PSYC-2900 Chapter 3.1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
dorsal/superior
the top of the brain or the back of the spine
ventral/inferior
the bottom of the brain or the front of the spine
anterior/rostral
the front of the brain or top of the spine
posterior/caudal
the back of the brain or bottom of the spine
medial
the centre of the brain
lateral
the side of the brain
ipsilateral
the same side of the brain
contralateral
the opposite side of the brain, commonly used to describe something occurring on the other side and motor functions
decussate
crossing over to the other side of the brain
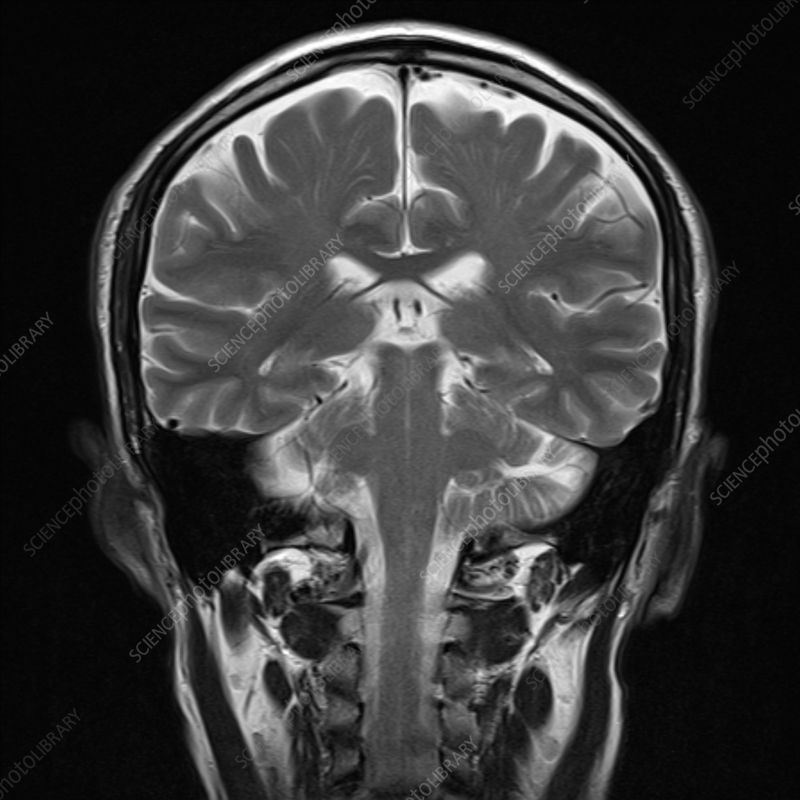
coronal/transverse plane
a plane of dissection that divides through the brain’s dorsal and ventral sides
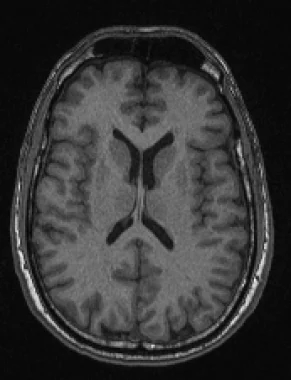
axial/horizontal plane
a plane of dissection that divides through the brain’s rostral and caudal sides
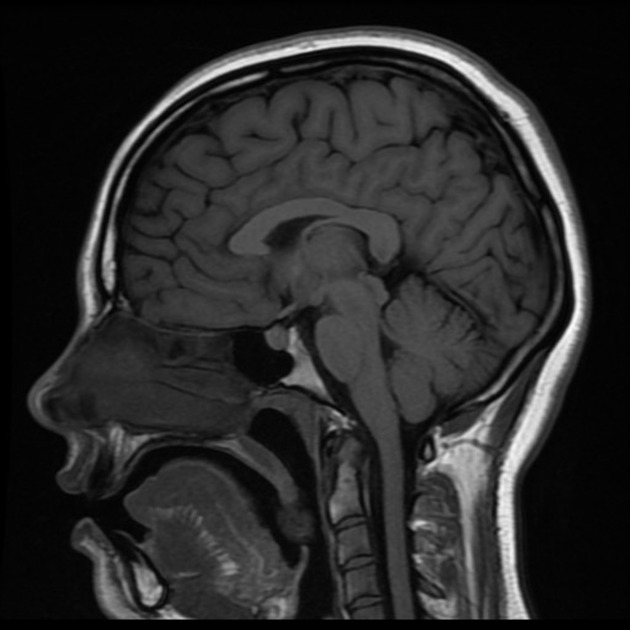
sagittal plane
a plane of dissection that divides the brain in two from the median
blood brain barrier (BBB)
a layer of protection of the brain that provides protection from blood-borne threats (e.g. toxins, illness)
skull and spinal column
a layer of protection of the brain that provides protection from physical damage by creating a bony shield in which the CNS is located
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
a layer of protection of the brain that is a clear fluid, and provides cushioning to the CNS and clears waste products. it has a pulsatile flow, which is related to the cardiac cycle
dura mater
the outermost meningeal layer closely adhered to the arachnoid membrane
arachnoid membrane
the middle meningeal layer, closely adhered to the dura mater
pia mater
the innermost meningeal layer, adhered to the brain surface
subarachnoid space
the space between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
ventricular system
2 “C” shaped ventricles, 1 found on both hemispheres of the brain, join in the midline and connect to the third ventricle. the cerebral aqueduct joins the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle
flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CFS)
first produced in by the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles. from the fourth ventricle, it will either continue down the central canal of the spinal cord or flow into the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord. it is reabsorbed into the bloodstream by arachnoid granulations
obstructive hydrocephalus
a condition caused by development or a tumour that causes the flow of cerebrospinal fluid to be blocked. it is surgically repaired with a valve/shunt and regulated by a pressure valve. the fluid flows to the abdominal cavity where it is absorbed into the bloodstream
development of the central nervous system (CNS)
the neural tube forms into subdivisions known as the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, and become further specialized into 5 subdivisions
forebrain
a major division in the development of the CNS that includes the lateral and third ventricle, the telencephalon and diencephalon subdivisions, and the structures of the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system, thalamus, and hypothalamus
telencephalon
a subdivision of the forebrain, forms into the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system
diencephalon
a subdivision of the forebrain that surrounds the third ventricle, forms into the thalamus and hypothalamus, and is located between the telencephalon and mesencephalon
midbrain
a major division in the development of the CNS surrounding the cerebral aqueduct, and is the most superior portion of the brainstem. it includes the mesencephalon subdivision, and the structures of the tectum and tegmentum
mesencephalon
a subdivision of the midbrain that forms in the tectum and tegmentum
hindbrain
a major division in the development of the CNS that surrounds the fourth ventricle, the metencephalon and myelencephalon subdivisions, and the structures of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata
metencephalon
a subdivision of the hindbrain that forms into the cerebellum and pons
myelencephalon
a subdivision of the hindbrain that forms into the medulla oblongata
cerebral hemispheres
the outermost layer of the brain with a surface made of gyri and sulci. the inner tissue is made of white matter, and the outer tissue is made of grey matter
gyri
a ridge on the cerebral cortex
sulci
a furrow on the cerebral cortex
fissure
a deep sulcus on the surface of the cerebral cortex
white matter
the inner tissue of the cerebral cortex made of bundles of myelinated axons, with the largest (of crossing) commissural fibres being the corpus callosum
corpus callosum
a large band of fibres extending from the anterior to posterior brain that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and allows for in-between communication
gray matter
the outer tissue of the cerebral cortex made of somas
primary sensory areas
the first level of processing, receives input from the parietal lobe through the primary somatosensory cortex, the temporal lobe through the primary auditory cortex, and the occipital lobe through the primary visual cortex. sensory input is sent to the contralateral side
sensory association areas
the second level of processing where information is sent from the primary sensory areas and performs higher processing functions (e.g. planning, learning, perception, integration)
primary motor cortex
located in the frontal lobe, has contralateral organization
premotor cortex
located anteriorly to the primary motor cortex, the motor association area (e.g. controls motor behaviour)
prefrontal cortex
located in the anterior frontal lobe, involved in planning and strategy
lateralization of function
the idea that the brain's left and right hemispheres have different functions, information processing, and behaviour controls. association areas in each hemisphere is connected through the corpus callosum
left hemisphere (lateralization)
responsible for serial activities
(e.g. verbal activities, talking, reading, writing)
right hemisphere (lateralization)
responsible for activities requiring synthesis
(e.g. visual perception, reading maps, drawing, bringing ideas together)
split brain
a severed connection between the brain’s two hemispheres, resulting in processing on each side occurring in isolation
limbic system
part of the cortex that includes the hippocampus, amygdala, fornix (forms part of the ventricle floor), and the mammillary bodies. its functions include learning, memory, and emotions
basal ganglia
a collection of nuclei all with similar function below the cortex that forms the lateral walls and anterior floor of the lateral ventricles and is involved in the control of movement. it includes the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus
Parkinson’s disease
a disease that affects midbrain neurons that project caudate nucleus and putamen, resulting in the loss of control of movement
thalamus
a part of the limbic system that is a relay station made of several nuclei that receive different types of signals and project them to other areas, located medial and caudal to the basal ganglia
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
a part of the thalamus that receives visual input from the eye and sends it to the primary visual cortex
medial geniculate nucleus (MGN)
a part of the thalamus that receives auditory input and sends it to the primary auditory cortex
ventrolateral nucleus (VLN)
a part of the thalamus that receives signals from the cerebellum and sends it to the primary motor cortex
hypothalamus
a part of the limbic system attached to the pituitary gland that controls the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems and organizes behaviours related to survival (i.e. feeding, fighting, fleeing, fornication)
pituitary gland
located inferiorly to the hypothalamus, releases hormones by signals from neurons from the hypothalamus
tectum
the “roof” of the midbrain, formed of four bumps: the superior colliculi (visual), and inferior colliculi (auditory) (two bumps on each side)
tegmentum
a part of the midbrain made of several nuclei: the reticular formation, the periaqueductal gray matter, and the red nucleus and substantia nigra
reticular formation
a part of the midbrain made of several connected nuclei that receives sensory signals and projects them to the cortex, thalamus, and spinal cord. it is involved in sleep, arousal, muscle tone, and vital reflexes
periaqueductal gray matter
a part of the midbrain made of neurons and dendrites involved in sequenced movements, fighting, mating, and pain pathways
red nucleus and substantia nigra
a part of the midbrain made of neurons that are important parts of motor pathways
pons
a part of the hindbrain that contains a portion of the reticular formation and nuclei involved in sleep and arousal, and relays information between the cortex and cerebellum
cerebellum
a part of the hindbrain attached to the pons by cerebellar peduncles that contains a set of deep nuclei that receive signals from the cortex. it integrates motor and sensory information to modify motor outputs (feedforward loop)
medulla oblongata
a part of the hindbrain that contains part of the reticular formation and other nuclei involved in vital functions (e.g. regulation of cardiovascular system, respiration, skeletal muscle tone)
spinal cord
a long, tube-like structure of neural tissue found in the spinal foramen, made of cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments, with each having a pair of spinal nerves that exit through intervertebral foramina. it is surrounded by ascending (conveys sensory inputs) and descending (conveys motor output) white matter tracts on the outside
lumbar cistern
the bottom of the vertebral column that holds only spinal roots that look like a tail (cauda equina). it is the area where anaesthetic is injected into cerebrospinal fluid during a caudal block, or where cerebrospinal fluid is sampled during a spinal tap
dorsal horn
gray matter butterfly shape on the inside of the spinal cord where the termination for primary sensory neurons is found
ventral horn
gray matter butterfly shape on the inside of the spinal cord where the cell bodies of motor neurons are found
intermediate zone
gray matter butterfly shape on the inside of the spinal cord where interneurons are found
dorsal root
spinal nerves made of sensory/afferent axons that enter the segments of the spinal cord. the cell bodies of these neurons are found in the ganglion
ventral root
spinal nerves made of motor/efferent axons exiting the segments of the spinal cord