Chapter 6: The Skeletal System [A&P I Lecture Exam 2]
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
“Organs” of the skeletal system:
Bones
Cartilages
Joints
Major cartilaginous structures of the adult body + type:
Cartilage in the external ear - elastic
Cartilages in the nose - hyaline
Articular cartilages, which cover the ends of most bones at movable joints - hyaline
Costal cartilages, which connect the ribs to the sternum (breastbone) - hyaline
Cartilages in the larynx (voice box), including the epiglottis, a flap that keeps food from entering the larynx and the lungs - elastic
Cartilages that hold open the air tubes of the respiratory system - hyaline
Cartilage in the discs between the vertebrae - fibrous
Cartilage in the pubic symphysis - fibrocartilage
Cartilages that form the articular discs within certain movable joints, the meniscus in the knee for example - fibrocartilage
Describe the perichondrium:
A dense layer of connective tissue that protects + functions in growth/repair of the cartilage.
Describe functions of the bony skeleton and bone tissue:
Skeleton function:
support, protection, movement, mineral storage, blood cell production, energy storage, metabolism
Describe the bone shapes (non-skull):
short
sesamoid
flat
irregular
long
short: cubelike
sesamoid: develop within a tendon. ie. patella (knee cap)
flat: ie. scapula
irregular: ie. vertebra, hip bones
long: based on proportion, not size. distinct ends upon a long portion.
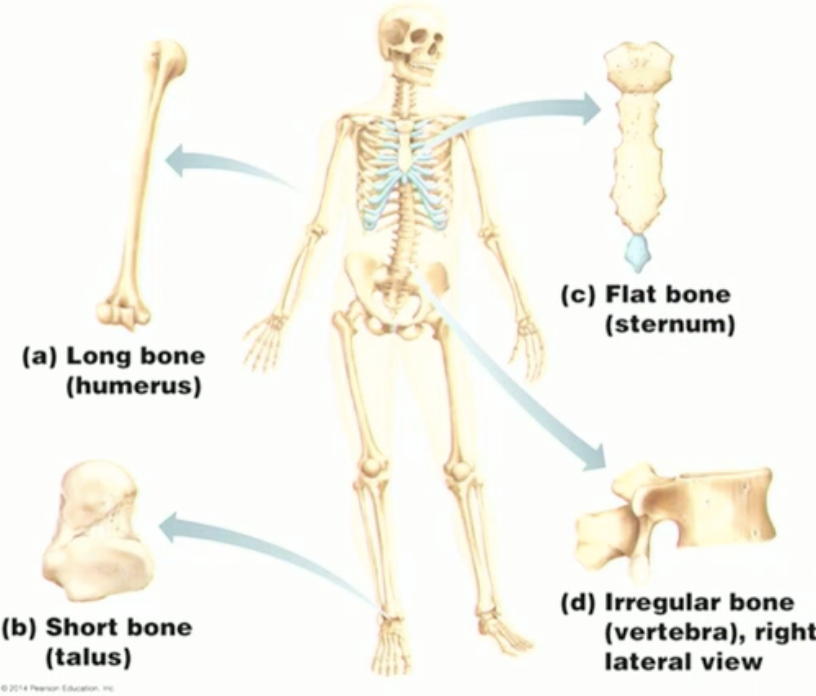
Classify the following bones based on shape:
scapula
clavicle
ribs
scapula → flat
clavicle → long
ribs → flat
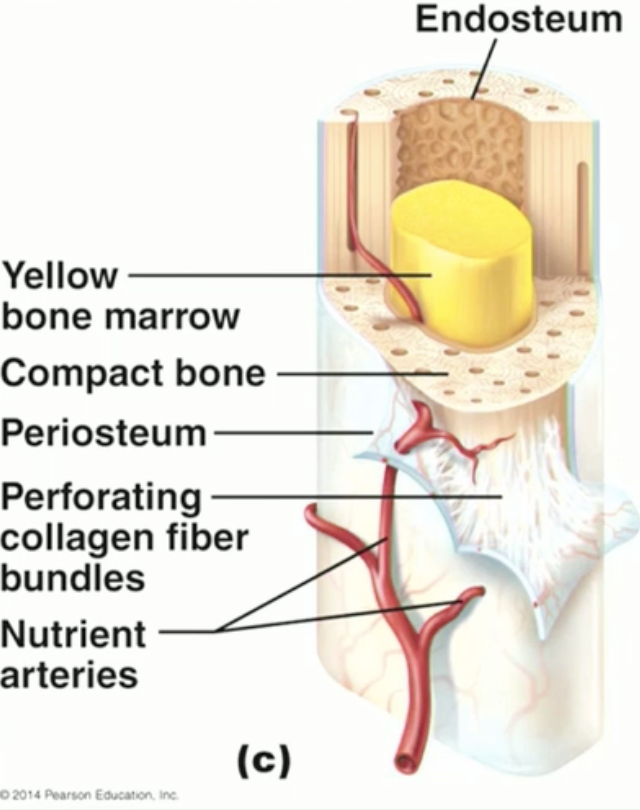
Gross and microscopic structure of compact bone + locations:
Gross:
Dense, outer layer of bone
In long bones, compact bone contains medullary cavity (lined by endosteum)
Nutrient artery runs along exterior dense irregular connective tissue (periosteum) and enters through “nutrient foramens”
“Sharpeys fibers” collagen bundles which attach the periosteum to the bone.
Microscopic:
“1 tree trunk unit” = osteon/Haversian system
“tree trunk core” = central canal (Haversian); contains nerve, vein+artery!
“tree trunk rings” = lamellae
“perimeter tree trunk rings containing multiple tree trunk units” = circumferential lamellae
Perforating Volkmann’s canal connects the osteon central canals to spongy bone.
Periosteum covers external circumerential lamellae.
Dark specks are osteocytes in a lacuna! Canaliculi connect these as tiny junctions.
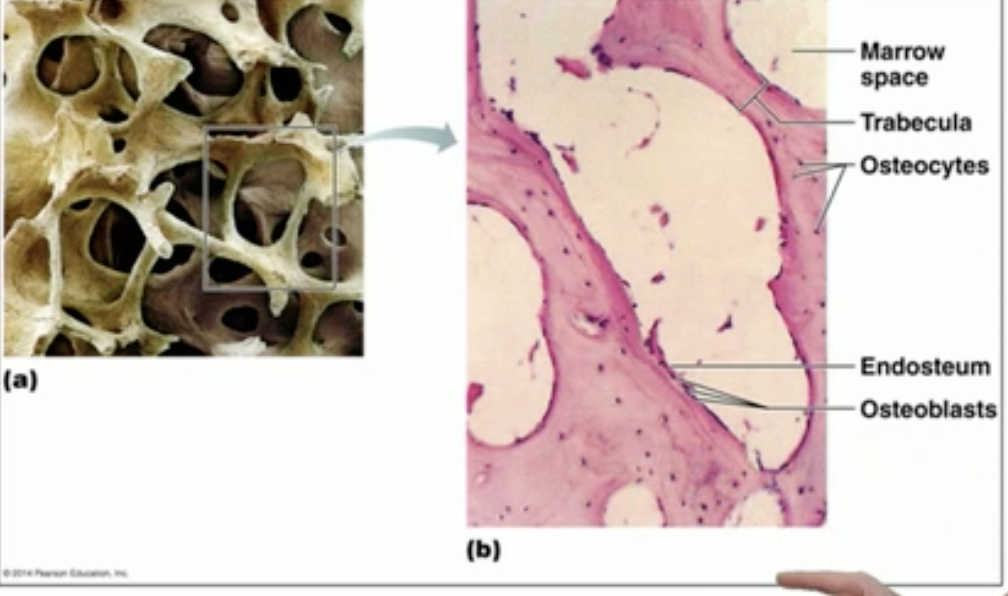
Gross and microscopic structure of spongy bone + locations:
Gross:
Internal layer of bone “trabecula”
Microscopic:
Receives nutrients from surrounding endosteum’s capillaries.
Dark specks are osteocytes.
Red bone marrow found in the spaces
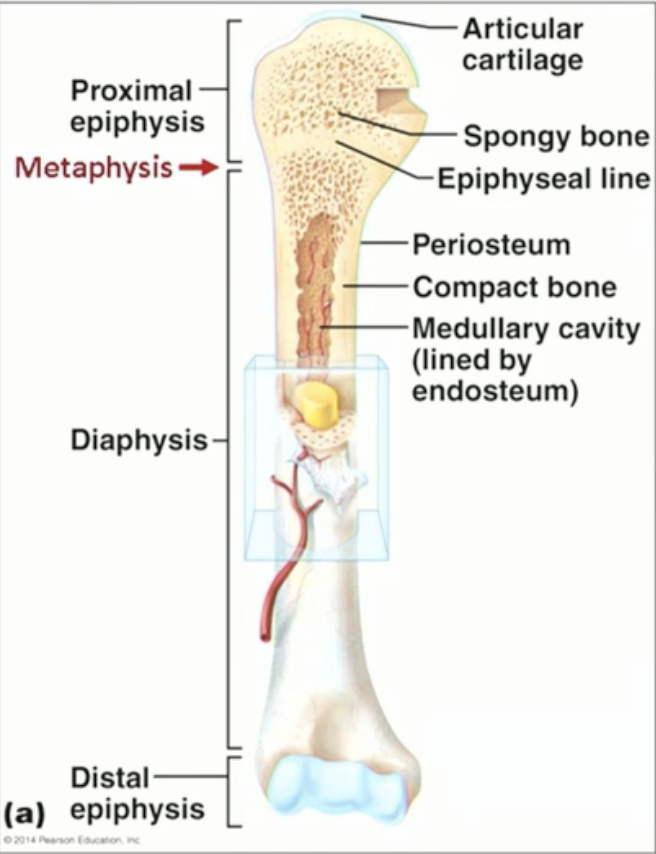
Describe detailed anatomy of typical long bone:
Shaft “diaphysis” + two ends “epiphyses”
Border between shaft and ends: “metaphysis” (where epiphyseal line exists)
Articular cartilage covers the epiphyses.
Periosteum CT covers the diaphysis.
Describe general anatomy of all other bone classes:
Top and bottom layer of compact bone; covered with periosteum.
Middle layer of spongy bone (continuous with compact bone); covered with endosteum.
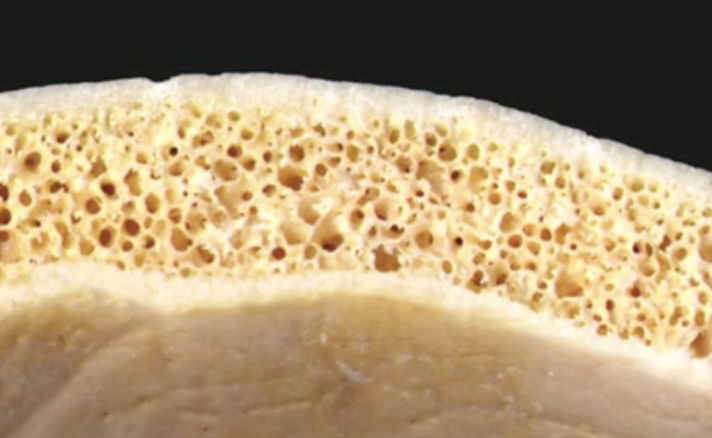
Periosteum and endosteum function+structure+location:
Periosteum:
Covers external bone surface w/ two layers. Superficial layer is dense irregular CT; deep layer is osteogenic (contains osteoclasts/blasts).
Attached via Sharpey’s fibers.
Located on compact bone where there is NO articular cartilage…
Endosteum:
Thin, osteogenic membrane covering internal bone surfaces.
Located - spongy bone trabecula (epiphyses of long bones, medullary cavity, short/irregular/flat bones)
Purpose of bone markings + examples of each kind:
Bone markings reflect the stresses applied to a particular location:
Projections (muscle/ligament attachment sites); ie. illiac crest.
Joint formation surfaces; ie. mandibular condyle.
Depressions & openings; ie. foramen, fissure.
Types of bones formed from endochondrial vs. intramembranous ossification:
Intramembranous ossification - formed directly from mesenchyme (embryonic tissue), includes most skull bones + the clavicles.
Endochondrial ossification - forms within hyaline cartilage to eventually replace, includes all bones from the base of the skull downwards (except the clavicles).
Epiphyseal plate vs. line:
Cartilagenous epiphyseal growth plates close in adulthood and become bone.
This bony structure is then called the epiphyseal line.
Osteoblasts vs. osteoclasts:
Osteoblasts add bone tissue
Become osteocytes once encased by bone matrix.
Osteoclasts remove bone tissue (at the same rate).
Secrete HCl + lymosomal enzymes to release Ca++ ions.
Possible symptoms of osteoblast and osteoclast dysregulation:
Osteoclasts functioning faster than osteoblasts = osteoporosis/brittle bones
Osteoblasts inadequately mineralizing = osteomalcia/softened and weak bones