the polymerase (almost like a reverse magnet between the two DNA strands)
DNA topisomerases
relieve the tension that builds up in front of a replication fork
Why does tension build up in the DNA?
there is tension in the overwound DNA because the chromosome is too large to rotate fast enough to relieve the buildup of torsional stress
How do the topoisomerases relieve the stress?
they generate temporary nicks in the DNA, once the tension is released, it reseals the nick before falling off
Without a special mechanism to replicate the ends of linear chromosomes, what would happen to the DNA?
DNA would be lost during each round of cell division
Why can’t the ends of the lagging strand be completed normally?
because once the final RNA primer has been removed there is no way to replace it with DNA
Why must the gaps created on the lagging strand be filled?
to keep the chromosome ends from shrinking during cell division
Telomeres
the end of a chromosome marked by several repeated sequences
Reverse transcriptase
responsible for the RNA template used to help synthesize more DNA repeats at the end of the chromosome
What do cancer cells have in relation to telomeres?
they make more telomerase to protect themselves since they are rapidly dividing