Plant Tissue Culture & Biotechnology: History, Applications, and GMOs
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Tissue Culture
The process of growing single cells artificially in the laboratory.
Plant Tissue Culture
The techniques of growing plant cells, tissues, organs, seeds or other plant parts in a sterile environment on a nutrient medium.
Haberlandt
The father of plant tissue culture who proposed that plant cells could be cultured.
T. Murashige
A key figure in the development of plant tissue culture techniques, known for the development of MS medium.
F. Skoog
A scientist who contributed to the first in vitro culture of tobacco and the development of plant tissue culture.
Milestones of Plant Tissue Culture
Key historical events in the development of plant tissue culture and genetic engineering.
1902
The year Haberlandt proposed that plant cells could be cultured.
1904
The year of the first attempt to embryo culture of selected crucifers.
1944
The year of the first in vitro culture of tobacco used to study adventitious shoot formation.
1949
The year of the culture of fruits in vitro.
1962
The year of the development of MS medium.
1967
The year haploid plants were obtained from pollen grains of tobacco.
1972
The year protoplast fusion was done in tobacco.
1977
The year of successful integration of transfer DNA (T-DNA) in plants.
1985
The year of infection and transformation of leaf discs with Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Micro-propagation
A technique used in plant tissue culture to produce a large number of plants from a small amount of plant material.
Biotechnology
The use of biological processes, organisms, or systems to develop products.
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Organisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques.
Transgenic Plants
Plants that have been genetically modified to contain genes from other species.
Global Workforce of Biotechnology
The collective professionals and researchers engaged in the field of biotechnology worldwide.
TSU Students Activities in Biotechnology
The involvement of Tennessee State University students in biotechnology-related projects and research.
Mass propagation of specific clones
Reproducing copies of an original parent plant.
Controlled aspects in tissue culture
Environment and plant growth regulators (PGRs) allow rapid propagation in large numbers.
Multiplication rate in tissue culture
Rate can be exponential; for example, a multiplication rate of fourfold in cultures subcultured every 4 weeks can result in 1,000,000 plants in 10 months.
Special needs for plants
Useful for plants with slow natural rate of clonal increase, high demand and valuable plants, difficult-to-root plants, endangered species, and plants that cannot be clonally propagated any other way.
Tissue culture disadvantages
Expensive and sophisticated facilities, trained personnel/specialized techniques, contamination can wipe out cultures, species- and genotype specificity, and production of off-types (variability).
Totipotency
The capacity of a cell (or a group of cells) to give rise to an entire organism.
Differentiation
Transition from meristematic cells to specialized cells, typically a one-way path.
Organogenesis
Direct production of organs (stems or roots) from differentiated or undifferentiated tissue.
Somatic embryogenesis
The production of embryos de novo and without fertilization; it does not occur in nature (only in-vitro).
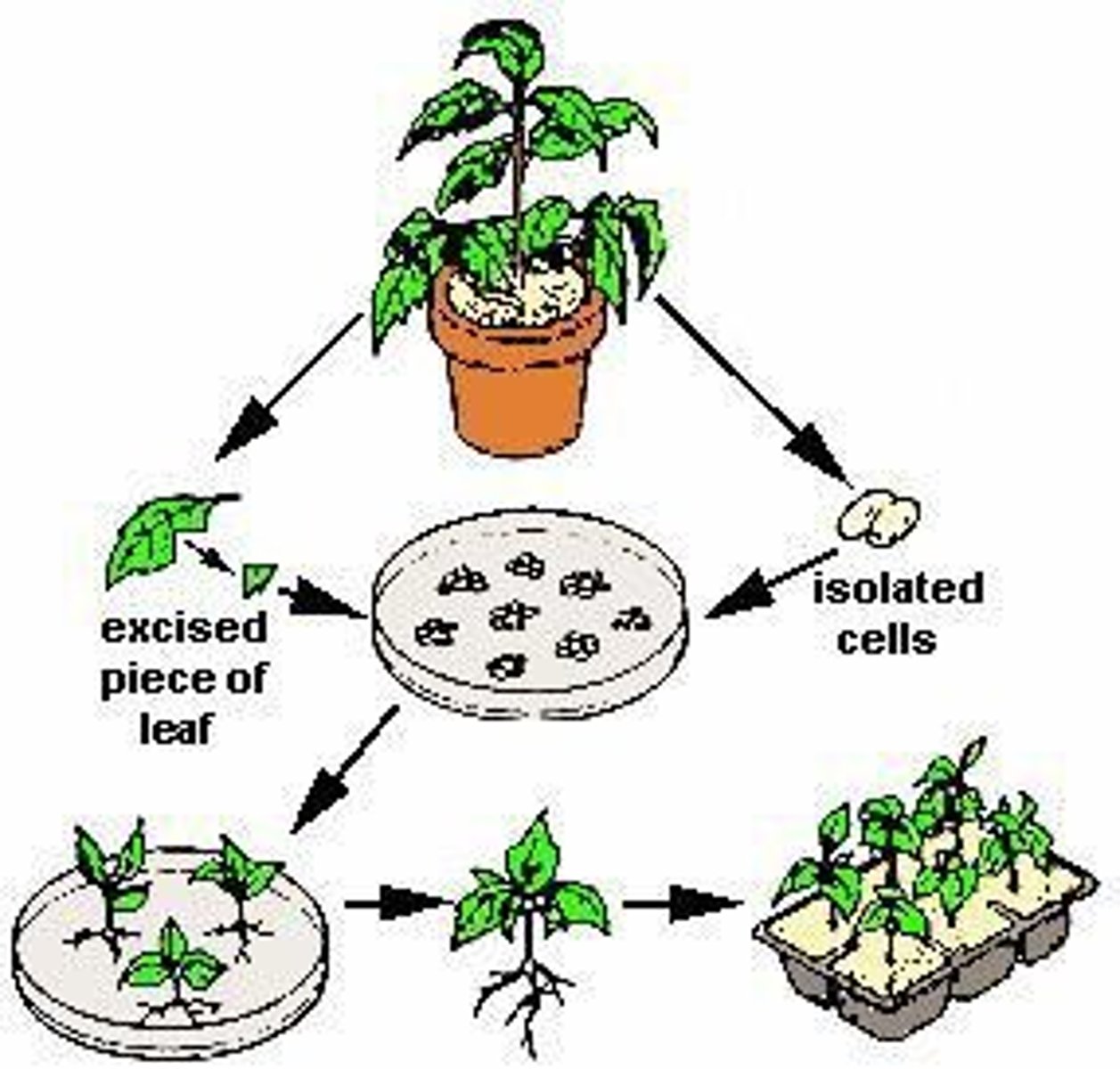
Explant
An excised piece of tissue or organ taken from the plant to initiate a tissue culture.
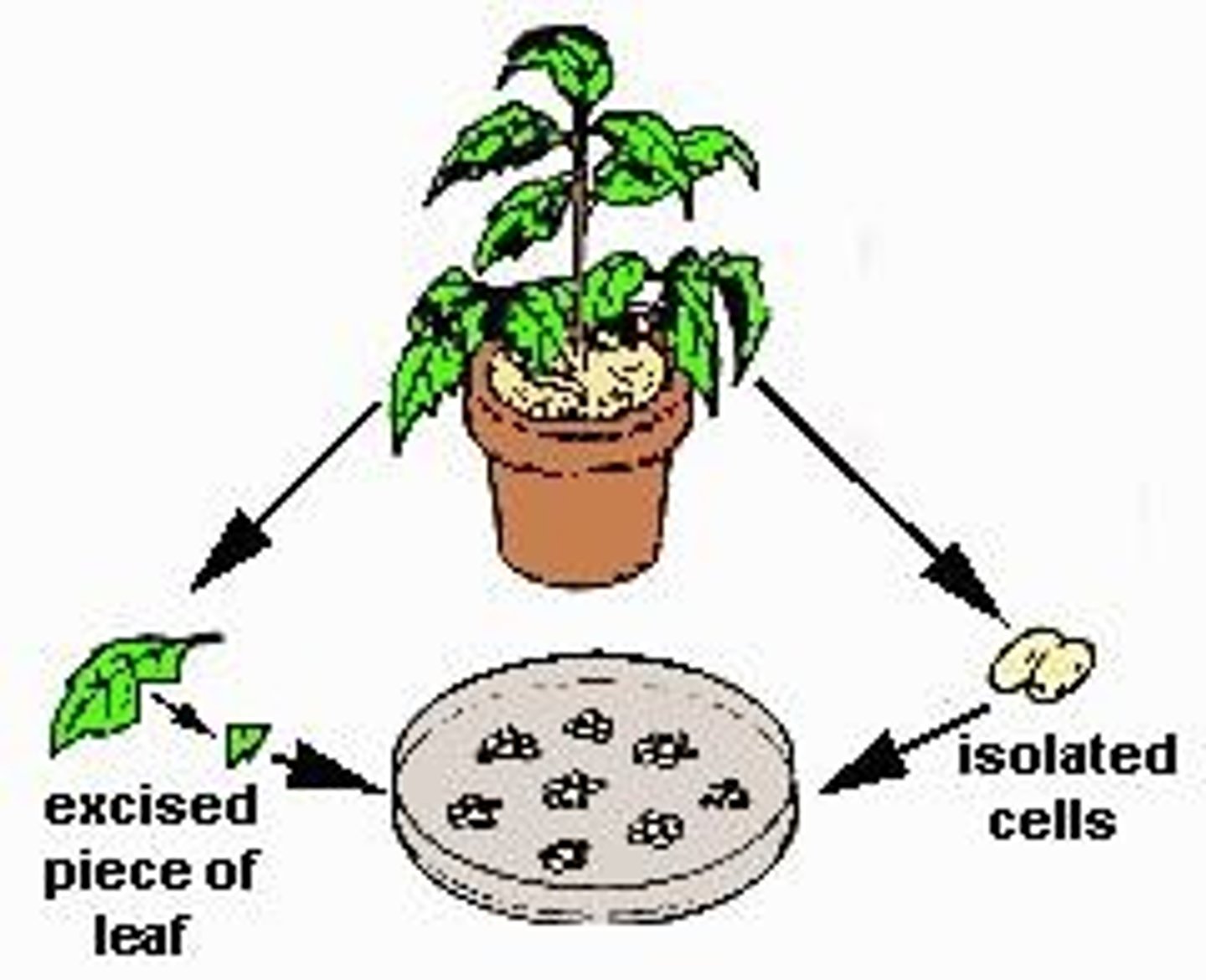
Source of explants
Explant can be from shoot meristem, tip, bud, leaf or stem (internode), root, anther/microspore, ovule, or embryo associated seed parts.
Surface sterilization of explants
The tissue has to be surface-sterilized to prevent contaminating bacteria or fungus before being placed into culture.
Tissue culture vessel
The container (dish, jar, box, etc.) that holds the explant and the required nutrients and plant growth regulators.

Germplasm preservation
The conservation of genetic material from plants for future use.
Micrografting
A technique used in tissue culture to join two plant parts together.
Reforestation/preservation
Using tissue culture techniques to restore or preserve plant populations.
Pathogen-free plants
Plants produced through tissue culture that are free from diseases.
Genotype modification
The process of altering the genetic makeup of a plant for desired traits.
Plant regeneration after transformation
The ability of a plant to grow back after genetic transformation.
Difficult-to-root plants
Plants that have challenges in traditional propagation methods.
Endangered species conservation
Using tissue culture to help preserve species at risk of extinction.
High demand and valuable plants
Plants that are sought after in the market, such as orchids.
Cortex
The outer layer of a stem or root, involved in storage and transport.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of cells covering the plant.
Endodermis
The innermost layer of the cortex in roots, regulating the flow of water and nutrients.
Vascular cambium
A layer of tissue that produces new vascular tissue (xylem and phloem).
Phloem
The vascular tissue responsible for the transport of nutrients and sugars produced by photosynthesis.
Pericycle
A layer of cells in plant roots that can give rise to lateral roots.
Xylem
The vascular tissue responsible for the transport of water and minerals from roots to the rest of the plant.
Pith
The central part of a stem, primarily involved in storage.
Exodermis
A layer of cells that can replace the epidermis in roots, providing additional protection.
Meristematic tissue
Tissue composed of undifferentiated cells capable of division and growth, found in apical and axillary shoot meristems.
Tissue Culture Initiation
The process of starting tissue culture by selecting and preparing explants.
Six Stages of Tissue Culture
The steps involved in tissue culture: goal setting, explant preparation, aseptic culture establishment, shoot production, rooting, and transfer to sterile conditions.

Tissue Culture Medium
A nutrient solution used to support the growth of plant cells in culture, containing water, mineral salts, carbon sources, vitamins, and plant growth regulators.

Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs)
Chemical substances that influence plant growth and development, including auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, and others.
Auxins
A class of plant hormones that stimulate cell elongation and division, and are involved in root and shoot formation.
Cytokinins
Plant hormones that promote cell division and shoot formation.
Gibberellins
Plant hormones that promote stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering.
Abscisic acid
A plant hormone that regulates stomatal closure and stress responses.
Jasmonic acid
A plant hormone involved in stress responses and defense mechanisms.
Ethylene
A gaseous plant hormone that regulates fruit ripening and flower wilting.
Adventitious root formation
The development of roots from non-root tissues, often stimulated by high concentrations of auxins.
Callus formation
The process of undifferentiated cell mass formation, often induced in tissue culture.
Kinetin
The first cytokinin discovered, a natural compound not made in plants, classified as a 'synthetic' cytokinin.
Zeatin
A naturally occurring cytokinin in plants, isolated from corn (Zea mays).
Stage 0 of Micro-propagation
Selection and preparation of the mother plant, including sterilization of the explant tissues.
Stage I of Micro-propagation
Initiation of culture, where the explant is placed into growth media.
Stage II of Micro-propagation
Multiplication stage, where the explant is transferred to shoot media and can be constantly divided.
Stage III of Micro-propagation
Rooting stage, where the explant is transferred to rooting media.
Types of Plant Tissue Culture
Includes shoot regeneration from callus culture, somatic embryo culture from seed, and shoot regeneration from pollen culture.
Regenerated shoot transfer
The process of transferring regenerated shoots to a jar containing MS for rooting.
Tissue cultured banana
Propagation of banana in the greenhouse through tissue culture.
Micro-propagation benefits
A single explant can be multiplied into several thousand plants in less than a year, providing a continuous supply of young plants throughout the year.
True to type clones
Clones produced through micro-propagation that are genetically identical to the mother plant, unlike seedlings which show greater variability.
Fast selection for crop improvement
Explants are chosen from superior plants and then cloned for better crop varieties.
Plant tissue banks
Collections of plant tissues that can be frozen and later regenerated through micro-propagation.
Disease and virus-free plants
Plants produced through micro-propagation that are free from diseases and viruses.
Phyto-sanitary perspective
The credibility gained in the international market as plantlets produced through micro-propagation are considered more reliable.
Micro-propagation feasibility
Micro-propagation is possible for almost all vegetables and fruit crops.
MS 1 μM BA
A specific concentration of benzylaminopurine (BA) used in tissue culture for shoot formation.
MS 0 μM BA
A control concentration of benzylaminopurine (BA) used in tissue culture for shoot formation.
MS 4 μM BA
A higher concentration of benzylaminopurine (BA) used in tissue culture for shoot formation.
MS 2 μM BA
An intermediate concentration of benzylaminopurine (BA) used in tissue culture for shoot formation.
IBA
Indole-3-butyric acid, a plant hormone used in rooting media for root formation.
3 μM IBA
A specific concentration of indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) used in tissue culture for root formation.
30 μM IBA
A higher concentration of indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) used in tissue culture for root formation.
100 μM IBA
The highest concentration of indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) used in tissue culture for root formation.
Somaclonal Variation
Genetic variation observed among plants regenerated from somatic cells.
Germplasm Conservation
The preservation of genetic material of plants for future use.
Mutation Breeding
A method of inducing mutations to create new plant varieties.
Inducing mutation
The process of causing genetic changes in plants to develop desirable traits.
Embryo culture
A technique involving the culture of embryos in vitro to develop into plants.
Haploid and Dihaploid production
The generation of haploid (single set of chromosomes) and dihaploid (double haploid) plants.
In Vitro Hybridization
The fusion of protoplasts in a controlled environment to create hybrid plants.
Production of Disease free plants
The process of cultivating plants that are free from pathogens.
Molecular farming
The use of plants to produce pharmaceutical substances.
Genetic engineering
The direct manipulation of an organism's genes using biotechnology.
Production of secondary metabolites
The cultivation of plants to produce compounds not directly involved in growth.