UFOR 300 final exam
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What are the two types of load? What do they do?
Dynamic: Changing, variable forces on a tree (Wind, impact forces, animals, swaying motion of tree and branches)
Static: Constant, unchanging forces on the tree (Gravity, weight on the tree itself, snow and ice, signs and other objects on the tree)
Both of these loads can cause tree failure
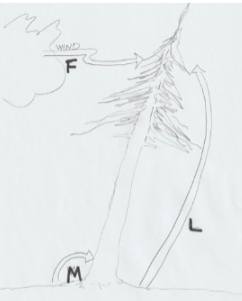
Formula for dynamic load
Bending moment (M) = Force (F) x Lever Arm Length (L)
Which level of tree risk assessment form is the ISA designed for?
Level 2- basic
What is the target zone radius?
1.5 x the height of the tree
Steps for risk assessment (basic, level 2)
360 degree tree check
Target assessment (Refer to scope of work, discuss with risk manager, timeframe), identify target zone (where the tree falls), identify occupancy rate, is the target movable?
Site assessment (Wind exposure, recent site changes (construction, soil excavation, removal of adjacent trees), regional weather conditions, topography (slope, aspect), soil (depth, drainage) root restrictions, evidence of nearby failures (root failures)
Likelihood of failure (Improbable, possible, probable, imminent)
Likelihood of impact (Very low, low, medium, high)
Likelihood of failure and impact
Mix the results o8f likelihood of failure and likelihood of impact with consequences of failure and impact
Mitigation strategy
What do decay tools do?
They do not tell you if the tree is likely to fail, or how to manage risks. Rather, they help you Which is used to detect locations of decay. Which is used to analyze the health of the whoel tree
What are some risk assessment tools?
Resistance drilling- drills a hole in the tree and makes a graph based on the wood quality of the tree- gives small portion of tree
Sonic topography - hangs the device around the tree, you then hammer some nails connected to the device, and demonstrates the results of the tree on the device - gives a small portion of the tree
Static pull test - tests how wind firm a tree is by attach a elastoeter on the trunk of the tree, measuring compression + tension forces, and a pulley wire (winch) to apply a large force, simulating wind, to to determine data.
Cable
-Support systems that uses wires or ropes between branches
Brace rods
Threaded with steel rods fastened with nuts, reinforces cracks and provides additional strength
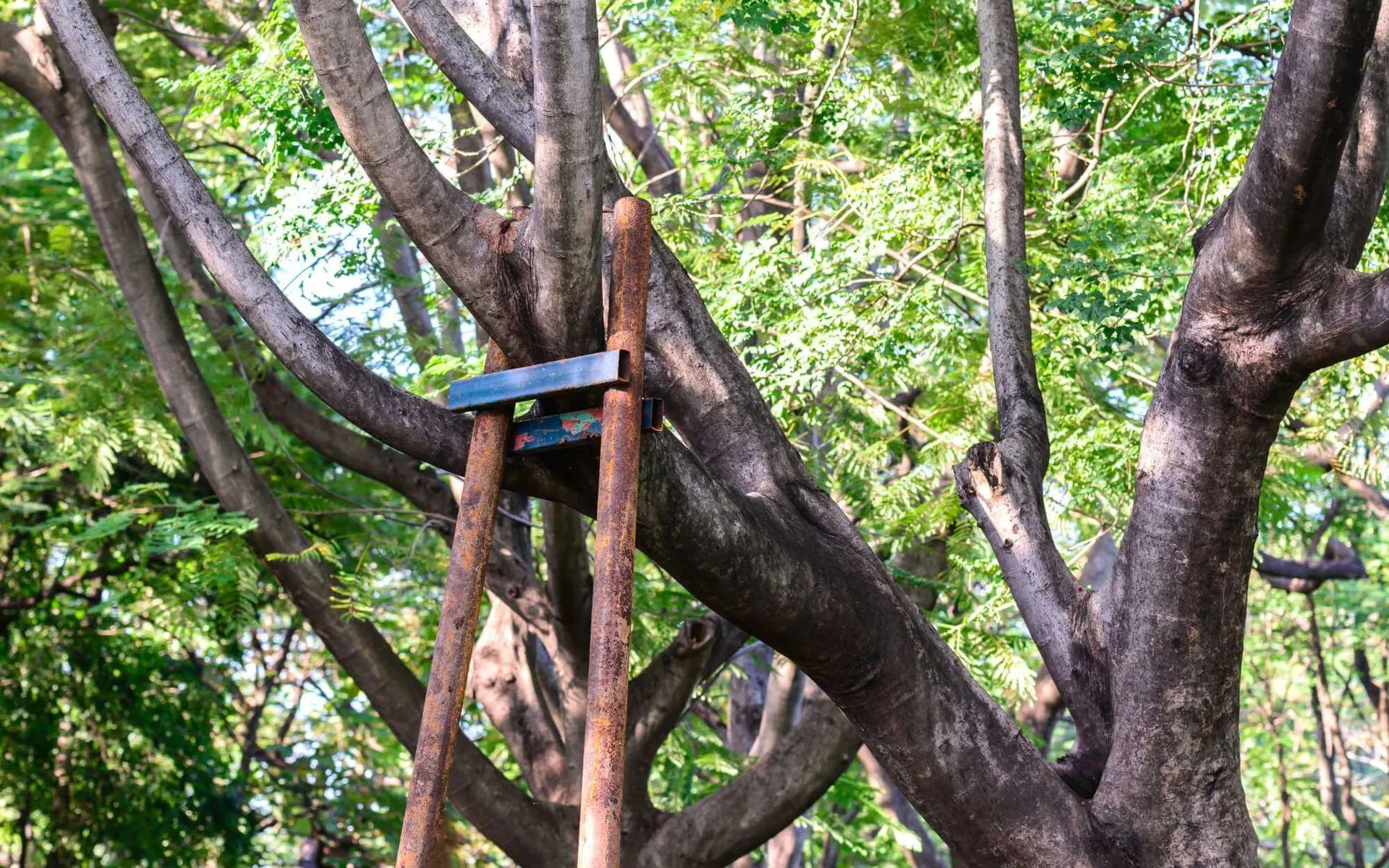

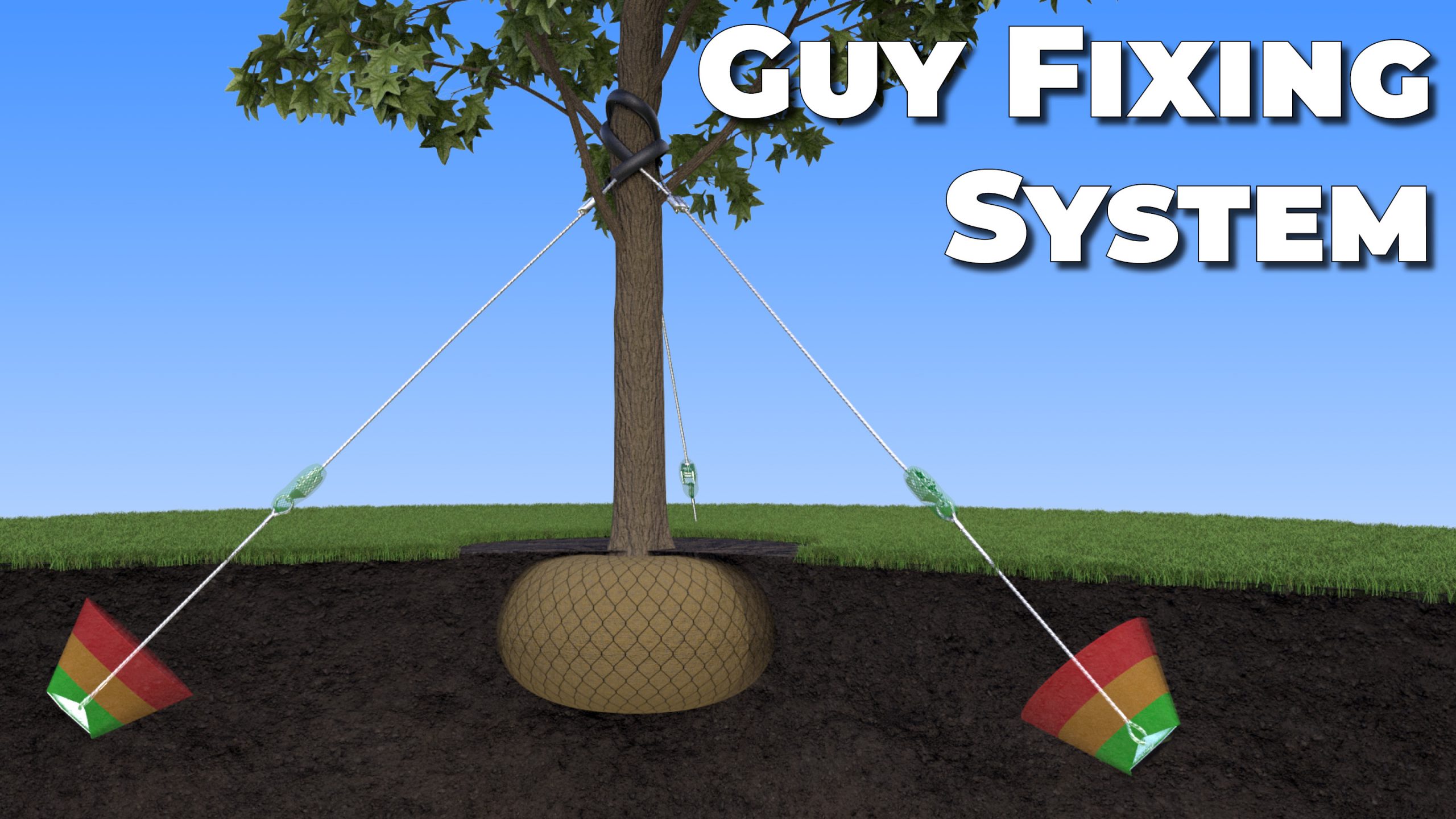
Guys
Support systems using wire or rope run from tree to soil or anchor tree
Prop
Support system using rigid structures to support weight from below

What is risk mitigation in arboriculture defined as?
An action taken to reduce risk
How does tree-based mitigiation rwork?
It reduces the likelihood of failure and/or impact
What is a way for target-based mitigation actions in the public city?
Rerouting pedestrian traffic
When is “retain and monitor” used?
When tree mitigation is not necessary
How can pruning reduce risk?
By reducing branch length and/or density
Why are support systems used?
To limit movement to reduce breakage likelihood
What is the primary goal of a cable in codominnt stems?
Restrict movement before reaching critical angles that cause failures of trees
When installing a cable in a tree, the standard attachment height is:
Two-thirds of the stem length above the union
For over-extended branches, cable should anchor aproximately
40-50% of the branch length
Extra High Strength (EHS)cable has:
-The highest tensile strength among common cable types listed
How long should fiber (rope) cabling systems be generally considered for?
Short term (<5 year) systems with annual inspection
When should brace rods be used?
Cracks are present or cables cannot be used
When should tree props be recommended?
Low, long horizontal branches are at high risk and cables are insufficient
What is a lightning protection system intended to do?
Carry electrical charge safely to the ground
A common target-based mitigation strategy is to
Move or restrict access to targets
What two things does risk mitigation do?
Involving reducing either the likelihood and/or of failure or likelihood of impact
Should dead end grips be cut
Never, since the structural integrity of it can be damaged when cut
A common threshold level of live crown ratio for conifers in our region (below which they do not respond well to land development) is...
30%
For an individual, specimen tree, the best way to estimate the size of the CRZ is based on...
Tree dbh
What is a Critical root zone
Also known as the tree protection zone, is the minimum area around a tree that must be protected to keep the tree healthy and structurally stable during construction, excavation, or site work
A 40-cm dbh red alder (Alnus rubra) that is in average condition is likely to be...
of low suitability for preservation because it is short lived and has low tolerance for construction
According to Table 6.2, compared to younger trees of the same size, older trees require...
larger tree protection zones (or CRZs)
A tree with a high height:diameter ratio may be likely to be...
Unstable when exposed to wind
You wish to preserve trees in Totem Park, a one-block park dominated by a stand of large evergreens. What is the primary risk of keeping a small group of trees and removing others?
that edge trees in this group will not be windfirm and will fail
Prior to approving a plan for land development, it is very typical for municipalities to require...
An estimate of the proportion of the site covered by tree canopy
What grows from callus tissue following root injury?
New roots
What is calus tissue
Response to mechanical stress and injury, form over the affected area to seal the wound and prevent decay, are a thickened mass of cells
What phases of site development should a arborist be in?
All of them
Which tree structure is commonly damaged during construction activities?
Root system
What is the primary purpose of ANSI A300 Part 5?
To provide guidelines for managing trees during site planning and construction
Which pruning method can reduce wind resistance when roots are damaged?
Crown reduction pruning
A minimum TPZ radius of 1.5 m (5 ft) is recommended for trees with DBH less than:
25cm
A one-sided root cut at 6× DBH typically does not affect tree stability in healthy, tolerant species.
True
What treatment is most important during post-construction recovery?
Irrigation
Which phase involves staking layout, demolition, and site clearing?
Preconstruction
Which actions help improve drainage post-construction?
Installation of drain pipes, drill holes, radial trenching
What is a defect in a tree?
Any condition that reduces structural strength
What are shear plane cracks?
Fractures in materials, especially trees, that occur when oppossing compression and tension forces slide past each,, occurs above ground
The “1/3 Rule” for hollow stems suggests a tree may have sufficient strength if the cavity is less than ___ of the stem diameter.
2/3rd
Included bark between co-dominant stems decreases the strength of the __________.
Union
Branch union
Where a tree branch joins the trunk
What is the likely outcome for newly exposed conifer stands with low live crown ratios (<20%)?
Probable failure of edge trees
Can girdling by roots cause possible failure before the tree actually die?
Girdling roots have potential to be fatal to a tree but also disrupt adequate formation of structural roots affecting tree stability. So, in a serious wind or excessive loading event, the tree can fail.
Where do shear planecracks occur?
Along the neutral plane between tension and compression forces
Are trees with multiple stems arising close to the ground less likely to fail than those with higher attachments?
Trees with higher attachments are more likely to fail, because of gravity and higher compression and tension wood as the tree is less stable.
Risk
A state of uncertainty where there is potential for something undesirable or even catastrophic to happen.
Failure
It means a piece of the tree broke or fell down.
Defect
It means that there is a tree characteristic that might contribute to failure.
Target
Something that could be damaged/injured by a failure.
According to research, many tolerant species can survive what percentage of root loss?
25-33%
Where are roots most often locate?
In shallow soil, wide-spreading soil configurations, because they cannot grow down.
A Tree Protection Zone (TPZ) radius is calculated by multiplying DBH by a factor based on:
Species and age
Four professional organizations relevant to urban foresters/arborists
ISA = International society of arboriculture
UCFS = The urban and community forestry society
PNCISA= Pacific Northwest Chapter of the ISA
CUFN = The Canadian Urban Forest Network
Certification
A voluntary program administered by a non-governmental organization. It grants the use of credential to individuals for a specific period of time
Qualification
This is awarded for achievement of a narrow body of knowledge body of knowledge with very learning objectives.