A-Level Chemistry AQA - Energetics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
define the term ‘enthalpy’
the thermodynamic property of a system linked to it’s internal energy
define the term ‘enthalpy change’
heat energy change at constant pressure
define the term ‘endothermic’
takes in heat energy from surroundings
define the term ‘exothermic’
gives out heat energy to the surroundings
what are standard conditions?
100kPa
298K
define the term ‘enthalpy of formation’
enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is produced from its elements under standard conditions
define the term ‘enthalpy of combustion’
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions
what does the term endothermic refer to in terms of bond breaking and bond making?
more energy taken in breaking bonds than is given out making bonds
what does the term exothermic refer to in terms of bond breaking and bond making?
more energy given out making bonds than is taken in breaking bonds
what is the difference between a reaction profile and a reaction pathway diagram?
reaction profile only shows enthalpy change
reaction pathway shows enthalpy change and activation energy
what does an endothermic reaction profile/reaction pathway diagram look like?
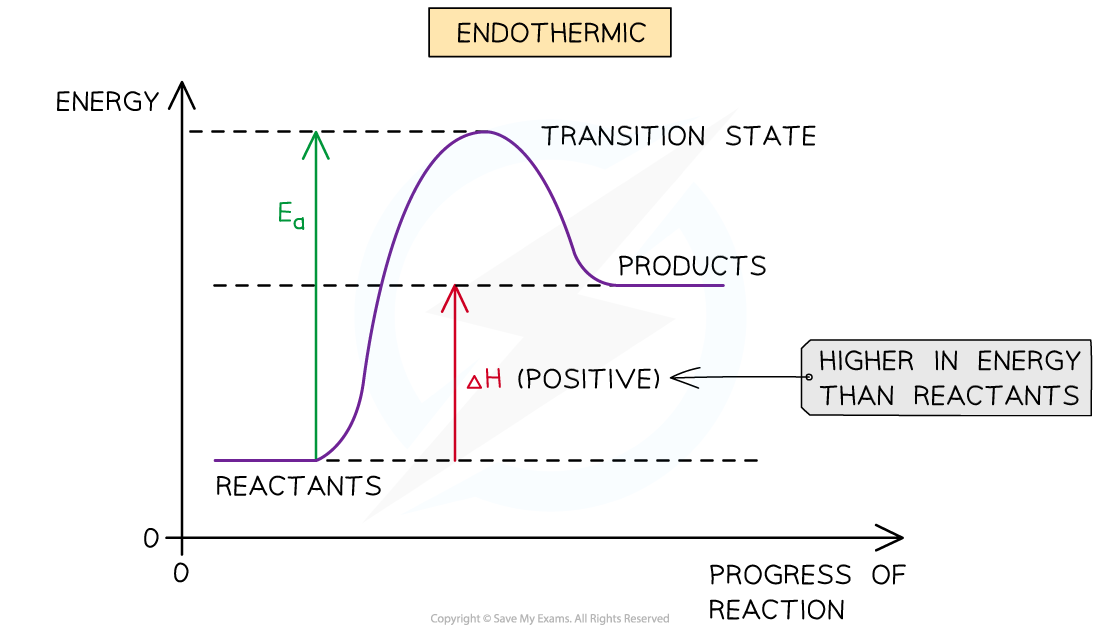
what does an exothermic reaction profile diagram look like?
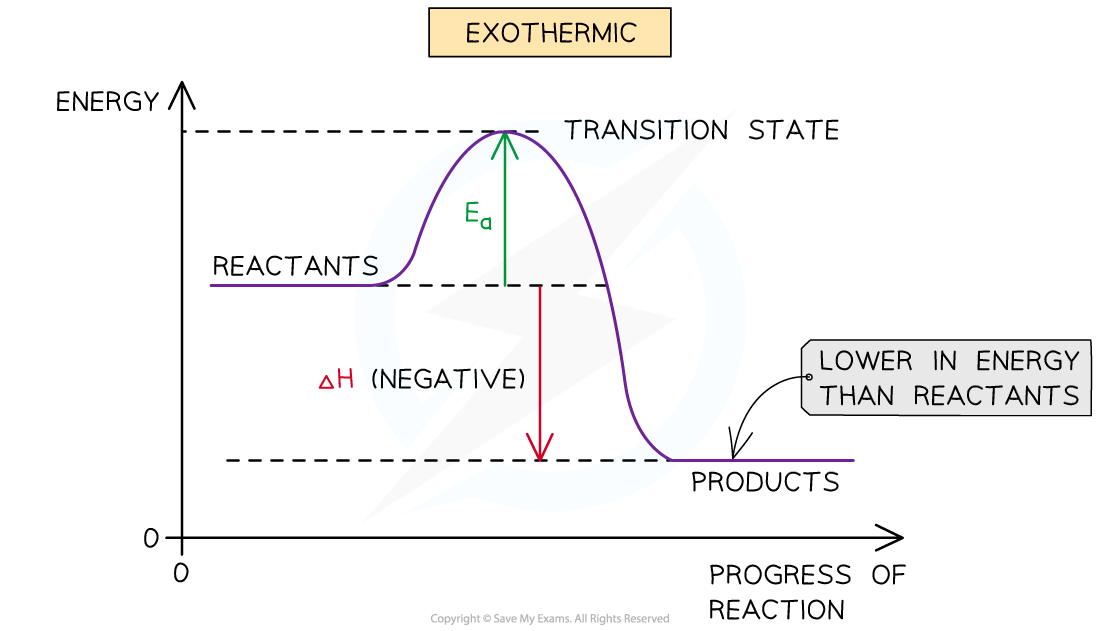
define the term ‘activation energy’
the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
what is calorimetry?
experimental methods used to find enthalpy change by measuring temperature change over time
what is the formula for energy change?
Q (J) = m (g) x c x Tc (K)
what is the formula for enthalpy change?
enthalpy change = -Q (KJ) / n (mol)
use moles of limiting reactant
describe how you would carry out the practical for measuring an enthalpy change (not combustion)?
measure out 25cm³ of NaOH
add to polystyrene cup in a beaker
measure out 25cm³ of HCl
record the temperature of NaOH at minute intervals for 3 minutes
at the 4th minute, add HCl and don’t record the temperature
continue recording the temperature every minute after that for 10 further minutes
plot a graph of temperature against time
draw two lines of best fit for before + after addition
extrapolate the two lines
find the maximum temperature at the point of addition
use this for calculations
what should a graph of temp against time for measuring enthalpy change look like?
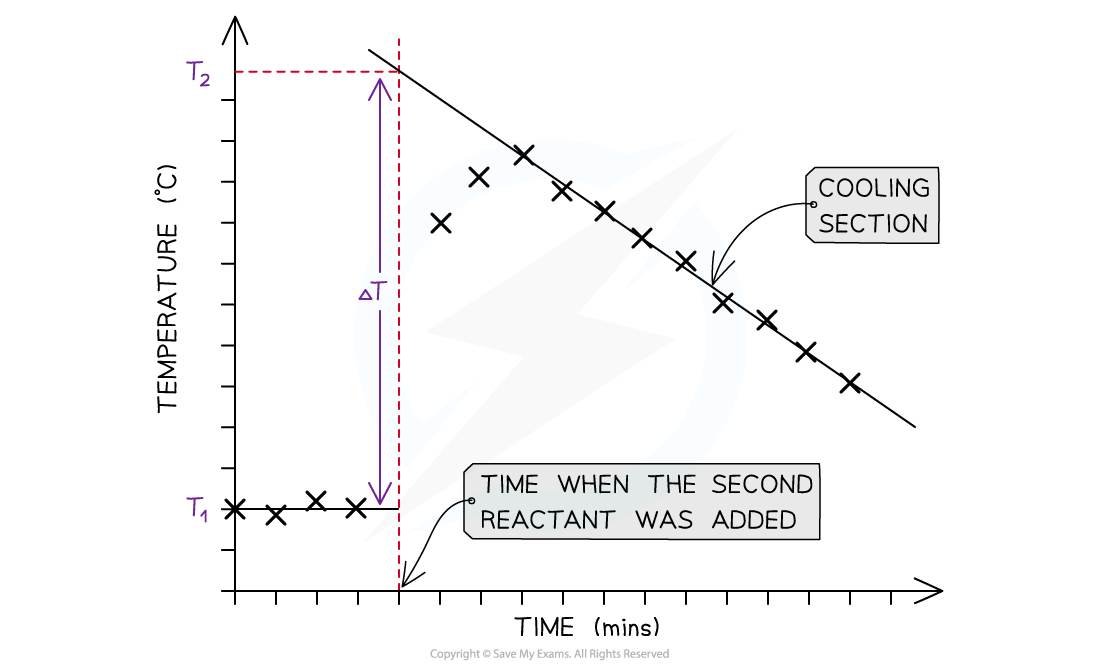
describe how you would carry out the enthalpy of combustion practical
set up apparatus as shown
measure temperature of 50cm³ of water (already added to copper cup) and record this
weigh the spirit burner with fuel in, record the mass
light the spirit burner and allow the water to increase in temperature until this temperature increase reaches 50C
extinguish the burner and reweigh it, recording the final mass of it
calculate energy and enthalpy changes
why might the enthalpy change value obtained experimentally be inaccurate?
heat energy transfer to or from surroundings
specific heat capacity of water might not be that of a solution (if used)
any heat absorbed by apparatus is ignored
reaction may be incomplete/incomplete combustion
density of solution (if used) is taken as the same as water
room temperature could have changed/not under standard condition
some water/fuel may have evaporated
how would you improve the accuracy of an enthalpy change experiment?
use an electronic temperature sensor and data logging software
bomb calorimeter used
what is the principle of conservation of energy?
energy cannot be created or destroyed
what is Hess’s law?
states that: overall enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the route taken
what does a Hess’s law diagram look like using enthalpies of formation?
arrows point out from elements
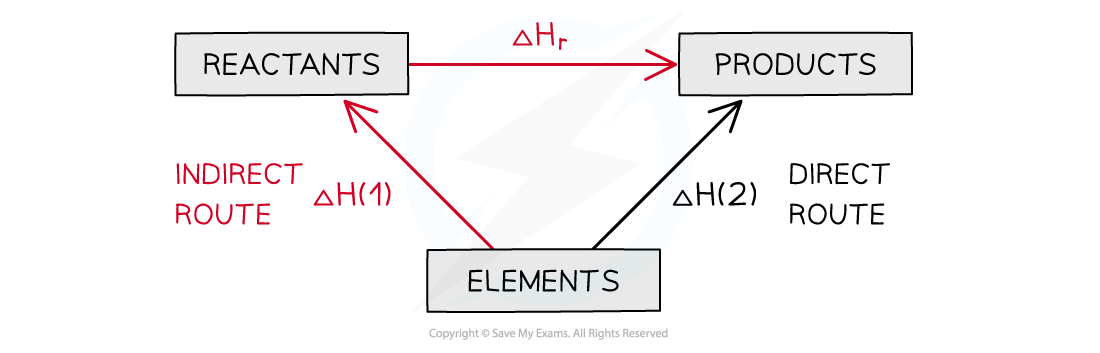
what is the overall equation for enthalpy change using enthalpies of formation?
enthalpy change of reaction = total enthalpy of products - total enthalpy of reactants
what does a Hess’s cycle using enthalpies of combustion look like?
arrows point to products of combustion
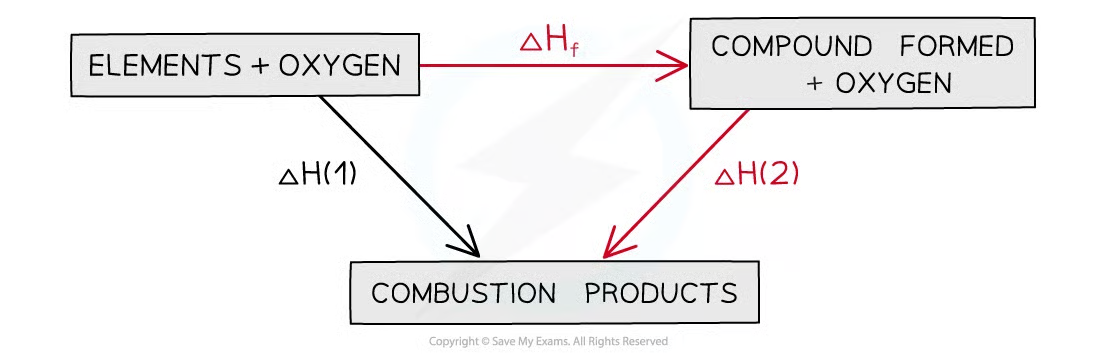
what is the overall equation for enthalpy change using enthalpies of combustion?
enthalpy change of reaction = enthalpy of reactants - enthalpy of products
what is the enthalpy of formation of an element?
0
what is an enthalpy of vaporisation?
the energy required to turn something into a gas
this is required as for enthalpy changes, enthalpies have to be measured in the gaseous state
define the term ‘average bond enthalpy’
energy required to break 1 mole of covalent bonds measured in the gaseous state in kj/mol under standard conditions
why are bond enthalpy values means?
it is an average of the energy required to break the same bond across different compounds (energy required will vary slightly)
what does a shorter covalent bond mean?
it is stronger
what is the increasing order of shortness of covalent bonds?
triple - shortest
double
single - longest
how do you calculate enthalpy change using bond enthalpies?
enthalpy change = total bond enthalpies of bond broken - total bond enthalpies of bonds made (reactants - products)
may have to include enthalpies of vaporisation