column and gas chromatography
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is the purpose of column chromatography?
purification technique
allows us to purify organic compounds
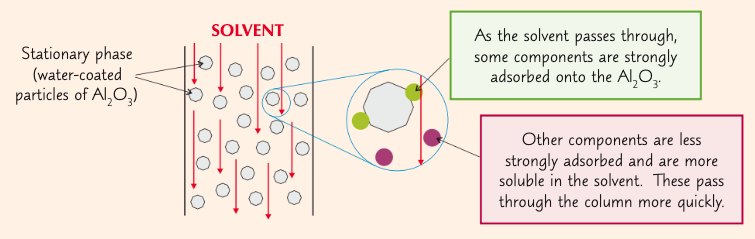
summarise how column chromatography works:
large glass column packed w/ solid powder (stationary phase)
sample to be purified added on top
solvent (mobile phase) flushed through column
this separates out of the components in the mixture (based on their affinity for the stationary phase or how well they dissolve in the mobile phase)
give 2 examples of what the stationary phase might be in column chromatography:
silica
aluminium oxide
what is retention and how is it affected by polarity?
how strongly a compound is absorbed onto the stationary phase
like Rf values, they allow certain substances to be identified
more polar groups will be retained longer through the column (they will come out later)
what is the stationary phase in gas chromatography?
powder packed inside a long capillary tube by an oil
what is the mobile phase in gas chromatography?
unreactive gas e.g. N/Ar that carries the sample along
summarise the process of gas chromatography:
sample injected - when gas begins to flow, some components flow along w/ gas
this is when mixture begins to separate - some is retained by oil
components leave the column (usually a coiled tube) at different times depending on their retention - retention time
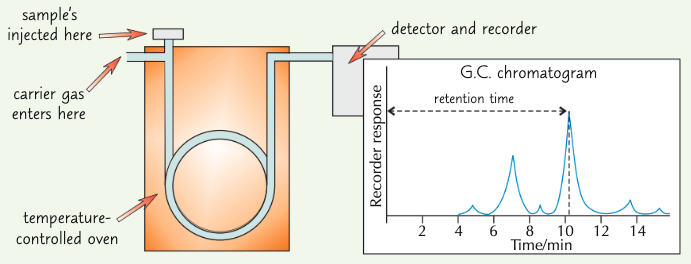
in gas chromatography, what does the retention time depend on?
how much time the component spent moving along w/ carrier gas
what does a GC-trace show?
how long component took to move through the gas column
area under peak = relative amount in mixture
give some uses of gas chromatography:
often coupled w/ a mass/NMR spectrometer to find mass/charge ratio / structure of components in mixture
extremely sensitive so can be used in blood/urine samples for testing drug-taking in athletes
can be used to match compounds by comparing retention times - if same mobile/stationary phases used
what is a GC-MS?
gas chromatography set up couples w/ a mass spectrometer (hence GC-MS)
separates out substances then produces mass spectrum for each component)