Whole Class PBL 2023 Set: Ch 25, 26, 27, 28
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
248 Terms
Chordates
an animal phylum that has a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, and gill slits at some time in its life cycle
Reptiles
vertebrates that live on land, scales cover body, lay eggs, cold blooded
Mammals
Animals that have hair and produce milk for their young
Birds
May or may not fly, with vertebra, lay eggs, have feathers
Cladogram of Chordates
a chart that classifies chordates
Cartilage
strong connective tissue that supports the body and is softer and more flexible than bone
Notochord
long supporting rod that runs through a chordate's body just below the nerve cord
Segmentation
Animal bodies divided into segments, segments are body parts repeated
cephalisation
The concentration of sense organs and nerve cells at the front end
invertebrate
An animal without a backbone, makes up 95% of all animals
Eukaryote
An organism that has a nucleus
Homeostasis
The process of maintaining a stable internal environment
Symbiosis
A relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other
Response
Reaction to Stimulus
Endotherm Insulation
body heat becomes trapped. ex) feathers
Amphibian
able to live both on land and in water
Tetrapods
animals with four limbs
ray-finned fish
thinner bones that hold up skin and fins
lobe-finned fish
have fleshy fins that are supported by a series of bones; ex. coelacanth and lungfish
Cartilaginous
bones held together by cartilage
jawless fish
hagfish and lampreys
Nonvertebrate chordate
Two Chordates who are non-vertebrates (have spinal chord with no backbone to protect)
Tunicates and Lancelets
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Reproduction
the process of producing offspring
Vertebrae
An organism that contains a backbone
Multicellular
made of many cells
Kingdom Animalia
The classification group of animals. All animals are part of Kingdom Animalia
Chordates
members of the phylum Chordata
pharyngeal pouches
paired structures in the throat region
hollow nerve cord
connects nerves to internal organs, muscles, and sense organs
Tail
an extension of the organism. Helps with balance and signaling when danger is near
Feedback inhibitions
known as negative feedback, a system to which the result of the process helps limit the process itself
types of chordates
fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
Chordates
nerve chord that runs down spine
vertebrates
Chordates with a back bone
Cartilage
Connective tissue stronger than skin but softer than bone
Tetrapods
A vertebrate that has four limbs
Fish
largest group of vertebrates
Amphibian
lungs, moist skin
Reptiles
scaly skin, shelled eggs
Birds
Endotherms, feathers
Mammals
Fur/hair, lungs, warm blooded, feed young with milk,
Cladogram
Diagram that shows characteristics and relationships
Rayfinned
Eels and goldfish
Lobefinned
large bones
Cartilaginous
Shark and sting ray
Jawless fish
Lampreys and hagfish
Radial symmetry
Symmetry starting in the middle and forming "slices" of an animal that are symmetrical
Bilateral symmetry
A body in which a single imaginary line can divide the body into left and right sides that are mirror images of each other
Germ layer
Developing fertilized eggs developed and start to differentiate into different layers such as the endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm
Endoderm
The innermost germ layer; develops into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer; develops into muscles and most circulatory, reproductive and excretory system
Ectoderm
The outer germ layer; its cells develop into organs of the nervous system
Coelom
Lined body cavity, space for organs
Zygote
An egg that has been fertilized
Blastula
A hollow ball of cells that develops when a zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions
Blastoma
The initial opening on a blastula
Protostomes
The blastopore becomes the mouth, and the anus forms from a second opening on the opposite end of the tube
Deuterostomes
An animal in which the blastoma becomes and anus, and the mouth is formed from the second opening that develops
invertebrate
makes up 95% of all animals
appendage
legs, antenna, limbs
larva
immature stage of life
sponge
Aquatic animal with few specialized cells, heterotroph
Cnidarians
soft body, Ex; jellyfish, coral
arthropod
segemented body, Ex; spiders
Nematodes
roundworms
Flatworms
unsegmented, flat worm
Annelids
segmented worms, Ex; leech, earthworm
Mullusks
soft body with inner OR outer shell, Ex; snail, clam
Echinoderms
have radial symmetry, spiney skin, inner 'skeleton', Ex; Sand dollar, sea urchin. sea star.
exoskeleton
hard outer covering
Chordate
Animals with a notochord, most have a backbone.
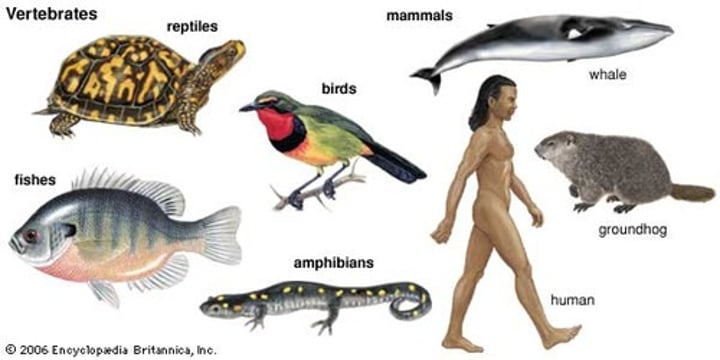
Vertabrates
animals with a backbone
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
Tetrapod
vertebrate with four limbs
Fish
Largest group of chordates
anphibian
Has lungs and moist skin
Reptiles
Has scaly skin and small eggs
Birds
Has feathers
mammal
A vertebrate whose body temperature is regulated by its internal heat, and that has skin covered with hair or fur and glands that produce milk to feed its young.
Cladogram
Shows patterns of shared characteristics.
rayfinned fish
Eels and gold fish
Lobefinned
Large bones
cartilaginous fish
sharks, rays, skates
jawless fish
hagfish and lampreys
radial symmetry
Symmetry starting in the middle and forming slices of an animal that are symmetrical

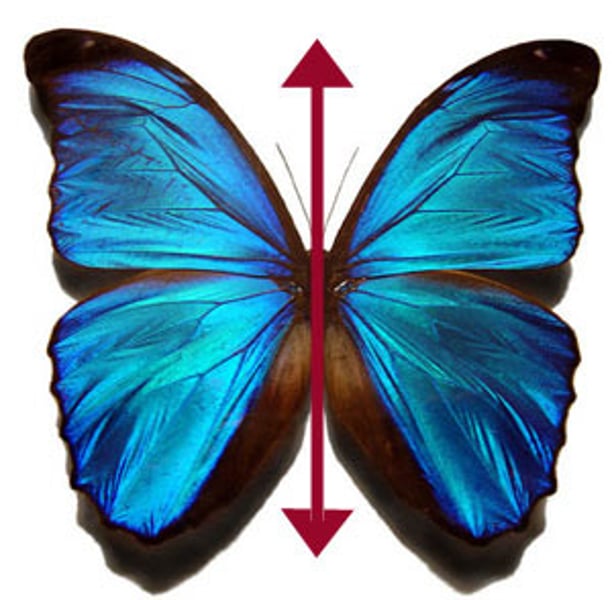
bilateral symmetry
the property of being divisible into symmetrical halves on either side of a unique plane.

Germ layer
developing fertilized eggs develop and start to differentiate into different layers such as the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm
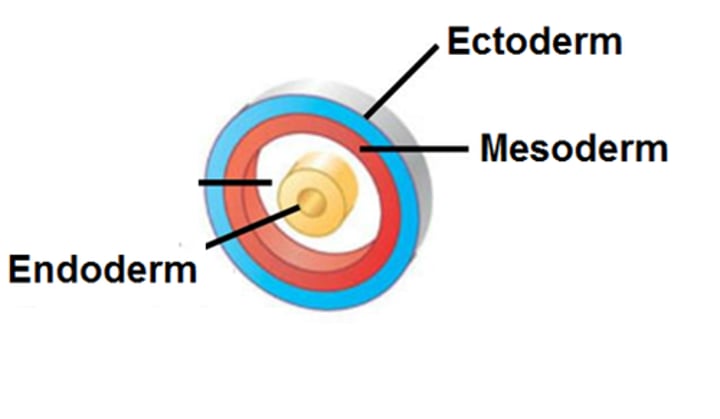
Endoderm
innermost germ layer; develops into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system
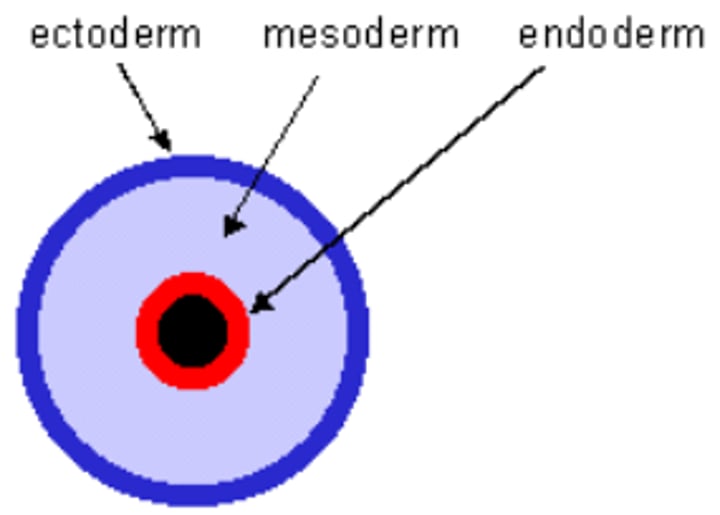
Mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
coelom
body cavity lined with mesoderm
Zygote
fertilized egg
Blastula
hollow ball of cells
Blastopore
Initial opening on a blastula
Protostomes
blastopore develops into mouth
Deuterostomes
blastopore becomes anus
Segmentation
the division of the body of an organism into a series of similar parts