Micro - Prokaryotic (bacterial) Structures - Internal (Ch. 4.4)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Define -- Genome, nucleoid, plasmid
Genome: the complete set of chromosomes and genes in an organism
nucleoid: the basophilic nuclear region or nuclear body that contains the bacterial chromosomes —> seen in bacteria
plasmid: Extrachromosomal genetic units characterized by several features. A plasmid is a double-stranded DNA that is smaller than and replicates independently of the cell chromosome; it bears genes that are not essential for cell growth; it can; and it is transmissible to other bacteria.
protective traits, the ability to resist drugs and produce toxins and enzymes—> important agent in DNA technology techniques
Be able to thoroughly compare and contrast DNA and the way it is organized and housed in Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cells (look at section 9.1 also)
Compare: both domains have ribosomes that are involved in translation, both must supercoil DNA, both contain the cell DNA, and a plasma membrane
Contrast:
Eukaryotes: divided through mitosis, contains histone-proteins that supercoil DNA, larger genome, greater then one linear chromosomes
Prokaryotes: divided by binary divisions, contain histone-like proteins that also supercoil (different structure), smaller genome (1000-10,000kilopb), one singular circular chromosome
Ribosome - function? What is the difference between the ribosome of Euk vs Prokaryotic cells?
Ribosome: A bilobed macromolecular complex of ribonucleoprotein that coordinates the codons of mRNA with tRNA anticodons and, in so doing, constitutes the peptide assembly site —> can occur in chains called polysomes
Function: produce proteins from amino acids during a process called protein synthesis or translation.
Differences: Bacterial ribosomes have a 70S (large 50S + small 30S) while Eukaryotes have a 80S
this difference where some protein effect ribosomal function in medication
Endospore - structure and formation
endospore: A small, dormant, resistant derivative of a bacterial cell that germinates under favorable growth conditions into a vegetative cell. The bacterial genera Bacillus and Clostridium are typical sporeformers.
they’re metabolically inactive and are resistant to “cell stress”
Structure: its a survival structure that protects a fully copy genetic DNA from harsh or unfavorable environment
contain high contain of calcium and dipicolinic acids→ removes water and leaves endospore very dehydrate, making less vulnerable to heat (not boiling)
has a impervious cortex and endospore coat that protects against radiation ad chemical
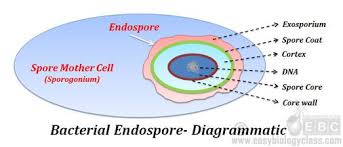
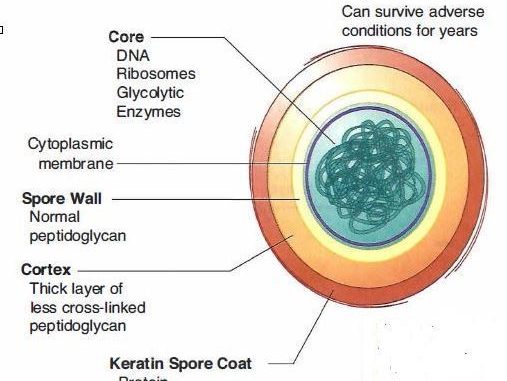
Carbon depletion and nitrogen depletion are common trigger for endospore formation
vegetative cell → sporangium → endospore
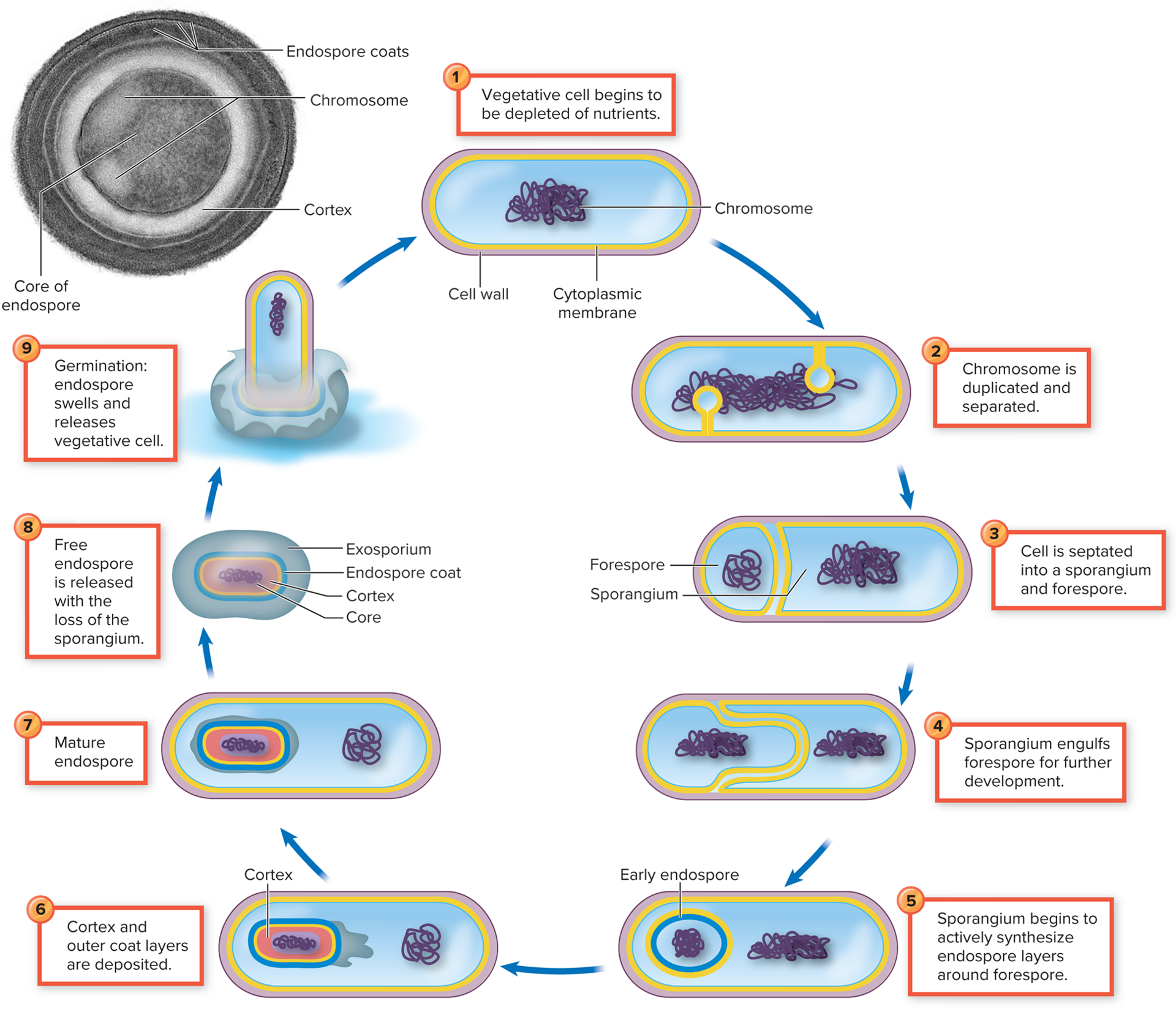
Why do some gram + bacilli undergo endospore formation? Why is it important? Of what advantage is it to bacteria to produce endospores?
They form endospores as a survival strategy when faced with unfavorable conditions, they form to protect capsule of keratin the genetic info of the bacteria so that it can continue to survive and transmit
Understand general process of sporulation and germination and when they occur
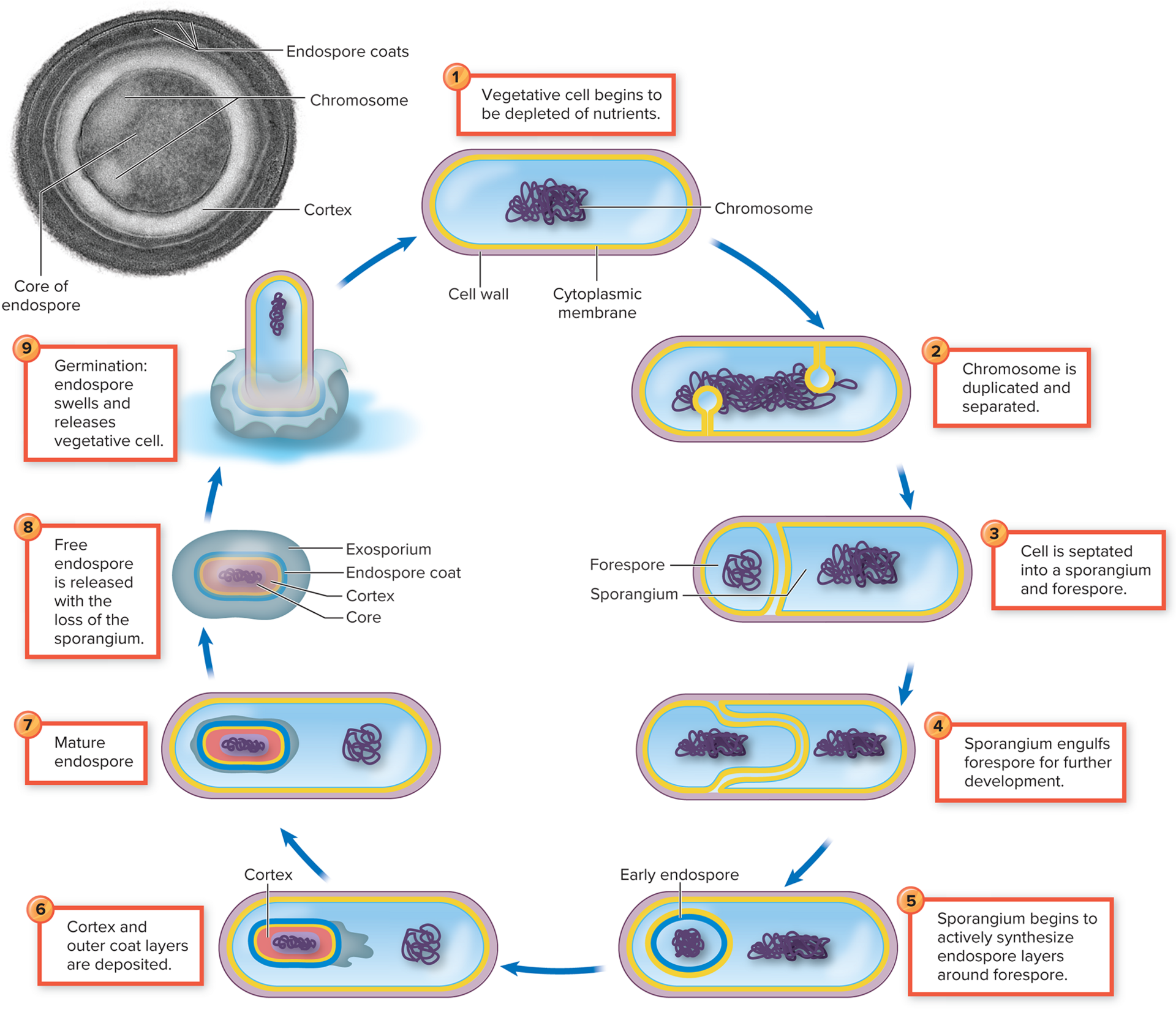
What is the Clinical significance of endsopores?
Bacillus anthracis- anthrax
Clostridium tetani- tetanus
Clostridium perfringens - gas gangrene
Clostridium botulinum - botulism (deadly food poisoning)
Endospore can imbedded in a wound that contains dead tissue, where they can grow and re
lease potent toxins—> can be found in soil and dust
they are highly resistant to ordinary cleaning methods and high boiling temp
Endospores enhance bacterial survival, making infections harder to control and treat.
endospore-forming bacteria are considered bioterrorism threats