1.2 The Periodic Table
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards are for Topic 1 - Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table in AQA GCSE Chemistry (Triple Higher). They cover specification points 4.1.2.1 - 4.1.2.6.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
In the modern periodic table, what are the vertical columns of elements called?
Groups
In the modern periodic table, what are the horizontal rows of elements called?
Periods
Elements are arranged in the modern periodic table in order of increasing _______ _________.
atomic number
They have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
They have the same number of electron shells.
Because elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals.
Who created an early version of the periodic table in 1869, arranging elements by atomic weight and leaving gaps for undiscovered elements?
Dmitri Mendeleev
To make iodine line up with other elements that had similar chemical properties (chlorine and bromine).
Isotopes
John Newlands arranged elements in order of atomic weight and noticed similar properties occurred every eighth element, which he called the 'law of _______'.
On the left of the stepped line and towards the bottom.
On the right of the stepped line and towards the top.
Positive ions (by losing electrons)
Negative ions (by gaining electrons)
The noble gases
They have a full outer shell of electrons, which is a stable arrangement.
The boiling points increase
The atoms become larger, leading to stronger intermolecular forces that require more energy to overcome.
The alkali metals
One
They are soft, have low densities, and have relatively low melting points.
The melting points decrease
The reactivity increases
The outer electron is further from the nucleus, attraction decreases and shielding increases and it is lost more easily.
A metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Universal indicator turns blue or purple
It burns violently with a lilac flame, melts into a ball, and disappears rapidly, often with a small explosion.
A metal chloride (a white solid)
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
A metal oxide
The halogens
Seven
Halogen elements exist as ___________ molecules, where atoms are joined in pairs.
A pale green gas
A brown liquid
A purple-black solid
The melting and boiling points increase
The molecules become larger, leading to stronger intermolecular forces that require more energy to overcome.
The reactivity decreases
The outer shell is further from the nucleus, making it harder for the atom to gain an electron due to decreased attraction and increased shielding.
An ionic compound (a salt)
A reaction where a more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its salt.
No, because bromine is less reactive than chlorine.
In the central block, between Group 2 and Group 3.
Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
An acidic solution
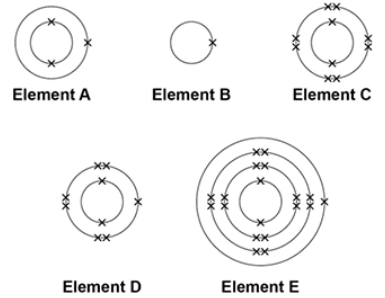
The electronic structure of the atoms of five elements are shown in the figure.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
Which element is hydrogen?
B

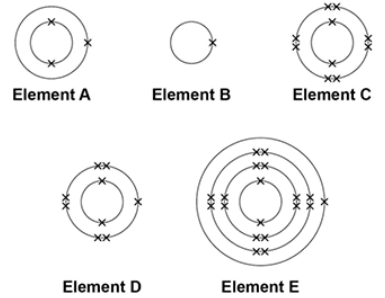
The electronic structure of the atoms of five elements are shown in the figure.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
Which element is a halogen?
D
The electronic structure of the atoms of five elements are shown in the figure.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
Which element is a metal in the same group of the periodic table as element A?
E
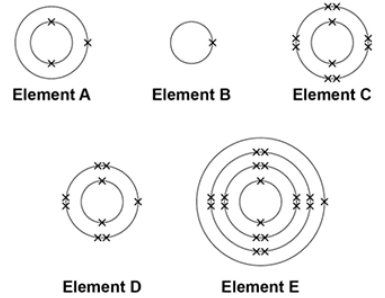
The electronic structure of the atoms of five elements are shown in the figure.
The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
Which element exists as single atoms?
C
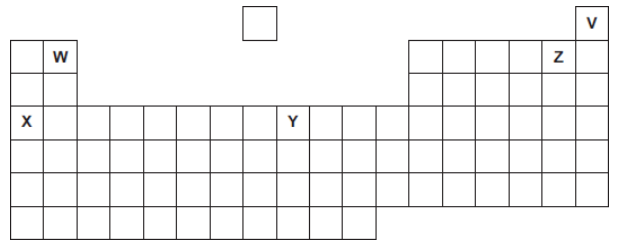
Five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z, are shown in the periodic table.
The letters are not the chemical symbols of the five elements.
Which element is a transition metal?
Y
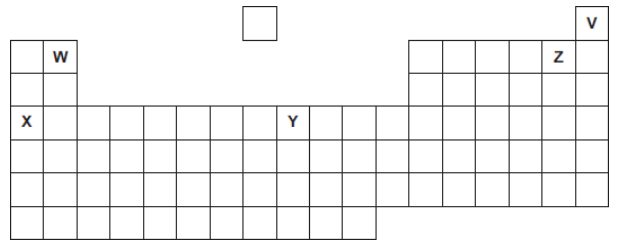
Five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z, are shown in the periodic table.
The letters are not the chemical symbols of the five elements.
Which element is in Group 2?
W
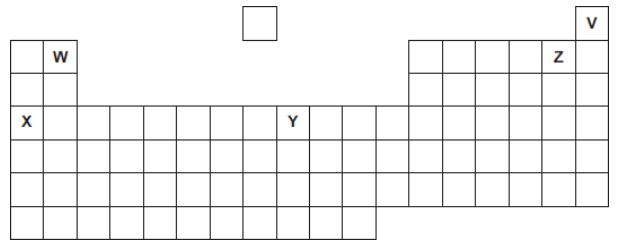
Five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z, are shown in the periodic table.
The letters are not the chemical symbols of the five elements.
Which element is a noble gas?
V
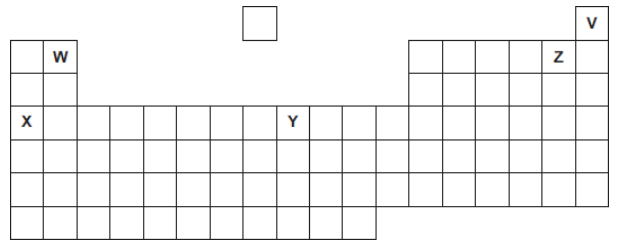
Five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z, are shown in the periodic table.
The letters are not the chemical symbols of the five elements.
Which element has an atomic (proton) number of 4?
W
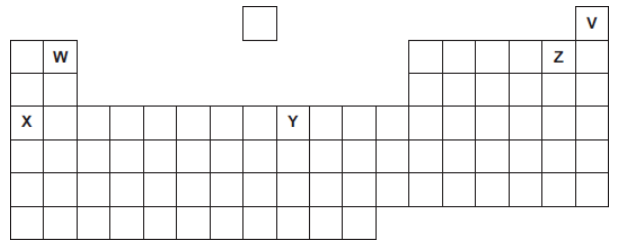
Five elements, V, W, X, Y and Z, are shown in the periodic table.
The letters are not the chemical symbols of the five elements.
Which element forms only 1+ ions?
X
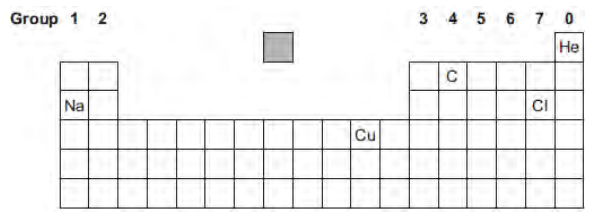
The diagram shows the chemical symbols of five elements in the periodic table.
Choose the correct chemical symbol to complete the sentence.
The element that is an alkali metal is __________.
Na
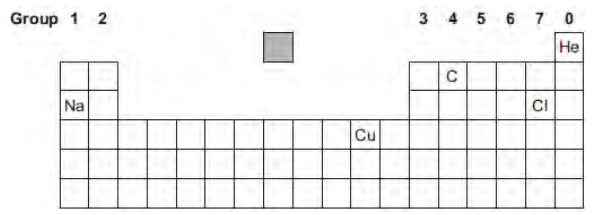
The diagram shows the chemical symbols of five elements in the periodic table.
Choose the correct chemical symbol to complete the sentence.
The element that is a transition metal is ________.
Cu
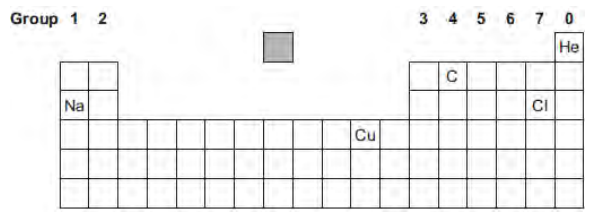
The diagram shows the chemical symbols of five elements in the periodic table.
Choose the correct chemical symbol to complete the sentence.
The element in Group 4 is ___________.
C
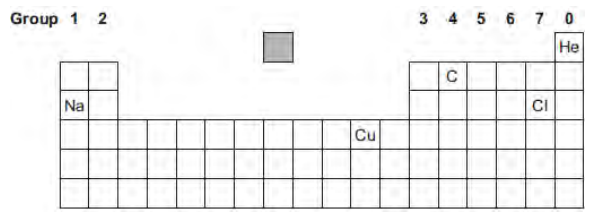
The diagram shows the chemical symbols of five elements in the periodic table.
Choose the correct chemical symbol to complete the sentence.
The element with a full outer energy level (shell) of electrons is _________.
He
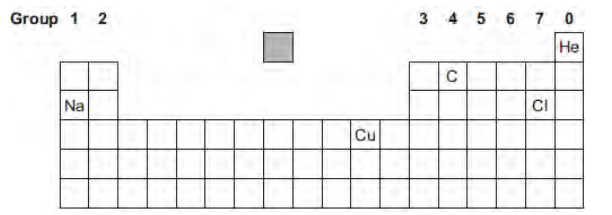
The diagram shows the chemical symbols of five elements in the periodic table.
Which other element goes in the shaded box?
Hydrogen
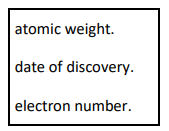
This question is about the periodic table of elements.
In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev produced an early version of the periodic table.
Choose the correct answer from the box to complete this sentence.
Mendeleev first arranged the elements in order of their ___________________.
atomic weight

This question is about the periodic table of elements.
In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev produced an early version of the periodic table.
Choose the correct answer from the box to complete this sentence.
Mendeleev then placed elements with similar properties in columns called _____________.
groups

This question is about the periodic table of elements.
In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev produced an early version of the periodic table.
Choose the correct answer from the box to complete this sentence.
When the next element did not fit the pattern, Mendeleev ___________________.
left a gap

This question is about the periodic table of elements.
In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev produced an early version of the periodic table.
Choose the correct answer from the box to complete this sentence.
Mendeleev was not able to include the noble gases (Group 0) in his periodic table, because the noble gases __________________.
has not been discovered by 1869

Use the correct word from the box to complete each sentence.
In the modern periodic table elements are arranged in order of the number of _________________ in their nucleus.
Elements in the same group have the same number of ________________ in their highest energy level (outer shell).
protons, electrons
Chlorine, bromine and iodine are in Group 7 of the periodic table.
Complete the word equation for the reaction between chlorine and sodium bromide.
chlorine + sodium bromide → ____________ + ___________ _________
bromine, sodium chloride
Chlorine, bromine and iodine are in Group 7 of the periodic table.
Why does iodine not react with sodium bromide solution?
Iodine is less reactive than bromine, so it will not displace it from an aqueous solution of its salt.

A chemistry teacher demonstrated the reaction between sodium and water to a class of students.
One of the students wrote the following notes.
Use the information in the box to help you answer these questions.
What evidence is there that: sodium has a low melting point
The sodium melted quickly to give a silvery ball.

A chemistry teacher demonstrated the reaction between sodium and water to a class of students.
One of the students wrote the following notes.
Use the information in the box to help you answer these questions.
What evidence is there that: sodium is soft
A piece of sodium was cut easily into smaller pieces with a knife.

A chemistry teacher demonstrated the reaction between sodium and water to a class of students.
One of the students wrote the following notes.
Use the information in the box to help you answer these questions.
What evidence is there that: a gas was produced?
The sodium fizzed.