Week 5 - Balancing redox reactions, voltaic and electrolytic cells, primary and secondary batteries
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Describe the process of balancing redox reactions in acidic solution
Write the skeletal form of each half equation
Balance all atoms except O and H
Balance O atoms with H2O molecules
Balance H atoms with H+ atoms
Add the electrons gained/lost
Balance both equations so the electrons are equal
Done

Describe the process of balancing redox reactions in basic solution
Balance as if the reactions were taking place in acidic solution
Cancel all H+ using OH- ions by adding OH- to both sides of the equation
The H+ and OH- ions form H2O molecules so cancel these out with the others
Describe the process of writing molecular equations from skeletal ionic equations
Balance the ionic equations
Add the spectator ion to each of the ions present in the ionic equation
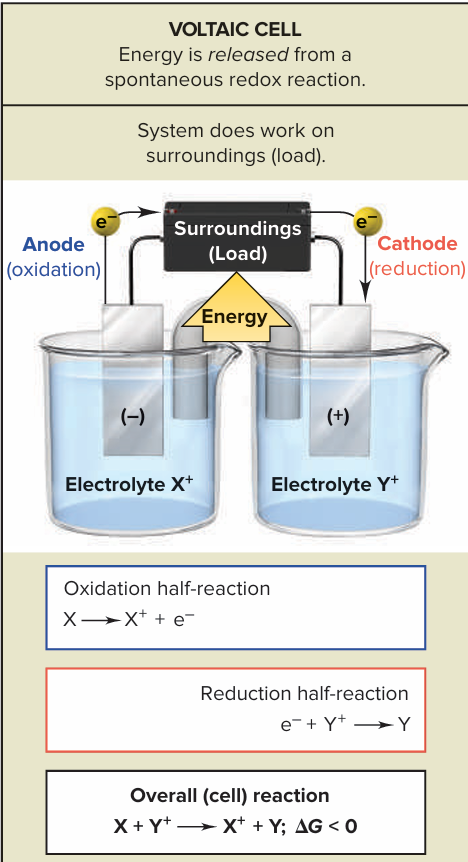
Describe the features of a voltaic cell of reactant electrodes and draw one using X+ and Y+ cations
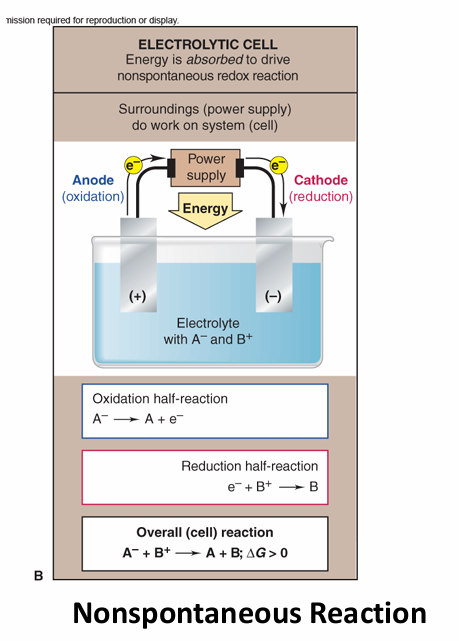
Describe electrolytic cells
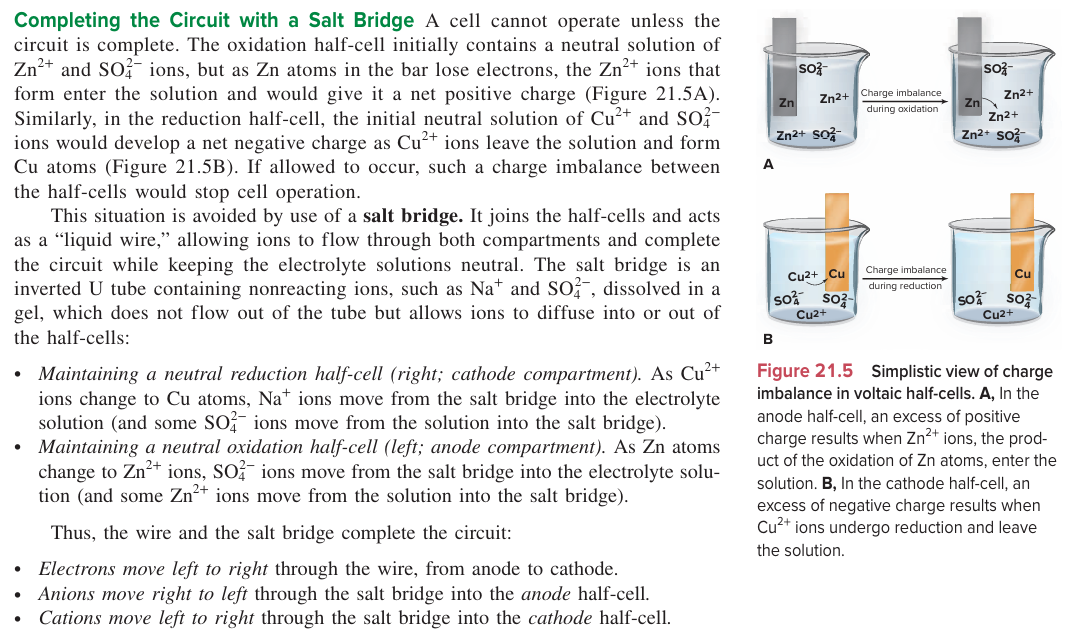
State the purpose of a salt bridge
To neutralize the solutions of both the anode and cathode
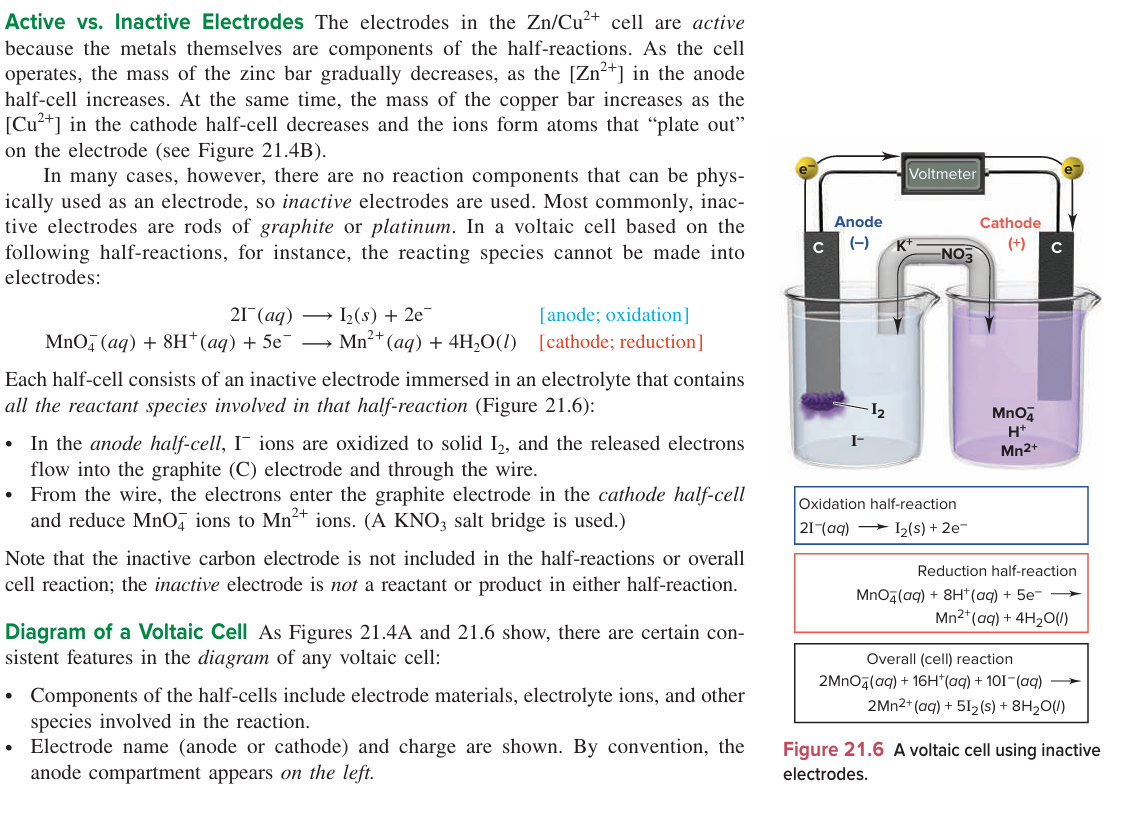
Draw a diagram of the voltaic cell of 2I- (to I2) and MnO4- (to Mn2+)
Define cell potential (Ecell)
The difference in electrical potential between half-cells
Also called voltage or e.m.f
State the what it means Ecell > 0, Ecell < 0 and Ecell = 0
When Ecell > 0, the reaction is spontaneous
When Ecell < 0 the reaction is non-spontaneous
When Ecell = 0 the reaction is in equilibrium.
Define Voltage
Work done per unit charge in driving that charge around a complete circuit
1V = 1 J/C
Define standard cell potential (E°cell)
The potential of a cell under standard conditions:
298K
1mol/dm3 concentration of all electrolytes
all reactants in their standard states
1 atm for gases
pure solids are used for electrodes
Define standard electrode potential (E°half-cell)
Standard half cell potential
The potential of an electrode measured against hydrogen under standard conditions
298K
1mol/dm3 concentration of all electrolytes
all reactants in their standard states
1 atm for gases
pure solids are used for electrodes
Describe how to find E°cell of the half-cells from thetheir E°half-cell
E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
Describe the trend of half cell potentials
More positive = more readily receives electrons (Stronger oxidizing agent)
More negative = more readily loses electrons (Stronger reducing agent)
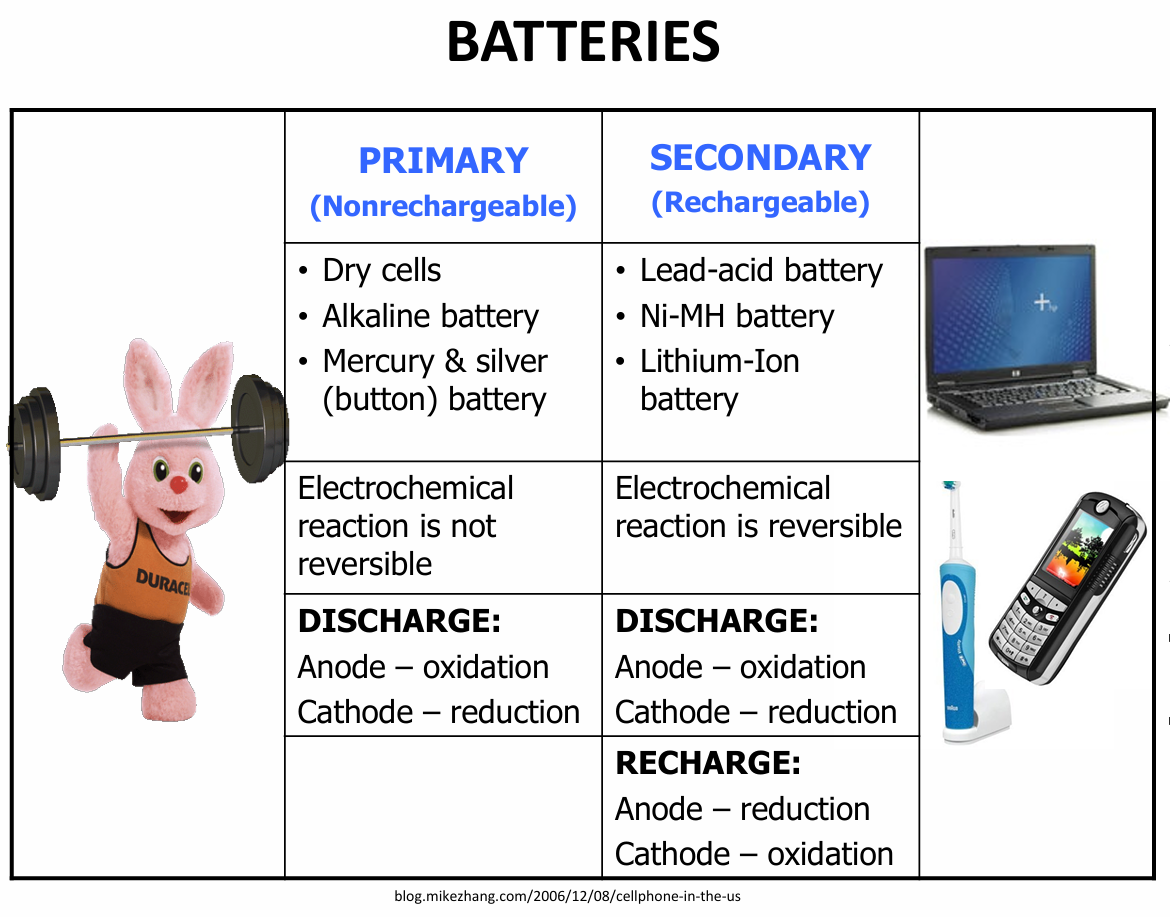
Describe a primary and secondary batter
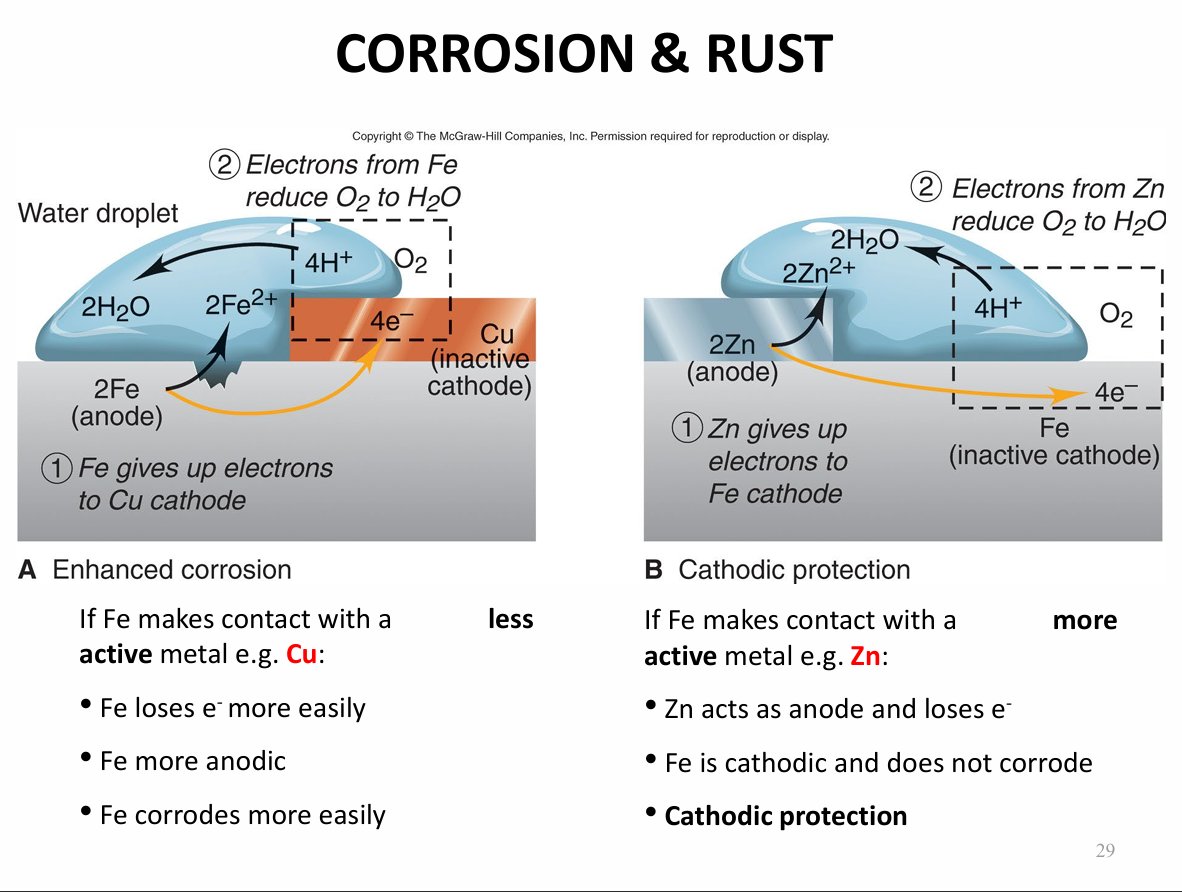
Describe the rusting of iron
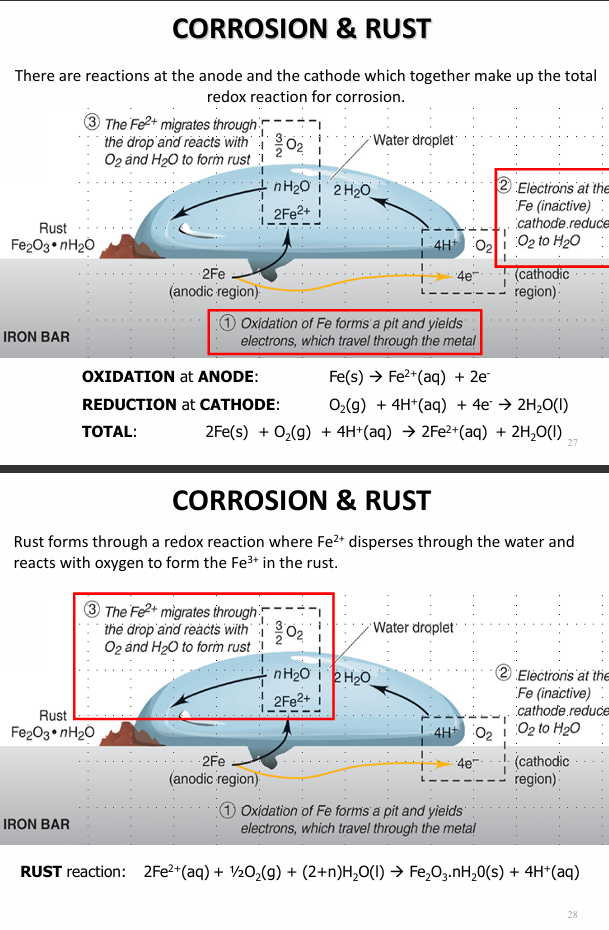
Describe the rusting of iron when there is a less active metal present and when ther is a more active metal Zn present
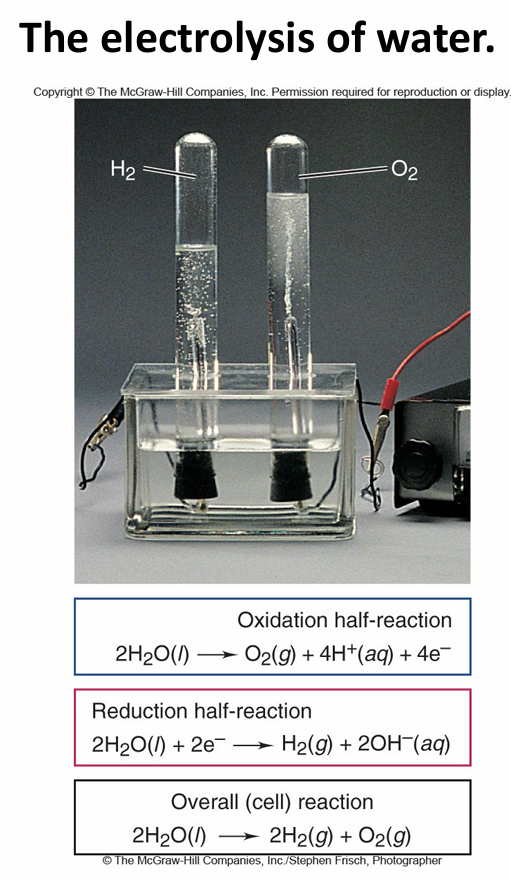
Describe the electrolysis of water