General - NHA CCMA
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:39 PM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
1
New cards
Needle lengths and gauges for intradermal
3/8 inch, 27-28
2
New cards
Needle lengths and gauges for subcutaneous
1/2 or 5/8 inch, 25-26
3
New cards
Needle lengths and gauges for intramuscular
1-3 inches, 20-23
4
New cards
Needle gauge for venipuncture
21 or 22
5
New cards
Syringe parts
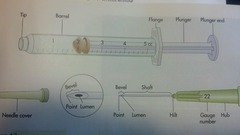
6
New cards
Common surgery procedures
-Mole/cyst removal
-Colposcopy/hyperoscopy (view inside of vagina)
-Toenail removal/ingrown
-Crytosurgery (involves cold probe to freeze and kill abnormal cells)
-Endoscopy (view internal parts such as gastrointestinal)
-Electrosurgery
-Colposcopy/hyperoscopy (view inside of vagina)
-Toenail removal/ingrown
-Crytosurgery (involves cold probe to freeze and kill abnormal cells)
-Endoscopy (view internal parts such as gastrointestinal)
-Electrosurgery
7
New cards
Sanitization
reducing the number of micro-organisms by removing debris with soap and water prior to disinfecting
8
New cards
Disinfection
to clean something (work area, equipment) using chemicals that kill pathogens but not their spores
9
New cards
Sterilization
a technique for destroying pathogens and their spores on inanimate objects, using heat, water, chemicals or gases
10
New cards
Medical asepsis
clean technique; the practice designed to reduce the number and transfer of pathogens; also helps in breaking the chain of infection
(hand hygiene, sanitization, disinfection)
(hand hygiene, sanitization, disinfection)
11
New cards
Surgical asepsis
complete removal of microorganisms and their spores from the surface of an object
(surgical scrub, sterilization techniques, autoclave, order of cleaning, packaging, quality control)
(surgical scrub, sterilization techniques, autoclave, order of cleaning, packaging, quality control)
12
New cards
Autoclave
Piece of equipment used to sterilize articles by way of steam under pressure and/or dry heat
-When spots are left on instruments its is caused by mineral deposits from tap water
-Instrument corrosion occurs when improper cleaning of the chamber occurs and exposure to hard chemicals
-Damp linens are caused by a clogged chamber drain
-When spots are left on instruments its is caused by mineral deposits from tap water
-Instrument corrosion occurs when improper cleaning of the chamber occurs and exposure to hard chemicals
-Damp linens are caused by a clogged chamber drain

13
New cards
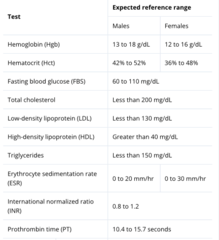
Common laboratory test values
Also:Urine
pH=4-6.8
specific gravity=1.001-1.035
urobilinogen=0.1-1
all other values=negative
pH=4-6.8
specific gravity=1.001-1.035
urobilinogen=0.1-1
all other values=negative
14
New cards
point of care testing
Tests performed at the patient's bedside or work of area, using a portable instrument.
-pregnancy, rapid strep, urinalysis, hemoglobin, spun hematocrit, blood glucose, cholesterol, helicobacter pylori, mononucleosis screening, nasal smear for influenza a and b, drug testing, and fecal occult blood
-pregnancy, rapid strep, urinalysis, hemoglobin, spun hematocrit, blood glucose, cholesterol, helicobacter pylori, mononucleosis screening, nasal smear for influenza a and b, drug testing, and fecal occult blood

15
New cards
CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments)
-CLIA-waived, moderate-high complexity (non waived), provider-performed microscopy procedures
-ensure quality of diagnostic testing through lab regulations ex. Pap test, blood typing and crossmatching (high-complexity), fecal leukocyte test (moderate-complexity)
-CLIA-waived (low-complexity) ex. human chrionic gonadotropin test (HCG)-> pregnancy
-ensure quality of diagnostic testing through lab regulations ex. Pap test, blood typing and crossmatching (high-complexity), fecal leukocyte test (moderate-complexity)
-CLIA-waived (low-complexity) ex. human chrionic gonadotropin test (HCG)-> pregnancy
16
New cards
Venipuncture needles
Evacuated tube, syringe, and butterfly needle
17
New cards
Order of draw
1. Yellow, 2. Light Blue, 3. Red, 4. Gold, Tiger Top, Red/Yellow/Black, 5. Green, Light Green, Green/Gray, 6. Purple/Lavender, 7. Pink, 8. Gray, 9. Royal Blue, 10. Tan
"You Better Remember Gods Loving Grace"
"You Better Remember Gods Loving Grace"

18
New cards
Tube colors and additives
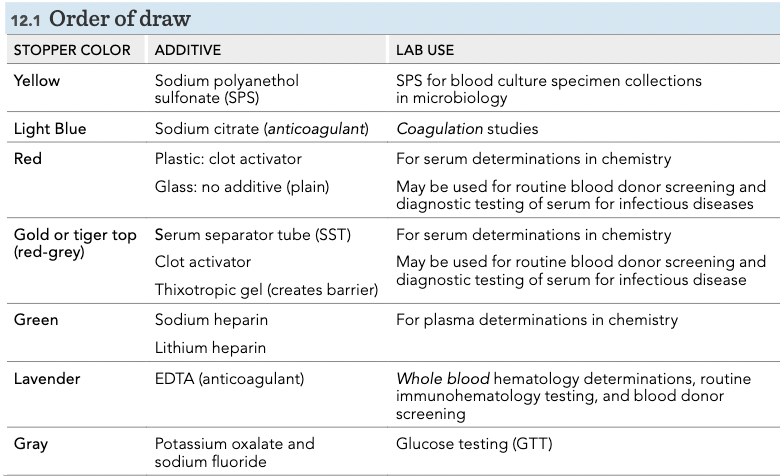
19
New cards
BCNHES
Blood culture-yellow
Citrate-blue
No additives-red
Heparin-green
EDTA-lavendar
Sodium fluroride-gray
Citrate-blue
No additives-red
Heparin-green
EDTA-lavendar
Sodium fluroride-gray
20
New cards
CBC (complete blood count)
lavender, EDTA additive should be used when performing CBC
21
New cards
SPS
for bacterial studies
22
New cards
Lithium heparin
Proper additive for chemical studies
23
New cards
Sodium citrate
Proper additive for coagulation studies
24
New cards
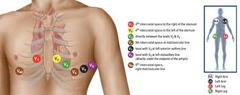
Chest Lead Placement
- V1: 4th intercostal space, right of sternum.
- V2: 4th intercostal space, left of sternum.
- V3: left side of chest, midway between V2 and V4 (V4 if place before V3)
- V4: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, midclavicular line
- V5: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, horizontal to V4, anterior axillary
- V6: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, horizontal to V5, midaxillary.
(electrode tabs downward on the arm)
- V2: 4th intercostal space, left of sternum.
- V3: left side of chest, midway between V2 and V4 (V4 if place before V3)
- V4: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, midclavicular line
- V5: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, horizontal to V4, anterior axillary
- V6: 5th intercostal space, left side of chest, horizontal to V5, midaxillary.
(electrode tabs downward on the arm)
25
New cards
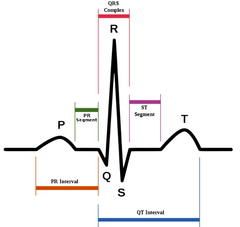
EKG waveform
-P wave=atrial depolarization/contraction
-QRS wave=ventricular depolarization/contraction (atrial repolarization)
-T wave=ventricular repolarization/relaxation
-U wave=not visible but represents repolarization of bundle of His and Purknje fibers
-QRS wave=ventricular depolarization/contraction (atrial repolarization)
-T wave=ventricular repolarization/relaxation
-U wave=not visible but represents repolarization of bundle of His and Purknje fibers
26
New cards
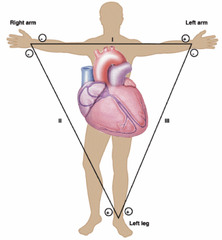
Bipolar leads
Leads I, II, III
they record impulses that travel from - to + pole
I=records impulses b/t left and right arm
II=records right and left leg
III=records left arm and left leg
they record impulses that travel from - to + pole
I=records impulses b/t left and right arm
II=records right and left leg
III=records left arm and left leg
27
New cards
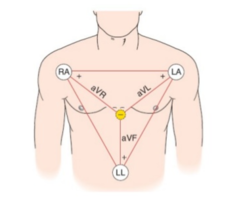
Unipolar leads
Leads aVR, aVL, aVF
AVL, the left leg and right arm assist with the left arm tracing. In AVR, the left arm and left leg assist with the right arm tracing. In AVF, the right and left arms assist with the left leg tracing.
AVL, the left leg and right arm assist with the left arm tracing. In AVR, the left arm and left leg assist with the right arm tracing. In AVF, the right and left arms assist with the left leg tracing.
28
New cards
Augmented
A unipolar recording that requires assisting in magnifying the tracing by drawing from other poles
29
New cards
Precordial
Located on the chest in front of heart
30
New cards
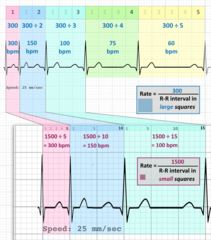
To calculate pt's heart rate from EKG tracing
Divide 1,500 by the # of small boxes b/t 2 R waves
31
New cards
Abnormal EKG Readings
-Arrhythmias: Sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, and arrest
-Atrial flutter and fibrillation
-Ventricular fibrillation
-Asystole
-Abnormal waves: P wave negative deflection, and premature ventricular contraction
-Atrial flutter and fibrillation
-Ventricular fibrillation
-Asystole
-Abnormal waves: P wave negative deflection, and premature ventricular contraction
32
New cards
Sinus bradycardia
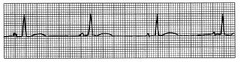
33
New cards
Sinus tachycardia
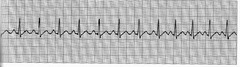
34
New cards
Sinus arrest
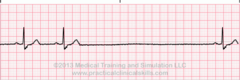
35
New cards
Atrial flutter
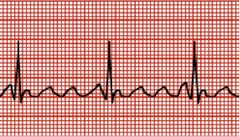
36
New cards
Ventricular fibrillation

37
New cards
Atrial fibrillation
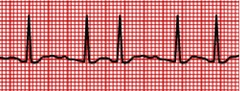
38
New cards
Asystole
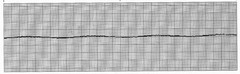
39
New cards
P wave negative deflection
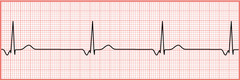
40
New cards
Positive deflection
Upward curvature of waves in an EKG tracing
41
New cards
Negative deflection
Downward curvature of waves in EKG tracing
42
New cards
Premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
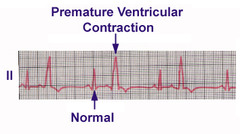
43
New cards
Where do cardiac electrical impulses originate in the heart?
sinoatrial node
44
New cards
Papules
solid, elevated spot or area on the skin that are less than 0.5cm in diameter, a common cause is allergic eczema
45
New cards
Macules
flat spots on the skin that are different color than surrounding skin, such as freckles
46
New cards
Vesicles
small, fluid-filled lesions/blisters, common cause is herpes viral infection
47
New cards
Pustules
pus-filled sacs such as those seen in acne, or pimples
48
New cards
Problem-focused examination
Limited examination of the single affected body area or organ system mentioned in chief compliant
49
New cards
Expanded problem-focused examination
Limited examination of the affected body area or organ system mentioned in chief compliant and other symptomatic or related organ system(s)
50
New cards
Detailed examination
Extended examination of the affected body area(s) and other symptomatic or related organ system(s) as well as patient's present and past medical history
51
New cards
Comprehensive examination
A general multisystem examination or complete examination of a single organ system.
52
New cards
Farenhiet to Celcius
C=(F-32)*5/9
53
New cards
Units of metric system
micro=÷1,000,000
mili=÷1,000
centi=÷100
base unit=1
kilo=x 1,000
ex. 1 g= 1,000 mg
1 mg= 1,000 mcg
mili=÷1,000
centi=÷100
base unit=1
kilo=x 1,000
ex. 1 g= 1,000 mg
1 mg= 1,000 mcg
54
New cards
Household measurements
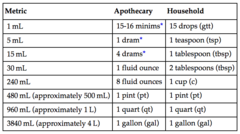
55
New cards
inches to feet
12 inches = 1 foot
divide by 12
divide by 12
56
New cards
feet to inches
multiply by 12
57
New cards
inches to cm
multiply 2.54
58
New cards
Convert pounds to kilograms
divide the weight in pounds by 2.2
59
New cards
to convert kilograms to pounds
multiply by 2.2
60
New cards
Body Mass Index (BMI)
a measure of body weight relative to height
18.5-24.9=normal
18.5-24.9=normal
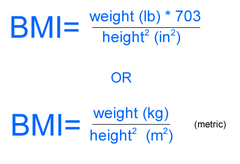
61
New cards
intramuscular injection
90 degree angle
ex. corticosteroid like dexamethasone
ex. corticosteroid like dexamethasone
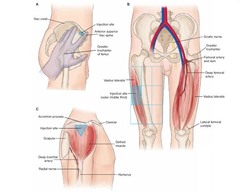
62
New cards
subcutaneous injection
45 degree angle
(slowly inject the medication)
90 degree angle for obese patients
ex. insulin
(slowly inject the medication)
90 degree angle for obese patients
ex. insulin
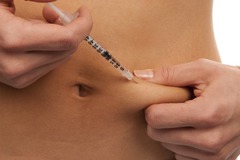
63
New cards
intradermal injection
10-15 degree angle
locate the area two to three finger widths below antecubital space
ex. PPD (Mantoux test for tuberculosis)
locate the area two to three finger widths below antecubital space
ex. PPD (Mantoux test for tuberculosis)
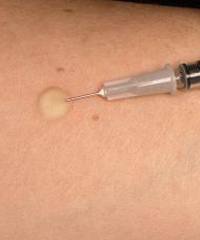
64
New cards
venipuncture injection
15 degree angle
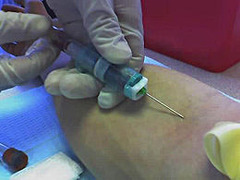
65
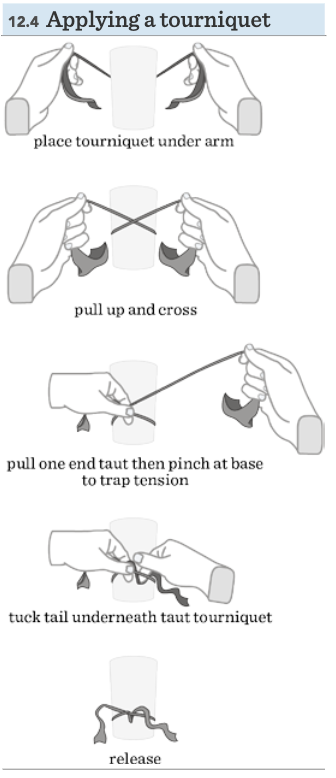
New cards
Apply tourniquet…
3-4 inches above venipuncture site, don’t leave it on longer than 1 min
66
New cards
Blood pressure measurement for children
60/30 to 100/80 mm Hg
67
New cards
Normal blood pressure measurement
100/60 to 140/0 mm Hg
68
New cards
Elevated blood pressure
128/78 mm Hg
systolic pressure b/t 120-129 and diastolic is less than 80 mm Hg
systolic pressure b/t 120-129 and diastolic is less than 80 mm Hg
69
New cards
Stage 1 hypertension
120-135/80-85 mm Hg
70
New cards
Stage 2 hypertension
150/95 mm Hg
Systolic pressure greater than 140 and diastolic pressure greater than 90
Systolic pressure greater than 140 and diastolic pressure greater than 90
71
New cards
Pre-hypertension
120-139/80-89 mmHg
72
New cards
If pt faints from injection...
Elevate legs above heart, apply cool washcloth to forehead, observe pt for 15 mins, and place in supine position
73
New cards
Checking allergy prior to administration of meds
Wait 10-15 mins before leaving for observation
74
New cards
Medication routes
Oral (in mouth), Buccal (b/t cheek and gums), Topical (locally and systematic absorption minimal, skin), Mucosal (mucous mems), Sublingual (under tongue), Transdermal (continuous slow absorption), Inhalation
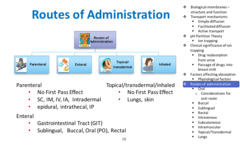
75
New cards
Immunizations
Varicella and polio vaccine for children, HPV vaccine for adolescents, andpneumococcal and zoster vaccine for adults.
These vaccines are given on a particular schedule,meaning that they require a certain number of doses given at certain intervals to be effective. Some aregiven yearly, while others confer immunity once the series is complete
These vaccines are given on a particular schedule,meaning that they require a certain number of doses given at certain intervals to be effective. Some aregiven yearly, while others confer immunity once the series is complete
76
New cards
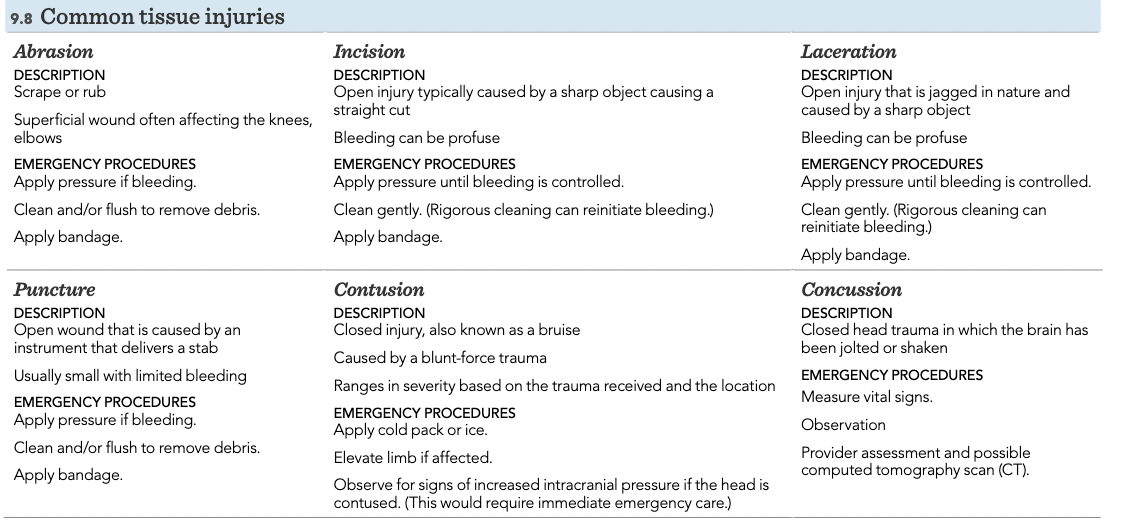
Common tissue injuries
Abrasion, incision, laceration, puncture, contusion, concussion
77
New cards
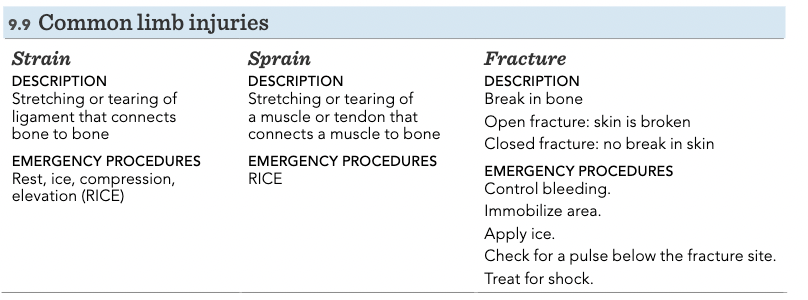
Common limb injuries
strain, sprain, fracture
78
New cards
Common emergencies
Anaphylaxis, acute abdominal pain, bleeding emergencies, burns, choking, diabetic emergencies, ear and eye injuries, seizures, stroke

79
New cards
5 stages of grief
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance

80
New cards
Providers that practice general medicine
- general practitioners
- family practitioners
- internists
- family practitioners
- internists
81
New cards
Internists
provide comprehensive care of adults, often diagnosing and treating chronic, long-term conditions. They also offer treatment for common illnesses and preventive care.
82
New cards
Providers that specialize
allergists, anesthesiologists, cardiologists, dermatologists, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, gynecologists, hematologists, neonatologists, nephrologists, obstetricians, oncologists, ophthalmologists, otolaryngologists, neurologists, pathologists, pediatricians, psychiatrists, radiologists, urologists
83
New cards
Hepatologists
specialize in the study of body parts such as the liver, biliary tree, gallbladder, and pancreas
84
New cards
Pathologists
specialize in body tissues, blood, urine, and other body fluids to diagnose or treat medical conditions.
85
New cards
Obstetricians
specialize in the care of women during and after pregnancy
86
New cards
Rheumatologist
specialist in the treatment of diseases of joints, muscle, and bones including fibromyalgia
87
New cards
Pulse oximetry
-An assessment tool that measures oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in the capillary beds
-Used when pt experiencing symptoms of pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis
**Nail polish interferes w/ results, can be clipped to earlobe instead, cold fingers can also give low reading while hyperventilation syndrome and carbon monoxide poisoning can give elevated readings
-Used when pt experiencing symptoms of pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis
**Nail polish interferes w/ results, can be clipped to earlobe instead, cold fingers can also give low reading while hyperventilation syndrome and carbon monoxide poisoning can give elevated readings

88
New cards
Glucose cuvettes
test strips that automatically takes precise amount of blood needed.
assistant should check coding everytime glucometer is used to ensure most accurate results therefore the cuvettes should be compared to the code on the glucometer before a pt is tested
assistant should check coding everytime glucometer is used to ensure most accurate results therefore the cuvettes should be compared to the code on the glucometer before a pt is tested
89
New cards
Glucometer
device for measuring blood glucose levels from a drop of blood obtained by a fingerstick
Blood sample should be obtained after inserting a test strip in glucometer
Blood sample should be obtained after inserting a test strip in glucometer
90
New cards
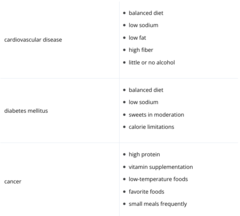
Specials needs/accommodations for certain conditions
-weight control=weight monitoring, exercise, diet
-diabetes=blood sugar monitoring, diet, exercise
-cardiovascular disease=weight monitoring, low sodium diet, chest pain
-hypertension=BP monitoring, low sodium diet
-cancer=preventative care monitoring (Pap smears, prostate exams, etc.)
-lactose sensitivity/intolerance=lactose-free diet, signs and symptoms
-gluten-free=gluten free diet
-food allergies=food labels, allergy testing
-diabetes=blood sugar monitoring, diet, exercise
-cardiovascular disease=weight monitoring, low sodium diet, chest pain
-hypertension=BP monitoring, low sodium diet
-cancer=preventative care monitoring (Pap smears, prostate exams, etc.)
-lactose sensitivity/intolerance=lactose-free diet, signs and symptoms
-gluten-free=gluten free diet
-food allergies=food labels, allergy testing
91
New cards
Dietary modifications for postoperative and medical impediments
-clear liquid=broth, gelatin, plain tea, apple juice
-full liquid=juices, milk, ice cream, custard, cooked eggs
-pureed=blenderized fruits, vegetables, meats
-soft=cooked/canned foods like fish and fruits, no chewy stringy or tough foods
-mechanical soft=cooked, chopped cauliflower, soft meatloaf
-full liquid=juices, milk, ice cream, custard, cooked eggs
-pureed=blenderized fruits, vegetables, meats
-soft=cooked/canned foods like fish and fruits, no chewy stringy or tough foods
-mechanical soft=cooked, chopped cauliflower, soft meatloaf
92
New cards
Common dietary modifications
+
-malabsorption syndromes=low fiber, supplements, low fat, small meals frequently
-gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)=low fat, not spicy, no coffee/mints/chocolate, lactose sensitivity, no dairy, chronic constipation, high fiber
-malabsorption syndromes=low fiber, supplements, low fat, small meals frequently
-gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)=low fat, not spicy, no coffee/mints/chocolate, lactose sensitivity, no dairy, chronic constipation, high fiber
93
New cards
Nutrition benefits
\-carbohydrates=used for energy -fats=essential healthy fats (omega 3 fatty acids) -proteins=aid in wound healing, used for energy -minerals/electrolytes=magnesium, potassium, sodium, etc. -vitamins= B, C, K, etc. -fiber=fruits, veggies, grains -water=transporting nutrients and oxygen throughout the body, remove wastes, regulate body temp (drink 2-3L)
94
New cards
Major nutrients
water, carbohydrates, lipids/fats, proteins, fiber, vitamins, minerals
95
New cards
Proteins
-Soy=complete protein
-Incomplete proteins can form complementary proteins such as black beans and rice, pea soup w/ toast, PB sandwich, wheat and soybeans, corn and beans
-5-6oz recommend daily
-Sources (animal protein): meat, seafood, poultry, milk, eggs, and cheese
-Sources (plant protein): legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, and vegetables
-Incomplete proteins can form complementary proteins such as black beans and rice, pea soup w/ toast, PB sandwich, wheat and soybeans, corn and beans
-5-6oz recommend daily
-Sources (animal protein): meat, seafood, poultry, milk, eggs, and cheese
-Sources (plant protein): legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, and vegetables
96
New cards
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
-Simple sugars: honey, candy, cane sugar
-Complex carbohydrates: fruits, vegetables, cereal, pasta, rice, beans, whole-grain products->starch (potatoes, wheat, rice, corn, barley, oats, fiber)
-Simple sugars: honey, candy, cane sugar
-Complex carbohydrates: fruits, vegetables, cereal, pasta, rice, beans, whole-grain products->starch (potatoes, wheat, rice, corn, barley, oats, fiber)
97
New cards
Fats/lipids
Long molecules made up primarily of carbon and hydrogen; used to store energy in the body
-Unsaturated fatty acids less dense and heavy
-Trans and Saturated fats raises LDL cholesterol levels
-Unsaturated fatty acids less dense and heavy
-Trans and Saturated fats raises LDL cholesterol levels
98
New cards
Fiber
A tough complex carbohydrate that the body cannot digest
-Prevents constipation, gallstones, hemorrhoids, IBS, diverticulosis
-Whole grains, beans, nuts, fruits, and vegetables
-Prevents constipation, gallstones, hemorrhoids, IBS, diverticulosis
-Whole grains, beans, nuts, fruits, and vegetables
99
New cards
Vitamins
Fat soluble: A, D, E, K
Water soluble: B1, B2, B3, B6, folate, B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, C
Water soluble: B1, B2, B3, B6, folate, B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, C

100
New cards
Minerals
Inorganic substances body needs in small quantities for building and maintaining body structures
(musculoskeletal, neurological, and hematological)
-Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, iron
(musculoskeletal, neurological, and hematological)
-Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, iron
