Chapter 14 - Flexibility Training Concepts
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:40 AM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
flexibility
the normal extensibility of soft tissues that allows for full range of motion of a joint
2
New cards
extensibility
capability to be elongated or stretched
3
New cards
range of motion (ROM)
the degree to which specific joints or body segments can move; often measured in degrees
4
New cards
mobility
optimal flexibility and joint range of motion; ability to move freely
5
New cards
myofascial
the body’s connective tissue that includes muscles and fascia
6
New cards
relative flexibility
the process in which the body seeks the path of least resistance during functional movements
7
New cards
human movement system (HMS)
the collective components and structures that work together to move the body: muscular, skeletal, and nervous systems
8
New cards
soft tissue
tissue connecting, supporting, and surrounding bodily structures and organs
9
New cards
which portion of a client’s exercise program should be designed **first**?
the flexibility portion
10
New cards
postural distortion imbalances
predictable patterns of muscle imbalances
11
New cards
muscle imbalances
when muscles on each side of a joint have altered length-tension relationships
12
New cards
force-couple relationships
the synergistic action of multiple muscles working together to produce movement around a joint
13
New cards
osteokinematic
movement of a limb that is visible
14
New cards
arthrokinematics
the description of joint surface movement; consists of three major types: roll, slide, and spin
15
New cards
reciprocal inhibition
when an agonist receives a signal to contract, its functional antagonist also receives an inhibitory signal allowing it to lengthen
16
New cards
altered reciprocal inhibition
occurs when an overactive agonist muscle decreases the neural drive to its functional antagonist
17
New cards
overactive
when elevated neural drive causes a muscle to be held in a chronic state of contraction
18
New cards
underactive
when a muscle is experiencing neural inhibition and limited neuromuscular recruitment
19
New cards
synergistic dominance
the neuromuscular phenomenon that occurs when synergists take over function for a weak or inhibited prime mover (agonist)
20
New cards
altered length-tension relationship
when a muscle’s resting length is too short or too long, reducing the amount of force it can produce
21
New cards
neuromuscular effciency
the ability of the nervous system to recruit the correct muscles to produce force, reduce force, and dynamically stabilize the body’s structure in all three planes of motion
22
New cards
muscle spindle
sensory receptors sensitive to change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
23
New cards
central nervous system
a division of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord
24
New cards
stretch reflex
neurological signal from the muscle spindle that causes a muscle to contract to prevent excessive lengthening
25
New cards
golgi tendon organ (GTO)
a specialized sensory receptor located at the point where skeletal muscle fibers insert into the tendons of skeletal muscle; sensitive to changes in muscular tension and rate of tension change
26
New cards
autogenic inhibition
the process by which neural impulses that sense tension are greater than the impulses that cause muscles to contract, providing an inhibitory effect to the muscle spindles
27
New cards
lengthening reaction
when a muscle is lengthened, a cascade of neurological reactions occur that allows the muscle to be stretched
28
New cards
static stretching
a type of stretch where the muscle is passively lengthened to the point of tension and held for a sustained amount of time
29
New cards
pattern overload
consistently repeating the same pattern of motion over long periods of time that can lead to dysfunction or injury
30
New cards
cumulative injury cycle
a cycle whereby tissue trauma will induce inflammation, muscle spasm, adhesions, altered neuromuscular control, and muscle imbalances
31
New cards
nociceptors
pain receptors located in the skin and fascial connective tissues
32
New cards
davis’s law
states that soft tissue models along the line of stress
33
New cards
collagen matrix
a complex meshwork of connective tissue, including collagen proteins
34
New cards
with regard to the cumulative injury cycle, current theory supports the idea that repetitive movements, such as long periods of poor posture, are believed to lead to which of the following?
tissue trauma and inflammation
35
New cards
self-myofascial techniques
techniques used for treating and breaking up adhesions of the fascia and the surrounding muscle tissues; examples include foam rolling or self-massage
36
New cards
fascial system
a web of connecting fibers made of connective tissues that are found just under the skin
37
New cards
mechanical effect
having a physical effect
38
New cards
neurophysiological effect
\
\
having an effect on the nervous system
39
New cards
delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS)
pain or discomfort often felt 24 to 72 hours after intense exercise or unaccustomed physical activity
40
New cards
SMR: calves
crossing one leg on top of the other is optional and is used to increase pressure to the calf
roll along the length of the calf muscles
roll along the length of the calf muscles

41
New cards
SMR: peroneals
stacking the legs is optional and is used to increase pressure on the peroneals
roll along the length of the muscle. Avoid rolling over the knee joint
roll along the length of the muscle. Avoid rolling over the knee joint

42
New cards
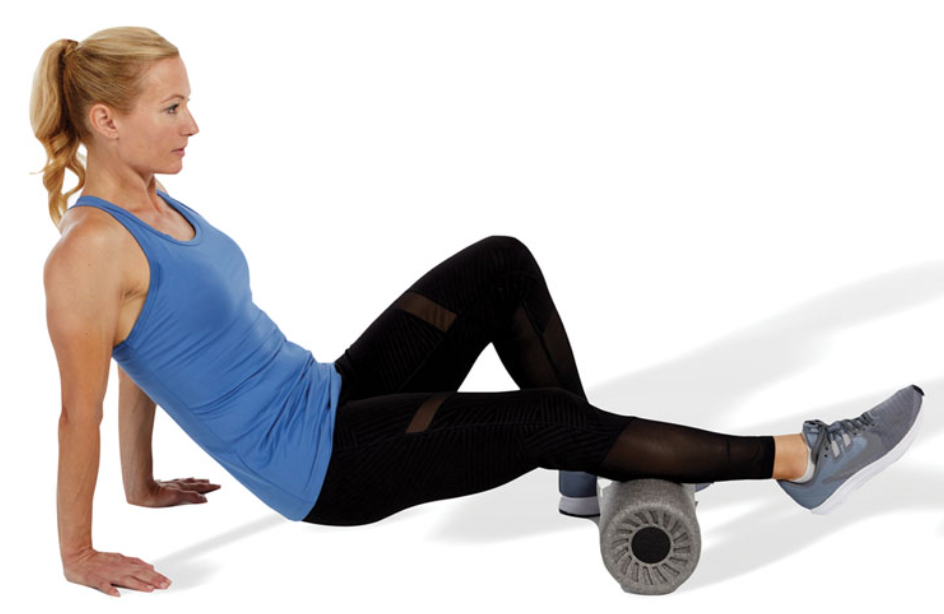
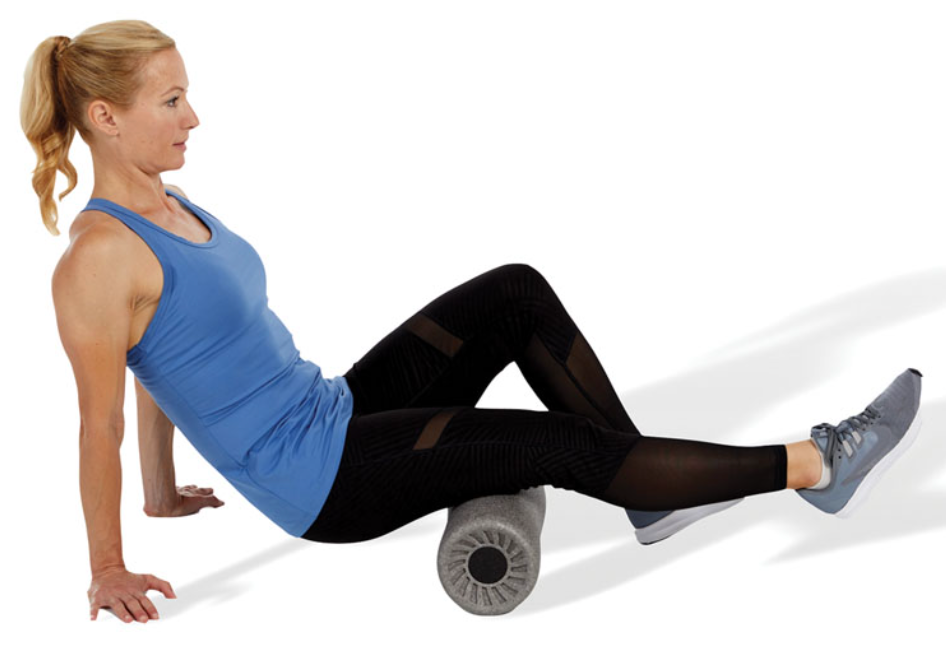
SMR: hamstrings
while sitting, the target leg is straight with the roller underneath the posterior thigh, and the opposite knee is flexed
roll along the length of the muscle
avoid rolling over the knee joint
using a massage ball instead of a foam roller is a progression for this exercise and can help pinpoint tender areas
roll along the length of the muscle
avoid rolling over the knee joint
using a massage ball instead of a foam roller is a progression for this exercise and can help pinpoint tender areas

43
New cards
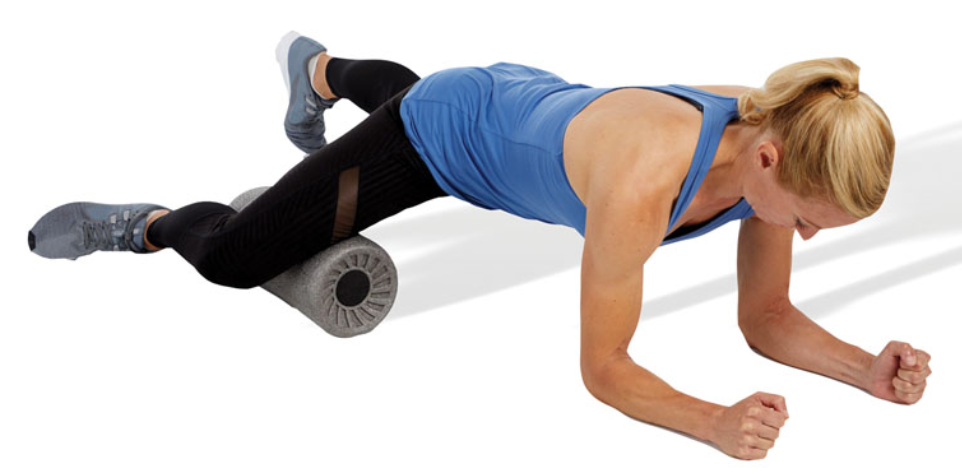
SMR: quadriceps
the client is in the plank position with knees straight and roller under the quadriceps
roll along the length of the muscle
this exercise can be performed bilaterally (both legs) or unilaterally (one leg at a time)
avoid rolling over the knee joint
roll along the length of the muscle
this exercise can be performed bilaterally (both legs) or unilaterally (one leg at a time)
avoid rolling over the knee joint

44
New cards
SMR: adductors
to perform this technique correctly, the foam roller should be placed perpendicular to the inner thigh
roll the length of the muscle
avoid rolling over the knee joint
roll the length of the muscle
avoid rolling over the knee joint

45
New cards
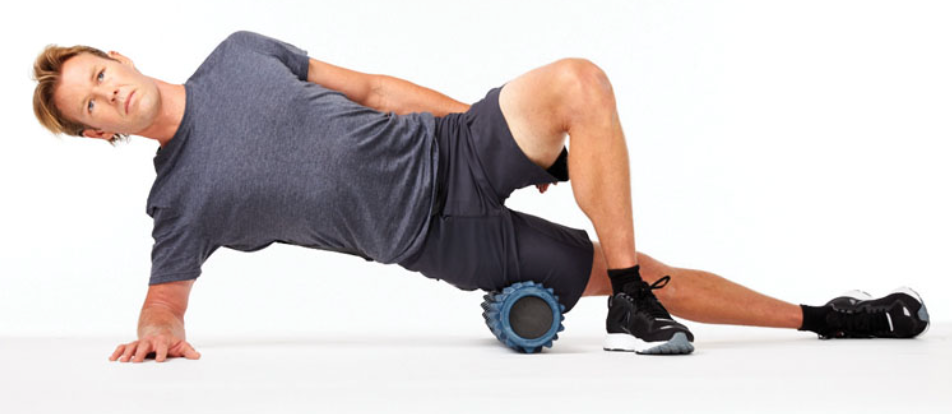
SMR: lateral thigh
the client is side-lying with the roller under the lateral thigh
the opposite hip and knee are bent with foot flat on the floor
roll along the length of the lateral thigh. Avoid rolling over the hip or knee joint
this exercise can be too painful for some individuals
if this occurs, opt for a handheld roller instead
the opposite hip and knee are bent with foot flat on the floor
roll along the length of the lateral thigh. Avoid rolling over the hip or knee joint
this exercise can be too painful for some individuals
if this occurs, opt for a handheld roller instead

46
New cards
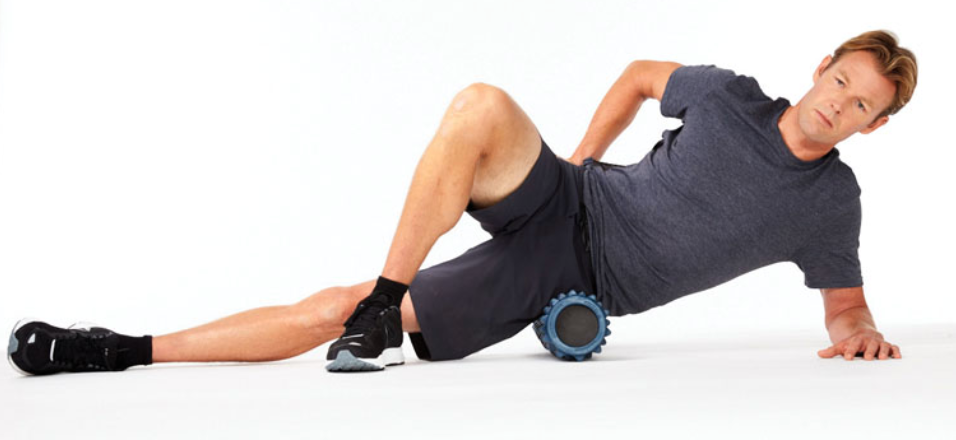
SMR: tensor fascia latae
the tensor fascia latae (TFL) is a small muscle, so this technique does not require lots of movement
to target the TFL, roll along the front and slightly lateral (outside) part of the upper thigh (just below the pelvis)
avoid rolling over the hip bone
to target the TFL, roll along the front and slightly lateral (outside) part of the upper thigh (just below the pelvis)
avoid rolling over the hip bone

47
New cards
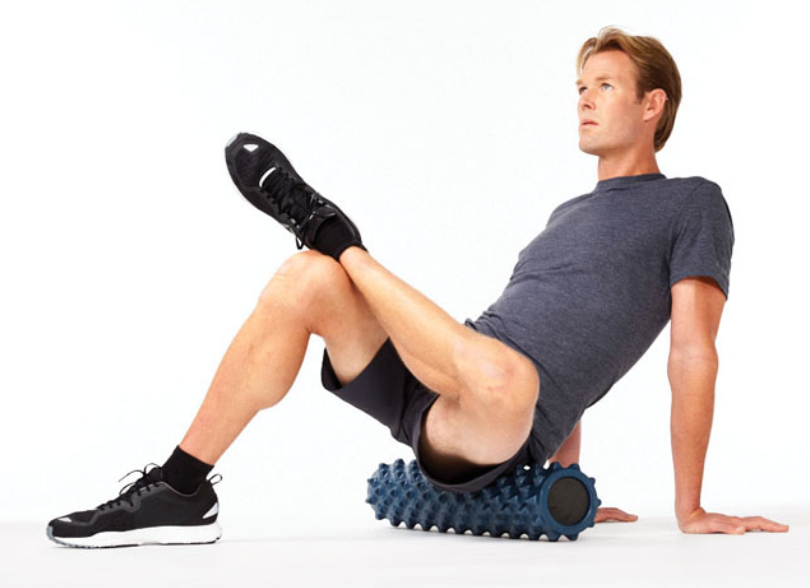
SMR: piriformis
the piriformis is a small muscle of the posterior hip that runs horizontally across the pelvis
to target the piriformis, sit on top of the foam roll, positioned on the back of the hip
cross one foot to the opposite knee and lean into the hip of the crossed leg. Roll back and forth over the muscle
avoid rolling over the hip bone
to target the piriformis, sit on top of the foam roll, positioned on the back of the hip
cross one foot to the opposite knee and lean into the hip of the crossed leg. Roll back and forth over the muscle
avoid rolling over the hip bone

48
New cards
SMR: thoracic spine
the client keeps the bridge position and rolls along the thoracic spine
the client can choose to support their head in their hands (as shown) or cross their arms in front of their chest
this is a good technique to gain thoracic extension of the spine
avoid rolling over the low-back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine)
the client can choose to support their head in their hands (as shown) or cross their arms in front of their chest
this is a good technique to gain thoracic extension of the spine
avoid rolling over the low-back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine)

49
New cards
SMR: latissimus dorsi
to target the latissimus dorsi, lie on the floor on one side with the arm closest to the floor outstretched and thumb facing upward
place the foam roller under the armpit area (axillary region) and slowly roll until a tender spot is identified
place the foam roller under the armpit area (axillary region) and slowly roll until a tender spot is identified

50
New cards
medical precautions
any medical conditions that could be potentially unsafe for a client
hypertension, osteopenia, pregnancy, diabetes, varicose veins, rolling over bony prominences or regions, abnormal sensations, sensitivity to pressure, recent injury or surgery, etc.
hypertension, osteopenia, pregnancy, diabetes, varicose veins, rolling over bony prominences or regions, abnormal sensations, sensitivity to pressure, recent injury or surgery, etc.
51
New cards
contraindications
a specific situation where a medication, procedure, or exercise should be avoided because it may prove to be harmful to the individual
skin rash, open wounds, blisters, local tissue inflammation, bruises, or tumors, deep vein thrombosis, osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, bone fracture of myositis ossificans, cancer/malignancy, hypertension (uncontrolled), etc.
skin rash, open wounds, blisters, local tissue inflammation, bruises, or tumors, deep vein thrombosis, osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, bone fracture of myositis ossificans, cancer/malignancy, hypertension (uncontrolled), etc.
52
New cards
TRUE OR FALSE: the mechanical effect of direct roller compression is the relaxation of the local myofascia by increasing local blood flow and reducing myofascial restriction and adhesions
true
53
New cards
stretch tolerance
the ability to experience the physical sensations of stretching to reduce the discomfort felt at the end range of motion
54
New cards
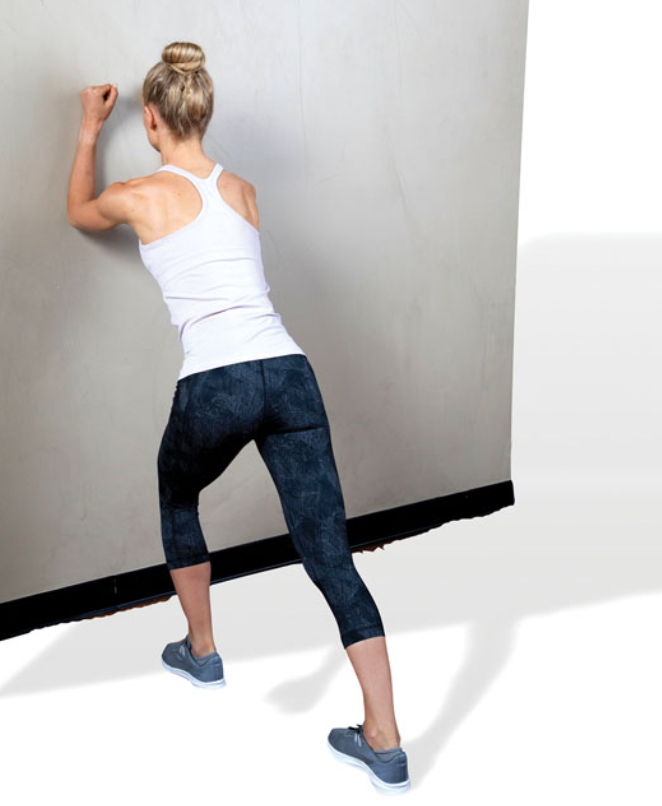
static gastrocnemius stretch
stand in a lunge position with both feet pointing straight forward
make sure to keep the rear foot flat on the ground
do not let the heel rise
shift weight forward until a stretch is felt in the rear calf muscle
make sure to keep the rear foot flat on the ground
do not let the heel rise
shift weight forward until a stretch is felt in the rear calf muscle

55
New cards
static soleus stretch
stand in a lunge position with both feet pointing straight forward and back knee slightly flexed
make sure to keep the rear foot flat on the ground
do not let the heel rise up
shift weight forward until a stretch is felt in the rear calf muscle
make sure to keep the rear foot flat on the ground
do not let the heel rise up
shift weight forward until a stretch is felt in the rear calf muscle

56
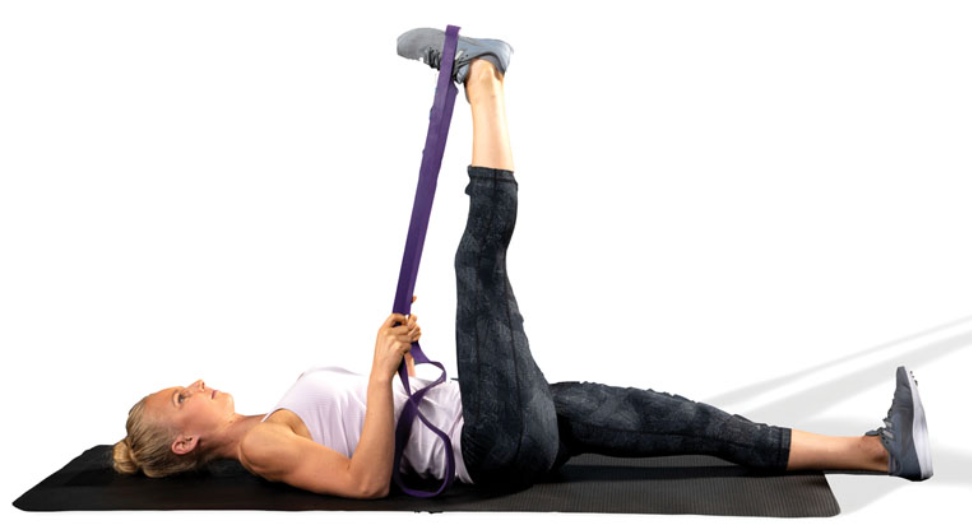
New cards
static 90/90 hamstring stretch
lie supine with one hip flexed 90 degrees (target leg) and the opposite leg straight and flat on the floor
straighten the target leg until a mild stretch is felt in the hamstrings
the use of a rope or band is suggested
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
straighten the target leg until a mild stretch is felt in the hamstrings
the use of a rope or band is suggested
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort

57
New cards
static supine bicep femoris stretch
lie supine with one hip flexed 90 degrees (target leg) and the opposite leg straight and flat on the floor
next, adduct the target leg across the body and extend the knee until a mild stretch is felt in the lateral hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
keep both shoulders flat on the ground during this stretch
avoid rotating the torso toward the stretched leg
next, adduct the target leg across the body and extend the knee until a mild stretch is felt in the lateral hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
keep both shoulders flat on the ground during this stretch
avoid rotating the torso toward the stretched leg

58
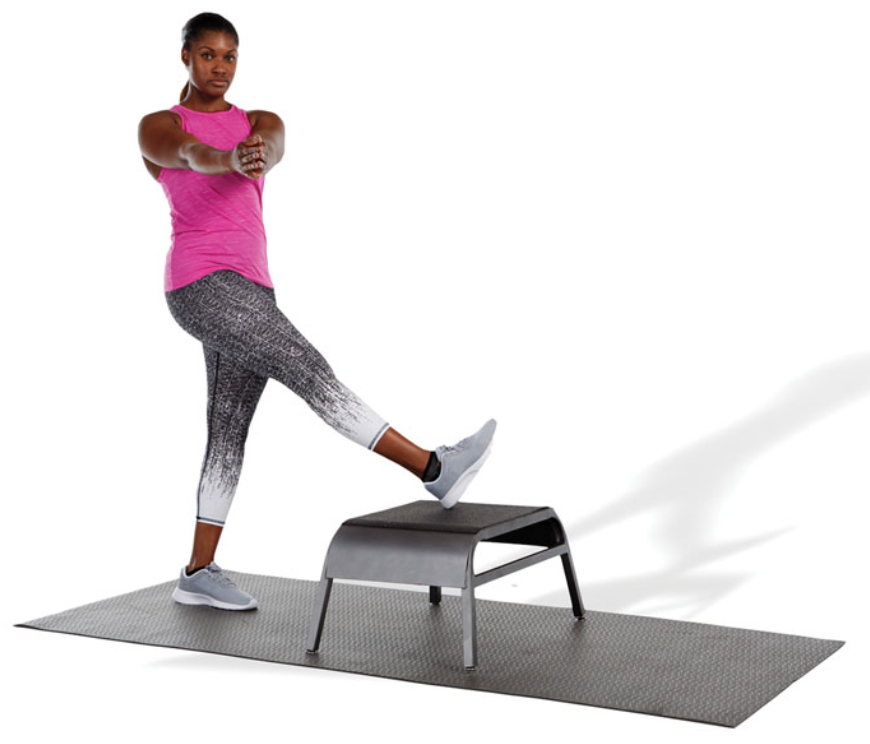
New cards
static standing bicep femoris stretch
use a low box or step to perform this stretch
place one leg on top of the box in an adducted and internally rotated position
then, locking the hands together, slowly rotate the torso in the opposite direction
the stretched leg does not need to be elevated above hip height
this stretch emphasizes the lateral hamstring
place one leg on top of the box in an adducted and internally rotated position
then, locking the hands together, slowly rotate the torso in the opposite direction
the stretched leg does not need to be elevated above hip height
this stretch emphasizes the lateral hamstring

59
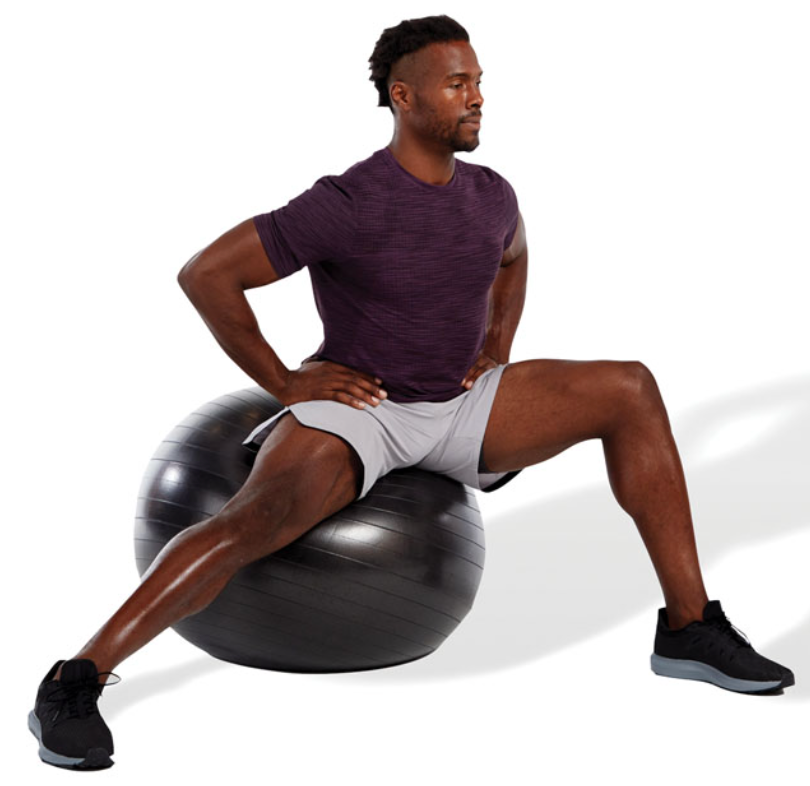
New cards
static seated ball adductor stretch
sit on a stability ball in a lateral lunge position until a stretch is felt in the inner thigh area
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch

60
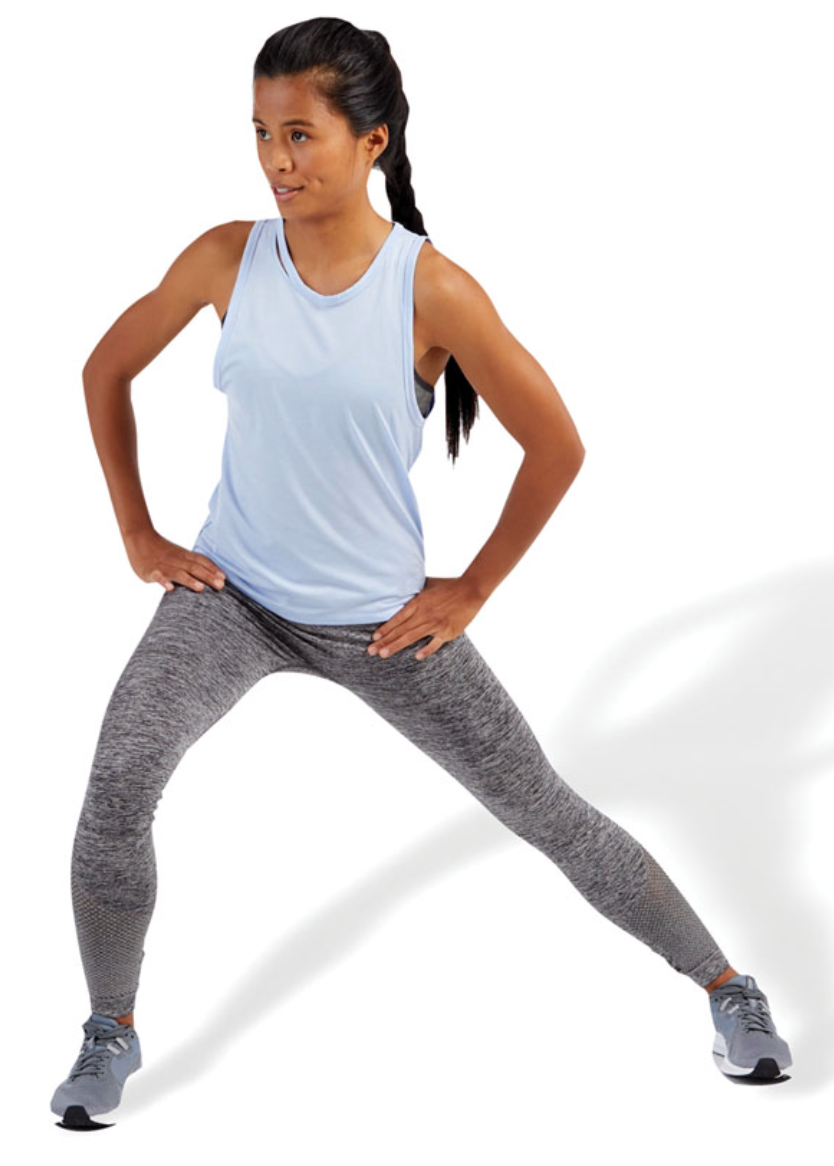
New cards
static standing adductor stretch
stand with legs apart and shift weight to one side (lateral lunge position) until a stretch is felt in the inner thigh of the target leg
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch

61
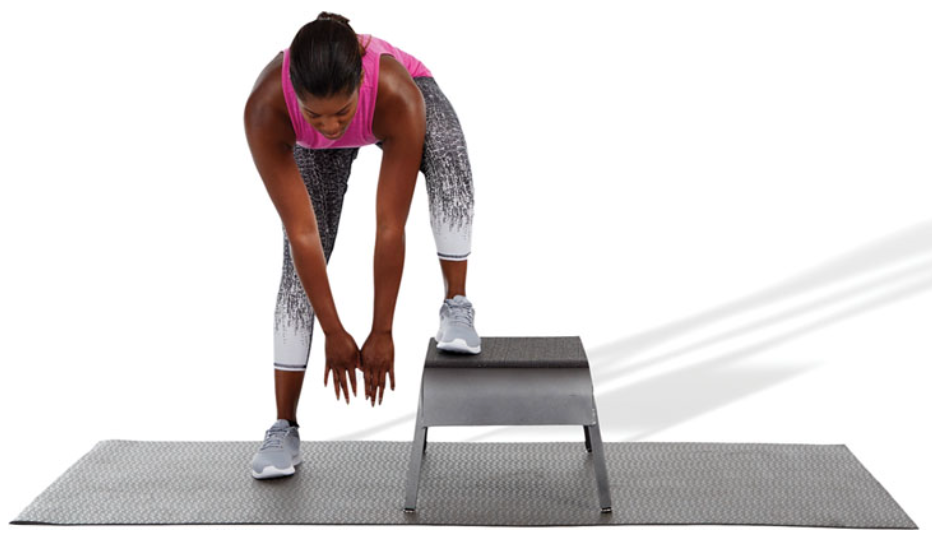
New cards
static adductor magnus stretch
while standing with one foot on a bench or plyo box, reach down to a comfortable position without excessively rounding the spine until a stretch is felt

62
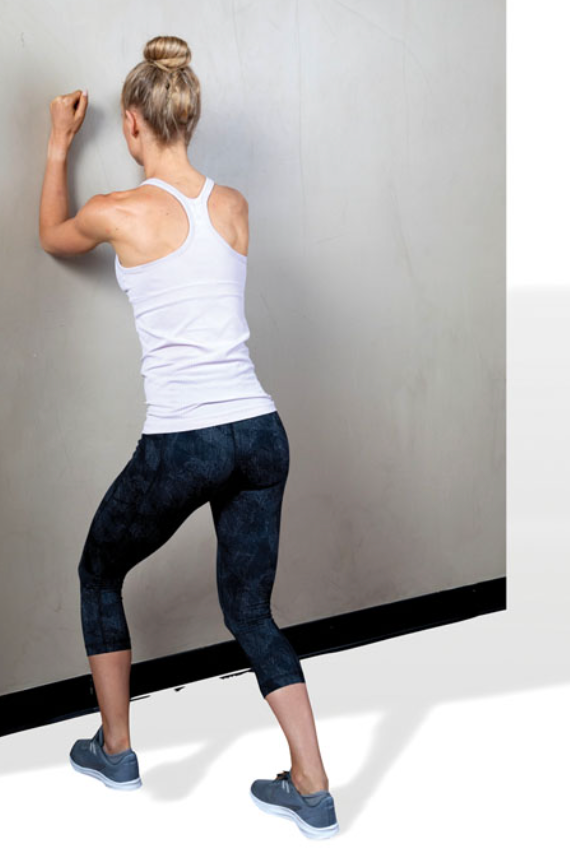
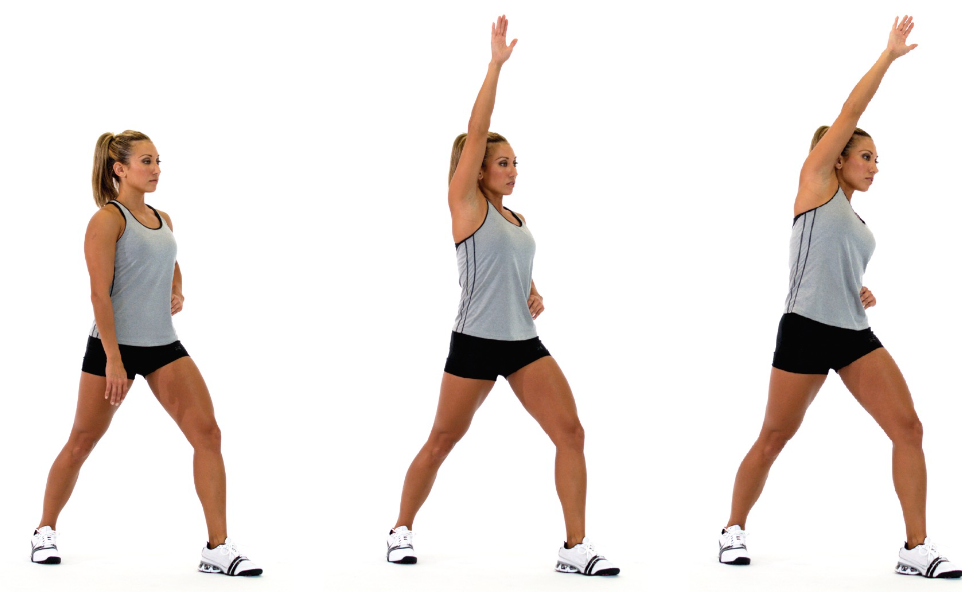
New cards
static standing TFL stretch
\
stand in a staggered stance with the front leg slightly bent and rear leg straight
externally rotate the rear foot, draw in the navel, and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position as illustrated
stand in a staggered stance with the front leg slightly bent and rear leg straight
externally rotate the rear foot, draw in the navel, and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position as illustrated

63
New cards
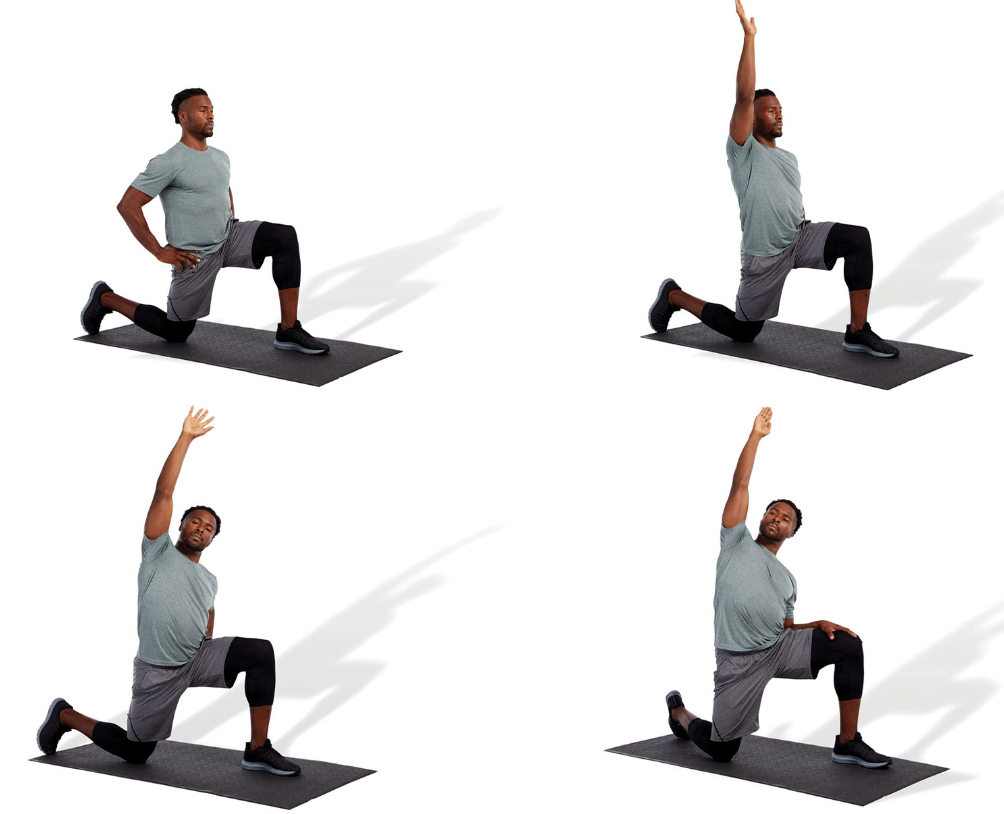
static kneeling hip flexor stretch
kneel with front and back legs flexed at a 90-degree angle
draw in the navel and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and slowly rotate posteriorly as illustrated
to emphasize the TFL, externally rotate the rear leg, whereas to emphasize the psoas, internally rotate the rear leg
draw in the navel and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and slowly rotate posteriorly as illustrated
to emphasize the TFL, externally rotate the rear leg, whereas to emphasize the psoas, internally rotate the rear leg

64
New cards
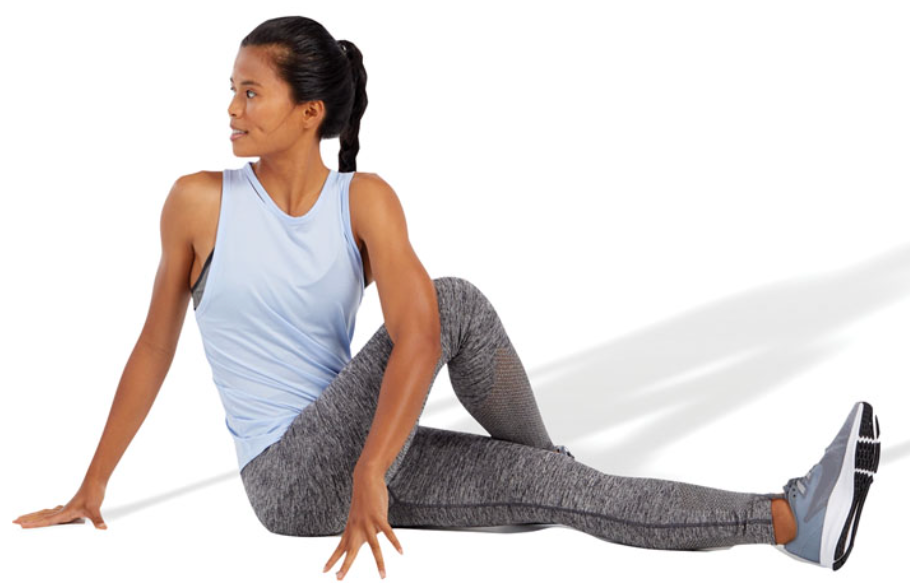
static supine piriformis stretch
lie supine and cross one leg over the opposite leg that is straight
keep the low-back in a neutral position while bringing the knee toward the opposite shoulder
keep the low-back in a neutral position while bringing the knee toward the opposite shoulder

65
New cards
stati erector spinae stretch
sit with one leg crossed over the other and opposite knee straight
rotate the torso to the right when the right leg is crossed over the left leg
rotate to the left when the left leg is crossed over the right leg
rotate the torso to the right when the right leg is crossed over the left leg
rotate to the left when the left leg is crossed over the right leg

66
New cards
static ball latissimus dorsi stretch
in the quadruped position, put one arm on top of a stability ball and roll forward until a stretch is felt
posteriorly rotate the pelvis, point the thumb up toward the sky, and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
posteriorly rotate the pelvis, point the thumb up toward the sky, and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch

67
New cards
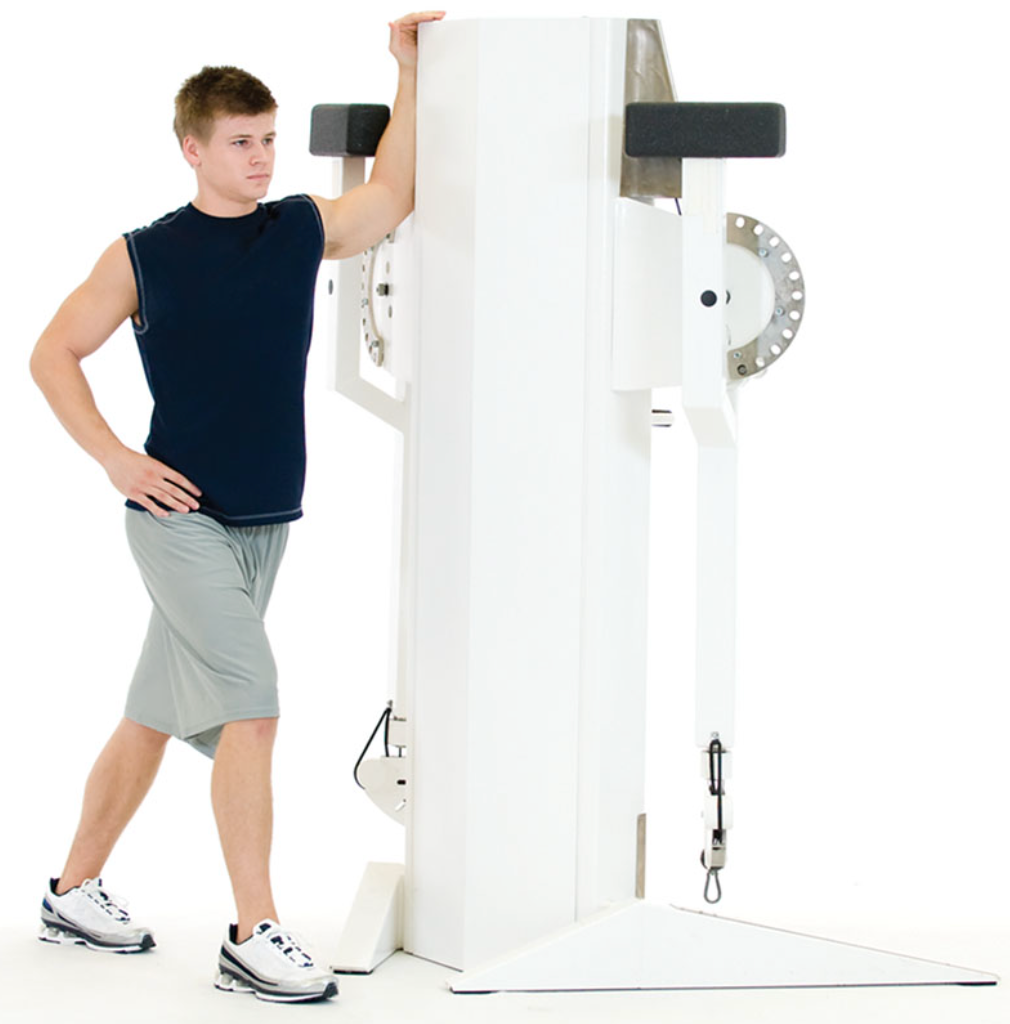
static pectoral stretch
standing with one arm in a 90/90 arm position, lean forward until a stretch is felt in the anterior shoulder and chest area
do not allow the shoulders to elevate (shrug) during this stretch
do not allow the shoulders to elevate (shrug) during this stretch

68
New cards
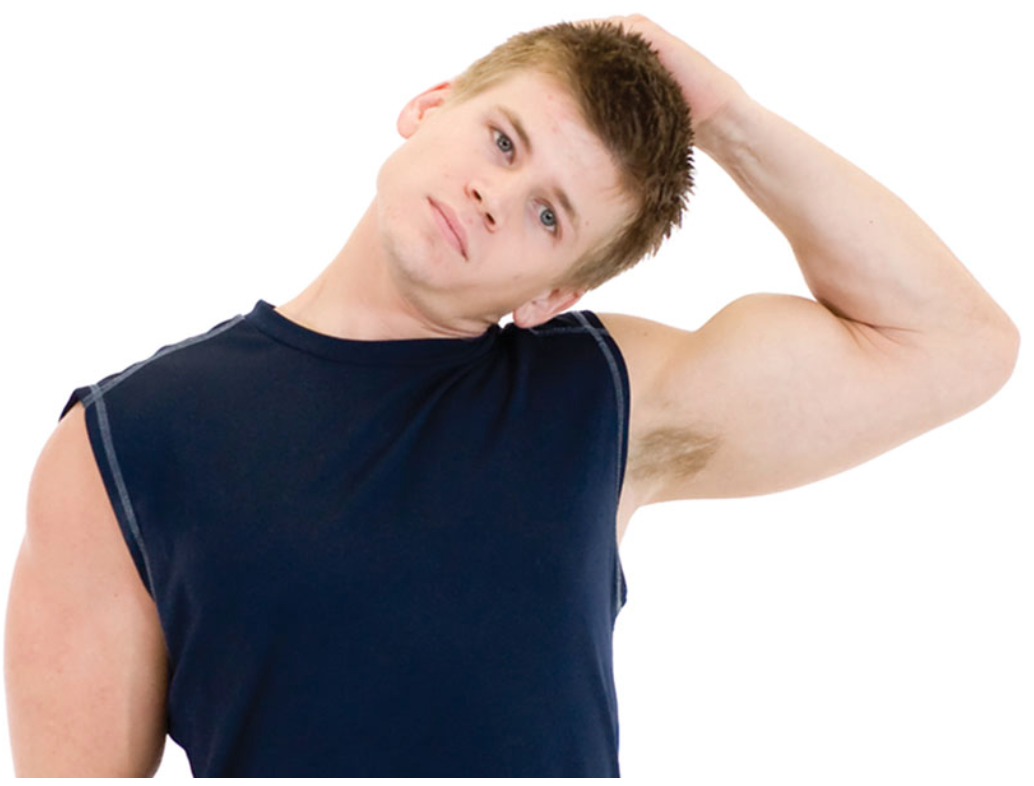
static upper trapezius/scalene stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch

69
New cards
static levator scapulae stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
next, slightly rotate the head to look in the axillary (armpit) region as shown
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
next, slightly rotate the head to look in the axillary (armpit) region as shown
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
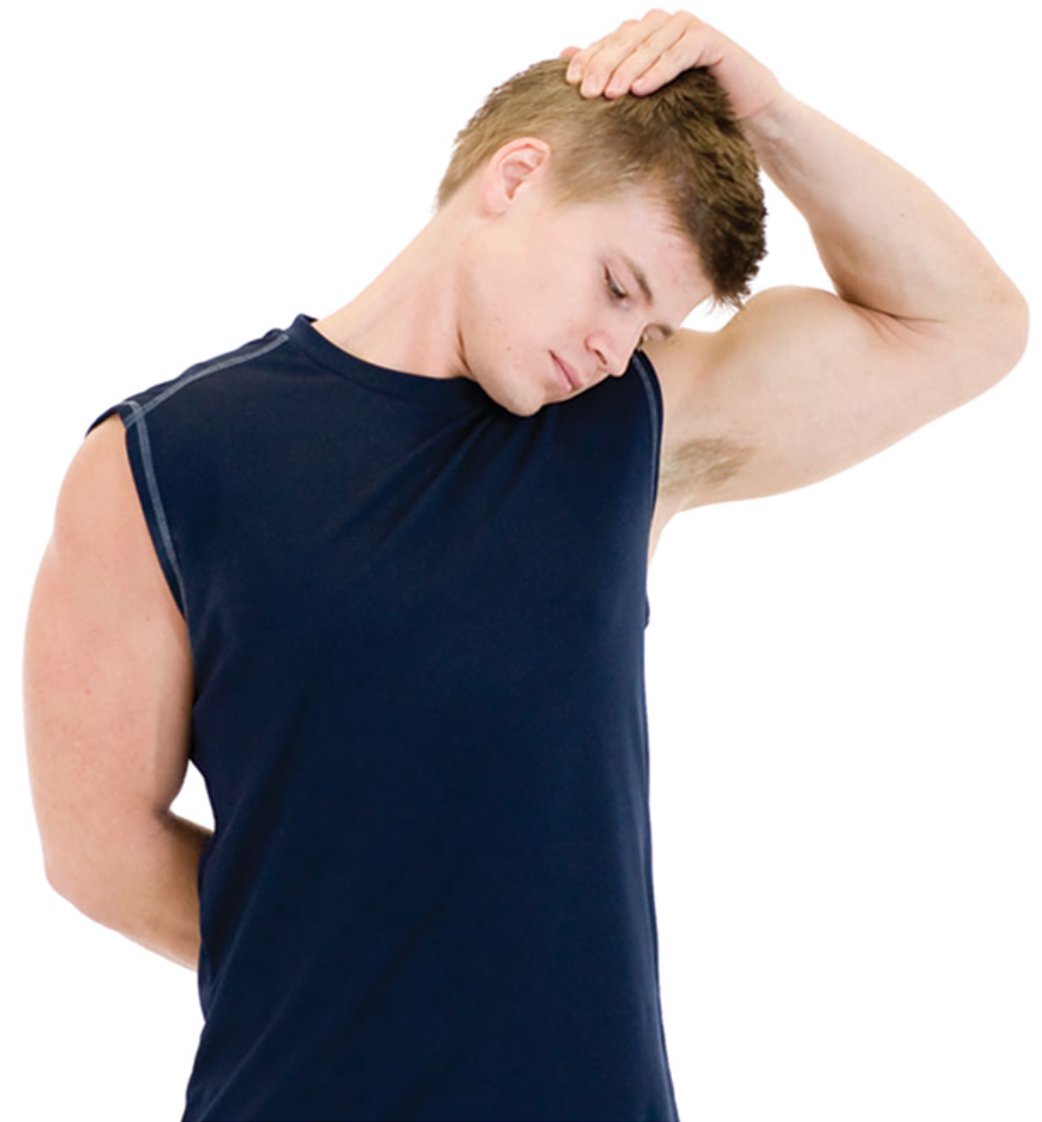

70
New cards
static sternocleidomastoid stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
rotate the head up and away as shown
only perform this stretch to the point of mild tension
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
rotate the head up and away as shown
only perform this stretch to the point of mild tension
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
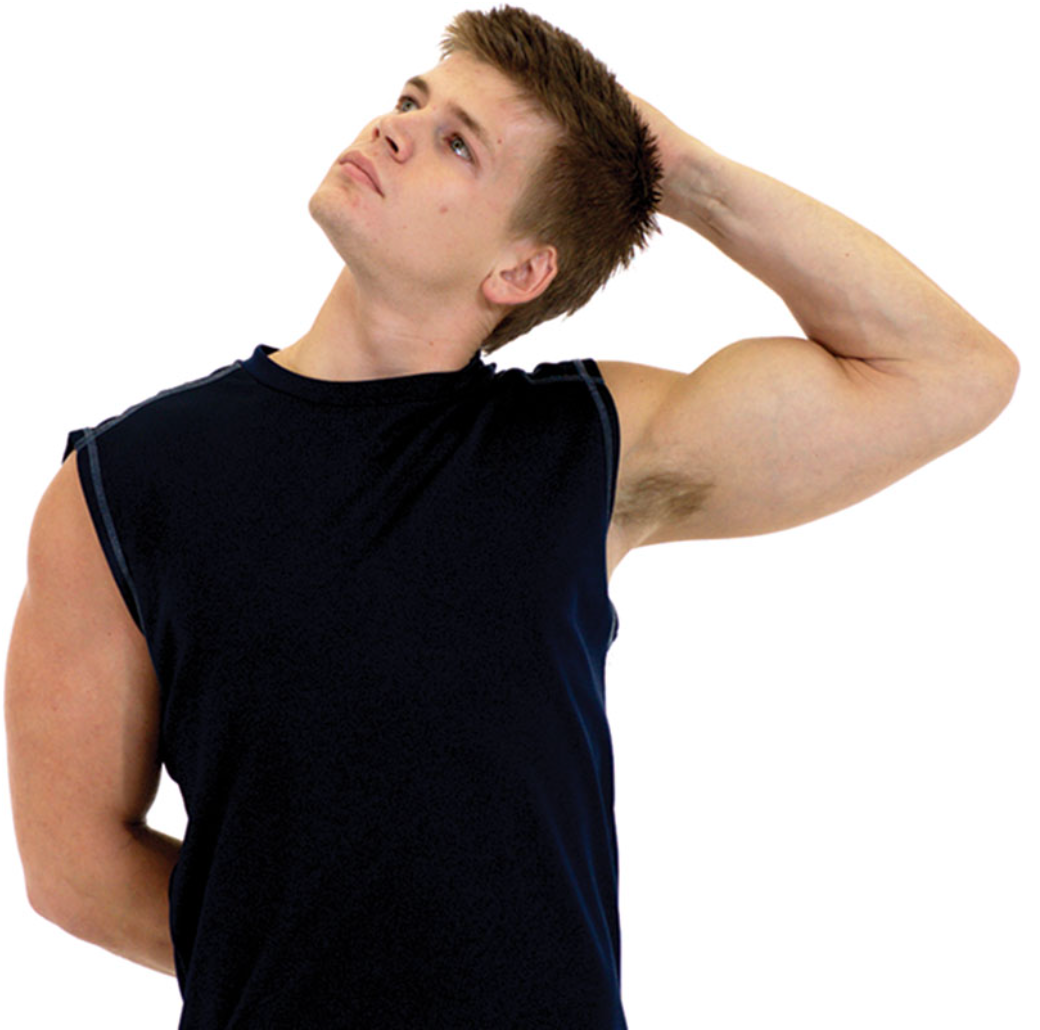

71
New cards
what is the **minimum** duration for which a static stretch should be held?
30 seconds
72
New cards
TRUE OR FALSE: static stretching, when performed for 30 seconds or less prior to every workout and followed by dynamic activities, impairs athletic performance
false
73
New cards
active stretching
a type of stretching that uses agonists and synergists to dynamically move the joint into a range of motion; includes holding the stretched position for 1–2 seconds and repeating for 5–10 repetitions
74
New cards
active gastrocnemius stretch
stand with back hip and knee straight (target leg)
the opposite hip and knee are flexed and swing back and forth across the body
this motion causes rotation at the back knee and eversion and inversion of the foot and ankle
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
the opposite hip and knee are flexed and swing back and forth across the body
this motion causes rotation at the back knee and eversion and inversion of the foot and ankle
repeat for the desired number of repetitions

75
New cards
active soleus stretch
stand with back hip and knee slightly flexed (target leg)
the opposite hip and knee are flexed and swing back and forth across the body
this motion causes rotation at the back knee and eversion and inversion of the foot and ankle
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
the opposite hip and knee are flexed and swing back and forth across the body
this motion causes rotation at the back knee and eversion and inversion of the foot and ankle
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
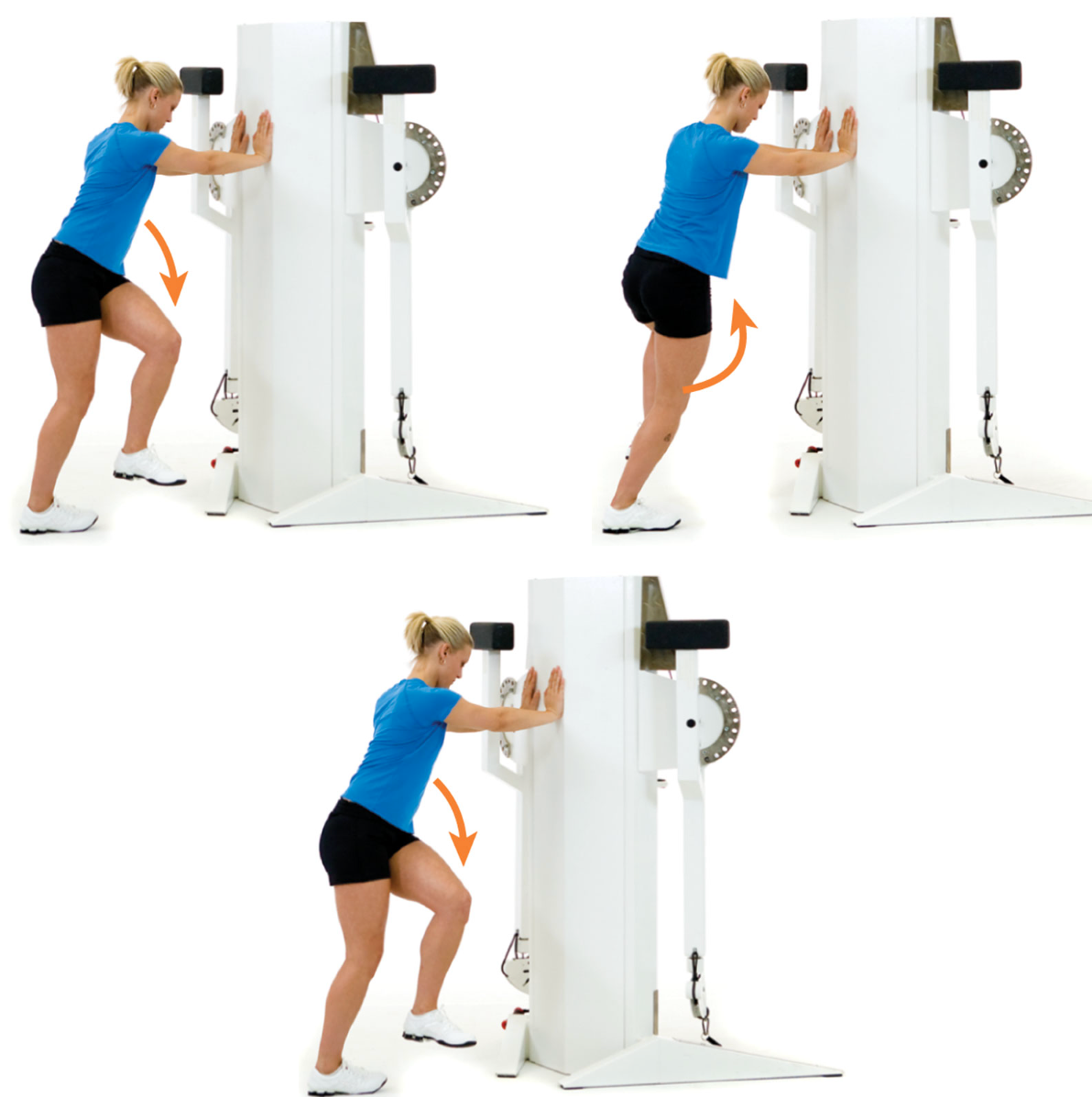

76
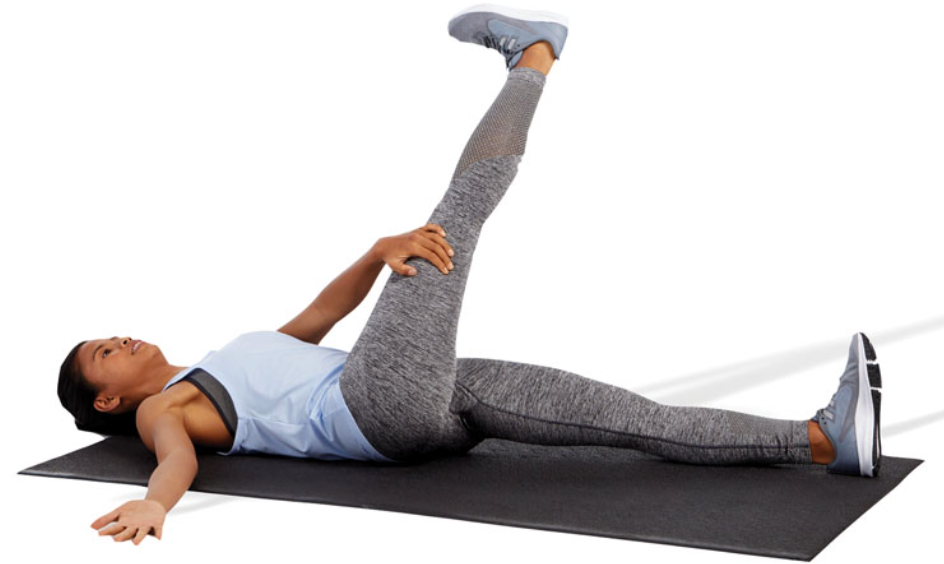
New cards
active 90/90 hamstring stretch
lie supine with one hip flexed 90 degrees (target leg)
straighten the target leg until a mild stretch is felt in the hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
straighten the target leg until a mild stretch is felt in the hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
repeat for the desired number of repetitions

77
New cards
active supine bicep femoris stretch
lie supine with one hip flexed 90 degrees (target leg) and the opposite leg straight and flat on the floor
next, adduct the target leg across the body and extend the knee until a mild stretch is felt in the lateral hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
keep both shoulders flat on the ground during this stretch
avoid rotating the torso toward the stretched leg
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
next, adduct the target leg across the body and extend the knee until a mild stretch is felt in the lateral hamstrings
the stretch should not cause pain or extreme discomfort
keep both shoulders flat on the ground during this stretch
avoid rotating the torso toward the stretched leg
repeat for the desired number of repetitions

78
New cards
active standing adductor stretch
stand with legs spread apart and shift weight to one side (lateral lunge position) until a stretch is felt in the inner thigh area
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
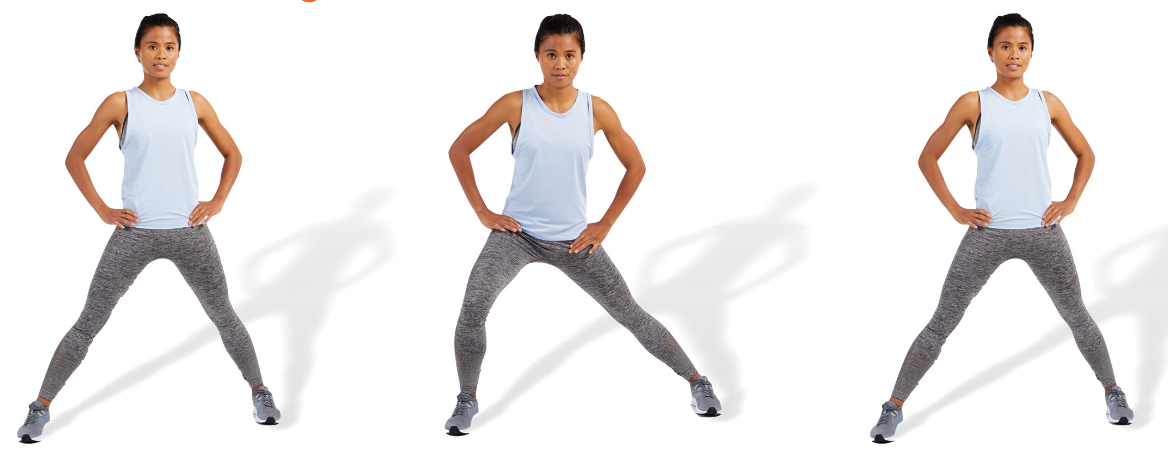

79
New cards
active ball adductor stretch
sit on a stability ball in a lateral lunge position until a stretch is felt in the inner thigh area
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
posteriorly rotate the pelvis and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
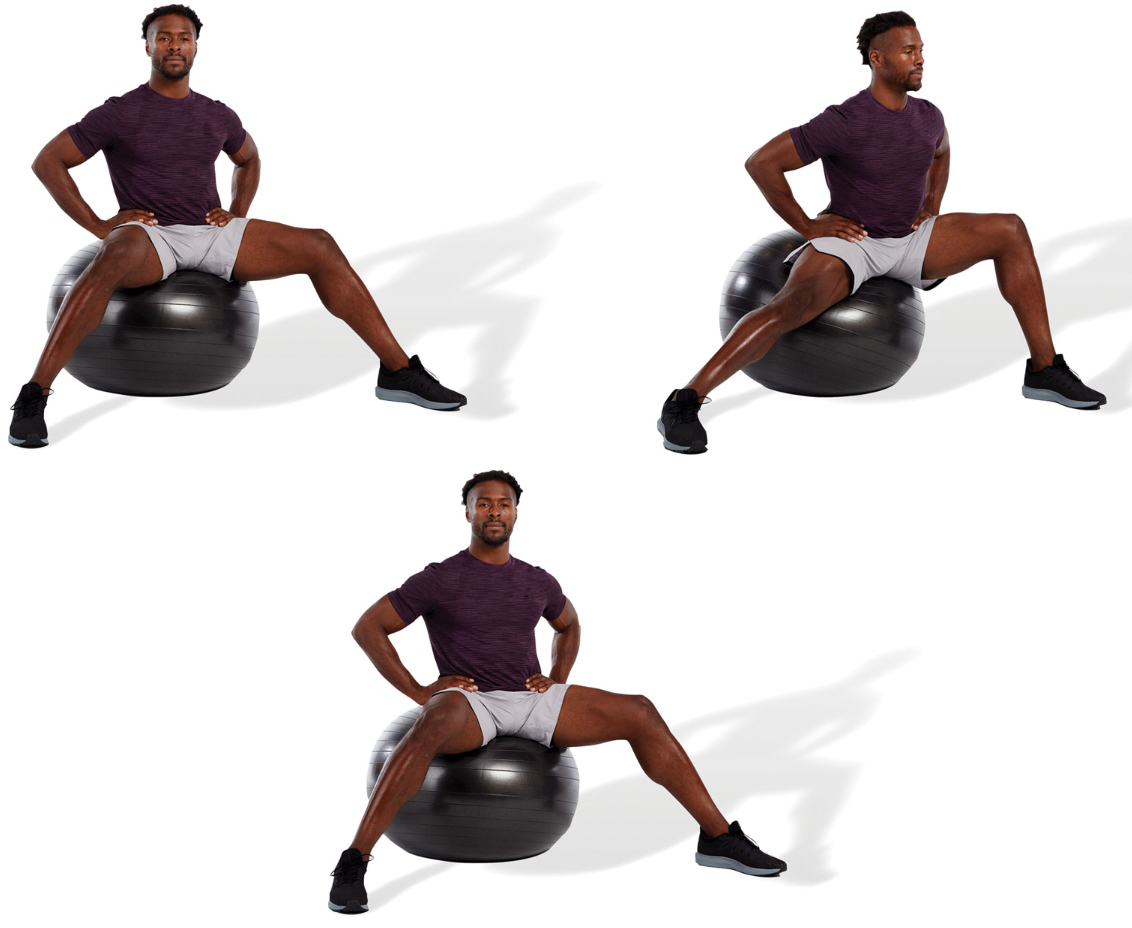

80
New cards
active adductor magnus stretch
while standing with one foot on a bench or plyo box, reach down to a comfortable position without excessively rounding the spine until a stretch is felt
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
81
New cards
active standing TFL stretch
stand in a staggered stance with the front leg slightly bent and rear leg straight
externally rotate the rear foot, draw in the navel, and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and repeat for the desired number of repetitions
externally rotate the rear foot, draw in the navel, and posteriorly rotate the pelvis
squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and repeat for the desired number of repetitions

82
New cards
active kneeling hip flexor stretch
kneel with front and back legs flexed at a 90-degree angle
draw in the navel and posteriorly rotate the pelvis. Squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and slowly rotate posteriorly as illustrated
to emphasize the TFL, externally rotate the rear leg, whereas to emphasize the psoas, internally rotate the rear leg
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
draw in the navel and posteriorly rotate the pelvis. Squeeze the gluteal muscles of the side being stretched
as a progression, raise the arm (on the same side as the back leg) up and over to the opposite side while maintaining pelvis position
hold side bend position and slowly rotate posteriorly as illustrated
to emphasize the TFL, externally rotate the rear leg, whereas to emphasize the psoas, internally rotate the rear leg
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
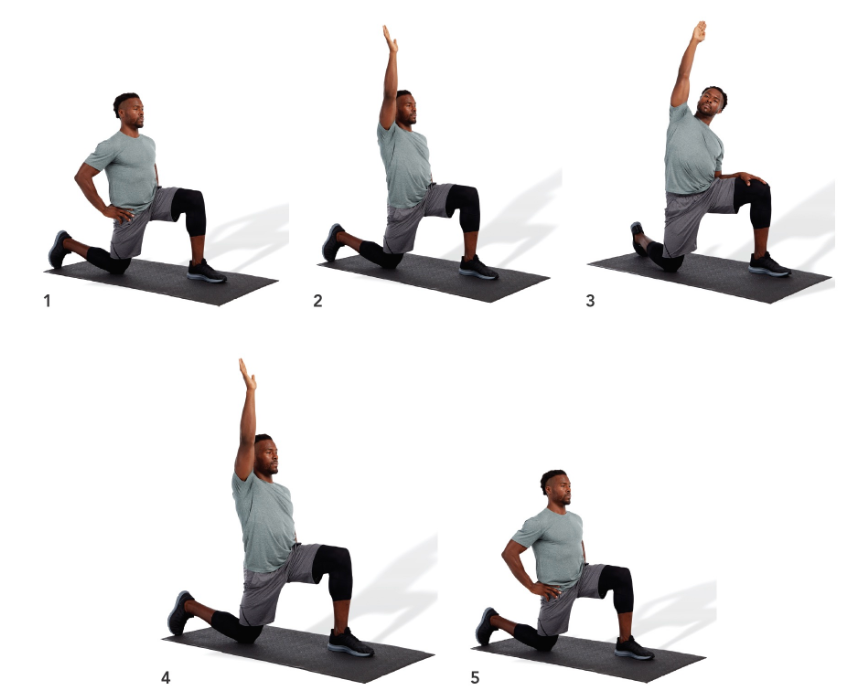
83
New cards
active latissimus dorsi ball stretch
in the quadruped position, put one arm on top of a stability ball and roll forward until a stretch is felt
posteriorly rotate the pelvis, point the thumb up toward the sky, and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
posteriorly rotate the pelvis, point the thumb up toward the sky, and draw in the abdominals when performing this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
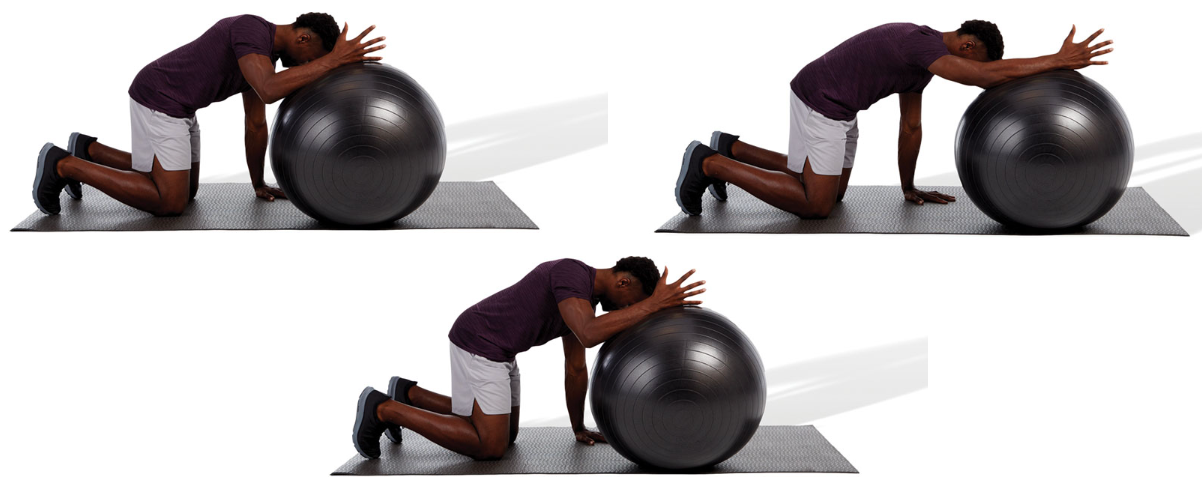
84
New cards
active pectoral stretch
standing with one arm in a 90/90 arm position, lean forward until a stretch is felt in the anterior shoulder and chest area
do not allow the shoulders to elevate (shrug) during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
do not allow the shoulders to elevate (shrug) during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
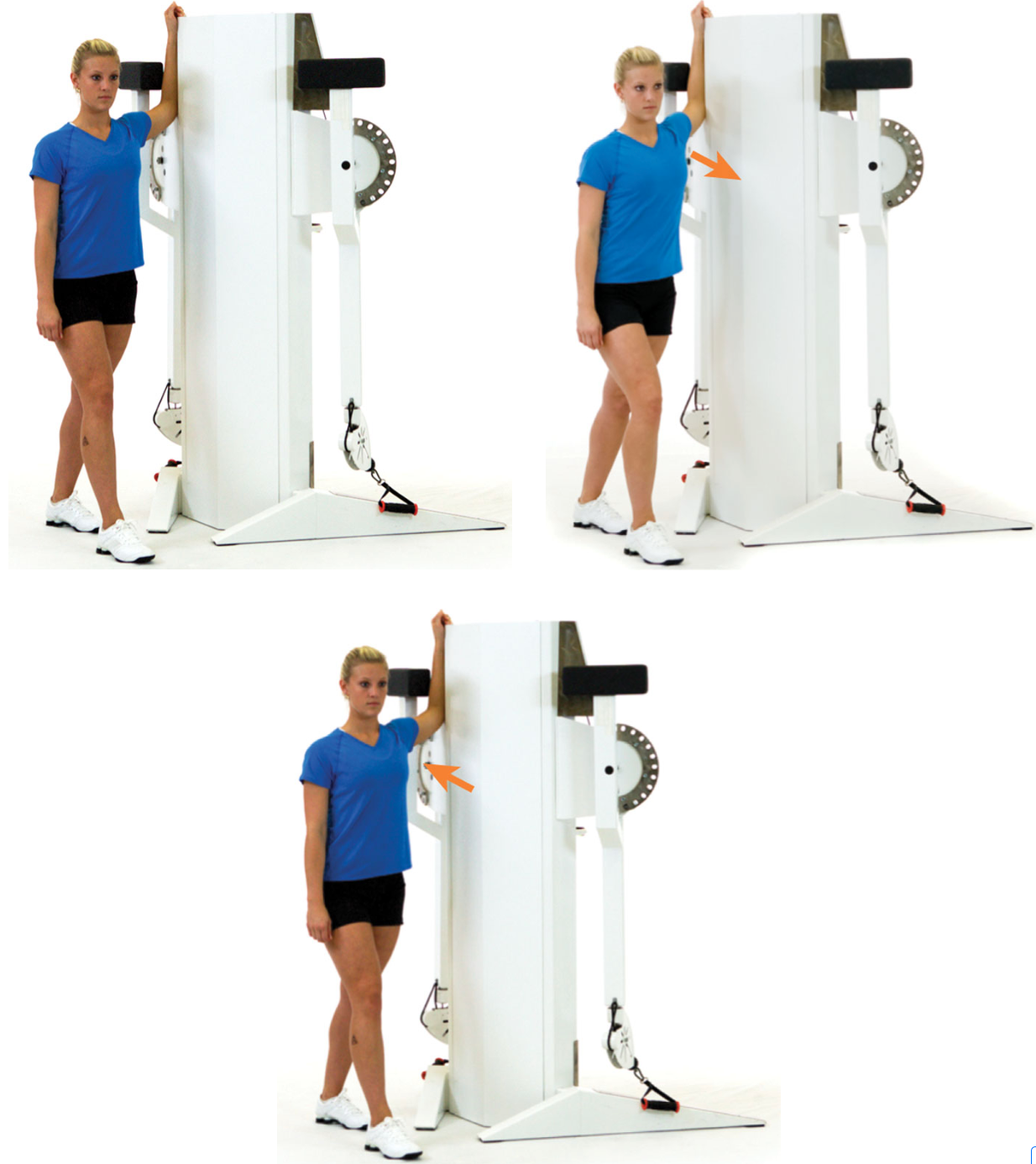
85
New cards
active upper trapezius/scalene stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
86
New cards
active levator scapulae stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
next, slightly rotate the head to look in the axillary (armpit) region as shown
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
next, slightly rotate the head to look in the axillary (armpit) region as shown
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions

87
New cards
active sternocleidomastoid stretch
grasp the top of the head with one hand and laterally flex toward the same shoulder
rotate the head up and away as shown
only perform this stretch to the point of mild tension
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions
rotate the head up and away as shown
only perform this stretch to the point of mild tension
do not allow the chin to jut forward or shoulders to shrug during this stretch
repeat for the desired number of repetitions

88
New cards
dynamic stretching
a type of stretching that uses the force production of a muscle and the body’s momentum to take a joint through the full available range of motion
89
New cards
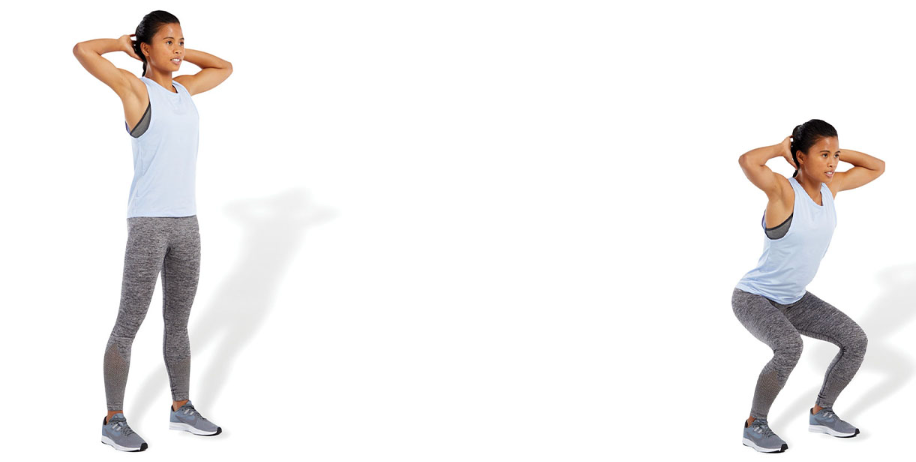
prisoner squat
with arms behind the head and feet approximately shoulder-width apart, perform a bodyweight squat
as a progression to this exercise, add a calf raise at the top position after performing the squat
as a progression to this exercise, add a calf raise at the top position after performing the squat

90
New cards
mutliplanar lunge with reach
perform the lunge in all three planes of motion: sagittal, frontal, and transverse
in other words, perform a forward lunge, lateral lunge, and turning lunge
in other words, perform a forward lunge, lateral lunge, and turning lunge

91
New cards
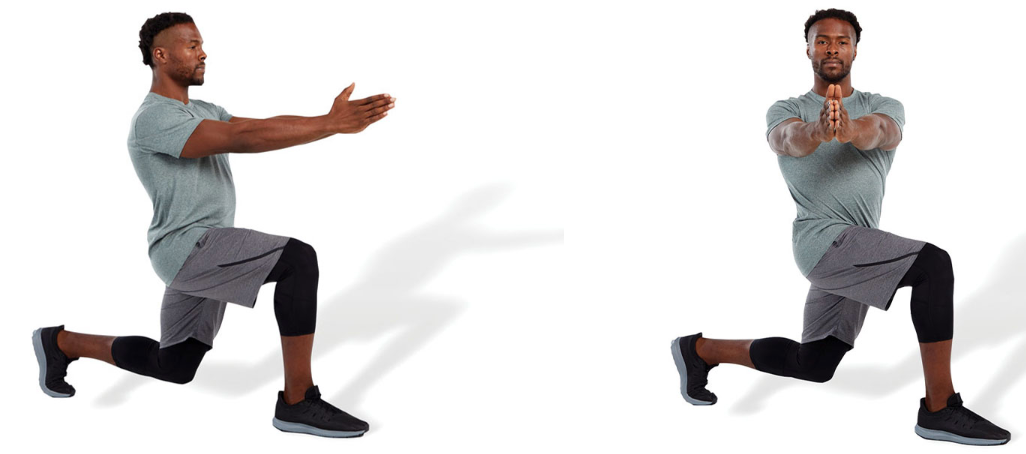

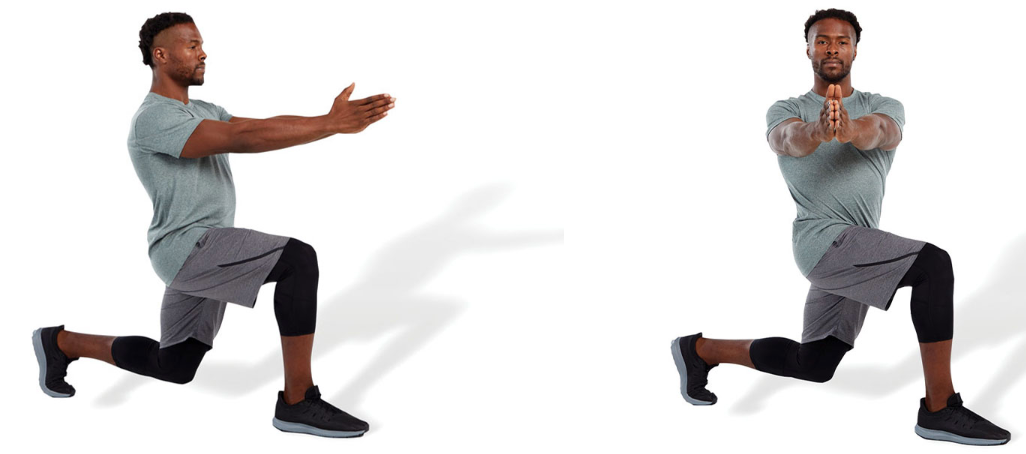
lunge with rotation
perform a forward lunge with trunk rotation toward the outside portion of the forward leg
this exercise can be performed with or without an external load, such as a medicine ball
this exercise can be performed with or without an external load, such as a medicine ball

92
New cards
tube walking: side to side
place elastic tubing around the knees, maintain a quarter squat position, and sidestep for the desired number of repetitions in each direction
make sure the knees are tracking in line with the second and third toes
do not allow the knees to cave inward
this exercise primarily targets the hip abductors, such as the gluteus medius
the band can also be placed around the ankles (as shown) as a progression to this exercise
make sure the knees are tracking in line with the second and third toes
do not allow the knees to cave inward
this exercise primarily targets the hip abductors, such as the gluteus medius
the band can also be placed around the ankles (as shown) as a progression to this exercise
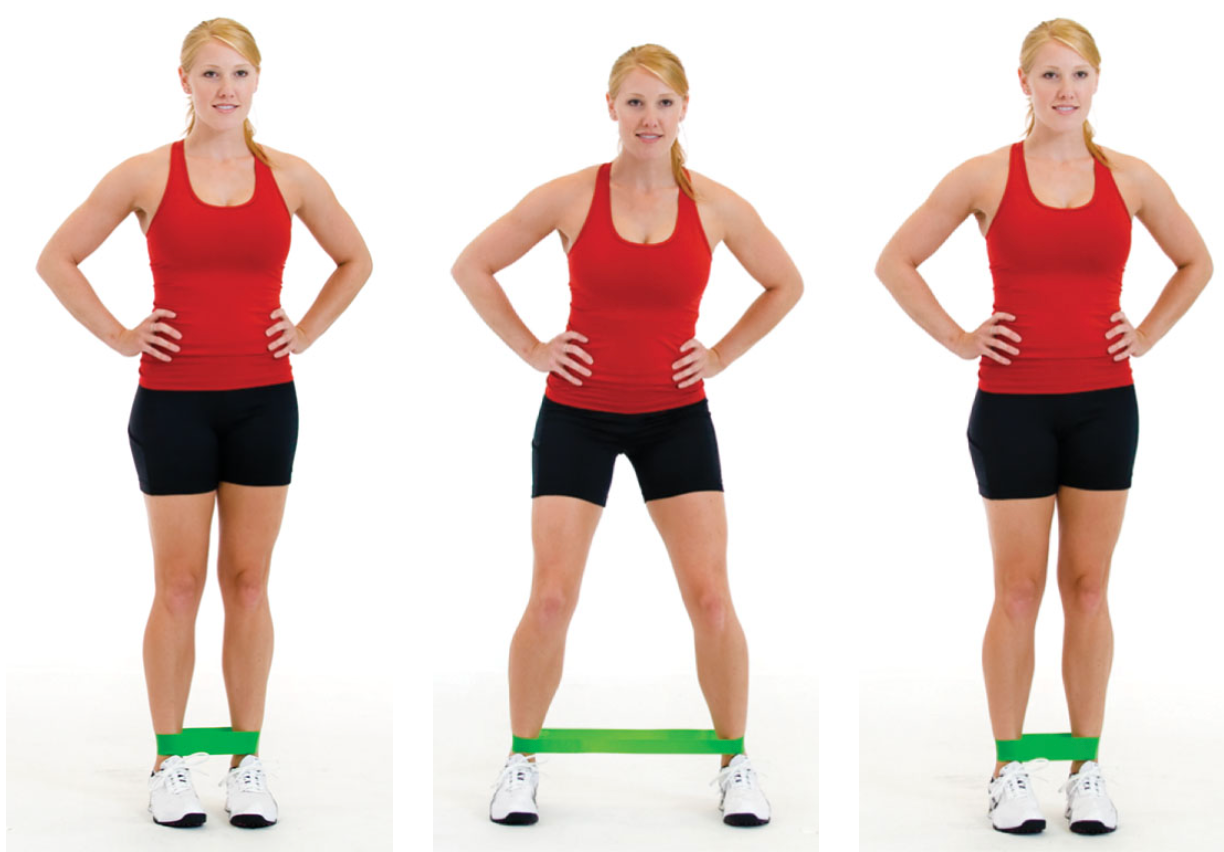

93
New cards
leg swings: front to back
in standing position, swing one leg in a controlled pendulum fashion to the front and back, only lifting the leg as high as can safely be controlled
keep a tall, upright posture with the abdominals drawn in during the duration of the exercise
keep a tall, upright posture with the abdominals drawn in during the duration of the exercise
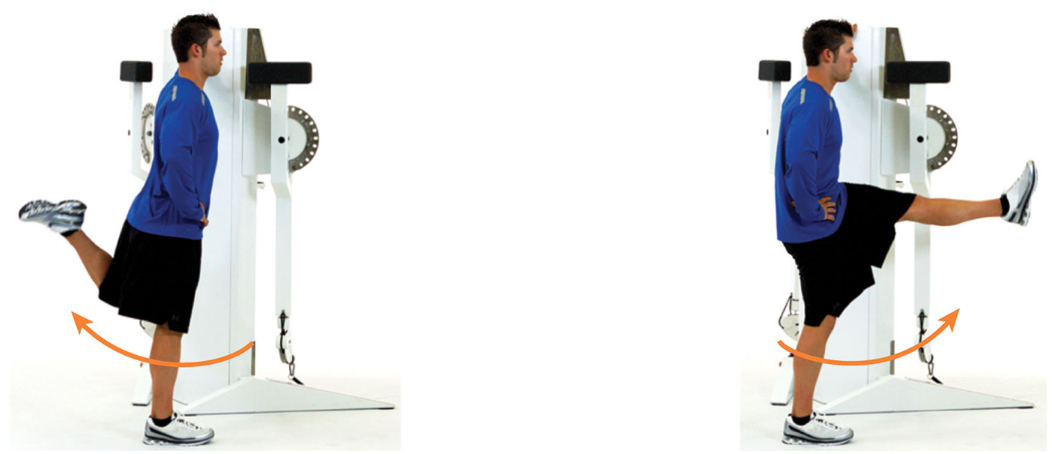

94
New cards
leg swings: side to side
in standing position, swing one leg in a controlled pendulum fashion from side to side
like front to back hip swings, keep a tall, upright posture with the abdominals drawn in during the duration of the exercise
like front to back hip swings, keep a tall, upright posture with the abdominals drawn in during the duration of the exercise
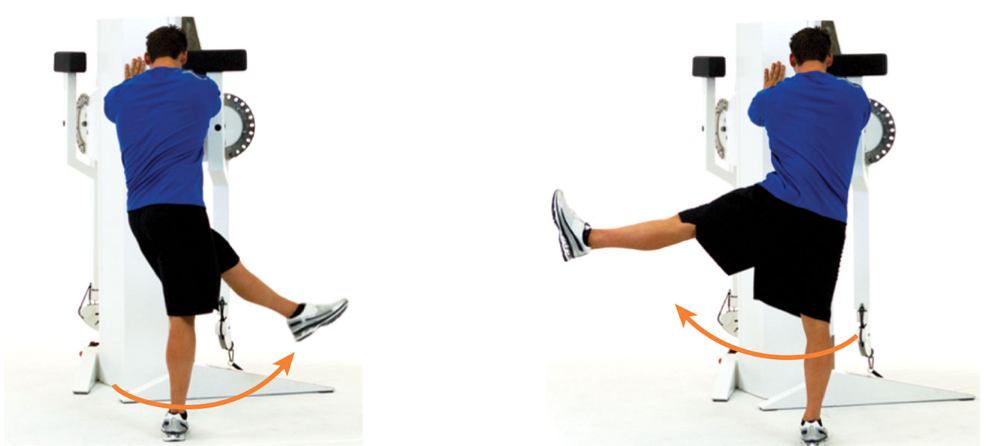
95
New cards
frankenstein
this technique is performed while walking forward with arms stretched out away from the body
only lift each leg as high as can be safely controlled while maintaining ideal posture
keep a neutral back without leaning to the left or right
this exercise helps stretch the hamstrings
only lift each leg as high as can be safely controlled while maintaining ideal posture
keep a neutral back without leaning to the left or right
this exercise helps stretch the hamstrings
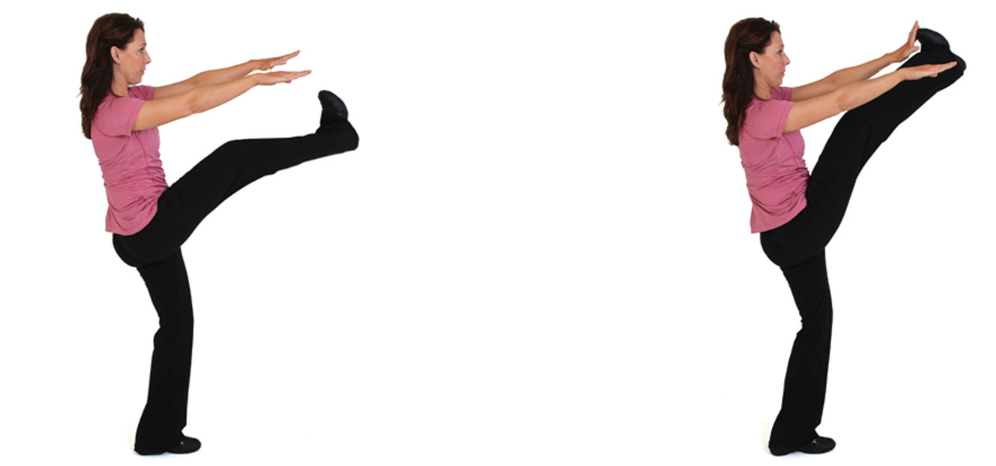

96
New cards
high knee
this technique is performed while walking forward
with each step, flex the hip as high as can be controlled, grasping the knee at the top with both hands
be sure to pause at the top and switch legs with each step
with each step, flex the hip as high as can be controlled, grasping the knee at the top with both hands
be sure to pause at the top and switch legs with each step

97
New cards
push-up with rotation
perform a bodyweight push-up with a trunk rotation at the top
keep the abdominals drawn in, chin tucked, and spine in a neutral position throughout the exercise
keep the abdominals drawn in, chin tucked, and spine in a neutral position throughout the exercise
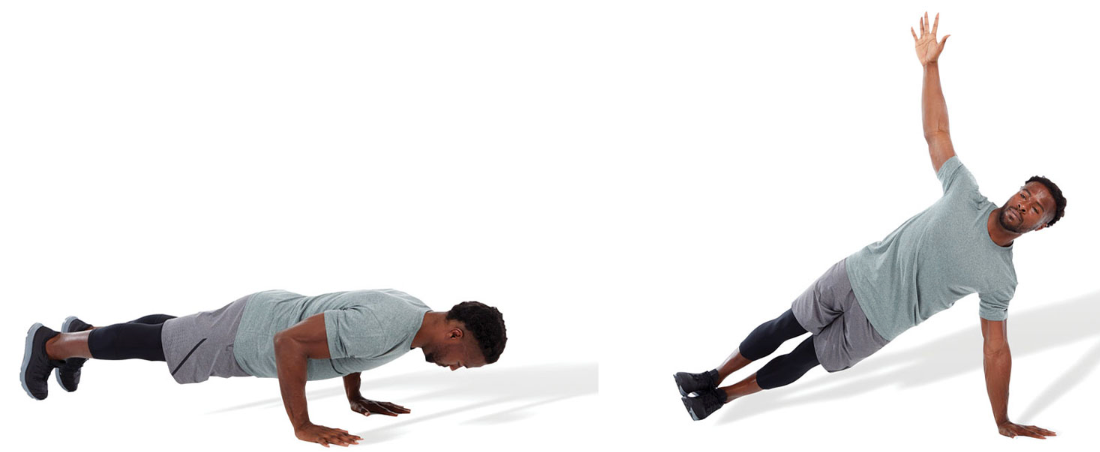

98
New cards
ball russian twist
while bridging on a stability ball, perform trunk rotation
this exercise targets the internal and external obliques in addition to the gluteus maximus because it requires the participant to maintain a bridged position
the exercise can be performed with or without external load, such as using a medicine ball
this exercise targets the internal and external obliques in addition to the gluteus maximus because it requires the participant to maintain a bridged position
the exercise can be performed with or without external load, such as using a medicine ball

99
New cards
arm circles
perform arm circles in both directions using a slow to moderate speed

100
New cards
jumping jacks
when performing jumping jacks as a dynamic warm-up, the goal is to slightly elevate heart and respiration rates without causing undue fatigue
