Organic Chemistry II Final Review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Kinetic Product = ?
Thermodynamic Product = ?
-Kinetic product is the one that forms at the fastest rate (from lowest energy transition state, look at carbocation)
-Thermodynamic product is the most stable final product (look at substitution around double bond)
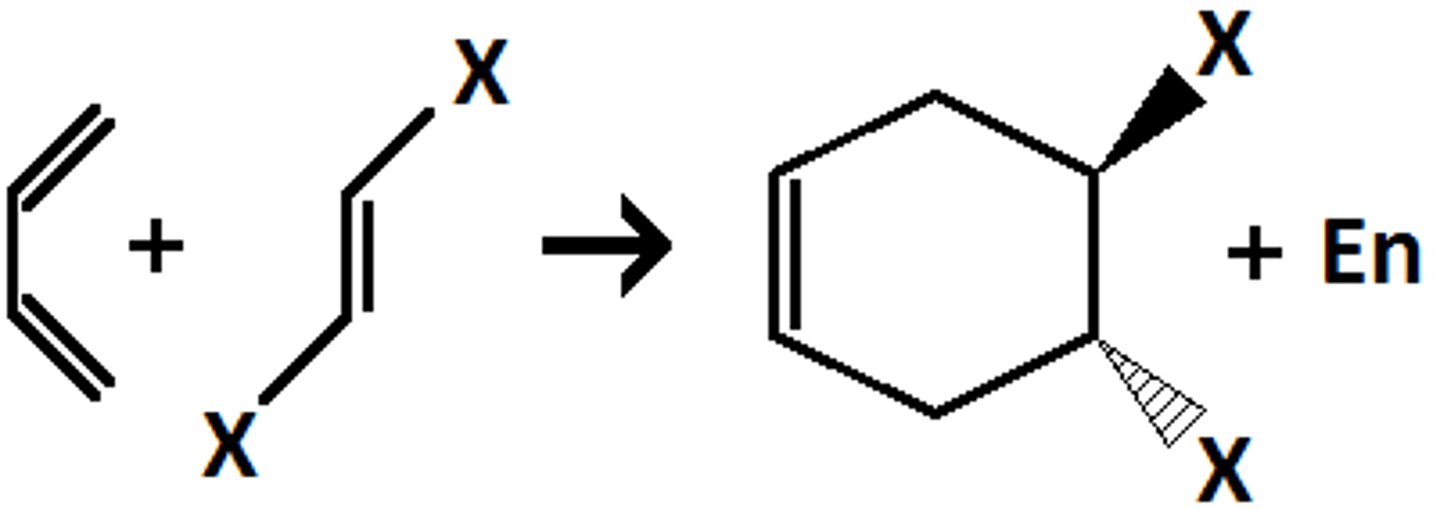
Diels Alder Reaction
-reagent?
-accelerated by ___ on diene and ___ on dienophile
-endo or exo?
-heat
-accelerated by EDG on diene and EWG on dienophile
-in bicyclic products, always get the endo product where bridge points away from the substituents
EDG or EWG?
a) -NR C=O R2
b) -CN
c) -NR1R2
d) -NO2
e) Br
a) EDG
b) EWG
c) EDG
d) EWG
e) EWG but directs ortho, para
What effect does it have on ortho, meta, para positions?
-Electron donating group
-Electron withdrawing group
-EDG: slight negative on ortho, para (direct electrophiles ortho, para)
-EWG: slight positive on ortho, para (direct meta)
Huckel's criteria for Aromatic Compounds (4)
1. Cyclic
2. Have one p-orbital on each ring atom
3. planar
4. Have 4n + 2 electrons in p-orbitals where n is a whole number
Cl2, FeCl3
Br2, FeBr3
Add Cl or Br to aromatic ring (Chlorination or Bromination)
(Mechanism: Cl+, FeCl4-, electrophilic addition, byproducts: HCl, FeCl3)
HNO3, H2SO4
Add NO2 to aromatic ring (Nitration)
(Mechanism: NO2+, electrophilic addition)
SO3, H2SO4
Add SO3H to aromatic ring (Sulfonation)
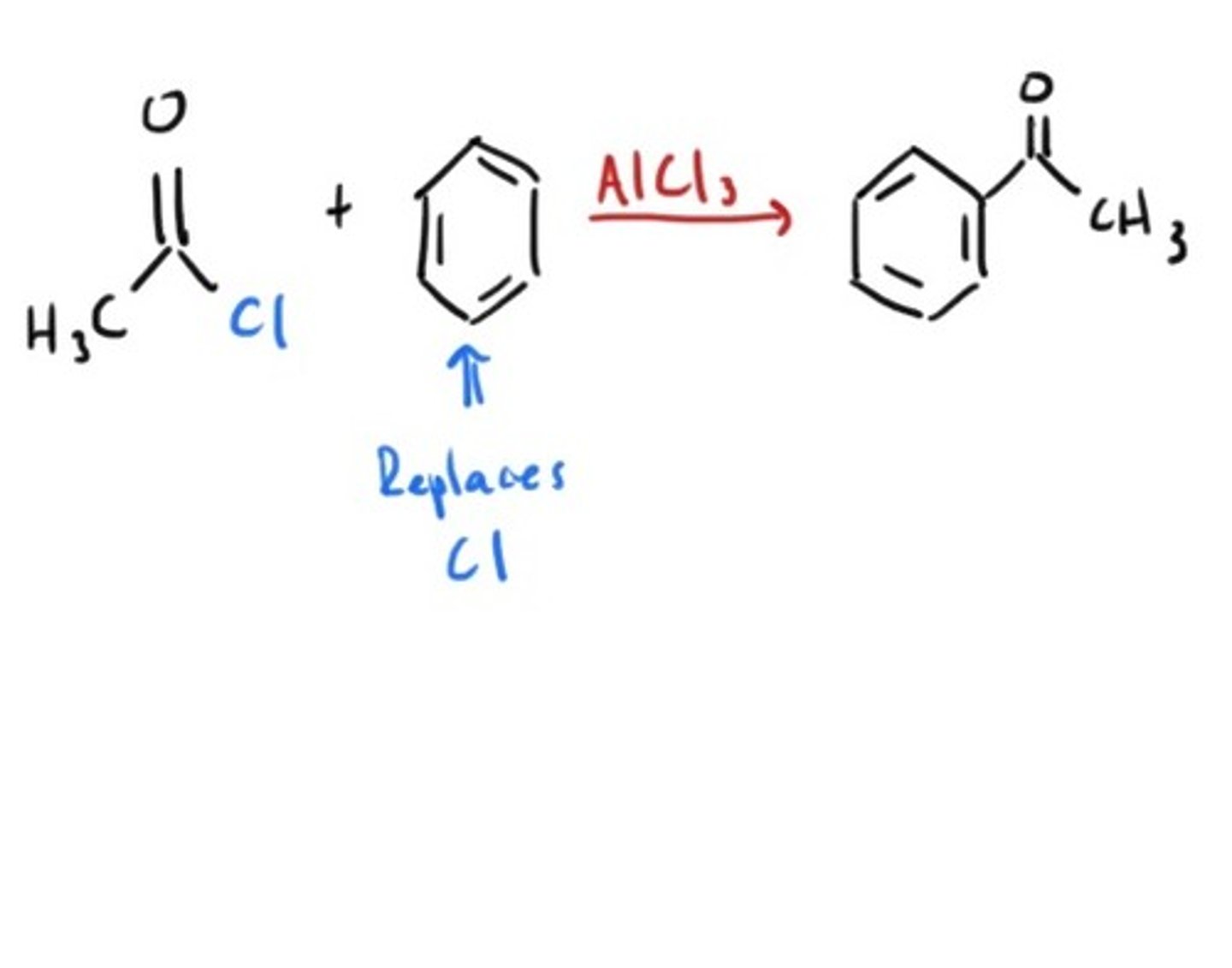
R C=O Cl
AlCl3
Friedel Crafts Acylation
RCl
AlCl3
Friedel Crafts Alkylation
N2H4, KOH
Wolff-Kishner reduction, reduce ketone to CH2 group
H2, Ni
Reduction of Nitro to Amino Group (NO2 --> NH2)
Draw Benzene, Pyridine, Pyrrole, Furan, Thiophene
Look online.
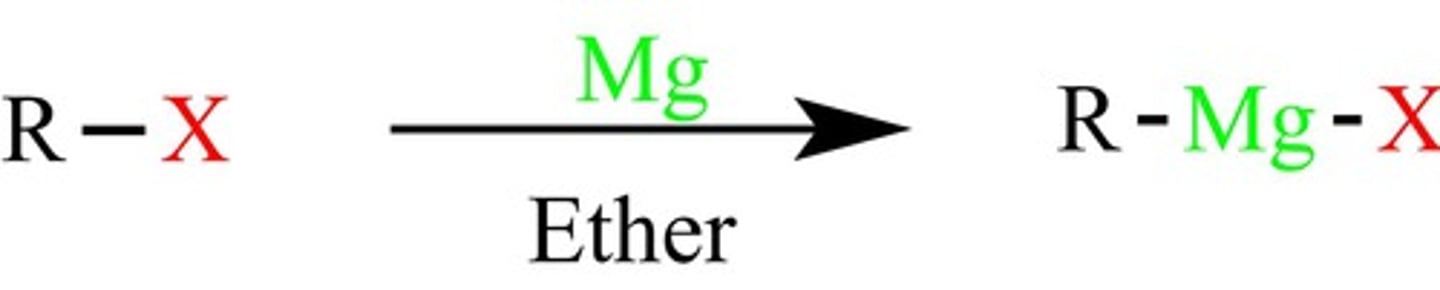
1. R-Mg-X (Grignard)
2. HCl, H2O
Grignard, Attack the carbonyl carbon and add new C-C bond, protonation of oxygen to form alcohol after
1. R-X + 2 Li
2. HCl, H2O
Organolithium reaction, attack carbonyl carbon and add new C-C bonds, protonation of oxygen to form alcohol after
Starting: R-Br
1) PPh3
2) nBuLi
3) R2C=O
Wittig Reagent (R2C = PPh3), reacts with carbonyl carbon
1,2) React with R1-X to make R-PPh3
3) PPh3 replaced by R1=CR2 (R1 added where =O was)
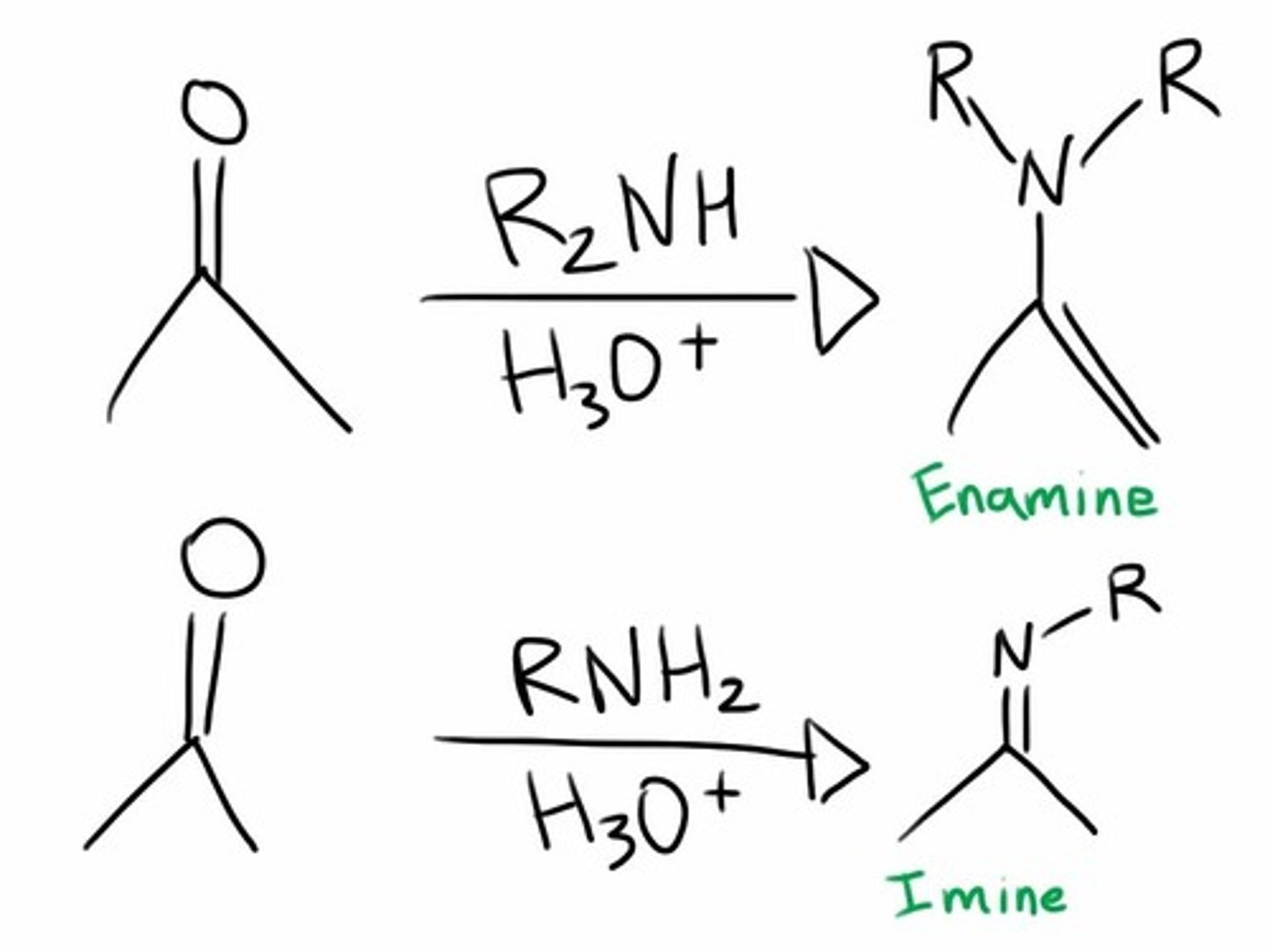
R-NH2 + aldehyde or ketone + H+(cat)
Nitrogen Nucleophiles to Aldehydes and Ketones
Primary Amine = Imine (C=O converts to C-NR, deprotonation turns to C=NR)
Secondary Amine = Enamine (same except deprotonation happens on hydrogen on alpha carbon next to carbonyl)
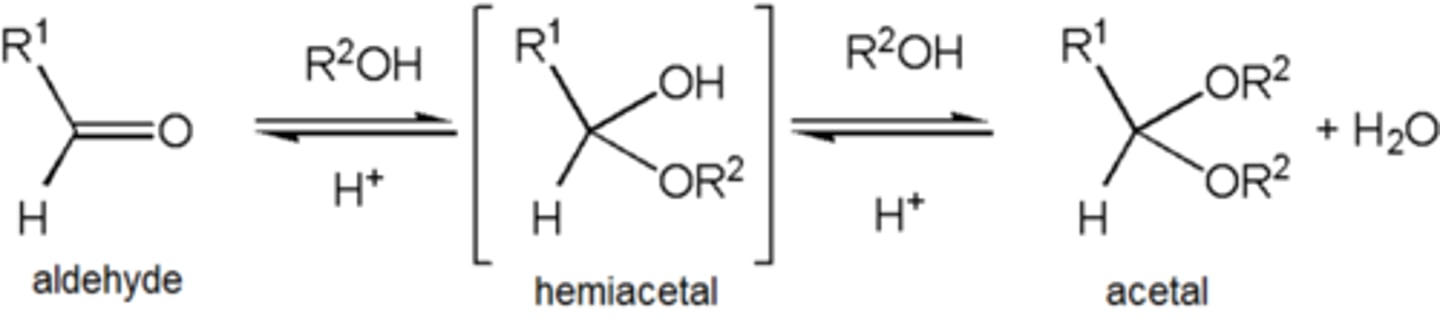
ROH (alcohol) + Aldehyde
Addition of Oxygen Nucleophiles to Aldehyes and Ketones, (Alcohols are too weak to attack carbonyl group by themselves, acid catalyst used to attach onto carbonyl oxygen) (Mechanism: Protonation, R-OH attacks, Hemiacetal, water leaves, R-OH attacks again, acetal)
End Result: R-OH + C=O to RO-C-OR (acetal)
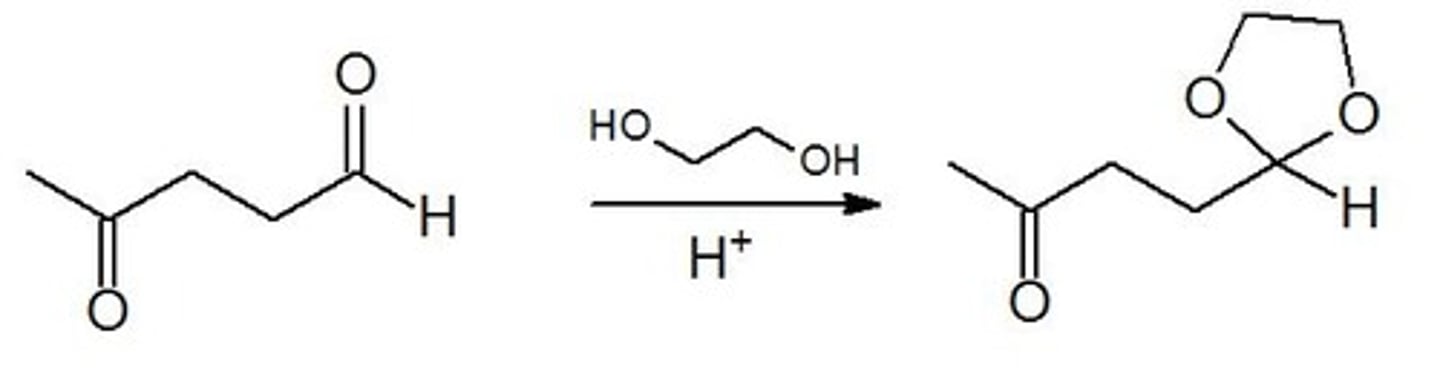
1. 1,2 Diols + Aldehyde or Ketone, H+ (cat)
2. HCl, H2O
1. Protecting Group for C=O
2. Deprotection
Chromic Acid H2CrO4
Strong Oxidation (primary OH--> COOH, aldehyde --> COOH, secondary OH --> ketone)
PCC
Mild Oxidation (Primary OH --> aldehyde, and secondary alcohol --> ketone, no rxn with aldehyde)
H2/Pt or H2/Ni
Catalytic Reduction (reduces both C=C (to C-C) and C=O (to OH)- only aldehydes, not COOH)
H2/Rh
Selectively reduces C=C bonds
NaBH4/ EtOH
Reduction, Reduces ketones and aldehydes to OH
1) LiAlH4 2) H+, H2O
Superreducer, Reduces everything to OH (not C=C bonds)
R- Aldehyde + NaOH, H2O
Aldol Product (ketone + alcohol) --> Dehydration Product
(Mechanism: alpha carbon of aldehyde deprotonated by OH-, attacks another aldehyde, alkoxide turns to OH b/c of H2O, remove hydrogen in between C=O and C-OH, enolate eliminates hydroxide anion creating a carbon double bond)
Starting Compound: Two Ketones or Aldehydes or Mix, one alpha hydrogen, 3 or 4 atoms separating alpha carbon of one carbonyl carbon from another
Intramolecular Aldol Reaction
Starting: R-Aldehyde or Ketone
Reagent: 1) LDA 2) Aldehyde-R 3) H2O
Directed Aldol Reaction (Favor formation of enolate on less substituted carbon)
Starting: Enolate (LDA and R-Aldehyde or Ketone)
Reagent: R-X
Reaction of Lithium (LDA) Enolates with Alkyl Halides (SN2, R adds onto negative charge on enolate)
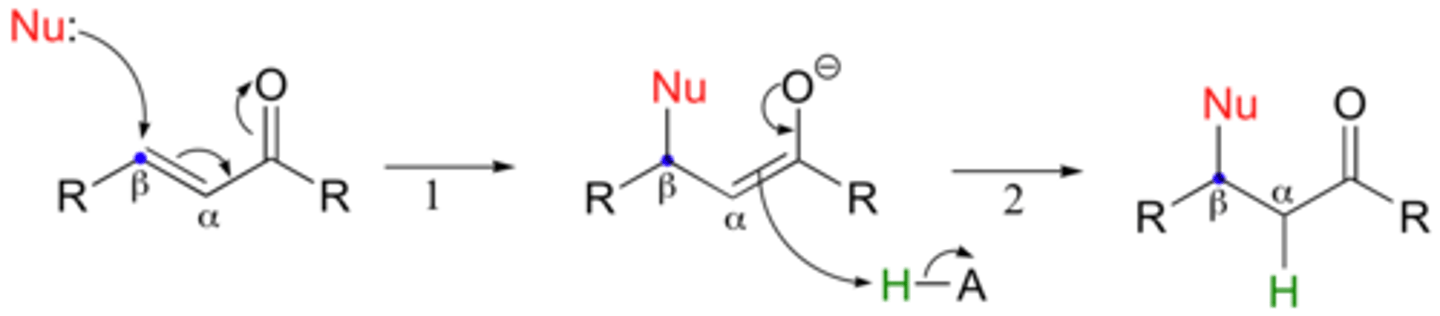
alpha, beta unsaturated aldehyde, ketone
1. What nucleophiles attack at C=O?
2. What nucleophiles attack at beta carbon?
1. R-Li and R-MgBr strong enough to interact with carbonyl carbon
2. Enolates, Gilman Reagents, and Amines interact with beta carbon
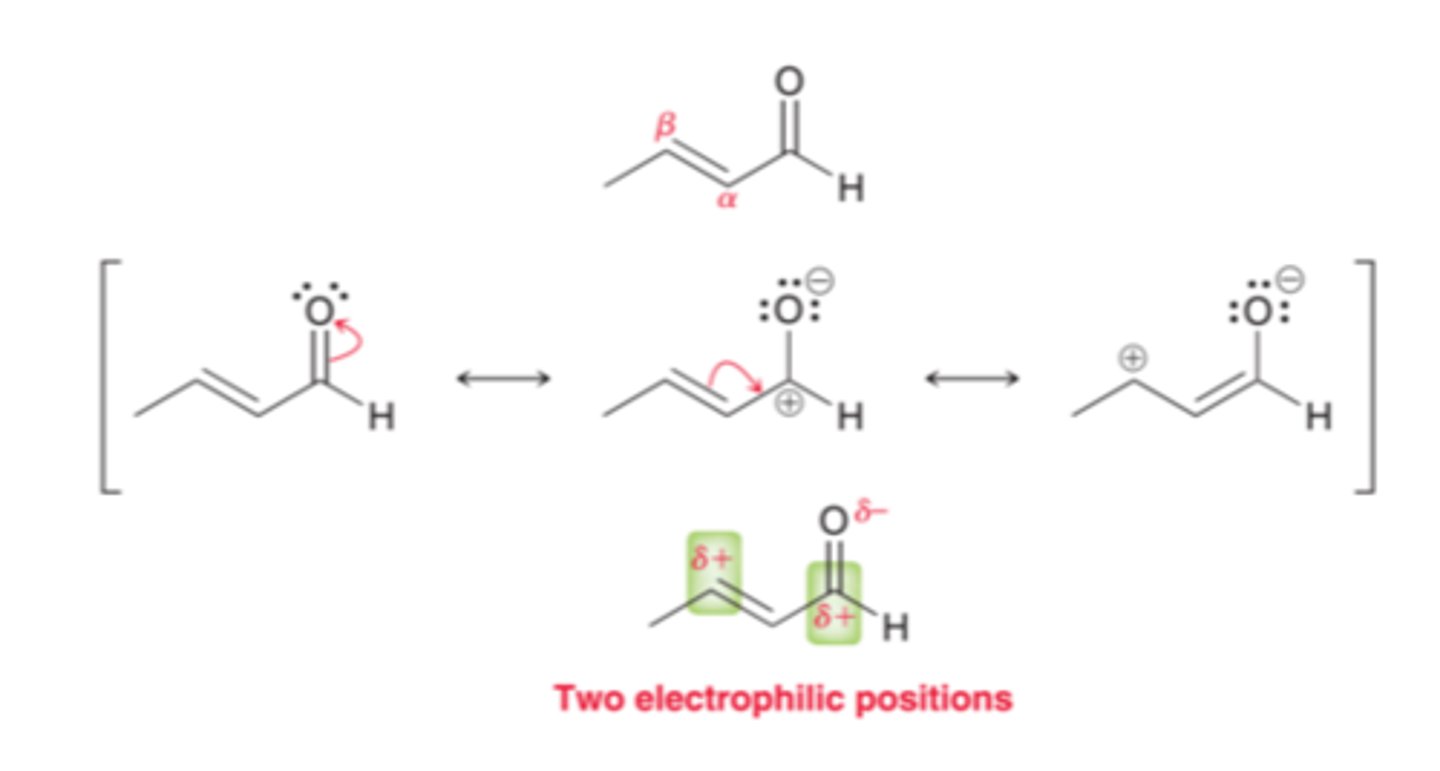
Starting: Enolate (LDA and R-Aldehyde or Ketone)
Reagent: Alpha-beta unsaturated ketone
Michael Reaction: generate 1,5-diketone
(in pic: Nu is enolate)
a) 1,3-diketone with at least one alpha-hydrogen in between two ketones
b) alpha-beta unsaturated ketone
c) moderate base like NaOH
Robinson Annulation: Base-catalyzed Michael reaction, intramolecular base-catalyzed aldol reaction and dehydration for final product
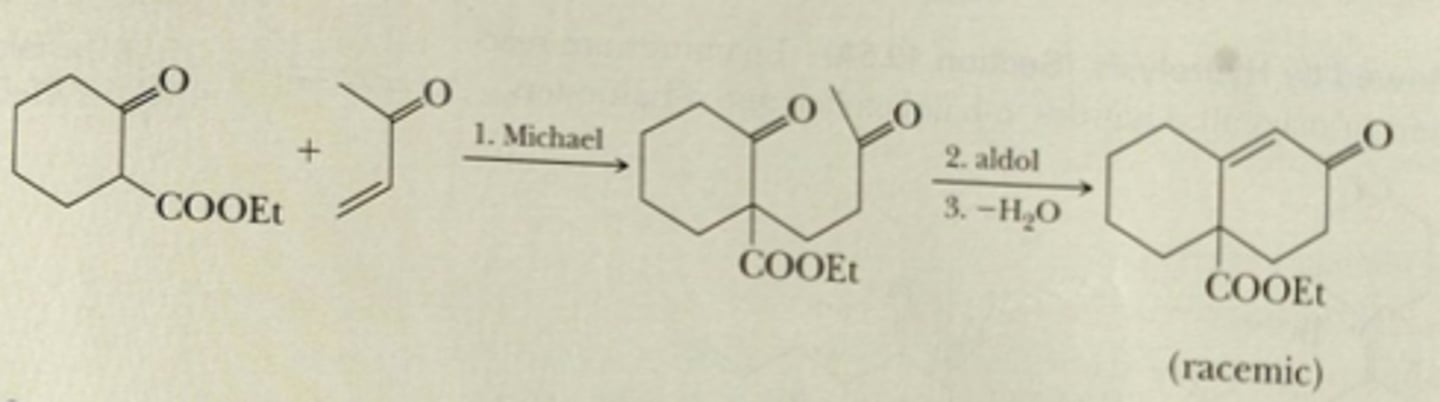
Starting: alpha beta unsaturated compound
1) (R)2CuLi, -78 C
2) H2O
Gilman Reagent with alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl compound
(Details: add just ONE R to beta carbon)
Starting: alpha beta unsaturated compound
Reagent: R1R2NH (ex. (CH3)2NH)
Reaction of Amines with alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl compound
(Details: NR1R2 added to beta carbon)
Chemical Shifts of important protons (ppm)
1) Aldehyde
2) Carboxylic Acid
3) Aromatic Protons
IR stretches
4) C=O
5) OH
1) 9.5-10.1
2) 10-13
3) 6.5-8
4) 1700
5) 2400-2400
Factors Contributing to Acidity of the Carboxylic Acid
a) Electronegativity
b) Number of Substituents
c) Location of Subtituent
a) more electronegative (Br=EWG) = more acidic
b) number of EWGs up = more acidic
c) closer EWG is to carboxylic acid group = more acidic
Starting Material = Aromatic Ring
KMnO4
Oxidation of Benzylic Carbons (carbon bonded directly to a benzene ring)
Starting: R-Li or R-MgBr
1) CO2 2) HCl, H2O
R-Carboxylic Acid
Carboxylic Acid + Alcohol
H+ (cat)
Fischer Esterification- Ester
(Mechanism: Protonation of Carbonyl Oxygen, Attack by ROH, Water Leaves, Formation of Ester) (Replace H with R on OH of COOH)
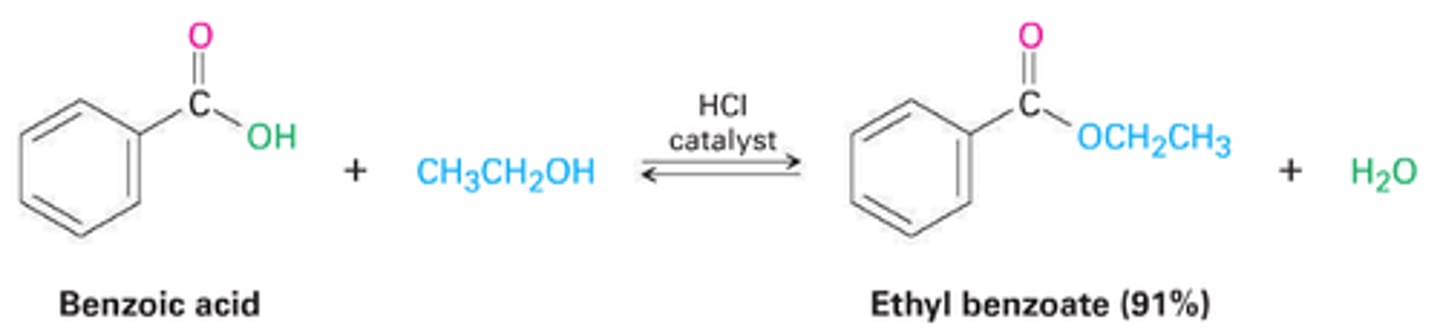
1. Carboxylic Acids undergo ____ with nucleophiles.
2. Ketones and Aldehydes undergo ____ with nucleophiles.
1. Addition then elimination
2. Addition then protonation
Reactivity Order of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Acid Chloride > Anhydride > Ester > Amide

Convert Carboxylic Acid to Acid Chloride
SOCl2 (Thionyl Chloride), pyridine
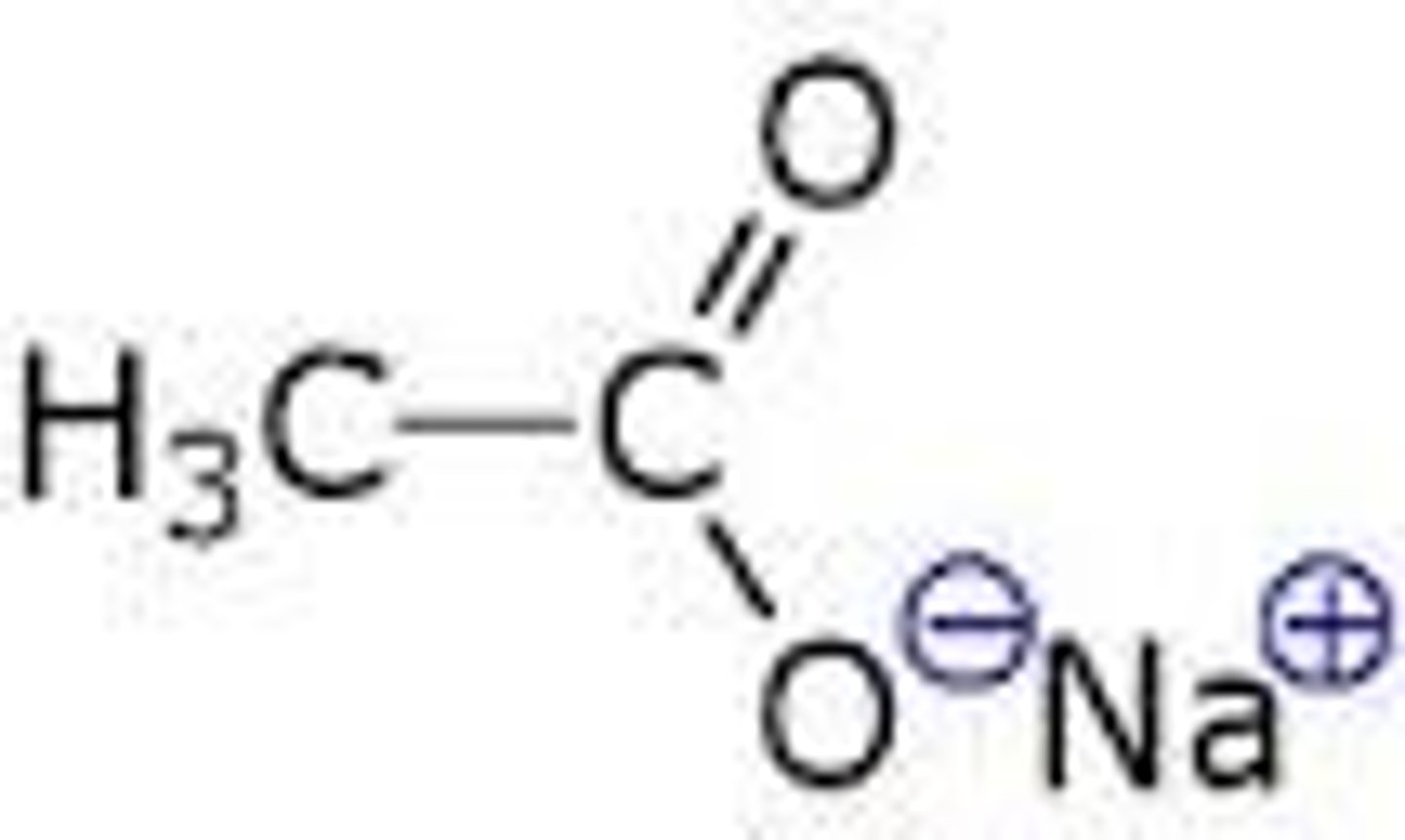
Acid Chloride + Carboxylate Salt, pyridine = ?
Anhydride, pyridine
Acid Chloride + R-OH, H+ = ?
Ester (Fischer esterification)
Acid Chloride + Amine, pyridine = ?
Amide
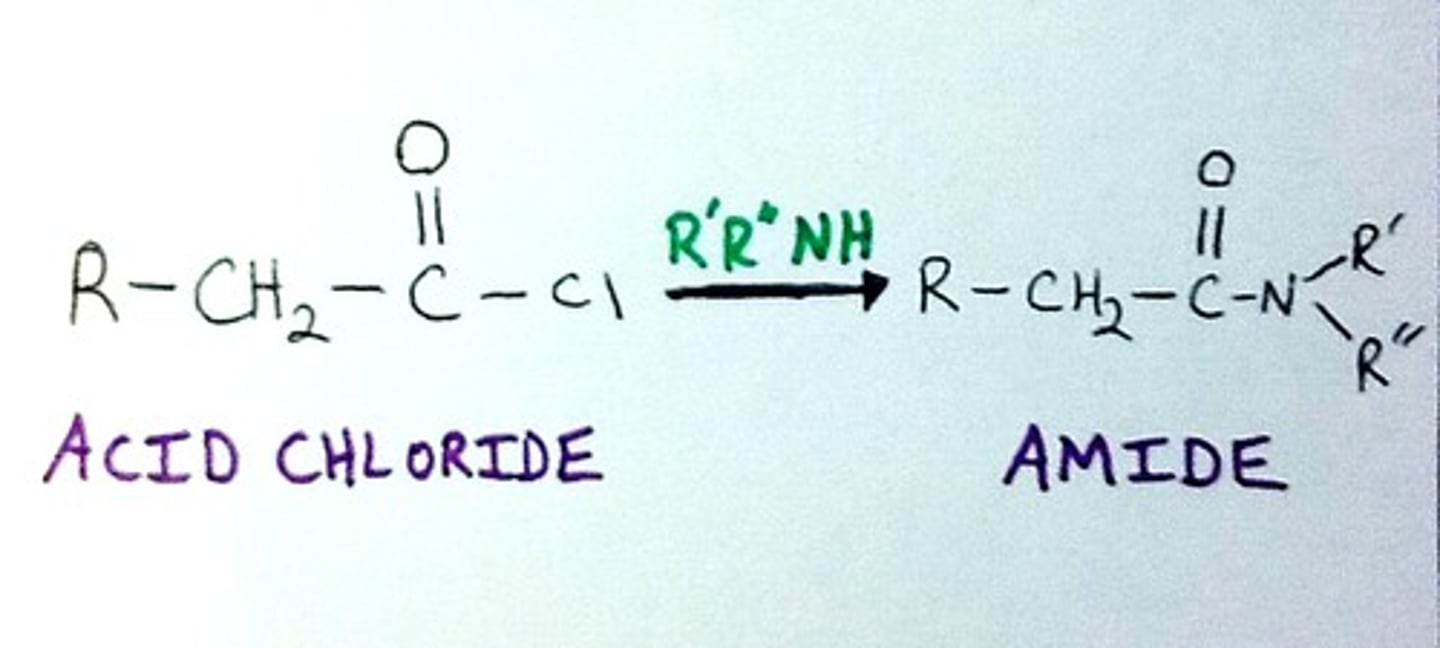
Convert Carboxylic Acid to Anhydride
R C=O Cl
Convert:
1) Anhydride to Ester
2) Anhydride to Amide
1) Alcohol, pyridine
2) Amine, pyridine
Convert Ester to Amide
Amine, pyridine
Convert Carboxylic Acid to Amide Directly
Amine, DCC
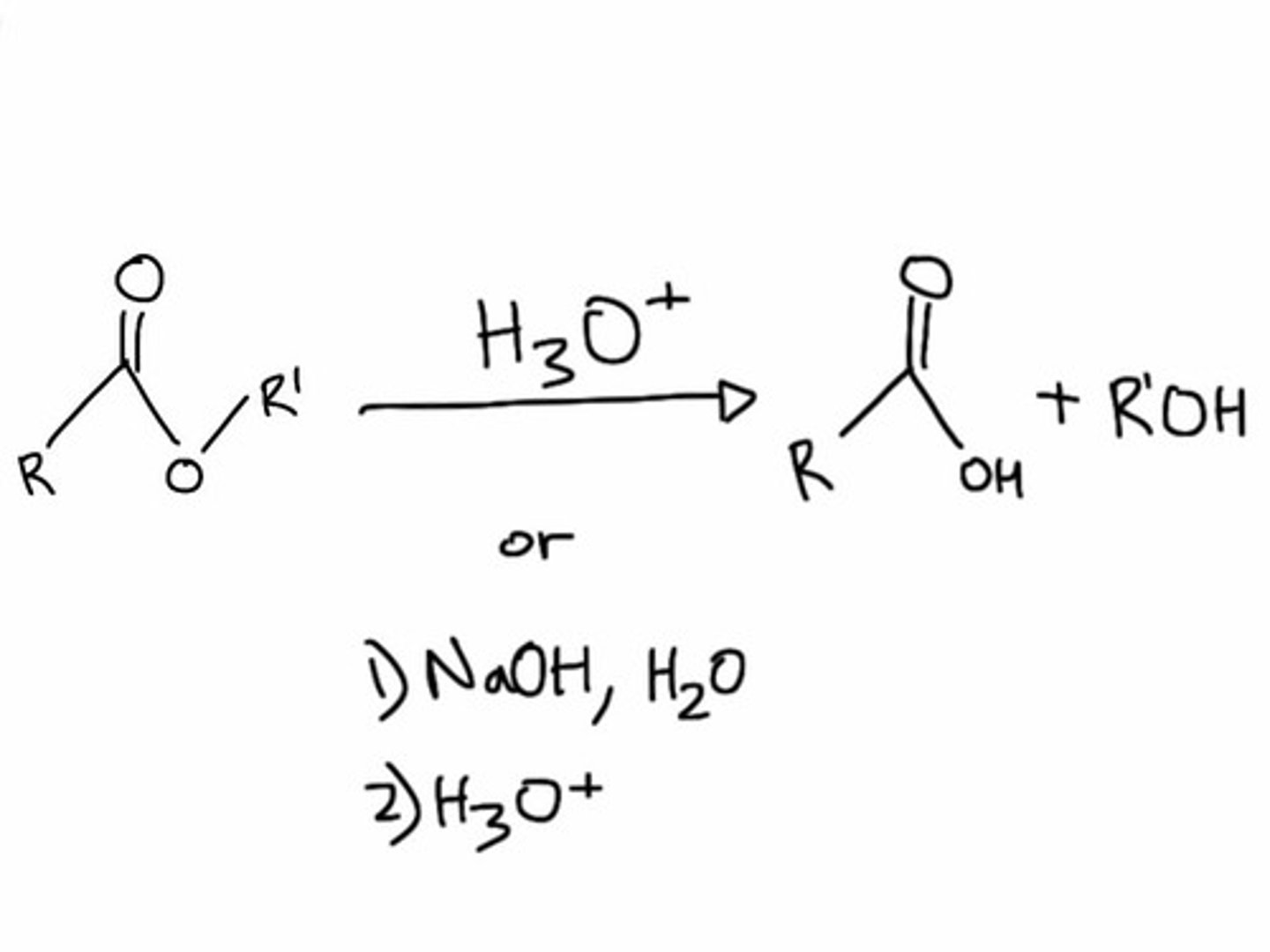
Starting: Ester
Reagents: 1) NaOH, H2O 2) HCl
Hydrolysis of Esters in Basic Conditions (OH-)
Convert Ester to Carboxylic Acid
(Mechanism: OH- attacks carbonyl carbon, elimination of OR-, deprotonation by OR-, protonation by HCl)
Starting: Ester
Reagents: H+ cat, H2O
Hydrolysis of Esters in Acidic Conditions
Convert Ester to Carboxylic Acid
(Mechanism: protonation of carbonyl oxygen, addition of H2O, protonation of OR, HOR leaves)
Starting: Amide
Reagents: H+ cat, H2O OR
NaOH, H2O
Hydrolysis of Amides in Basic or Acid Conditions
Convert Amides to Carboxylic Acid
(Mechanism Acid: Protonation of Carbonyl Oxygen, Addition of H2O, Protonation of NHR, NH2R leaves, Deprotonation to form COOH)
(Mechanism Basic: OH- attacks carbonyl caron, NHR leaving group, deprotonation by NHR)
Polyesters are formed from ____ and _____.
alcohol
carboxylic acid, acid chloride, or anhydride
Polycarbonates are formed from _____ and ______.
Phosgene Cl C=O Cl and 2 ROH or diol (HO-R-OH)
Polyamides are formed from ____ and _____.
amine
carboxylic acid, acid chloride, anhydride, or ester
Starting Chemical Synthesis of Polypeptide
Bead-Ch2Cl
Attach COOH to the Bead?
K2CO3 (deprotonates COOH, and attaches to Bead-Ch2Cl, displacing Cl)
1. Amine Protecting Group
2. Removal of Amine Protecting Group
3. Coupling Reaction (activation of COOH)
1. BOC
2. TFA (RNHBoc --> RNH2)
3. DCC
HF
cleavage of peptide from bead, bead-CH2-F
Starting: Ester
1) R-MgBr (2 equiv.)
2) HCl, H2O
Reaction of Esters with Grignard and Organolithium Reagents
(Effect: Ester (R C=O OR), C=O --> C-OH, OR' leaves and replaced by two R from R-MgBr)
Starting: Acid Chloride
1) (R)2CuLi -78 C
2) H2O
Reaction of Acid Chlorides with Gilman Reagents
(Effect: Cl replaced by one R from (R)2CuLi)
Starting: Ester
1) LiAlH4
2) HCl, H2O
Reduction of Esters and Amides by Hydride Reagents
RC=OOR --> RCOH
1) DIBALH, -78 C
2) H2O
Conversion of Ester to Aldehyde
Starting: Amide
1) LiAlH4
2) HCl, H2O
Reduction of Amides with LiAlH4 converts Amide to amine (gets rid of =O)