( Chapter 8 - Photosynthesis )
✦ Photosynthesis - converts light energy to chemical energy. This is done by capturing CO2 and using it as a starting point to build sugars or other organic molecules
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
:: Two major reactions
Light Independent (Calvin cycle)
Light (dependent) - used to make ATP & NADPH
occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where photophosphorylation takes place, converting light energy into chemical energy.

The thylakoid space has a high H+ and the stroma has a low H+ concentration.
This is regulated by a cyclic system that PS 1 does with the proton pump, which helps maintain the gradient necessary for ATP synthesis during photophosphorylation.
:: Calvin Cycle - energy in NADPH and ATP is used to reduce CO2, creating sugars and other organic molecules.
. step 1 ~ Carbon fixation occurs when CO2 is attached to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) by the enzyme RuBisCO, resulting six-carbon compound.
6 ATP are converted to 6 ADP, then to 6Pi. This provides energy
. step 2 ~ Reduction of CO2 occurs as the molecules of 3-PGA are phosphorylated by ATP, then reduced by NADPH, forming 6 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
6 NADPH are converted to 6 NADP+. This is used to provide electrons & H+
One of the molecules can be removed to make sugars, while the remaining five continue in the cycle to regenerate ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) for ongoing fixation of carbon dioxide.
. step 3 ~ regeneration of RuBP involves a series of reactions where the five remaining G3P molecules are rearranged using/costing ATP, resulting in three molecules of RuBP. This regeneration allows the cycle to continue, facilitating the ongoing fixation of carbon dioxide and the synthesis of glucose.
+ Producers - plants, algae, & cyanobacteria are the main photosynthetic organisms
Plants are the main producers in terrestrial environments
Algae and CB are the main producers in the aquatic environments
+ Side note ; Light
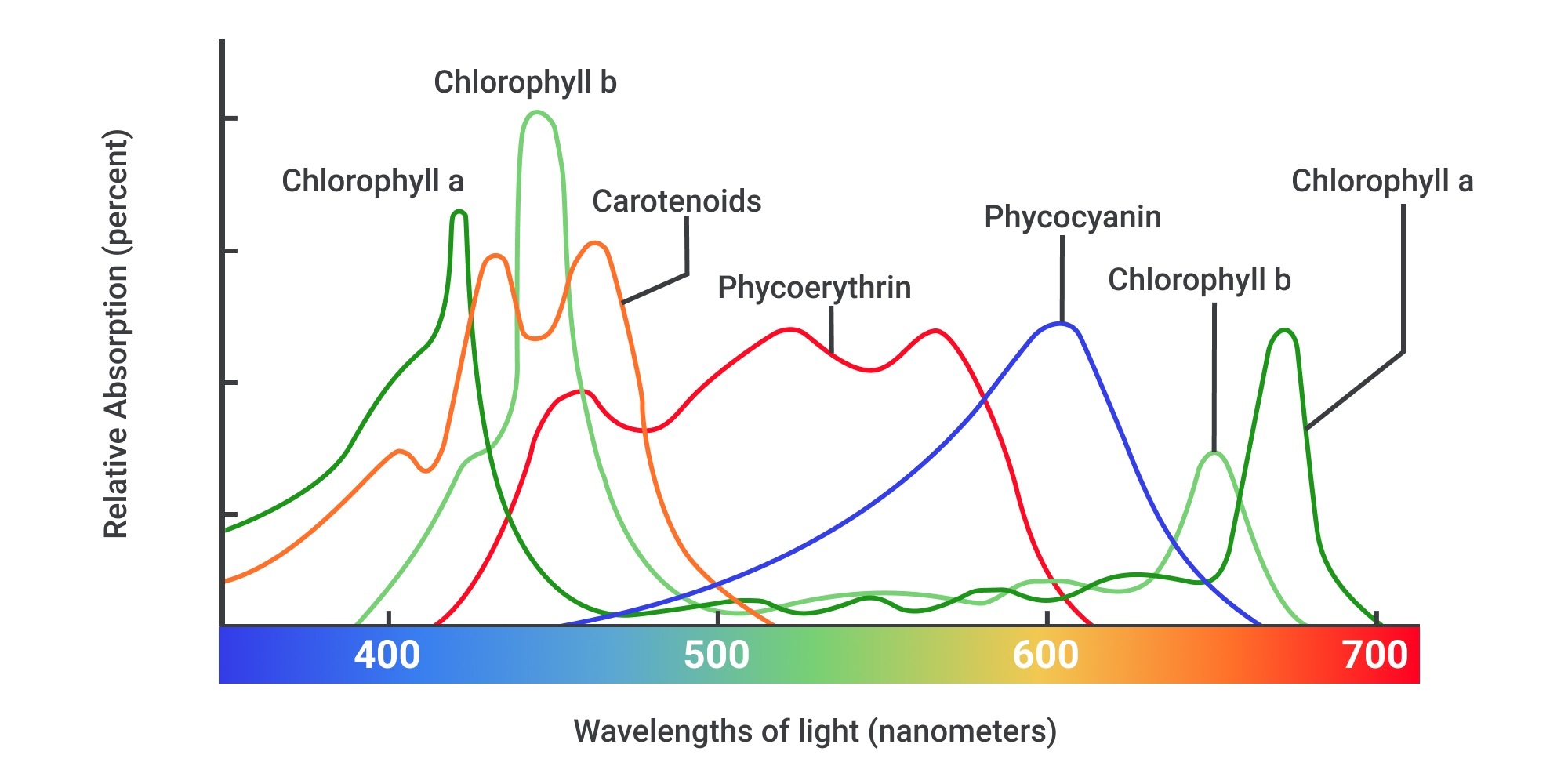
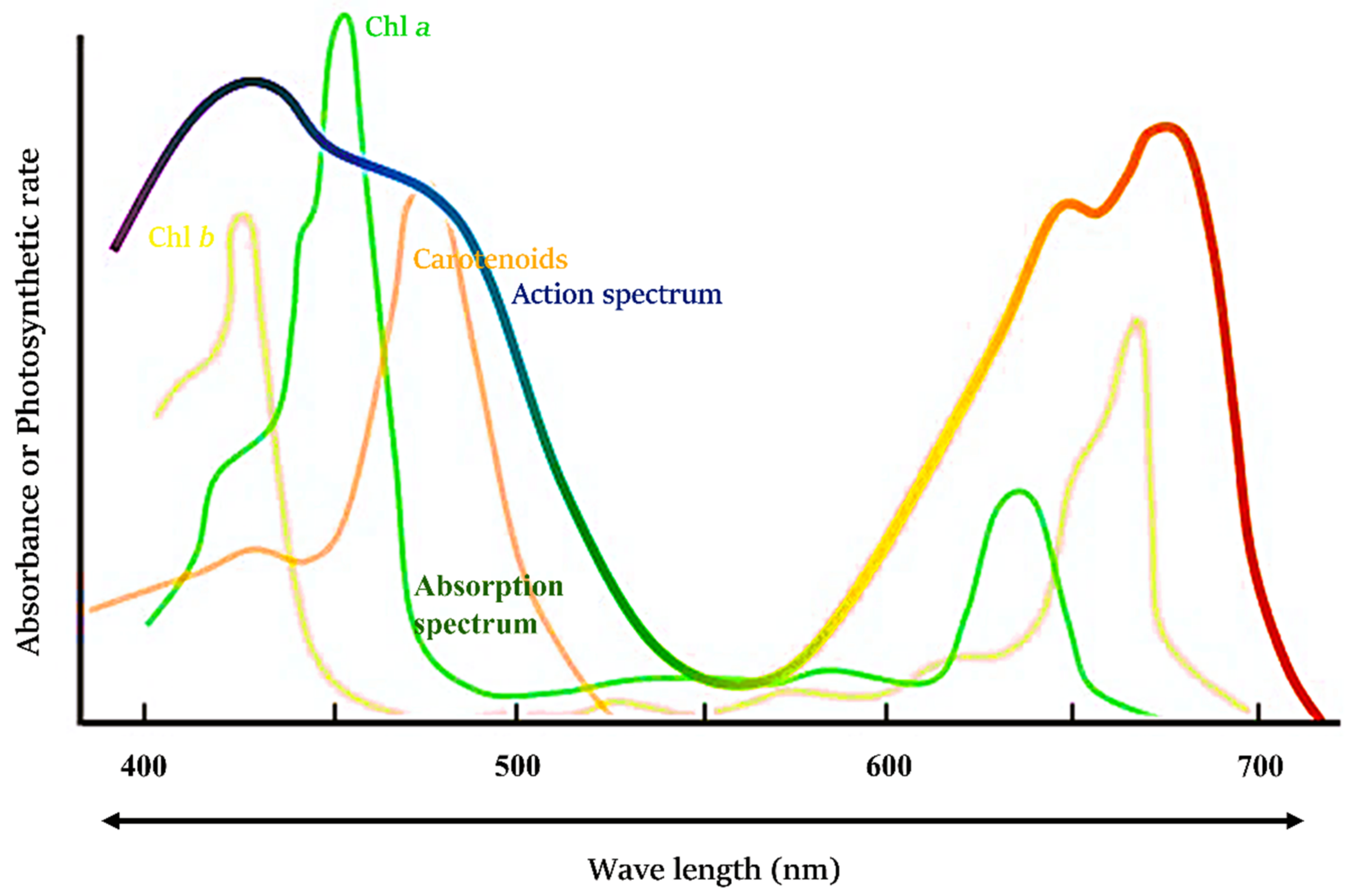
Pigment molecules absorb light energy and reflect light wavelengths they don’t absorb
White light is visible light. Photons in different wavelengths can drive the process of photosynthesis at varying efficiencies, with chlorophyll primarily absorbing blue and red light while reflecting green light.
✦ Photosynthetic pigment
main/most abundant: Chlorophyll A primarily absorbs blue-violet and red light
. Accessory pigment: chlorophyll B absorbs blue and red-orange.
Carotenoids: orange or yellow pigments that help capture light energy and protect plants from oxidative damage. Expands what type of light it can absorb
PRACTICE
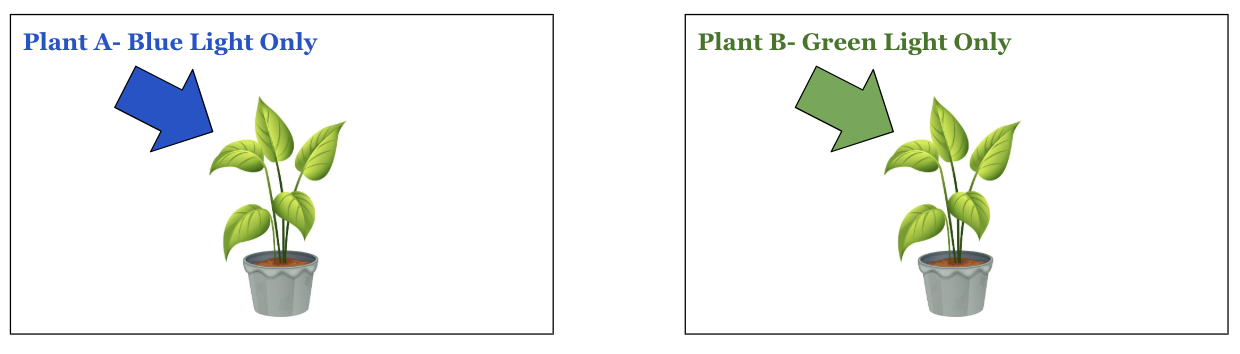
Which plants will do better, A or B? Justify
Plant A: If plant A contains a higher concentration of accessory pigments such as chlorophyll B and carotenoids, it will likely perform better in low-light conditions since these pigments allow it to capture a broader spectrum of light energy.
Plant B: Conversely, if plant B lacks these pigments, its ability to absorb light efficiently may be limited, which can reduce its overall photosynthetic capacity and growth.
What would those plants look like if you were to enter the room without external light?
Plant A would be a deep color close to black, and Plant B would still be green because we are giving it green light, which is the light wavelength that it reflects.
✦Where does mass come from?
Carbon from the atmosphere is the ultimate formation of mass.