Linguistics final exam
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Lexical semantics
Coneventional and arbitrary meaning of words
Compositional semantics
Meaning of sentences
Sense
Mental concept of words meaning
ex: dictionary definition
Reference
Things in the real world that the word refers to
ex: apple, orange, pear, are references for fruit
Hypernyms
a board category that words (hyponyms) can be apart of
Hyponyms
A proper subset
Truth value
Entailment
A relationship between the truth values of a sentences propositions
a bigger sentence entails a smaller sentence
If A is true, then B is true. A entails B.
Logical entailment
A entails B for logical reasons, requires no prior knowledge
I ate an red apple
I ate an apple
Word specific entailment
A entails b because of world knowledge or lexical meaning
I am from Oregon
I am from the U.S
Mutual entailment
A entails B and B entails A
I am a woman
I am a female
List notation
Defining a set by listing out the elements
ex: birds = {goose, duck, eagle}
Predicate notation
Defining a set in overarching terms/ symbols
ex: birds = {x | x is a bird}
The symbol “|” stands for “such that”
venn diagram
Shows what parts overlap in a set
Cardinality
The number of elements in a set, shown with vertical bars
ex: | A | is cardinality of A
Null set
A set with no elements in it
written as: {}, or ø
Equality
A set relation that shows that two sets are identical
Symbol: =
Subset
a set relation that has every element of their set in another set, can be identical
ex: A is a subset of B, if every element of B is in A
Symbol:

Proper subset
a set relation where all the elements of one set are in another set, but they cannot be identical
A is a subset of B if all the elements in A is in B, and B has extra elements
Symbol

Is symbol
Symbol that means “Is a”

Union
symbol: U
Set operation that involves two sets combining that produce a new set
Includes all elements of old and new set
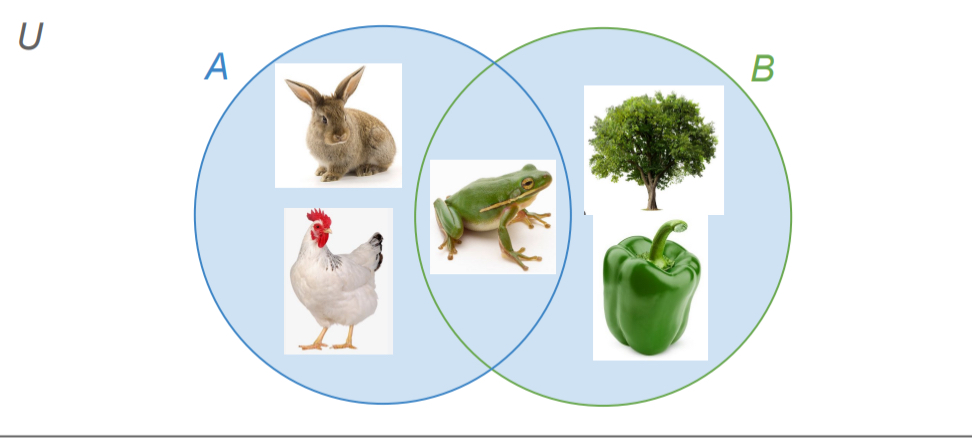
Intersection
symbol:
Set operation that only includes the overlapping part of 2 new sets
Middle section on vent diagram

Difference
Symbol: -
ex: A - B means “belongs to A but not B”
Set operation that only involves one side of then vent diagram

Complement
symbol: ‘
Ex: A’ → everything but A
Everything except that one specific set
principle of semantic Compositionality
The meaning of a sentnce is determined by the meanings of the indidvual words, and the grammar used to combine them (syntax)
Pragmatics
The study of language in context, studied implied ,meaning
Presuppositions
inferences that can be made from a sentence
ex: i had lunch → presupposition: i exist
Utterances
Language spoken in a particular context
Definite expression
Presupposition trigger that presuppose the existence of something
my boyfriend likes cake → i have a boyfriend
Iterative expressions
Presupposition trigger that presuppose the repetition of something
ex: she came here again → presupposition: she was there before
Change of state verbs
Presupposition triggers via verbs that imply change in an action or state
ex: she stopped working our → presupposition: she used to previously work our
Factive verbs
Presupposition triggers that refer to someone’s feelings or knowledge about something, introducing a dependent clause (presupposition) and main clause (proposition)
ex: She regrets submitting her paper late. → dependant clause: her paper was late/ main clause: she regrets it.
Clefts
Presupposition triggers that take simple sentences and add a dependant clause to it
X Y’ed → It was X that Y’ed, X was who Y’ed, etc
ex: I like Pie → Pie is what i like to eat.
→ presupposition: someone likes pie.
→ main clause: i am that person
Common ground
The idea of a consistent figure/ topic while having a conversation, preventing the need to reference it every time
ex; referring to a topic as “it, that, or what” during a conversation
Presupposition accomodation
Assuming a presupposition is true
sounds reasonable
Presupposition failure
A sentence that has a presupposition that seems false.
ex: there is a Martian in my house.
Ex: Did u stop embezzling money?
Cooperative principle
Participants in a conversation tend to say what’s appropriate for the situation and goals of the conversation.
Maxim of quality
Be truthful, don’t say what u think is false
we assume other peopel are telling the truth in convos
Maxim of quantity
Give as much information as required, do not give too cut or too little
ex: how was ur exam? “Good, i think it went well,” compared to “fine” and “good it went well i think …………………..”
Maxim of relevance
Say whats relevant to the question being asked, even if there is another answer that is technically correct
ex: where do u live now? “I live north of here” compared to “on earth”
Maxim of manner
Say things in the correct order, try to avoid confusion
ex: “i’m sick and i went to the doctors.’ Compared to “i went to the doctors and i’m sick”
Cancelling implicatures
Sentences that cancel out previous presuppositions
ex: how is Sam’s boyfriend? “Oh she is single now.”
→ implies that they broke up/ Sam doesnt have a bf
Reinforces
Parts of the conversation that reinforce presuppositions
Ex: how is Sam’s boyfriend? He’s good.
→ implies Sam still has a boyfriend.
Segment/ phones
Discrete individual sounds represented by IPA
ex: vowel consonant, glide
i (cardinal vowel)
sounds like eee in bee
High Front unrounded vowel
E (cardinal vowel)
Sounds like ay in “bay”
mid front unrounded vowel
A
sounds ahhh
Low central unrounded vowel
O (cardinal vowel)
sounds like oh
Mid back rounded vowel
U (cardinal vowel)
sounds like oo in boo
High back rounded vowel
Glide
Letters like y or w, resembles vowels and consonants
Diphthong
Two vowels that are combined into 1 sound
ex: oj → sounds like oy
What do vowels have that consonants do not?
Constant airflow and voicing
tounge height, tounge blackness, lip rounded nests
Place of articulation
Location of obstruction in vocal tract
where?
Columns in IPA consonant chart
Manner of articulation
Type of obstruction
What?
Rows on consonant chart
Larynx
An organ in throat that vibrates, helps create sounds
Consonants
Letters with total or partial obstruction in vocal tract, blocking or restricting airflow
Voiced
left side of consonant chard, on IPA
Larynx is vibrating, creating vocals
Voiceless
Consonants where air passes freely, larynx is not vibrating
Right of IPA consonants
Labials
Place of articulation Consonants/ words said with lips
ex: tofu, pa, vote
Coronals
Place of articulation Consonants/words said with the front part of the mouth
Ex: too, now
Dentals
Coronals said with tounge, tip, and teeth
ex: think, that
Alveolar
Place of articulation Coronals said with tongue, tip, blade, and alveolar ridge
ex: tea, day
Post-alveolars
Place of articulation where Consonants said with tongue, blade, and area behind alveolar ridge
Ex: shake, vision
Retroflexes
Place of articulation Consonants said with the tongue tip arched backwards
ex: the d in diya
Plosive/ stop
Complete obstruction, release with burst
Fricative
Manner of articulation, Narrow obstruction, hissing sound
ex: f, v, s, z, h
Affricate
Complete obstruction, release to narrow obstruction
Nasal
Consonants that Complete obstruction in mouth, air flows through nose
Ex: m,n
Lateral
Obstruction on centerline of mouth, air flows on the sides
ex: l
Approximant
Narrow obstruction, now harrow enough for hissing
Ex: j,w
Tap/flap/thrill
Very brief obstruction, repeated for thrills
Obstruents
Plosives, affricate am fricatives (greater airflow)
Sonorant
Nasals, laterals, approximants (less airflow)
Rhotics
R sounds
Liquid
Laterals + rhortics, l and r sounds
Phoneme
A set of sounds that speakers of a language treat as being the same
Allophone
Each individual sound that’s apart of the phoneme
Phonemic contrast
Phonemes can sound different, allophones cannot
the same allophone wont sound different in various words (t in tie and stop) , but phonemes can (tie vs die)
Do all phonemes sound the same in all languages?
Each language have different phonological inventories and differnet phonotactics, meaning they sound and act differently in each language.
Phonemic analysis
Allophones occur in complimentary distribution, they can never be in the same place in the same word
Phonemes occur in contrastive distribution ,they can be in the same place in different words
Minimal pairs
A pair of words that differ only by one sound
-ex: pat and bat, ship and sheep
Assimilation
A sound segment changes to become more similar to another nearby sound segment
ex: cats (kats) and dogs (dogs).
Dissimilation
A sound that changes to become less similar to another segment
ex: kindergarten (German) → kindergarten (American) The “t’ sound dissimilated to a “d” sound
Insertion
A sound segment is added to a word
English glide insertion: I am sounds like “i yam”
Deletion
A sound is removed from a word
ex: rock and roll sounds like rock n roll
Strengthening
Sounds become more strong in sonority
Weakening
Words become weaker in sonority