Chapter 7 - Liabilities
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Current assets and long-term assests combined
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Liabilities
Sources of funding
Assets
Uses of funding
Can be financed by:
Debt
Liabilites
Equity
Common shares
Retained Earnings
Capital structure
Mix of debt and equity
Which is risker: Debt financing or equity financing
Debt financing is risker than equity financing
Why is debt financing riskier?
Interest payments on debt are legal obligations
Creditors can force bankruptcy if a business fails to meet these obligations
Why use debt financing even if it is riskier?
Businesses that use debt financing are leveraged
Financial leverage
Borrowing money (debt) to increase potential returns on equity (investment)
Still is a financial risk as the company must pay back the debt + interest
How is financial leverage measured
Using financial ratios such as:
Debt-to-equity
Debt-to-total-assets
How does leverage affect Return on Equity (ROE)
It magnifies gains and losses.
Interest Rate includes:
Contractual interest rate
Market (effective) interest rate
Contractual interest rate
Used to calculate interest payments
Also called:
Coupon rate (≠ market rate)
Nominal rate
Face rate
Market (effective) interest rate
Demanded by investors
Also called the yield
Value includes:
Face value
Makret value (or issues price)
Face value
Principal due at maturity
Market value (issues price)
Price for a bond on the bond market
What is a bond?
Fixed income security that allows investors to receive interest payments for loaning their money to a government or corporation for a set period of time.
Why do companies issue bonds?
To borrow large amounts of money from many lenders at once.
What is a bondholder?
An investor who lends money to the company by buying a bond.
How often is bond interest usually paid?
Twice a year
What are term bonds?
Bonds that all mature at the same time.
What are serial bonds?
Bonds that mature in installments.
What are secured bonds?
Bonds backed by specific assets.
What are unsecured bonds (debentures)?
Bonds backed only by the issuer’s reputation.
Bond price
% of the face value (maturity) of the bond
Bonds are taded at:
Face value
Discount
Premium
Bond pricing - Face value
market value = face value
Traded when the coupon rate = the market value
Bond pricing - Discount
Market value < face value
Traded when coupon rate < the market value
Bond pricing - Premium
Market value > face value
Traded when the coupon rate > the market value
Bonds Interest Payment
Regardless of face, discount and premium value
Interest payment = face value x coupon rate
Bonds Interest Expense
Interest expense is based on the market rate
Bonds Interest Expense - Face value
Interest expense = interest payment
Bonds Interest Expense - Discount
Interest expense > Interest payment
Bonds Interest Expense - Premium
Interest expense < Interest payment
Amortization
Gradually write down the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life
Journal Entry for bonds issues at Discount
(DR) Interest Expense
(CR) Cash
(CR) Discount on bonds payable
Journal Entry for bonds issues at Premium
(DR) Interest Expense
(DR) Premium on bonds payable
(CR) Cash
Methods to Amortize Bonds Discount and bonds premium
Effective Straight Line Method
Straight line method
Why issue shares instead of debt?
No interest payments + no mandatory repayment.
Why issue debt instead of shares?
No dilution of ownership + potentially higher Earnings per share (EPS).
The payment of the face amount of a bond on its maturity date is regarded as what?
A financing activity
Amortizing the discount on bonds payable does what?
Increases the recorded amount of interest expense
Bond carrying value equals Bonds Payable
Plus Premium on Bonds Payable.
Minus Discount on Bonds Payable.
Liabilities (according to IFRS)
Something your business already owes
Can be paid by:
Cash
Give another asset
Deliver goods or services you own (i.e unearned revenue)
Converted to shares (creditor accepts equity instead of cash)
Current liabilities
Obligation due within one year or within a company's operating cycle
Operating cycle
The time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory into cash flows from sales
Typically is one year
Types of current liabilities
Known amounts
Provisions (less certainty about timing or amount)
Types of known current liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accrued liabilities
Income tax payable
Unearned revenue
Current portion of long-term debt
Payroll liabilities
Sales tax payable
Short-term notes payable
Dividend Payable
Accounts Payable
Amounts owed to suppliers
Accrued liabilities
Expenses incurred (used), but not paid
insurance payable
Rent
payable
Interest payable
Unearned revenue / Deferred revenue
Cash advances from customers for services that have not been delivered yet
Current portion of long-term debt
Business has a debt that is due after 1 year
Long-term liability on the balance sheet
As time passes, the business must reclassify the portion of debt into a current liability
Payroll liabiliites includes;
Payroll deductions
Payroll expenses
Payroll deductions
Paid by employers to the government on behalf of employees
Income taxes
Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
Retirement fund
Employment Insurance (EI)
Security in case they lose their job at some future date
Payroll expenses
Salary expenses
Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
Employer's CPP contribution = Employee CPP contribution
Employment Insurance (EI)
Employee EI contribution x 1.4
Why are Income taxes, CPP and EI considered a liability?
The liabilities will remain in the books until the company pays the money to the government
Hence why they owe this, making it a liability
Sales tax payable
The tax added to purchases when shopping
3 Types of Sales Tax Payable
Goods and services tax (GST)
Provincial/regional sales tax (PST)
Harmonized sales tax (HST)
Harmoinized sales tax (HST)
Ontario only has HST
HST combines GST and PST = 13% in Ontario
Value-added sales tax
Businesses that buy a product and resell it for a profit will receive an input tax credit (ITC) for the HST they paid
Input tax (or Tax recoverable)
Tax paid when purchasing goods
Output Tax (or Tax payable)
Tax collected when selling goods or services
Notes Payable and Notes Receivable (OR promissory notes)
Written promise to pay a sum at the maturity date
Plus interest
Why are notes payable and notes receivable issued?
Gives the lender stronger legal protection
The borrower signs it, the lender keeps it as proof
Example of issues N/R/NP
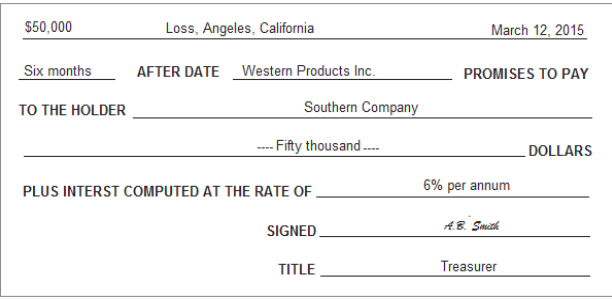
Dates in which journal entries should be made for notes payable/receivable
Initial transaction
End of accounting period
First interest payment date
Final payment
Interest
The cost of borrowing money
Stated as an annual percentage date
Maturity date
The date at which the debtor must pay the note
Principal
The amount of money borrowe dby the debtor
Term
The length of time the debtor must repay the note