CSU BMS 302 EXAM 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
law of diffusion equation
Q=[Ya-Yb]xTyx(Sy/sqrtMwy)XA/D
Na+ concentration gradient and permeability
Out to in, not permeable
K+ perm/grad
In to out, perm
A- perm/grad
In to out, not perm
Cl- perm/grad
out to in, perm
excitability
ability to generate AP
conductivity
ability to propagate AP
Action potential steps
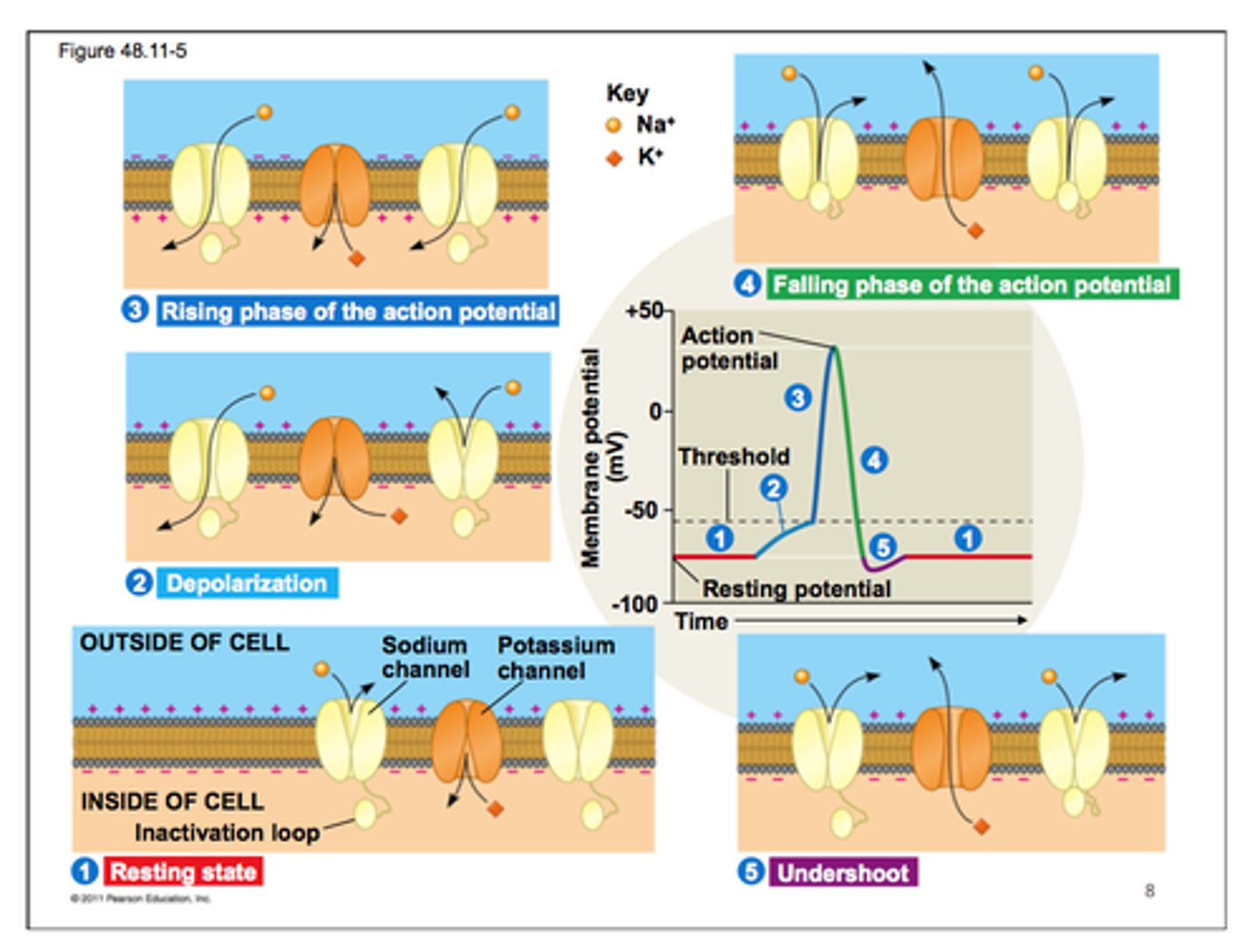
Before myosin can bind to active binding site, it must be in high E state. What happens>
ATPase in myosin head hydrolyzes ATP from previous relax cycle
Muscle potential steps
1. Stim motor neuron - AP
2. Ach from axon to cleft
3, Ach binds receptors on sarcolemma
4. Na moves through chem gated channels
5. Na voltage gated channels, Na floods in
6. Action potentials to Ttubules
7. SR depolarizes and releases Ca
8. Ca binds troponin
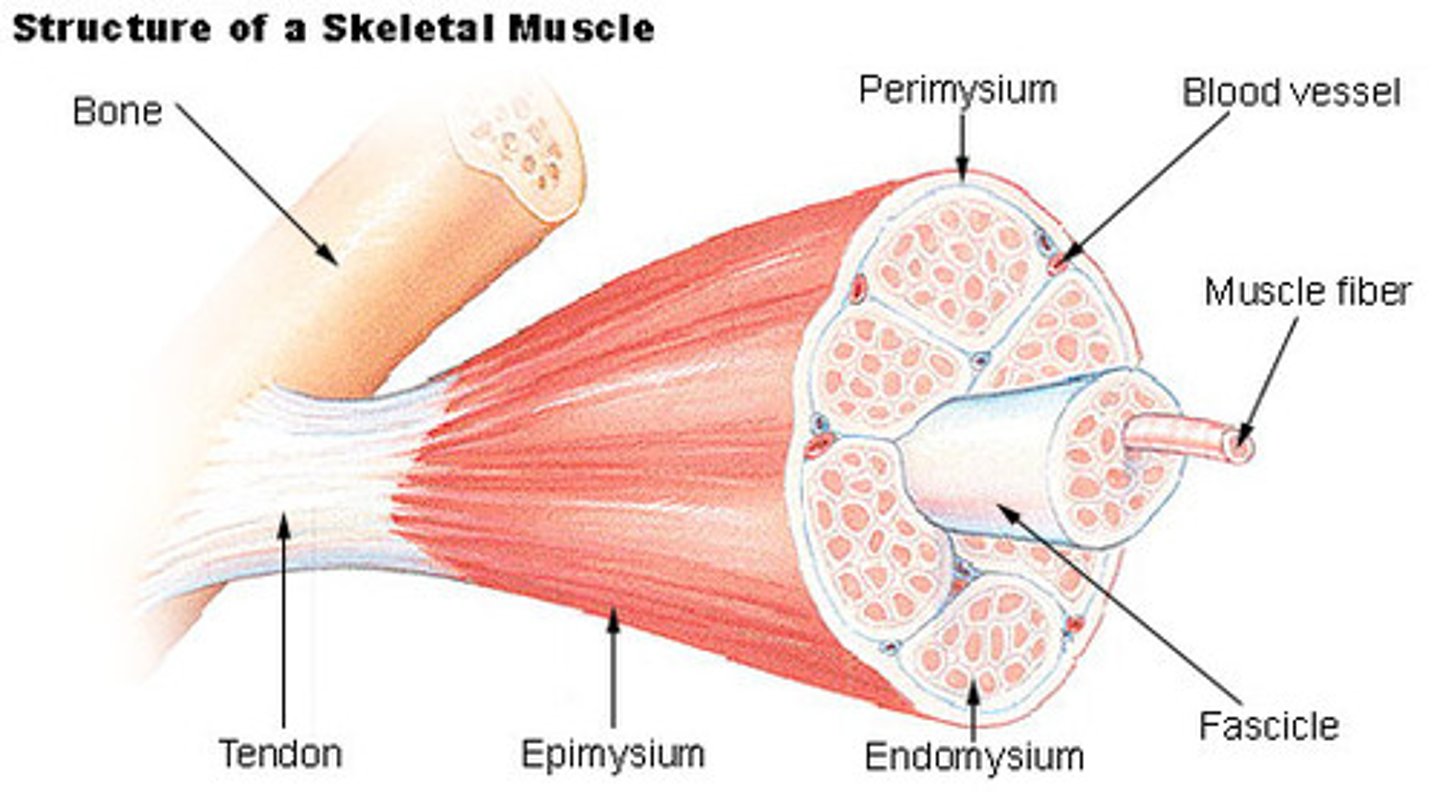
muscle fiber organization
fascicle - fiber - myofibril - myofilaments
somatic (1/2, ganglion, NT, effector)
1, no, ach, skel musc
autonomic
2, yes, ach and ne, smooth, cardiac, glands
Symp NT, short long pre
ach , NE, short preganglion
Parasymp NT, length
ACh, long
skel musc latent period
duration of contraction
caclium
excitation
3 msec, ms, SR, nervous
Visc smooth much
latent period
duration
ca
excitation
200-300 msec
seconds
extracellular
pacemaker, cell to cell junctions
Visceral smooth rhythm
AND
innervation
yes, modifies, not all fibers innervated
multiunit smooth muscle
no rhythm, ANS initiates, each fiber innervated
norepi/epi on ileum
inhib
ach on ileum
stim
atropine on ileum
none
norepi/epi
ad ag
ach
chol ag
atropine
chol antag
chol agon on ileum
stim
ad ag on ileum
inhib
cholinergic
parasymp
adrenergic
symp
medulla
secretes epi
procaine
reduces AP amp, prevents NA voltage opening