mental health chp 15 - schizophrenia (week 7) , mental health chp 14 - substance abuse (week 9) , mental health chp 22 - personality disorders (week 10), mental health chp 20 - somatic disorders (week 10), mental health chp 23 - children and adolesce…
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
What is psychosis?
Disorganization of personality, deterioration in social functioning, and loss of contact with or distortion of reality
What are the types of psychosis?
- Substance induced psychosis
- Schizoaffective disorder
- Schizophrenia
What is substance induced psychosis?
- can be caused by meds
- can be a really bad trip from weed, etc.
- goes away after drug goes down
- see/hearing things while on whatever drug
ex: you go to a diff plug and the weed is different and you have a bad trip
What is schizoaffective disorder, and how long must it occur for?
- Schizophrenia traits with mood disorders (bipolar or depression on top of hallucinations or delusions)
- PYSCHOSIS AND MOOD DISORDER
- Must occur for at least two weeks in the absence of a major mood episode
What is schizophrenia, and how long must it occur for?
- Two or more positive or negative symptoms must be present
- Symptoms negatively affect daily functioning and interpersonal relationships (debilitating)
- Symptoms are continuous and persist for at least six months
What are positive symptoms?
"Extra" things we don't see in a normal person
ex: you dont hear voices or see things that aren't there EXTRA existence
What are examples of positive symptoms?
- Abnormal motor behavior: catatonia
- Disorganized thinking: how they approach a sentence
- Delusions: false fixed beliefs
- Hallucinations: auditory/visual
What is catatonia?
Bizarre posture or decreased responsiveness to things around them
ex: vegetative state, not responding, staring blankly either at you or out into the distance
What are the types of false fixed beliefs (delusions)?
- Persecutory: someone is out to kill/get them (cameras are watching them and it’s the FBI)
- Ideas of reference: sense/see/hear everyone/everything is talking about them/to them (news talking directly to them, billboard announcing abt them)
- Delusions of grandeur: think they are an almighty figure (president/king)
What are delusion interventions, especially for persecutory delusions?
- Don't deny belief: acknowledge it and redirect
- redirect: let them know that they are at the hospital and that they are a patient
- Redirect them to reality especially towards persecutory delusions: open medications in front of them to show them its not tampered with, open their meals in front of them
How can disorganized thinking be assessed?
Talking to the patient (mental status exam)
What are types of disorganized thinking?
- Loose association
- Tangential
- Circumstantial
- Word Salad
- Neologisms
- Clang associations
- Echolalia
- Echopraxia
What is loose association?
Speech in which ideas shift from one unrelated subject to another (no correlation)
ex: start talking abt plants and plants they take care of then they switch to video games and the newest one out - they combine it
What is tangential?
The speaker introduces many unrelated topics until the original topic of discussion is lost (inability to get to the point of a story)
ex: drawing to mac n cheese recipe on tiktok then assignment done over weekend for school (THEY NEVER GO BACK TO ORIGINAL TOPIC)
What is circumstantial?
The delay of an individual to reach the point of a communication, owing to unnecessary and tedious details (go back to the original conversation)
ex: mac n cheese then youtube video abt downfall of a really niche video game then they go back to the mac n cheese recepie (idea A to B then back to A)
What is word salad?
Group of words that are put together in a random fashion without any logical connection (mixing words)
ex: book leather carpet fortnite v bucks card
What is neologisms?
New words that an individual invents
ex: skibbidy (words not in dictionary)
What is clang associations?
A pattern of speech in which the choice of words is governed by sounds (rhyming/rapping)
What is echolalia?
Repetition of words or phrases spoken by another person
ex: imitating a noise that they make like yelping the way someone else did while tripping
What is echopraxia?
Involuntary imitation of movements made by another person
ex: walking and swinging their arms like another pt
What are hallucinations?
Sensing things that are not there
How do you assess for hallucinations?
- "Are you seeing or hearing anything that's not there?" (ALWAYS START W THIS)
- If no, you can stop there
- If yes, ask to describe extent of hallucination (especially if auditory to assess safety): "What are the voices telling you" or "what are you seeing"
- Once described, validate their feelings but let them know you don't hear anything "that sounds really scary, that must be really hard for you but I personally do not hear anything, you are safe"
What are negative symptoms?
"Lack of" normal behaviors (the As)
missing something that should be presented in a not schizophrenic person
What are examples of negative symptoms?
- Affect lacking
- Avolition
- Alogia
- Anergia
- Anhedonia
What is affect lacking?
Blunted/flat affect
ex: no facial expression
"what you see on the face"

What is avolition?
No motivation to complete purposeful activities (ADLs)

What is alogia?
Decreased verbal communication (can be selectively mute)
ex: pt will not respond when talking w them but they will talk to someone else and not you
What is anergia?
Decreased energy

What is anhedonia?
Decreased pleasure in doing things

What are typical antipsychotics?
Treats only positive symptoms, more potent side effects (1st generation - old school)
What are atypical antipsychotics?
treat positive and negative symptoms, less potent side effects (2nd/3rd generation - more modern )
What are antipsychotic side effects?
Extrapyramidal side effects (EPS): tardive dyskinesia (TD), pseudoparkinsonism, akathisia, and dystonia
What is tardive dyskinesia in EPS?
- Wink at you
- Stick their tongue out
- Pucker their lips
- Sway their hips

What is pseudoparkinsonism in EPS?
- Shuffling gait
- Rolling thumb and index finger (asking for money) - pill rolling
- Tremors
drug induced parkinsons

What is akathisia in EPS?
- Restless
- Jittery
- Hyper

What is dystonia in EPS?
- Tilt their head up/twisting neck up
- Roll their eyes back
- Lock the jaw
- Voice box closes (can be fatal) - they sound like they’re possessed (groaning/screeching) - laryngeal spasms
MEDICAL EMERGENCYYY!!!

What is given when a patient experiences dystonia?
IM Cogentin - anticholinergic
main go to!
What medication address extrapyramidal side effects (EPS)?
Anticholinergics (ABCs)
What is the anticholinergic medication list?
- Trihexyphenidyl (Artane)
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Benztropine (Cogentin)
What are the anticholinergic side effects?
- Can't see (blurry vision)
- Can't spit (dry mouth)
- Can't shit (constipation)
- Can't piss (low urine output)

What are the 1st generation antipsychotics?
- Haloperidol (Haldol)
- Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
- Fluphenazine (Prolixin)
- Loxapine (Loxitane)
- Perphenazine (Trilafon)
- Pimozide (Orap)
- Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
- Thioridazine (Mellaril)
- Thiothixene (Navane)
- Trifluoperazine (Stelazine)
Halo is a 1st gen student whos a germaphobe - he always uses clorox and hates the flu and pimples
His perfect day consists of having a lox bagel w/o his twin brothers thiodaz & thioxene who he refers to as "pro triflers"
What are the 2nd generation antipsychotics?
- Ziprasidone (Geodon): cardiac side effects (qt prolongation & dysrhythmia) - routine EKGs
- Risperidone (Risperdal)
- Paliperidone (Invega)
- Lurasidone (Latuda)
- Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
- Quetiapine (Seroquel): orthostatic hypotension is BIG (FALLS!!!!)
- Clozapine (Clozaril): agranulocytosis (decreased white blood cell count - look out for infection! they are prone to infection!)
this is the 2nd time this guy named pali w/ weird heart(cardiac side effects) zippers said hola & tried to rizz me up
he almost lured me in bc I thought he was cute but I almost fell(orthostatic hypotension) when I came close cuz he was so ugly I literally felt like I got an eye infection(agranulocytosis-prone to infection) from looking at him
What are the 3rd generation antipsychotics?
Aripiprazole (Abilify) - tamest side effects bc not at potent
What are special routes of antipsychotic administration?
- Orally disintegrated tablets (under the tongue and dissolves to prevent cheeking)
- Depot formulation: requires loading dose and monthly injections (long acting IM injection)

Why would patients receive antipsychotics through IM?
- Noncompliant
- Do not want to take PO
- easier for out patient
What is a complication of antipsychotics?
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
What are manifestations of neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
- Fever
- Altered level of consciousness
- Muscle rigidity
- Fluctuating blood pressure
What is administered for neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
Dantrolene (muscle relaxant)
*main intervention: just stop the med in general
What labs are assessed when administering antipsychotics?
- Lipid panel: HDL, LDL, and cholesterol
- Hemoglobin A1C
taken bc pts are eating more carbs and sugar
pts are not exercising
both of these = metabolic syndrome (weight gain)
**taking antipsychotics = risk for metabolic syndrome
**1st gen is most potent for metabolic syndrome 3rd gen is least

What is the relationship between withdrawal and intoxication?
Seesaw relationship (will be the opposite)
alch: is a downer & when withdrawing symptoms are like uppers
meth: is a stimulant & when withdrawing symptoms are like downers (meth crash)
What is addiction?
Excessive or compulsive use even when they know it's bad (not limited to substances)
What is intoxication?
Excessive use of substance
What is withdrawal?
Physiological symptoms that occur upon discontinuation
What is dual diagnosis?
Mental issue (depression/schizophrenia) + substance abuse
What is codependency?
Enabling behaviors between two people taking a certain substances
ex: husband drinks a lot and the wife always has the fridge stocked up w beers and alcohol
What makes someone codependent, what is the driving force of codependency?
Low or lack of self-esteem (insecure)
they dont want to fight it and stand up for themselves
no one wants to say no, no one wants to say you should stop - they just keep going bc you’re afraid they’ll think of you in a negative way and you don’t want to drink w them anymore
The codependent person is able to achieve a sense of control only through fulfilling the needs of others. Personal identity is relinquished, and boundaries with the other person become blurred. The codependent person disowns their own needs and wants in order to respond to external demands and the demands of others. Codependence has been called “a dysfunctional relationship with oneself.”If partners are not happy, codependents feels responsible for making their partners happy
■ Taking care of others at the expense of one’s own needs
■ Feeling responsible for fixing other people’s problems
■ Having low self-esteem; expecting to perform perfectly but never feeling “good enough”
■ Desperately seeking approval from others; often identified as “people pleasers”
■ Generally unhappy and seeking things outside oneself to attempt to fulfil unmet needs
■ Tending to have come from dysfunctional families where there was abuse or neglect
■ Having weak boundaries that lead to feelings of resentment, lack of trust, and anger toward others
What are predisposing biological factors of substance related disorders?
- Genetics
- Biochemical: how the brain seeks pleasure and processes addiction
What are predisposing psychosocial factors of substance related disorders?
Conditioning: learned response that occurs after repeated exposure to stimuli (once your body is exposed you crave it)
What are complications of alcohol use disorder?
- Esophageal varices
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Wernicke-Korsakoff (big complication)
What is esophageal varicies?
Veins that become distended due to excessive pressure through cirrhotic liver
What is hepatic encephalopathy?
Damaged liver doesn't remove ammonia in the body resulting in altered mental status
What is Wernicke-Korsakoff?
- Results from a vitamin B/thiamine deficiency
- Lack of vitamin B/thiamine + alcohol use
What does Wernicke-Korsakoff cause?
Impairs cognitive functioning: confabulation, disorientation, amnesia, and ataxia (neuro complications)
What are intervention for Wernicke-Korsakoff?
- Identify what it looks like
- Give vitamin B1 (banana bag)

What is alcohol intoxication?
Takes place before withdrawal

What are the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and how is it addressed?
- Overstimulated
- Sweaty - from fever
- Tremors
- Elevated vital signs
- Agitated
- Crawling on the skin
- Anxious
- Headache
- Overwhelmed
- n/v
can be very fatal!
address by giving a downer: know how much to give by using CIWA scale
What is the CIWA scale and how is treatment gone about?
- Assess how intense alcohol withdrawal is
- 10 sections
- Varying scales for scores
- Max score 67 (higher score indicates worse withdrawal) - need to be aggressive w downer tx and you need to act quickly as it leads to delirium tremens!
What is the alcohol withdrawal timeline?
- 6 hours after last drink: mild withdrawal (CIWA scale of 8-10)
- 12-24 hours after last drink: moderate withdrawal
- 24-48 hours after last drink: severe withdrawal
- 48-72 hours after last drink: (delirium tremens): psychotic, hallucinations, seizures
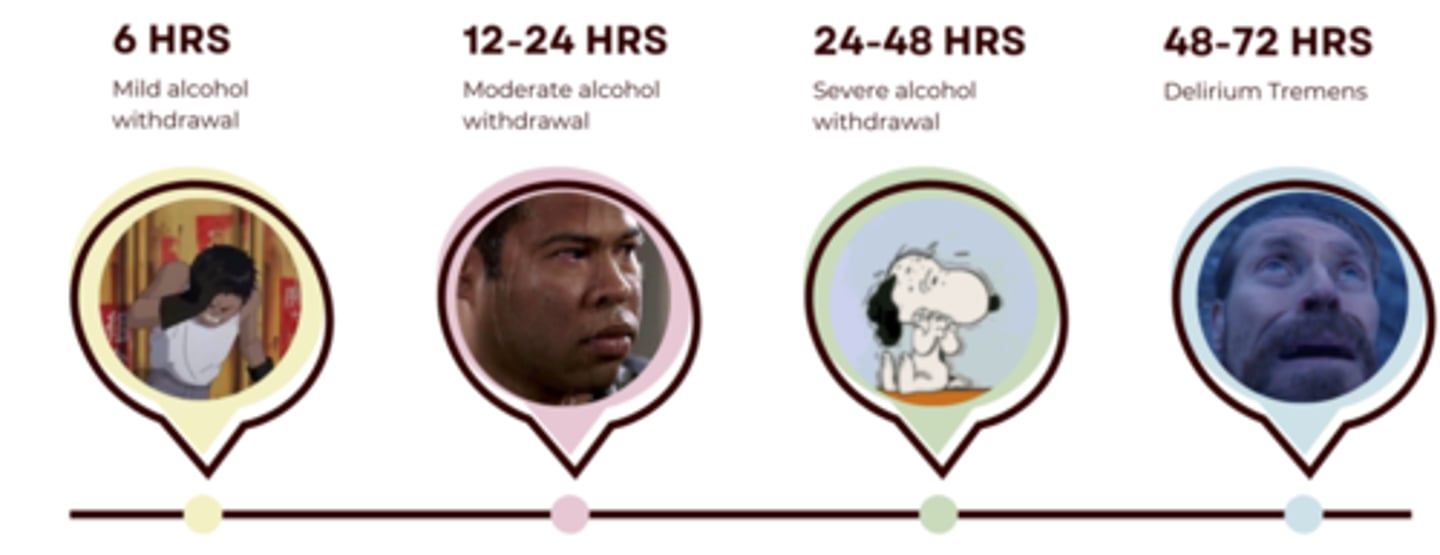
What happens in severe withdrawal (delirium tremens)?
Psychosis (psychotic), hallucinations, and seizures
WANT TO ABSOLUTELY AVOID THIS
What are interventions for acute alcohol withdrawal?
- Benzos: -pam, -lams: librium, ativan (MAIN INTERVENTION) - dose depends on how high the CIWA score was (this is short term tx)
- Decrease stimuli
- Pad side rails (seizure precautions)
What are interventions for long term alcohol withdrawal?
- Alcoholics anonymous
- Psychopharmacology: Disulfiram (Antabuse) makes alcohol uncomfortable
What is an intervention for a patient taking disulfiram (antabuse)?
Avoid alcohol: mouthwash, perfume, nail polish remover, hand sanitizer, and vanilla extract
What are the list of substances in sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic use disorders?
- Barbiturates: Phenobarbital, Metharbital, Amobaribtal
- Nonbarbiturate hypnotics: Zolpidem (Ambien), Diphenhydramine (Benardryl), and Temazepam (Restoril)
- Anxiolytics: -pams, -lams, Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
What are the physical effects (downers) of sedative, hypotonic, or anxiolytic use disorders?
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Slurred speech
- Respiratory depression
- Lower vital signs
What are withdrawals symptoms in sedative, hypotonic, or anxiolytic use disorders that you must call the doctor for?
- Muscle twitching
- Seizures
- Delirium
- High vital signs
What are the list of substances in stimulant use disorders?
- Methamphetamines
- Cocaine
- Nicotine products
- Caffeine products
What are symptoms of intoxication in stimulants use disorder?
- Irritability
- Tremors
- Hallucinations
- Tachycardia
What are symptoms of withdrawal in stimulants use disorder?
- Fatigue
- Sleeping! (meth crash)
- Depression: monitor for suicide ideation
non-life threatening
What are the list of substances in opioid use disorders?
- Codeine
- Heroin
- Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
- Oxycodone
- Hydrocodone
- Methadone
- Fentanyl
- Tramadol
What are signs of intoxication in opioid use disorder?
- Respiratory depression
- Pinpoint pupils
- Excessive sleepiness
What are signs of withdrawal in opioid use disorder?
- Rhinorrhea (runny nose)
- Diaphoresis
- Tachycardia
Substances used in inhalant use disorder
- gas
- solvent
- adhesive
- paint
- lighter fluid
why are inhalants misused
easily accessible
what are the intoxication and withdrawal symptoms of inhalants
- similar to alcohol
- not as severe
Substances used in hallucinogen use disorder
- mdma
- pcp
- ketamine
- lsd
effects of hallucinogens
trippy in a good and bad way
cannabis use disorder side effects
effects resemble cns depressants
What is a gambling disorder (process addiction)?
- Persistent and recurrent problematic gambling behavior
- Involves brain's reward system
- High suicide attempt
- Impulse control dysregulation
- Frontal lobe dysfunction
What are signs of a chemically impaired nurse?
- Calling off a lot
- Poor concentration
- Medication errors all over the place
What do you do if you suspect a chemically impaired nurse?
Report to BRN and refer to peer assistance programs
What is a personality disorder?
- Happen when someone's personality becomes pathological (dangerous)
- Someone can get hurt, they can hurt themselves, or they can hurt other people
- Can co-occur with other mental health disorders (substance abuse, depression, bipolar)
Do people with personality disorders believe they have a problem?
No, believe "it's just who I am" (egosyntonic)
What are cluster A personality disorders?
Odd or eccentric traits
What is the list of cluster A personality disorders?
- Paranoid
- Schizoid
- Schizotypal
What is paranoid personality disorder?
Distrust and suspiciousness towards others (think there is an ulterior motive)
What are interventions for paranoid personality disorder?
- 1:1 patient teaching: more comfortable and prevents feeling ganged up on
- Clear and simple communication (direct)
you’re in a group setting and they only trust you, how do you want to get out of that scenario - they are very overwhelmed
ask if they want to step out and do a 1:1 teaching together
What is schizoid personality disorder?
- Detached (average emo)
- Doesn't want to form close relationships
- Keep to themselves (isolated)
- Don't perform well under stress, will cause them to become psychotic

What are interventions for schizoid personality disorder?
Don't force them to socialize - they will get stressed and upset with you - they won’t thrive in a social setting bc they prefer to be alone
What are occupation opportunities for schizoid personality disorder?
Online/remote jobs: tech and data analysis