Abdomen
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
The abdomen is considered from the
Diaphragm to brim of pelvis
The abdomen is divided into
4 quadrants
How to imagine left, right upper/low quadrants
Look down at yourself. It is your left or right on self.
Other person their left will be your right.
Location of aorta
Left of midline in upper abdomen
Upper abdomen name
Epigastric
Middle abdomen name
Umbilical
Lower abdomen name
Hypogastric or suprapubic
Peritoneum lies
Between muscles and organs
Small intestines location
All 4 quadrants
LUQ contains which organs
Stomach
Spleen
Left lobe of liver
Body of pancreas
Left kidney and adrenal gland
Splenic flexure and colon
Part of transverse and descending colon
RUQ contains which organs?
Liver
Gallbladder
Duodenum
Head of pancreas
Right kidney and adrenal gland
Hepatic flexure of colon
Part of ascending and transverse colon
RLQ contains which organs?
Appendix
Cecum
Right ureter
LLQ contains which organs?
Part of descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Left ureter
Midline contains
Bladder
Can you palpate the spleen?
No
Can you palpate the pancreas?
No
Can you palpate the kidneys? Why?
No bc its protected by the ribs and musculature
Which kidney is lower? And why?
Right kidney 1-2cm bc of liver placement
What is the costovertebral angle?
Angle formed by the 12th rib and verterbral column on the posterior thorax overlying the kidneys
Infants and children structure abdomen
Liver takes up more space
Urinary bladder higher
Easier to palpate organs b/c less muscles
Aging adult structure of abdomen
Fat accumulates in suprapubic area in females
Males also show some fat
Musculature relaxes in both genders
Why does fat accumulate in the suprapubic region of the female aging adult?
Decreased estrogen levels
How is adipose tissue redistributed in aging adults?
From face and extremities to abdomen and hips
Salvation in aging adult
Decreases=dry mouth and decrease taste
Esophagus and aging adult
Emptying is delayed=increases risk for aspiration
Aging adult fed in supine position?
Increases risk for aspiration
Gastric acid secretion decreases with age causing
Pernicious anemia, iron deficiency anemia, malabsorption of calcium
Pernicious anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Gallstones in the aging adult:
Increases with age especially females
Think FFF (fat , 40s, fertile)
liver and aging adult
Size and metabolism decrease, especially after 80
If drug metabolism by liver is impaired what are nursing implications?
Elevated drug serum levels
Be careful with dosing question provider
Bowel and aging adult
Constipation
common causes of constipation
Decreased physical activity
Inadequate intake of water
Low-fiber diet
Side effects of medications
Irritable bowel syndrome
Bowel obstruction
Hypothyroidism
Inadequate toilet facilities
Overall aging adult is most likely (general concepts)
Under nutrition or over nutrition
Poor health, isolation, alcoholism, limited functional, poverty, polypharmacy
Decline in family support
Reasons that interfere with aging adult nutrition
Facilites for meal prep, transportation to grocery store, physical limitations, income, and social isolation
Physiological changes in aging adult that directly affect nutritional status
Poor teeth
Poor vision
Poor smell and taste
Decreased saliva production & gi absorption
Slowed GI motility
Subjective data abdomen
Appetite
Dysphagia or odynophagia
Dyspepsia (heart burn)
Food intolerance
Abdominal pain
Nausea and vomiting
Bowel habits
Past abdominal history
Medications
Alc, drug and cigs
Nutritional assessment (24 hour recall)
Abdominal history disease processes
Ulcer
Gallbladder disease
Hepatitis/jaundice
Appendicitis
Colitis
Hernia
Surgeries
X-ray
Any painful areas? When do you exam those
Exam painful areas last to avoid muscle guarding
Use distraction during assessment by
Breathing exercises, emotive imagery, low soothing voice, person relating abdominal history while palpating
Which measures before assessment will enhance the abdominal wall relaxation?
Empty bladder
Warm room
Supine, head on pillow, knees bent or on pillow, and arms at side or across chest
Stethoscope warm, hands warm, short fingernails
Discourage the pt from placing their hands where? Why?
Over head b/c it tenses abdominal muscles
inspect what on abdomen
Contour, symmetry, umbilicus, skin, pulsation/movement and demeanor
How to inspect contour
Stand on right side and look down
Then stoop to gaze across abdomen
scaphoid abdomen contour and caused by
abdomen caves in. Caused by malnourishment
Normal findings from contour
Flat or rounded
proturberant abdomen countour. Causes?
Abdomen sticks out farther than usual caused by excess fat, obesity, buildup of substances
how to inspect symmetry of the abdomen?
Shine a light across abdomen toward you or lengthwise across person
Abnormal findings of symmetry abdomen
Bulges, masses, hernia, asymmetrical
What is a hernia?
protrusion of abdominal viscera through abnormal opening in muscle wall
If any abnormal findings on symmetry of abdomen what should you do?
Recheck by stepping to foot of examination table
Ask person to take deep breath
Umbilicus of abdomen inspection normal findings
Normally midline and inverted, no discoloration, inflammation, or hernia
Abnormal findings of umbilicus
Everted w ascites or underlying mass
Deeply sunken w/ obesity
Enlarged and everted w umbilical hernia
Inspection of skin abdomen normal findings
Surface smooth and even w/ homogenous color
Skin findings on abdomen that may be normal
Striae (stretch marks)
Pigmented nevi (moles)
What reflects healthy nutrition on abdomen skin
Good skin turgor
If a scar is present on abdomen,
Draw in person's records, indicate length and cm
Ascites
abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen
Skin will be glistening and taut
spider angioma
Red center with radiating red legs (enlarged small vessels)
spider angioma is a finding on the abdomen for which disease processes
Portal hypertension and liver disease
How to inspect pulsation or movement of abdomen
Use penlight, shine across
Normal findings inspection pulsation or movement abdomen
Pulsation from aorta in epigastric area mostly thin people
Respiratory movement seen, mostly in males
Abnormal findings pulsation/movement inspection of abdomen
Aorta w/ widened pulse pressure=hypertension, aortic insufficiency, thyrotoxicosis
Visible peristalsis w/ distention=intestinal obstruction
order of abdomen assessment
Inspect, Auscultate, Percuss, Palpate
When auscultating the abdomen use which part of stethoscope
Diaphragm (high pitch sounds)
auscultation order of abdomen
RLQ, RUQ, LUQ, LLQ
(RLQ is first bc ileocecal valve w/ bowel sounds always present here)
normal bowel sounds
high-pitched, gurgling, cascading sounds, occurring irregularly anywhere from 5 to 30 times per minute.
(They occur irregularly so don't count)
hyperactive bowel sounds
loud, high-pitched, rushing, tinkling sounds that signal increased motility
Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds
diminished or absent, slower motility
Hyperactive sounds disease processes
Early mechanical obstruction, gastroenteritis, brisk diarrhea, laxative use, subsiding paralytic ileus
Causes of Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds
Abdominal surgery
Inflammation of peritoneum
Late bowel obstruction
Fairly common hyperactive bowel sound when you feel your stomach "growling"
borborygmus
Perfectly "silent abdomen" is uncommon so
you must listen for 5 minutes by your watch before deciding bowel sounds are completely absent
Auscultation of vascular sounds abdomen
Note presence of vascular sounds or bruit
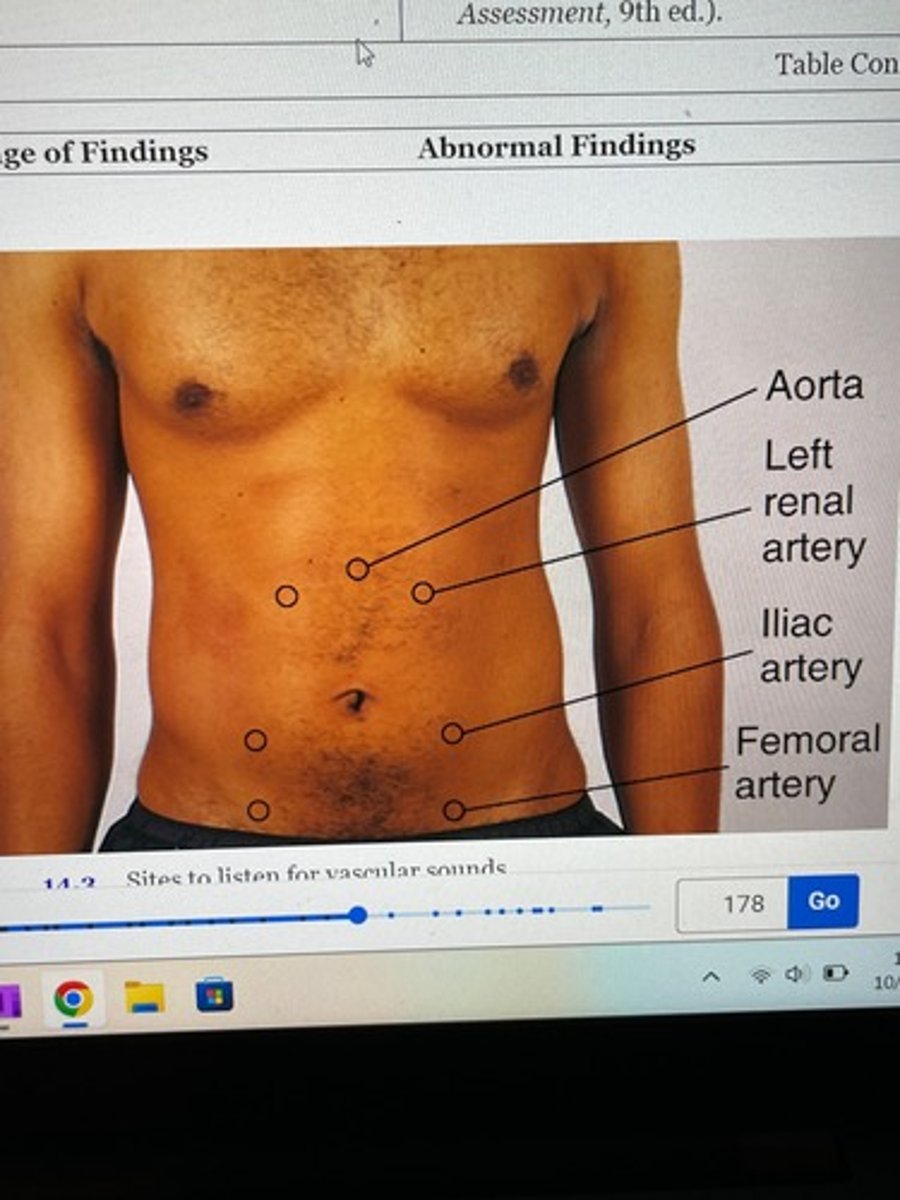
Normal findings of vascular sounds in abdomen
Usually no such sound
What is a systolic bruit?
pulsatile blowing sound and occurs with stenosis, occlusion or aneurysm of artery
venous hum (innocent murmur) and peritoneal friction (peritonitis) rub vascular sounds of abdomen
are rare
tympany in abdomen
loud high pitched musical or "drum like" over air/gas
tympany, the normal sound percussed over the abdomen, is caused by what
hollow (air filled) organs
When percussion the abdomen you are percussing for general
Tympany
How to percussion for general Tympany?
Lightly percuss all 4 quadrants
Tympany usually predominates bc air in intestines rises to surface when supine
Abnormal findings of abdomen while percussing
Dullness=distended bladder, fat, fluid, or mass
Hyper-resonance=gaseous distention
costovertebral angle tenderness
Indirect first percussion causes tissues to vibrate instead of producing a sound
How to assess kidneys with percussion?
Place hand over 12th rib at CVA on back
Thump that hand with ulnar edge of your other first
Normally feels thud but no pain
When palpating ticklish patients
Have them Move their hands on top of yours around as you palpate; ppl aren't ticklish to themselves
Or pretend to auscultate and curl fingers around stethoscope then slide it out as pt becomes use to it
Voluntary guarding vs involuntary rigidity
V: pt cold, tense, ticklish, bilateral, muscles relax slightly during exhalation
IV: constant hardness of muscles, protective mechanism from acute inflammation of peritoneum. Area usually painful as they try to sit up. May be unilateral
How to light palpate the abdomen
First 4 fingers together depress skin 1 cm
Rotary motion
Do not drag, lift fingers to next location
Do not search for organs
How to deep palpate abdomen
5-8 cm (3-4in)
Same technique as light
How do you overcome the resistance of a large abdomen?
Use bimanual technique
How to perform bimanual technique?
Two hands on top of each other
Top hand pushes, bottom hand relaxes to concentrate on palpation
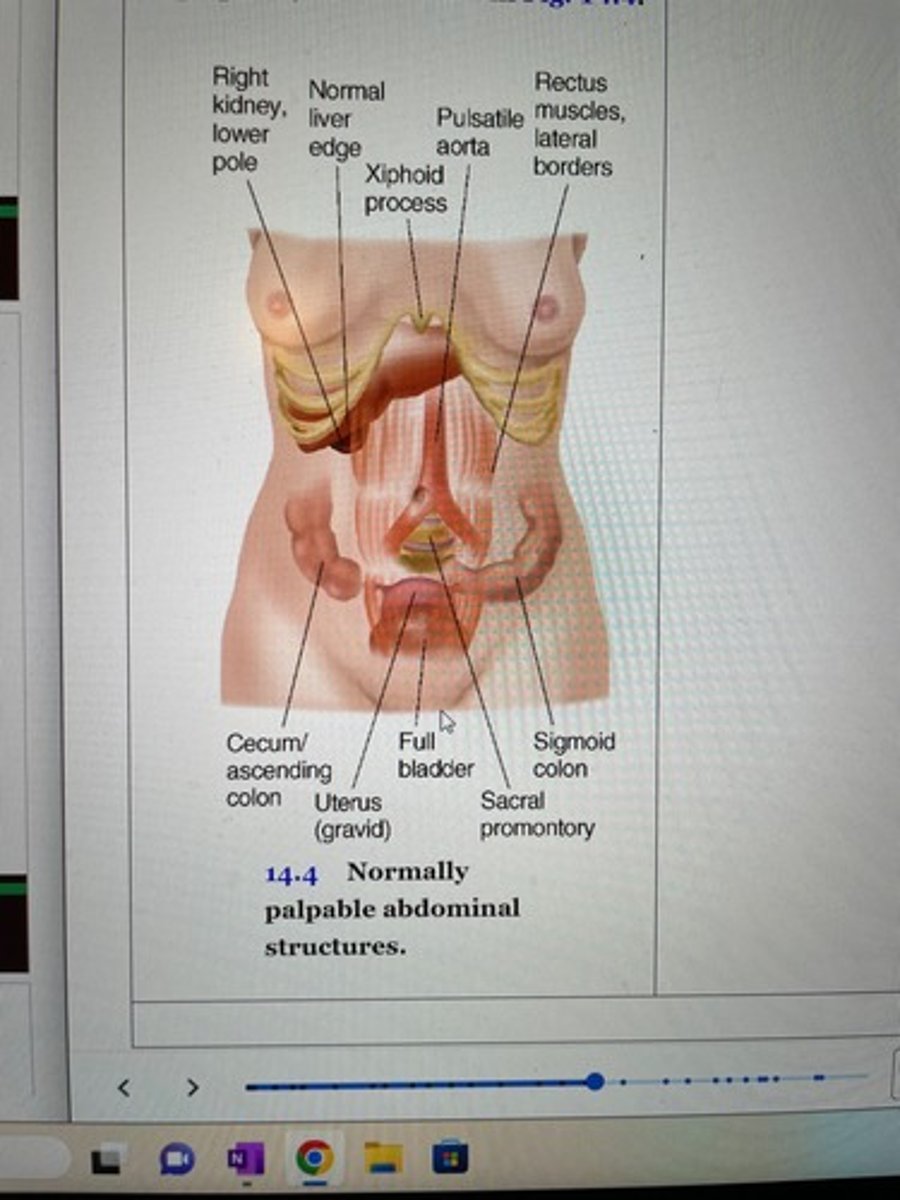
Normally deep palpable abdominal structures
Right Lower pole of kidney
Normal liver edge
Xiphoid process
Pulsatile aorta
Rectum muscles, lateral borders
Cecum/ascending colon
Uterus
Full bladder
Sacral promontory
Sigmoid colon
Normal tenderness is noted when palpating the
Sigmoid colon LLQ bc poop is being formed there
How to palpate liver
Left hand under back parallel to 11th and 12th ribs and lift up
Right hand on RUQ, fingers parallel to midline
Push deeply down under right costal margin
Ask pt to take deep breath (normal to feel edge of liver during inhalation should feel like a firm regular ridge)
Hooking technique-Murphy's sign
Alternative method of palpating liver
Stand up at pt shoulders and face feet
Hook fingers over costal margin from above
Ask pt to take deep breath (try to feel liver edge)
Enlarged liver is called
hepatomegaly
palpating the spleen: describe the technique
Reach left hand over abdomen and behind left side at 11th and 12th rib, lift up
Right hand obliquely on LUQ w/ fingers pointing toward left axilla just inferior to rib margin
Push deeply down and under left costal margin
Ask person to breath (should feel nothing)
How large is a palpable spleen
3 times normal size
If you palpate a spleen do what?
Do not palate bc it is friable and can rupture easily
Enlarged spleen
splenomegaly
Why would the spleen be enlarged?
Mononucleosis, leukemia, trauma, HIV (This organ plays a role in immune system)