kin 110: HUMAN ANATOMY PART 1
1/183
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lectures 2 & 3 (anatomical position, skull...)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
regional anatomy
based on the organization of the body into parts → EMPHASIS on the relationship of various systems and structures (ex: muscles, nerves, arteries) within the region
surface anatomy
focused on the knowledge of what structures are visible in the body at rest and in action ex: stab wound, doctor should be able to visualize the deep structures that are injured
systemic anatomy
organized by organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions ex: nervous system
clinical (applied) anatomy
emphasizes the aspects of the structure and function of the body in practice, encompassing both regional and systemic approaches to studying anatomy
anatomical position
body positioning used as a reference for anatomy: head, eyes, and toes directed anteriorly (forward), upper limbs by the sides with the palms facing anteriorly, lower limbs close together with the feet parallel and the toes directed anteriorly
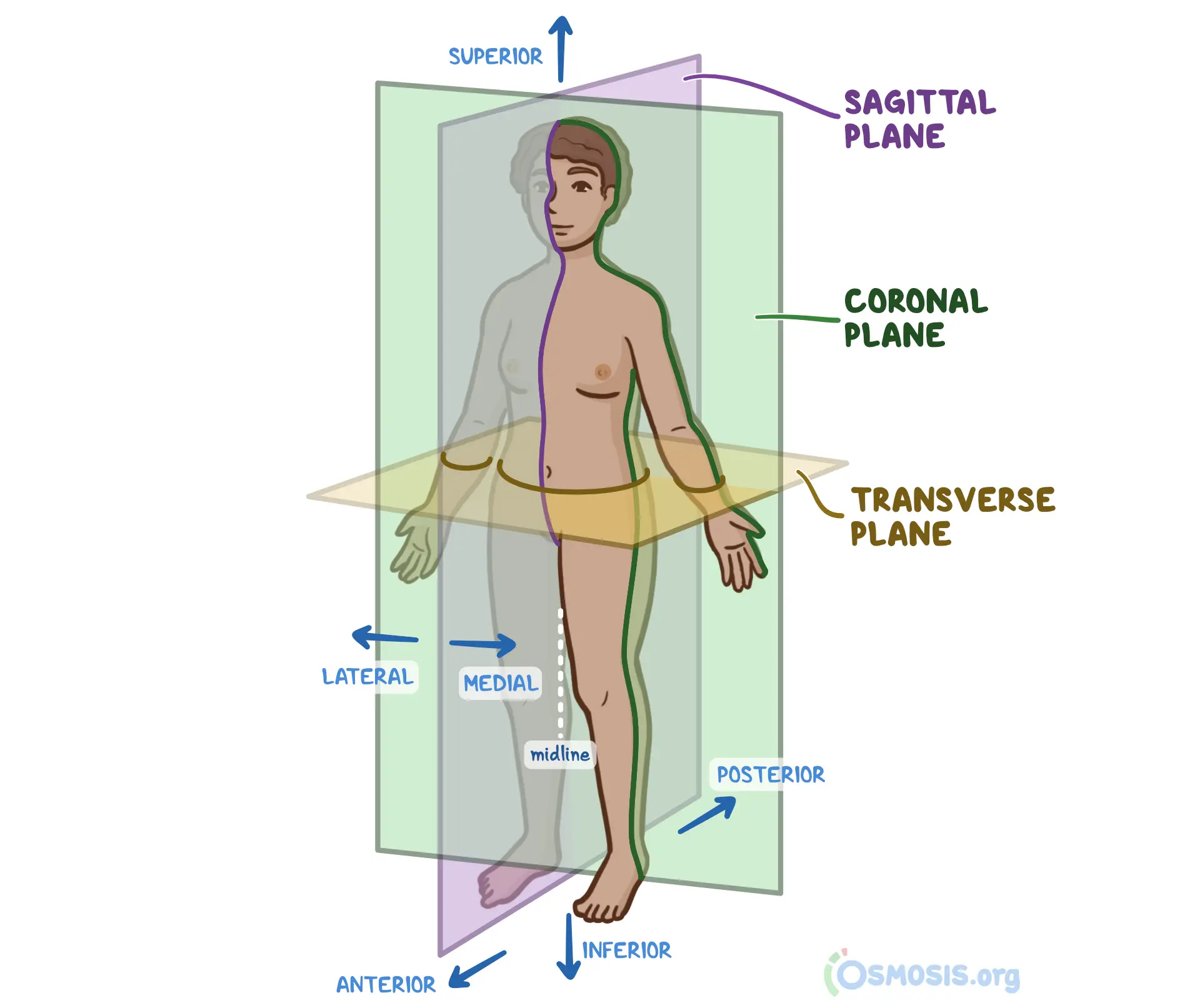
median (median sagittal plane)
the vertical plane passing longitudinally through the center of the body, dividing it into right and left halves
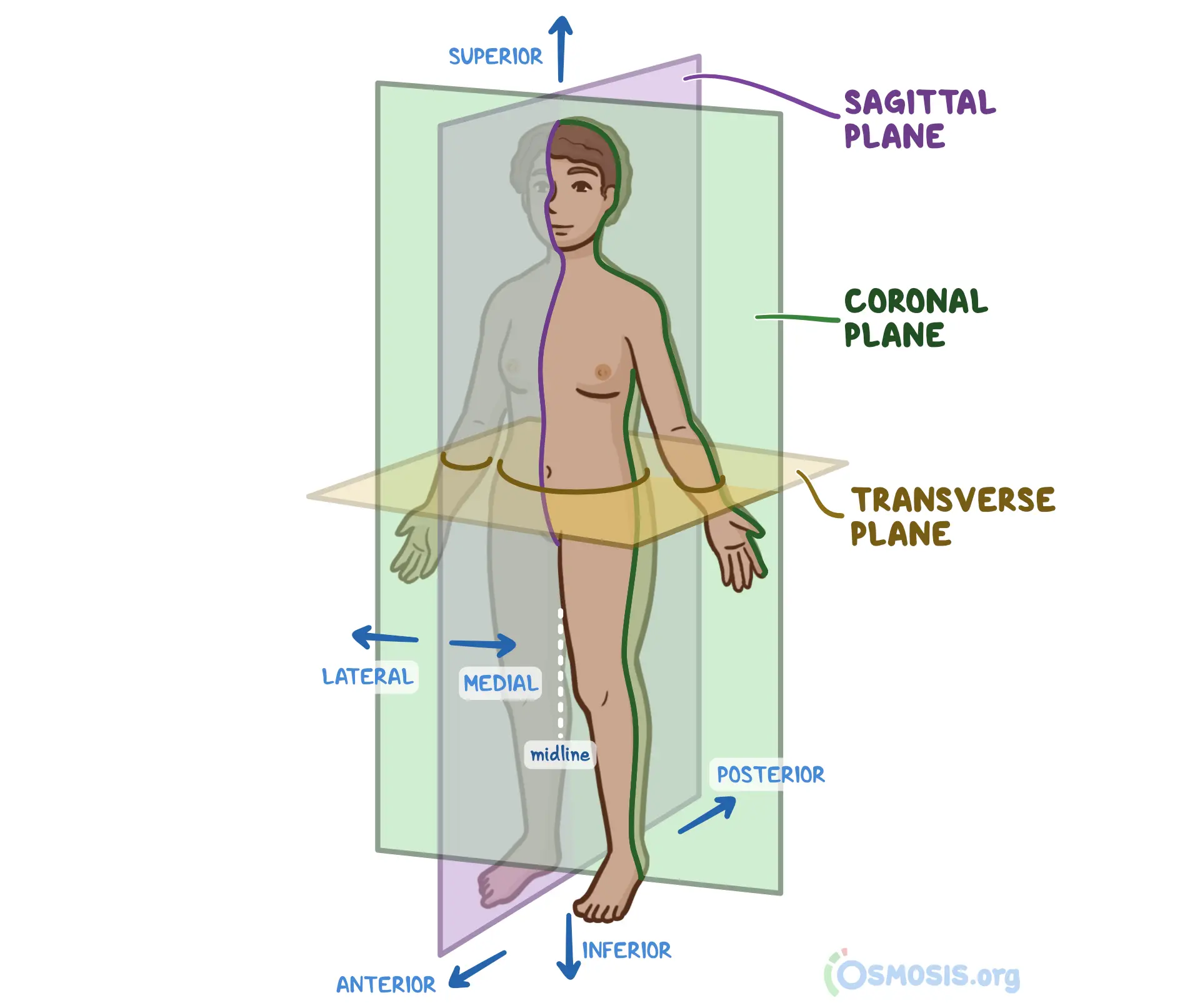
sagittal planes
vertical plans passing thru the body PARALLEL TO MEDIAN PLANE, helps give a point of reference to indicate the position of a specific plane for ex: a s____ plane through the midpoint of the clavicle
what is a plane parallel to and near the median plane called?
paramedian plane
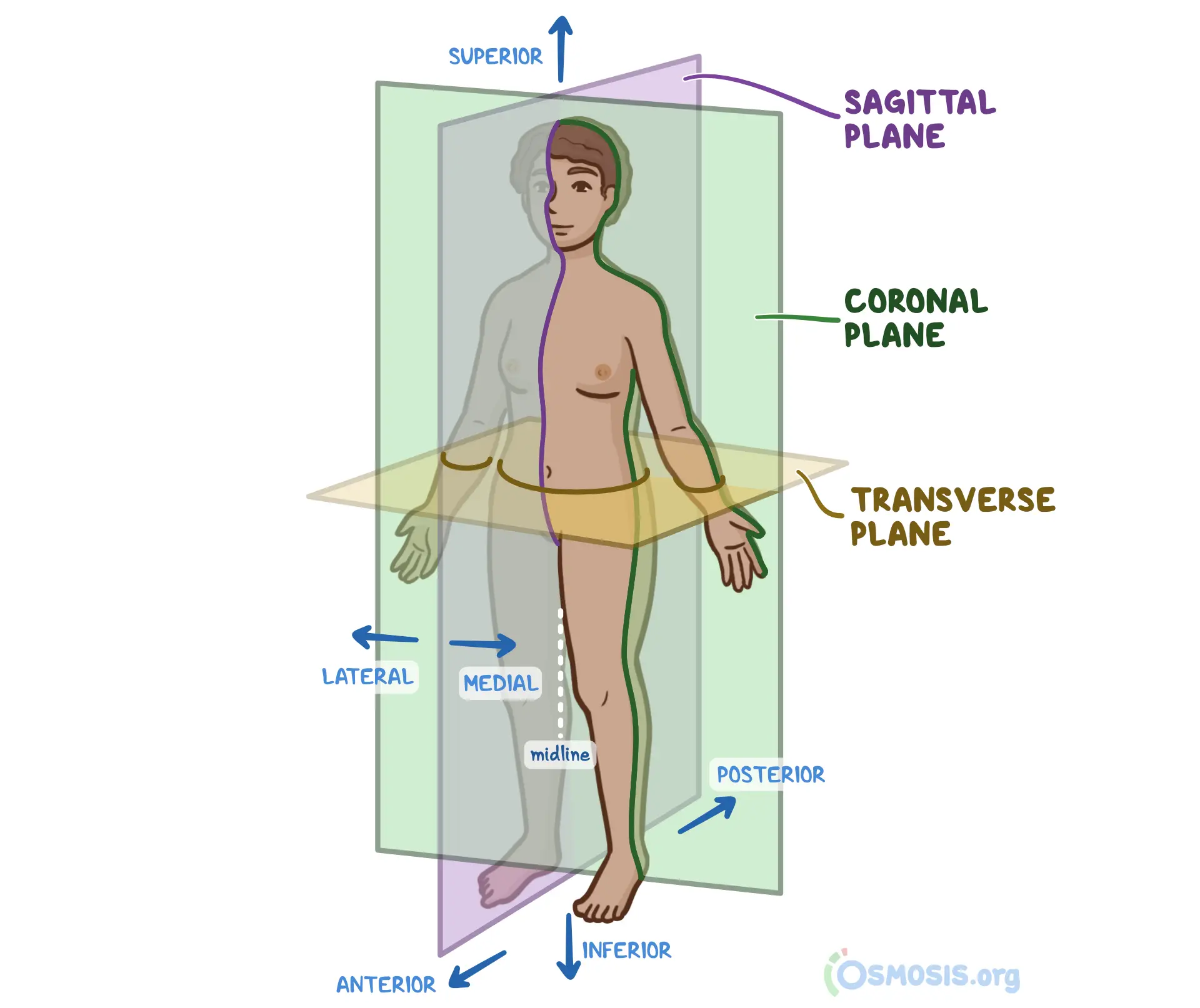
frontal (coronal) planes
vertical to planes passing through the body at right angles to the median plane, dividing it into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions for ex: a f____ plane thru the heads of the mandible
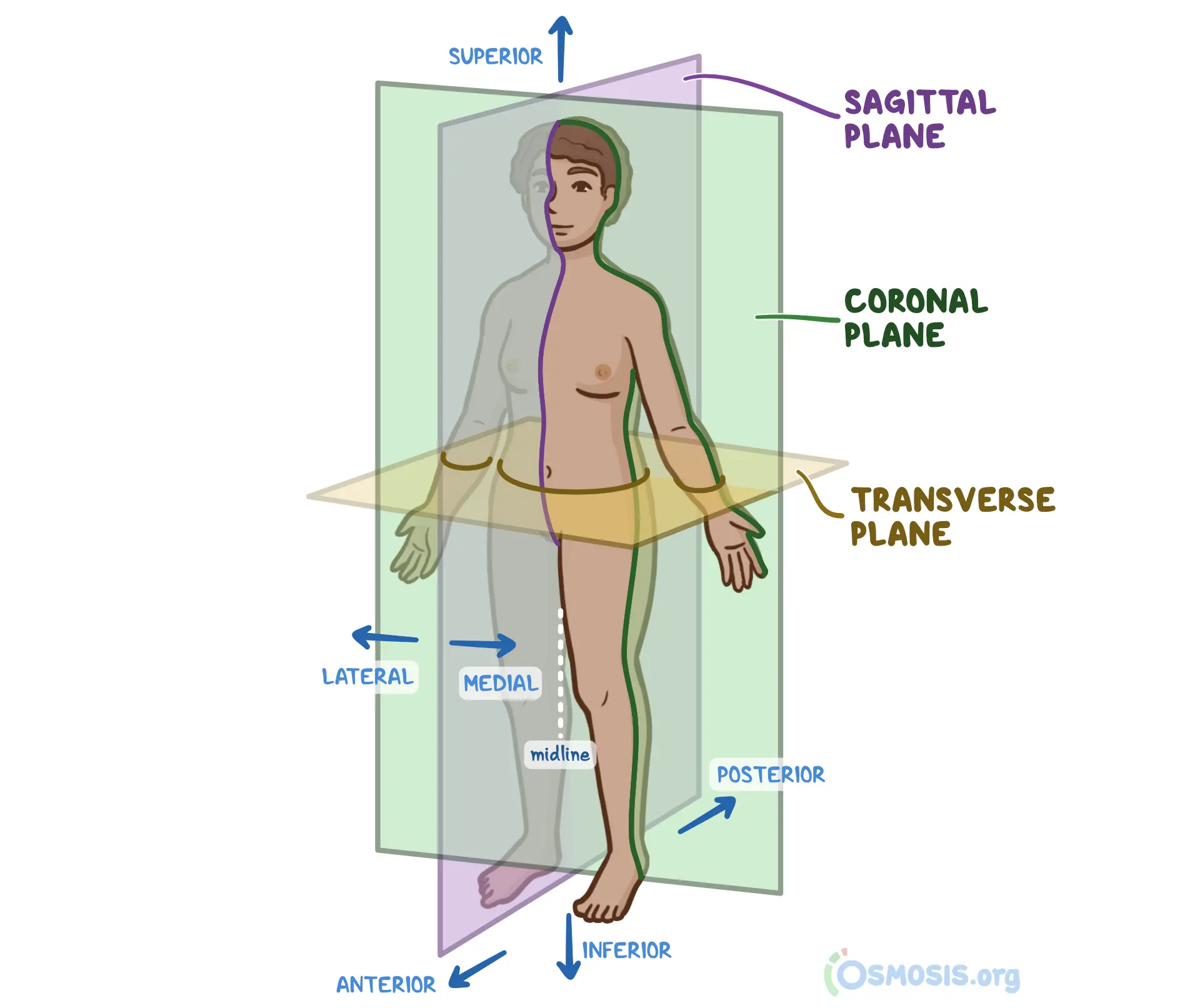
transverse planes
passing thru the body at right angles to the median and frontal planes, divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts for ex: a t_____ plane thru the umbilicus
oblique planes or sections
planes that do not align with the preceding planes ex: mri or ct scans → oblique views are used to better visualize complex structures such as the heart or spine, which have axes of symmetry not aligned with the standard vertical or horizontal planes
inferomedial
nearer to the feet and closer to the median plane ex: the anterior parts of the ribs run inf_____
superolateral
nearer to the head and father from the median plane
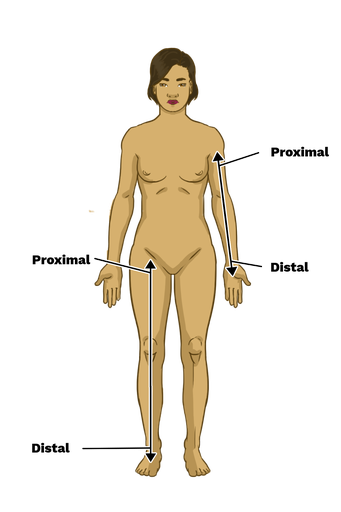
proximal
a body part that is closer to the trunk or point of origin of a limb or appendage ex: elbow is pro____ to the wrist
distal
body part farther from trunk/point of origin ex: the wrist is d___ to the elbow, and the d___ part of the upper limb is the hand
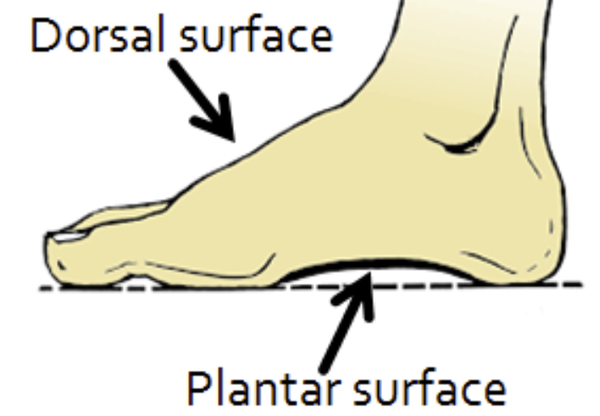
dorsum
the superior or dorsal surface of any part that sticks out anteriorly from the body such as the dorsum of the foot, hand, penis, tongue
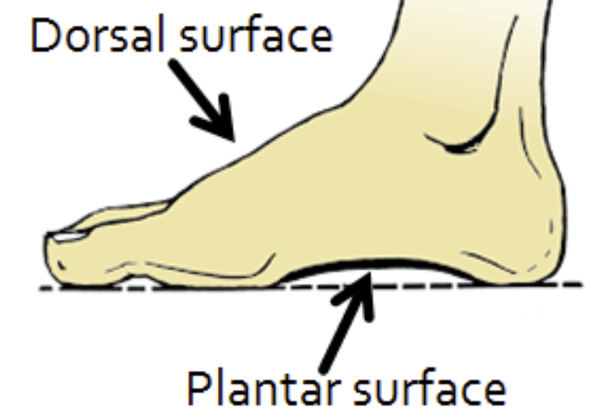
sole (plantar surface)
indicates the inferior aspect/bottom of the foot in contact with the ground
inferior foot surfce=sole/plantar
superior foot surface=dorsum/dorsal
palmer surface (palm)
the flat anterior aspect of the hand
anterior hand=palm/palmar
posterior hand=dorsum/dorsal
bilateral
paired structure having right and left members (kidneys)
unilateral
no right and left members, functions occurring on one side only (spleen)
ipsilateral
occurring on same side of the body ex: the right thumb and right big toe
contralateral
occurring on the opposite side of the body ex: right hand is c____ to the left hand
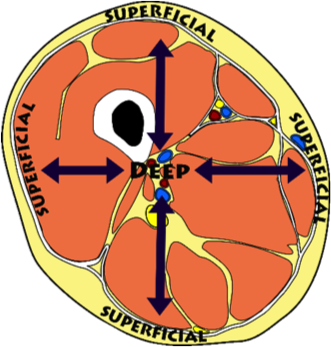
superficial
nearer to surface ex: muscles of the arm are sup___ to its bone
intermediate
between a superficial and deep structure ex: bicep muscles is int____ between the skin and humerus
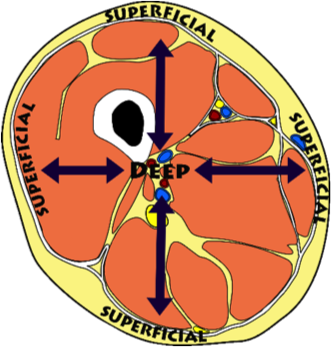
deep
far from surface ex: humerus is d___ to the arm muscles
posterior/dorsal
back ex: the heel is posterior to the toes
anterior/ventral
front ex: toes are anterior to the ankle
medial
near to median plane ex: the little finger is on the m___ side of the hand
lateral
farther from median plane ex: thumb is on l___ side of the hand
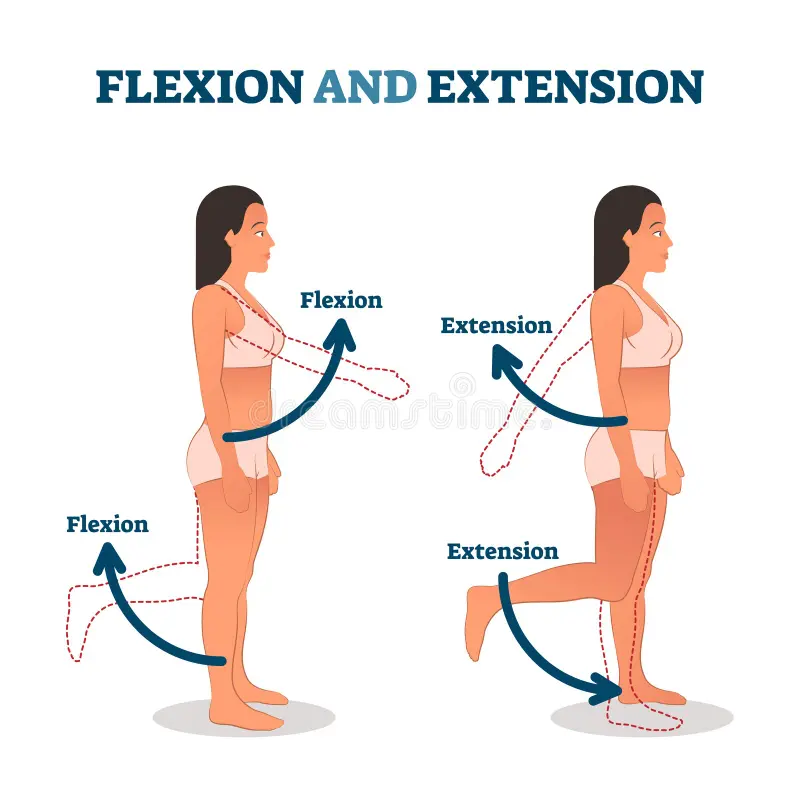
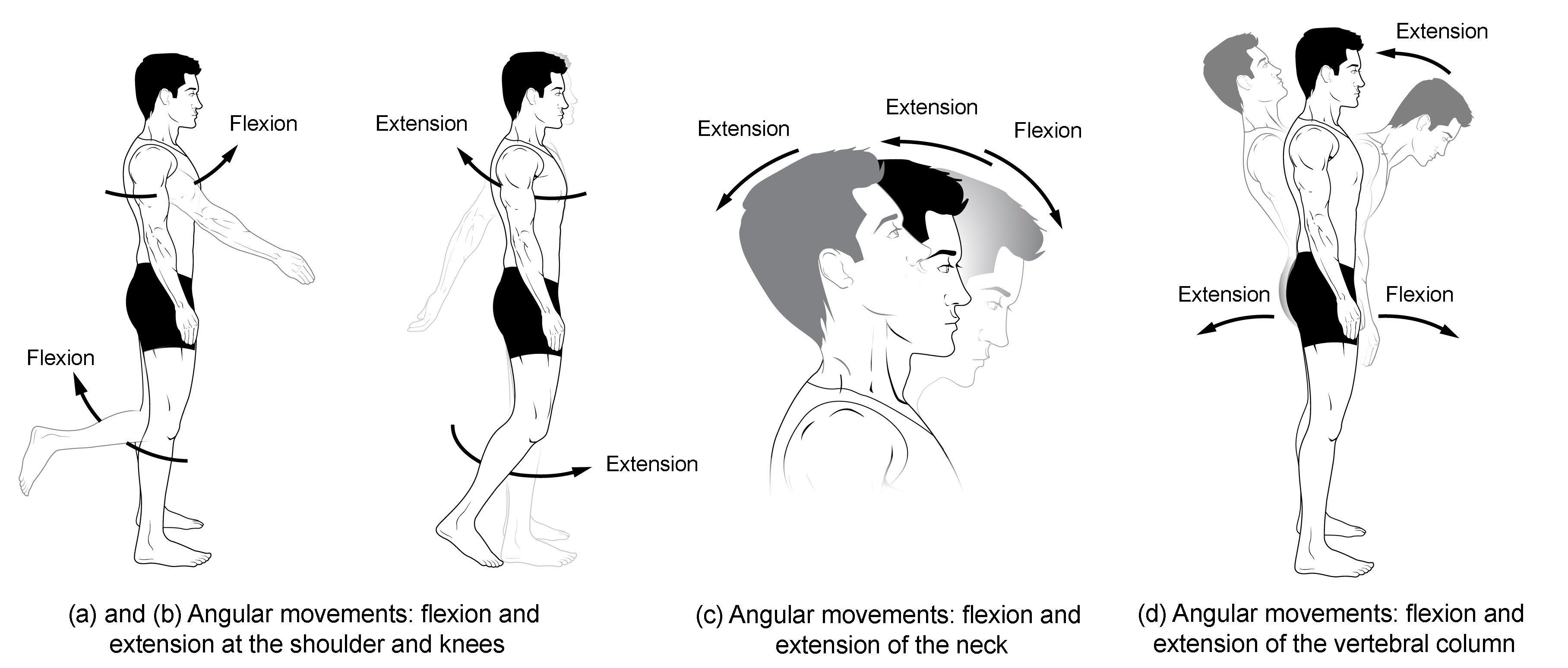
flexion
the bending of the angle between two body segments or bones, effectively bringing them closer together, movement occurs in the sagittal plane around a frontal axis
ex: bending your elbow to bring your forearm toward your upper arm, clenching your hand into a fist
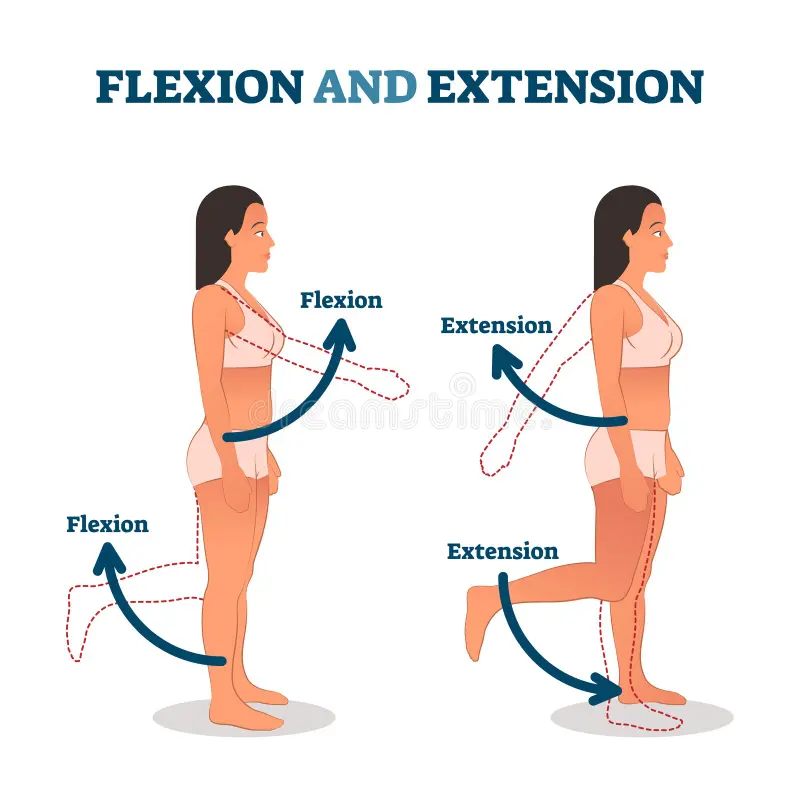
extension
the movement of a joint that increases the angle between two body parts, resulting in a straightening/opening of the joint, occurs in sagittal plane
Ex: straightening your arm at the elbow, standing up from a seated position
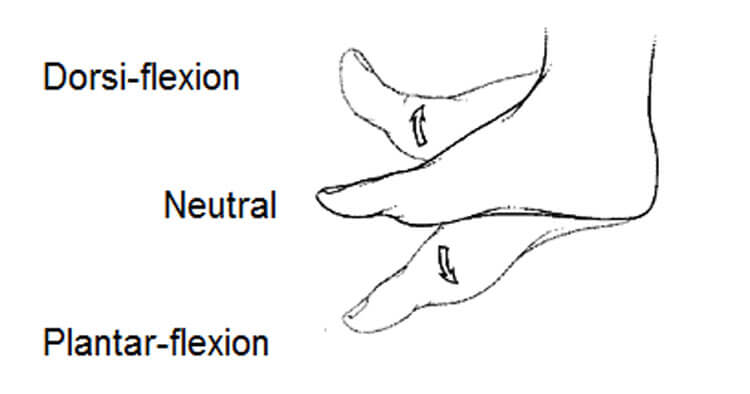
dorsiflexion
movement of the foot or hand in an upward, backward direction, bringing the toes or fingers closer to the shin or forearm, occurs in the sagittal plane
Ex: walking on your heels or bringing the palms of your hands together in a "prayer pose"
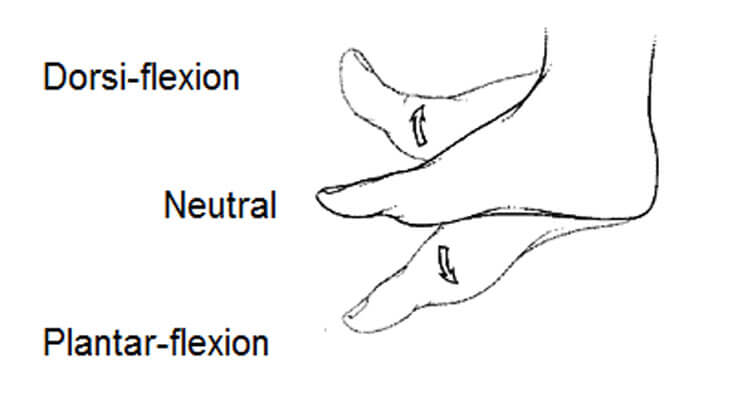
plantarflexion
downward movement of the foot at the ankle where the top of the foot points away from the leg and the toes point towards the floor, occurs in the sagittal plane
Ex: standing on tiptoes, pressing the gas pedal in a car
eversion
Movement that tilts the sole of the foot away from the body’s midline so the sole faces outward, movement within the frontal plane
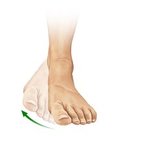
inversion
movement of the foot where the sole of the foot turns inward towards body's midline, frontal plane
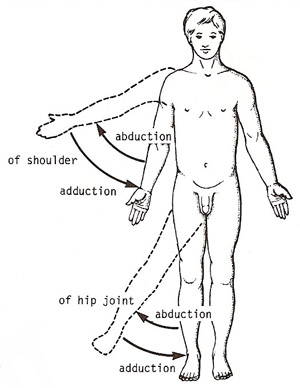
adduction
movement of a body part toward the body's midline
Ex: bringing your arm down to your side from a raised position, squeezing your legs together.
abduction
movement away from the midline
Ex: Raising your arm out to the side of your body
circumduction
movement of a body region in a circular manner by combining flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
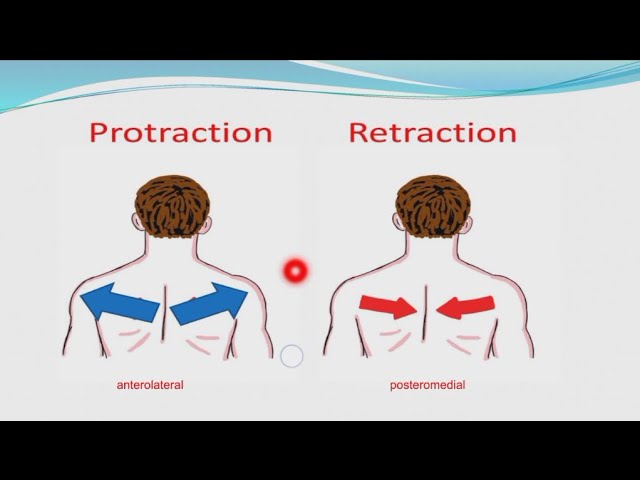
protraction
movement of a body part forward
Ex: sticking out your chin, pushing your shoulder blades forward
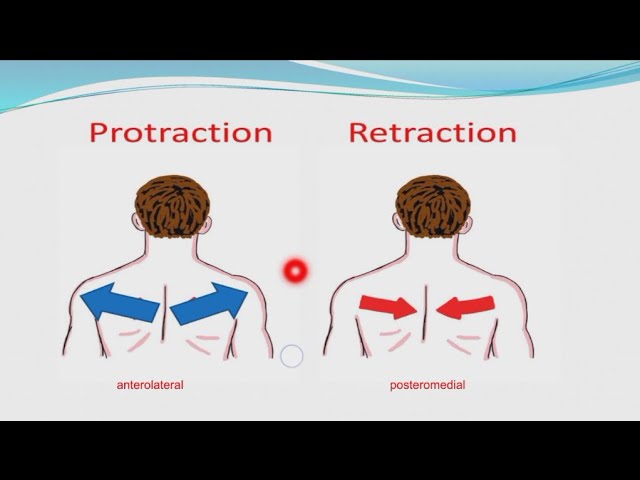
retraction
movement of a body part backward toward its original position or midline
Ex: pulling your chin in, bringing your shoulder blades together
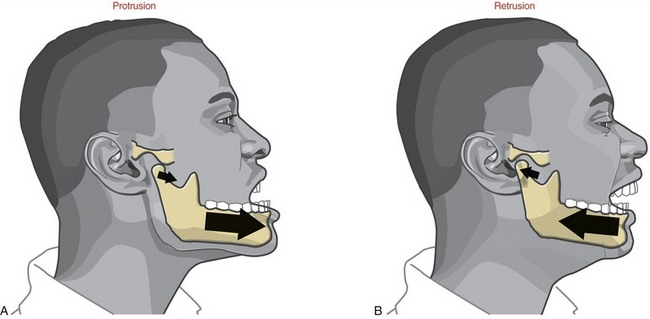
retrusion
posterior (backward) movement of body part, primarily occurring in the sagittal plane
Ex: pursing your lips back to normal after puckering, putting ur tongue back in mouth after sticking it out
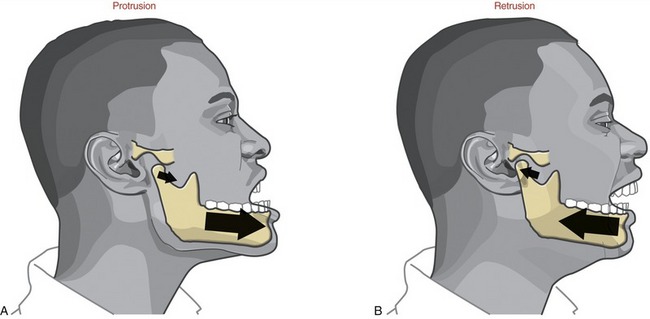
protrusion
anterior (forward) movement of a body part, primarily occurring in the sagittal plane
Ex: puckering ur lips
lateral bending/lateral flexion
A joint action, commonly involving the vertebral column (neck of trunk), where a body part bend or tilts to the right/left away from the midline, occurs in the frontal plane
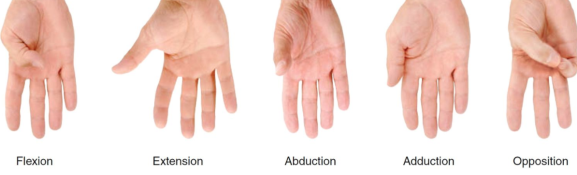
opposition (thumb)
thumb movement that brings the tip of the thumb to touch the tip of any other finger or the palm, allowing for grasping of objects
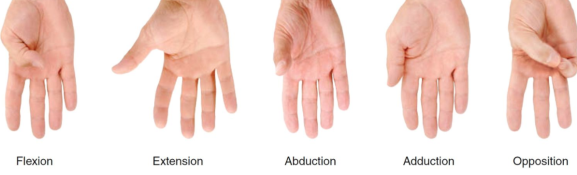
reposition
movement of the thumb or little finger away from the other fingers and back to its anatomical position, separates the thumb and finger after their tips have touched
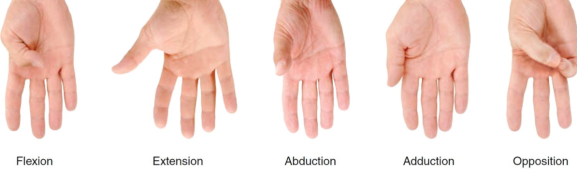
abduction & adduction of the thumb
Thumb abduction: movement away from the body's midline, moving the thumb perpendicular to the palm
thumb adduction: movement back to the anatomical position, bringing it toward the index and other fingers
joint
plane of union or junction between two or more rigid components (bones, cartilages)
fibrous joints
bones of fibrous joints are united by fibrous tissue, mostly immovable/allow for very slight movement
Found in; skull, gomphoses (jaw)
cartilaginous joints
joints where bones are connected by cartilage rather than by a joint cavity
Found in: rib, hip bones
Two main types: Syndesmosis & Synchondroses
synovial joints
two bones separated by the joint cavity (containing synovial fluid) but are joined with an articular capsule (fibrous capsule lined with synovial membrane), most common & important joint as they provide free movement between the bones they join
pivot joints (synovial)
uniaxial, rounded process of a bone fits into a bony ligamentous socket, permitting rotation
Ex: atlantoaxial joint in the neck, which enables head to turn side-to-side
ball & socket joints (synovial)
multiaxial, rounded head fits into a concavity, permitting movement in three planes
Ex: shoulder joints and hip joints
saddle joint (synovial)
biaxial, saddle shaped heads permit movement in two diff planes
Ex: carpometacarpal joint of the thumb which allows for the thumb's range of motion
condyloid joint (synovial)
biaxial, permits flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction
Ex: the wrist joint (radiocarpal)
hinge joint (synovial)
uniaxial, permit flexion and extension only
Ex: elbow, knee, and interphalangeal joints (joints in your fingers and toes)
plane joint (synovial)
usually uniaxial, permit gliding or sliding movements
Ex: intercarpal joints in the wrist, the intertarsal joints in the foot
syndesmosis (fibrous)
joint that unites the bones with a sheet of fibrous tissue, either a ligament or fibrous membrane, allows for some partial movement
gomphosis (fibrous)
joint found in teeth, helps regulate how hard we chew or clench our teeth by anchoring teeth in jaw
primary cartilaginous (SYNCHONDROSIS) joint
a type of immovable joint where two bones are united by hyaline cartilage, typically found in growing bones or the adult skeleton
Ex: epiphyseal plates (growth plates) in children
secondary cartilaginous (SYMPHYSIS) joints
slightly movable joints where the two articulating bones are covered with hyaline cartilage and united by a pad of fibrocartilage, movement is limited but allows for essential functions like the bending of the vertebral column and widening during childbirth, strong slightly mobile joints
Ex: intervertebral discs between vertebrae, the pubic symphysis in the pelvis (aiding in childbirth)
uniaxial
joint allows for movement in only one anatomical plane or around a single axis
multiaxial
allows movement along all three anatomical planes (sagittal, frontal, and horizontal)
biaxial
joint that allows movement in two different anatomical planes
hyaline cartilage
smooth/glassy appearance, providing a low-friction surface in joints (ex: knee joints), serves as template for bone formation in fetal skeleton
fibrocartilage
strongest cartilage type, resists high tension and compression
Found in: invertebral discs and knee menisci
pronation vs supination
pro: turning the palm/forearm to face downward or backwards
sup: turning the palm/forearm to face upward or forward
axial skeleton
consists of the bones of the head (cranium/skull), neck (cervical vertebrae), trunk (ribs, sternum, vertebrae, and sacrum)
appendicular skeleton
consists of the bones of the limbs, including those forming the pectoral (shoulder), pelvis (hips), enables movement
synovial fluid
nourishes the articular cartilage and lubricates the joint surface
extrinsic vs intrinsic
extrinsic: located outside the part of the body they act upon, originating in one location and connecting to another
intrinsic: located where they act upon
Ex: extrinsic hand muscles originate in the forearm to control finger movement, intrinsic are smaller muscles located in the hand itself
three types of muscles fibers
skeletal striated muscle, cardiac striated muscle, smooth muscle
skeletal striated muscle
moves bones and other structures (ex: eyes)
cardiac striated muscle
forms most of the walls of the heart and adjacent parts of the great vessels
smooth muscle
forms part of the walls of most vessels & hollow organs, moves substances thru viscera such as the intestine, controls movement thru blood vessels
tendons vs aponeuroses
noncontractile portion of skeletal muscle, tend=rounded, apon=flat sheets
pennate muscle
feather-like in arrangement of their fascicles (fiber bundles), can be unipennate/bipennate or multipennate (multiple rows of fibers looking like a feather)
Ex: deltoid/shoulder
fusiform muscle
spindle-shaped, round thick belly and tapered ends, type of parallel muscle
Ex: biceps brachii
parallel muscle
fascicles lie parallel to the long axis of the muscle; flat muscles with parallel fibers often have aponeuroses (flat sheets)
Ex: biceps brachii or external oblique
convergent muscle
have a broad attachment from which the fascicles converge to a single tendon
Ex: pectoralis major/chest
circular muscle
surround a body opening or orifice (opening in human body like nostril), constricting it when contracted to control the passage of substances (food, waste)
Ex: orbicular oris (encircles the mouth)
digastric muscle
feature two bellies in series sharing a common intermediate tendon
Ex: movement you feel in neck when swallowing or opening wide, d_____ muscles contact to elevate your hyoid bone and depress your lower jaw/mandible —> has anterior belly at front of jaw and posterior belly on side of skull that connect by a central tendon to work tgt to aid chewing, speech and swallowing
strongest kind of muscle
pennate muscle: their design allows for a greater number of fibers to be packed into a given volume, therefore increasing their cross-sectional area and enhancing force production
downside: reduced range of motion & speed as the angled fibers shorten less during contraction
neurocranium/cranial vault
bony case of brain and its membranous coverings (cranial meninges), contains proximal parts of the cranial nerves and vasculature (blood vessel network) of brain
nasion
intersection of the frontal and nasal bones
angle of mandible
point where the lower back of the mandible (jawbone) curves upward to meet posterior edge of the mandibular ramus
calvaria
skullcap/dome-like roof of neurocranium
glabella
smooth area between the superciliary arches (raised bony areas above superior margin of each eye socket)connecting them tgt (bony areas found above each eye socket)
mandibular ramus
part of lower jaw (mandible) that extends upward from the body of mandible, ramus serves as an attachment site for chewing muscles such as the masseter and temporalis, its condyle (rounded protuberance at the end of bone that forms with another) forms part of the temporomandibular joint that allows the jaw to articulate with the skull
perpendicular plate of ethmoid
thin vertical bone that forms upper part of nasal septum, dividing nasal cavity into 2 sides, provides structure & support to nasal septum which aids breathing and protection of nasal passages
vomer
unpaired, forms the lower back portion of nasal septum: wall that separates the R/L nasal passages, works with perpendicular plate of ethmoid
eight bones the neurocranium is composed of
singular bones centered on the midline: FRONTAL, ETHMOID, SPHENOID, OCCIPITAL
two sets of bones occurring as bilateral pairs: TEMPORAL AND PARIETAL
which bones in the skull come in pairs, which stand solo, where are they found
unpaired skull bones: frontal, sphenoid, occipital, ethmoid
two pairs of skull bones: temporal & parietal bones
paired FACIAL bones: maxillae (upper jaw), nasal, palatine, zygomatic (cheekbones), lacrimal bones and inferior nasal conchae
viscerocranium
facial skeleton, forms the anterior part of the cranium and consists of bones surrounding the mouth, nose, and most orbits
cranial base/basicranium
base of neurocranium comprised of 15 irregular bones
bones of the cranial base
three singular bones lying in midline: MANDIBLE, ETHMOID, VOMER
six paired bones occurring bilaterally: MAXILLA; INFERIOR NASAL CONCHA, ZYGOMATIC PALATINE, NASAL, LACRIMAL BONES
orbit vs arch vs process
orbit: socket in skull for eyes/any empty cavity
arch: curved structure (ex: zygomatic arch forming the cheekbone)
process: bony projection
processes often form important structures like: THE TEMPORAL PROCESS OF THE ZYGOMATIC BONE BURSTING INTO THE ZYGOMATIC ARCH
frontal aspect of cranium consists of what
frontal bone, zygomatic bones, orbits, nasal region, maxillae, mandible
frontal bone
forms the skeleton with the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal and zygomatic bones
also articulates with the lacrimal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones to form the roof of the orbit and part of the cranial cavity
supra-orbital margin
frontal bone; the angular boundary between the flat and orbital parts, has either a supra-orbital foramen (complete enclosed hole) or notch (open ended indention in bone)
→both are passage to supraorbital nerve or artery!
zygomatic bones
form prominences of the cheeks
lie on the inferolateral (below & lateral to reference point) sides of the orbits (eye sockets) and rest on the maxillae (upper jaw)