Invertebrate Zoology Protozoa/Protists
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Kingdom Protista
Unicellular, specialized organelles (no organs), protoplasm, nucleus + ribosomes, locometry structures, flagellated: 9+2 fibril structure
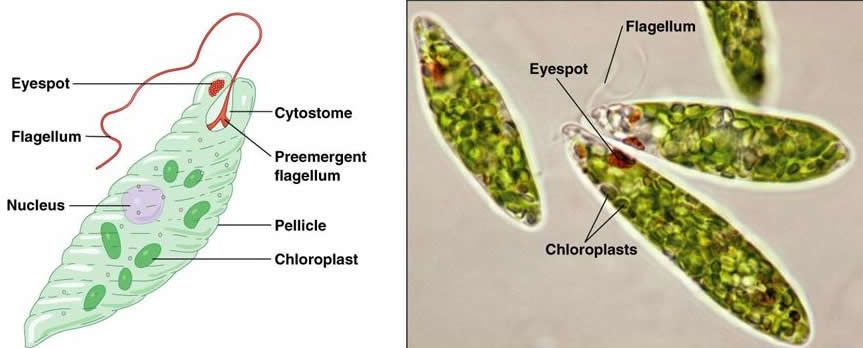
Phylum Euglenozoa
Free-living flagellated protozoan. Many are photosynthetic, have chloroplasts, eyespot (light sensitive pigment), common in freshwater

Phylum Dinoflagellata
Free-living protozoa, Flagella in grooves, naked or with theca (plate covering). Marine. Most synthetic, some heterotrophic, some switch between.
Phylum kinetoplastida
Parasitic protozoa, 1-2 flagella, undulating membrane, kinetoplast (DNA mass) within one mitochondria.
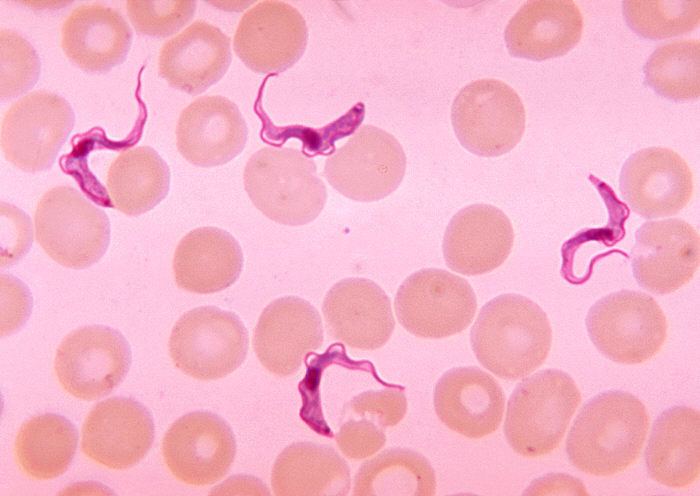
Trypanosoma
Kinetoplastida. African sleeping sickness. Carried by TseTse fly.
Phylum Retortamonada
Parasitic protozoan. Only 4-8 flagella, 1 trails behind the rest (retro), no mitochondria
Giardia
Retortamonada, spread through fecal contamination in water
Phylum Axostylata
Parasitic Protozoan, 4-thousands of flagella, bundle of tubules (axostyles) extends length of body
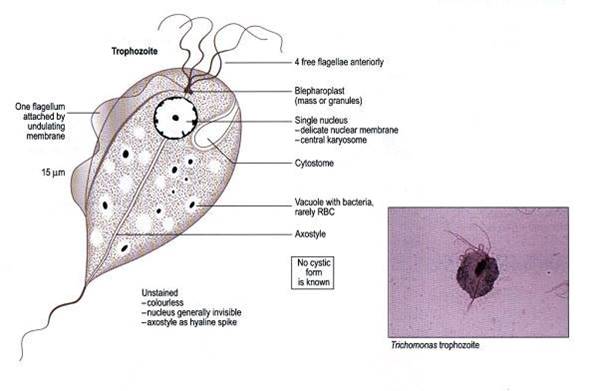
Trichomonas
Axostylata, sexually transmitted in mammals
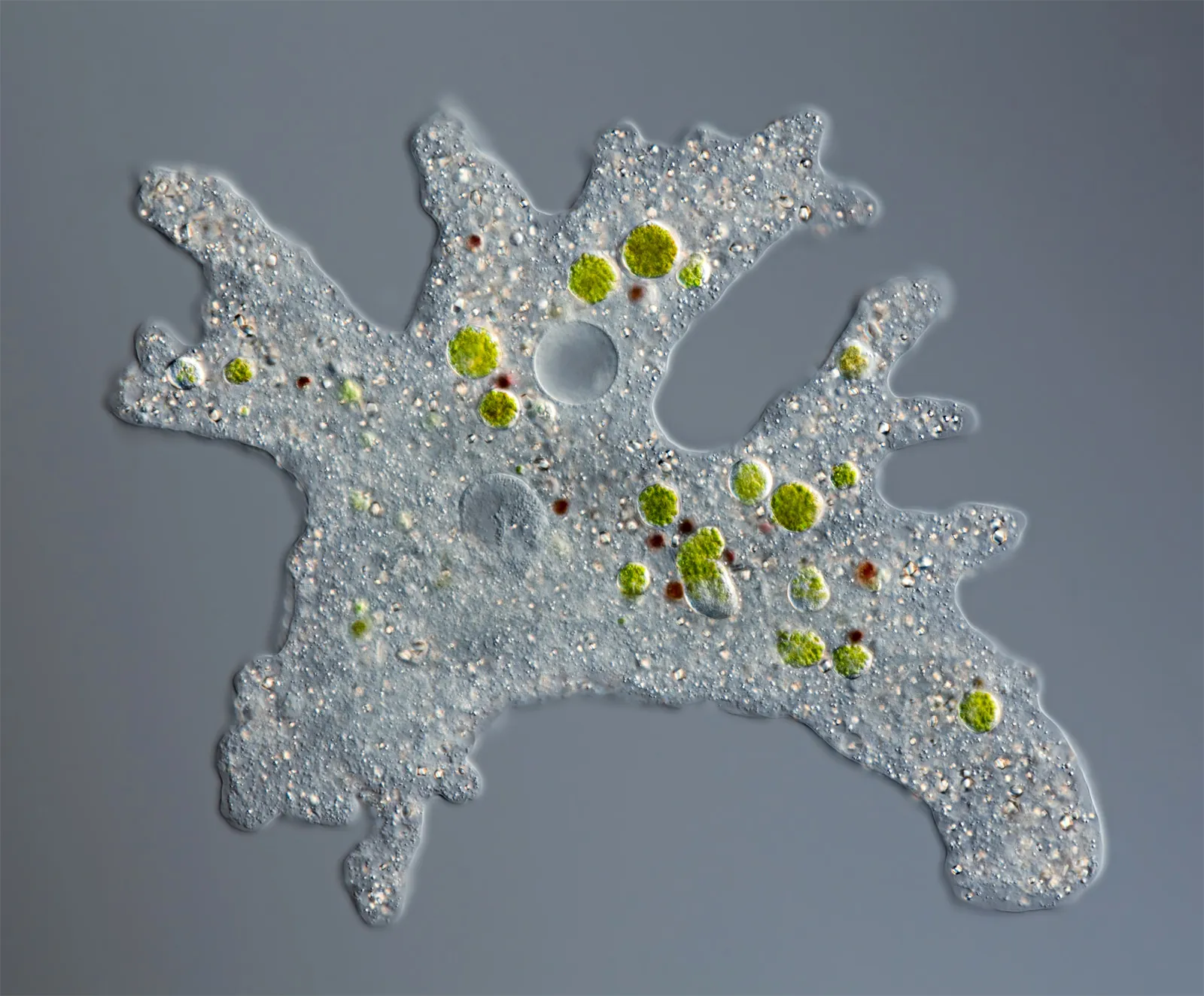

Amoeboids
protozoans, glide on psuedopodia, phagocytosis, naked or with skeleton, reproduce by fission. Nucleus, vacuoles.
Slime mold
social ameba, largest protozoan
entamoeba histolytica
amebic dysentery, causes diarrhea, can form resistant cyst

Phylum Granuloreticulosa “Foraminferan”
Protozoan with many pores, naked or with skeleton made of calcium carbonate, shell shape based on temp, 2 body forms, elongate reticulopodia, predatory
Phylum Radiolaria
Skeleton of silicon dioxide, catch prey with axopods (psuedopodia), marine, found atop sediment.
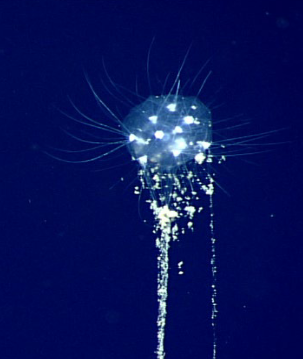
Phaeodarea
Look like radiolaria but are not
Apicomplexa (Sporozoa)
subphylum aveolata (have alveoli, calcium storing vesicles below cell membrane), Parasitic, apical complex, produce spore-like structure
Plasmodium
Malaria, Apicomplex (sporozoa), life cycle has 2 hosts (humans and anopheles mosquito)
Phylum (subphylum) Ciliophore: ciliates
Rows of cilia with infracilliary network, metachronal beat, glide, T-shaped trichocysts (defense, capture prey), pellicle (outer covering), some have hard “shell” Lorica, 2 nuclei (micro and macro)
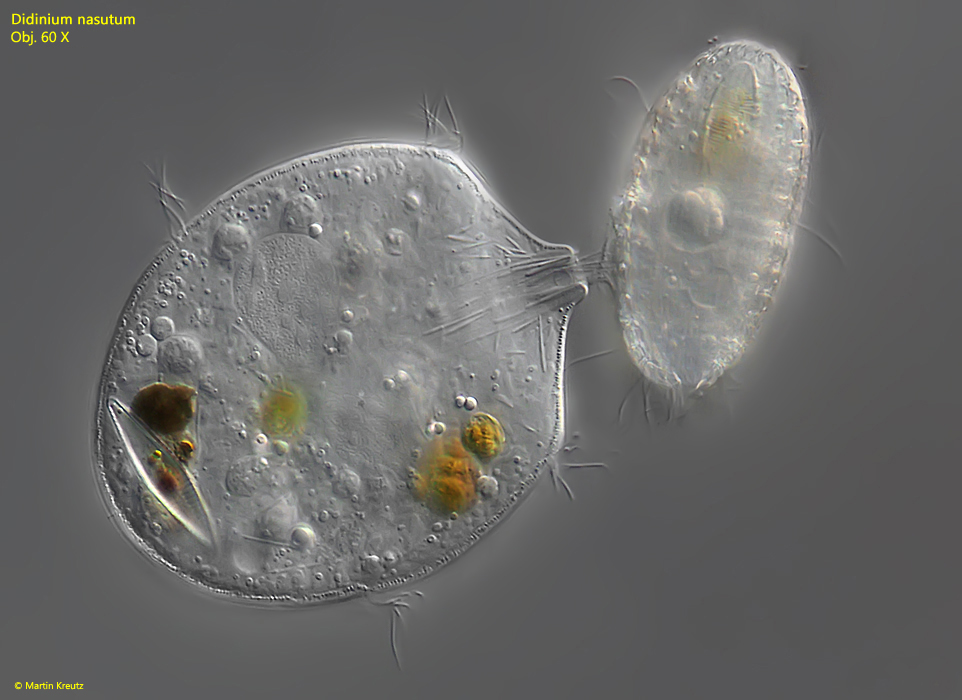
Didinium
Ciliate, feeds on other ciliates
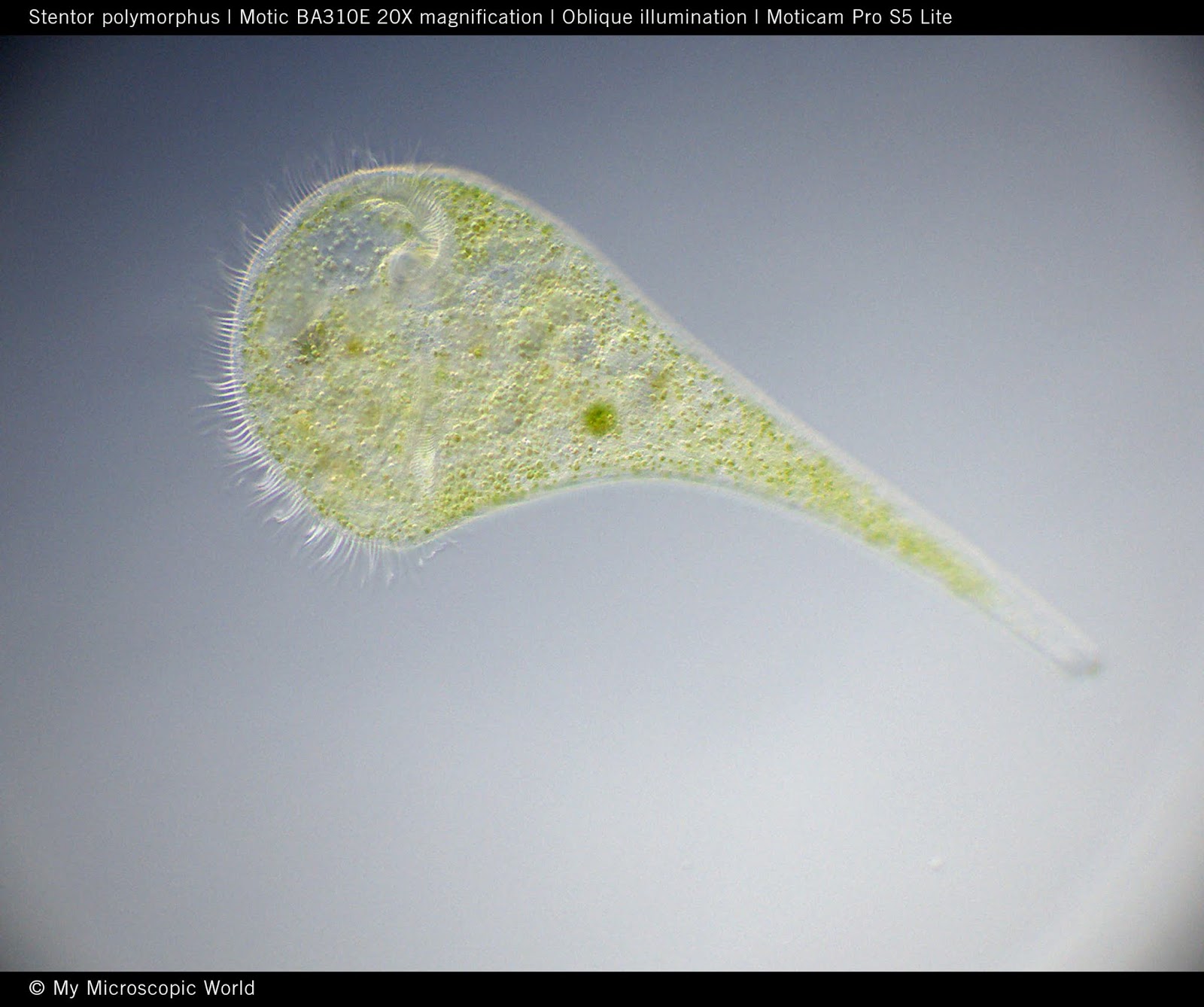
Stentor
Ciliate, uses cilia to create whirlpool to capture prey
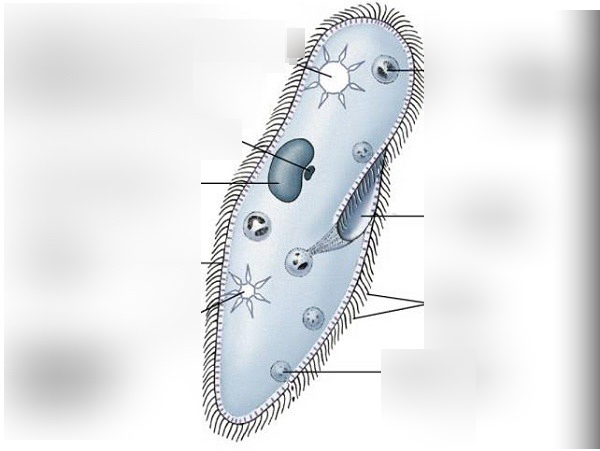
Paramecium
Ciliate, follows acids and eats decomposing matter
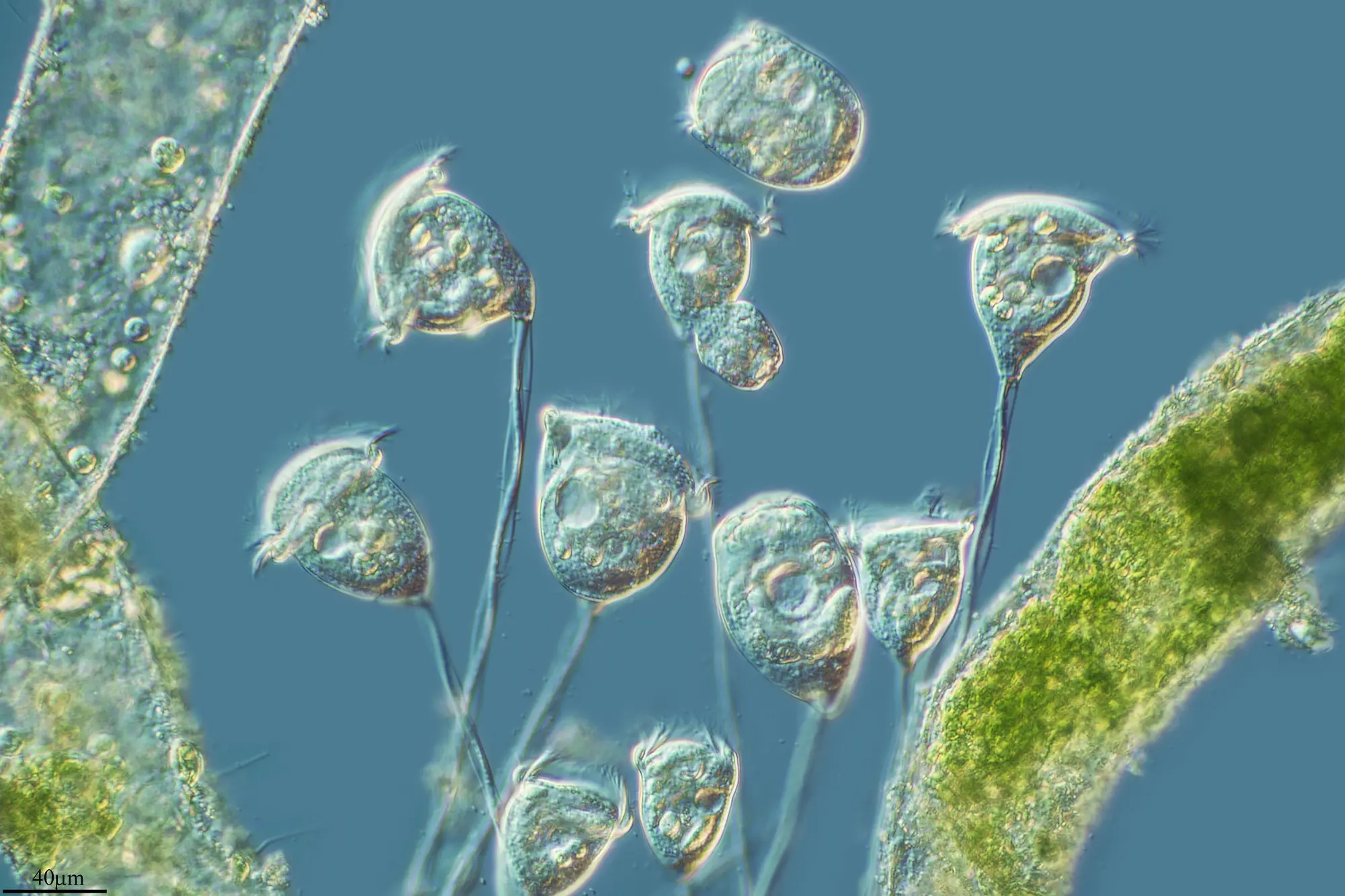
Vorticella
Ciliate, contractile stalks, form colonies by asexual reproduction
ciliate sexual reproduction
macronucleus involved in RNA and DNA synthesis, a+ and a- adhere, macronuclei degenerate, 2 meiotic divisions of micronuclei, all but one micronuclei degenerate, remaining micronucleus divides → stationary and wandering nuclei, bridge forms between cells, exchange wandering nuclei, Nuclei fuse and form skyaryon (2N), conjugates separate, additional nuclear divisions → 4 daughter cells formed (not truly sexual, no eggs or sperm)
Ceratium
Dinoflagellate common along texas coast (name means horns)
Noctiulca
bioluminescent Dinoflagellate
Karenia
Dinoflagellate that causes “red tide” toxic/poisonous to fish, can infect oysters and be deadly to people