Lecture 21: Brainstem Clinical Conditions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
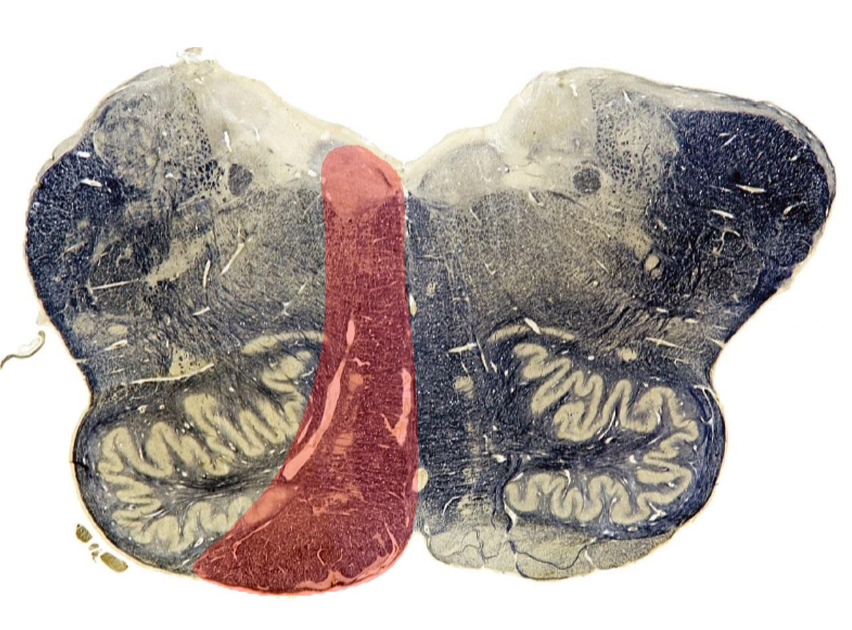
Inferior alternating hemiplegia (medial medulla)
ASA
corticospinal tract: contralateral spastic hemiplegia (UMN)
medial lemniscus: loss of tactile, vibratory sense and proprioception in contralateral body (Romberg sign)
CN XII nucleus/nerve: LMN ipsilateral tongue (dysarthria; deviation to ipsilateral side)
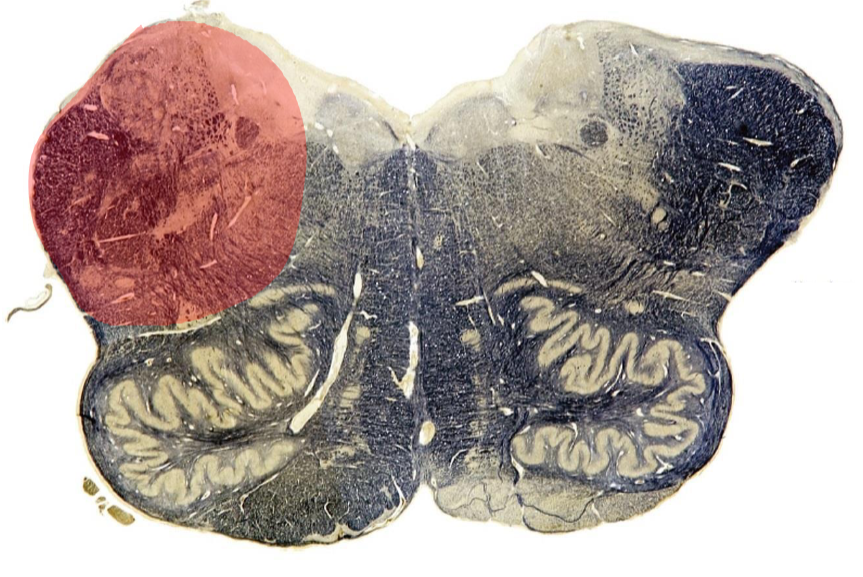
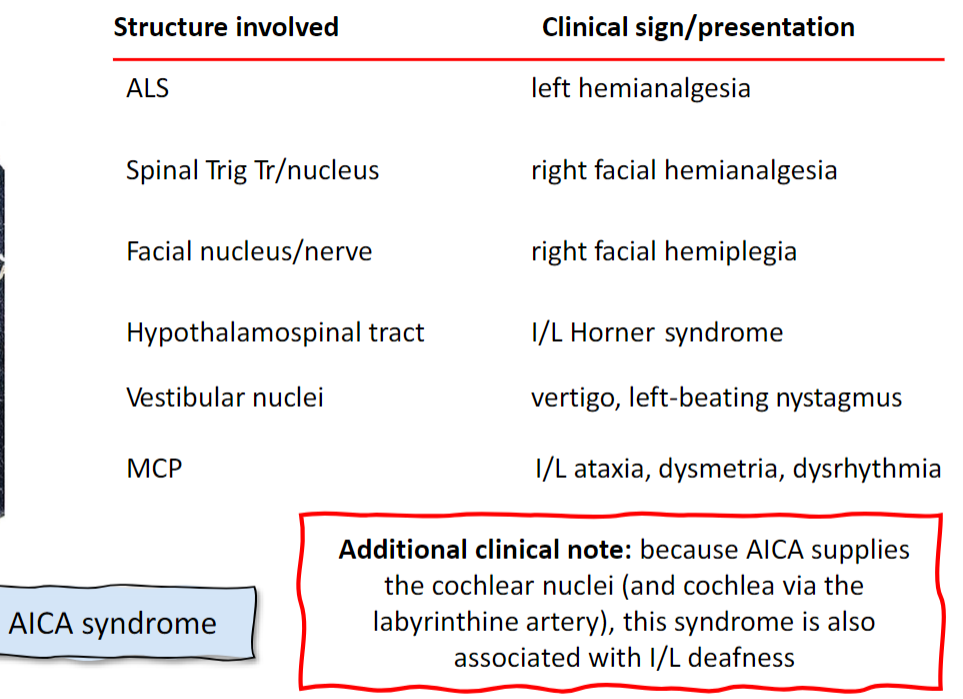
Lateral medullary syndrome/ Wallenberg syndrome
PICA
ALS: contralateral hemianalgesia
Spinal Trigeminal nucleus/tract: ipsilateral facial hemianalgesia
Nucleus Ambiguus: LMN, uvula to contralateral side, diminished gag, dysphagia, hoarse voice
Vestibular Nuclei: contralateral-beating nystagmus, vertigo, nausea
ICP: Ipsilateral ataxia
Hypothalamospinal tract: ipsilateral Horner syndrome
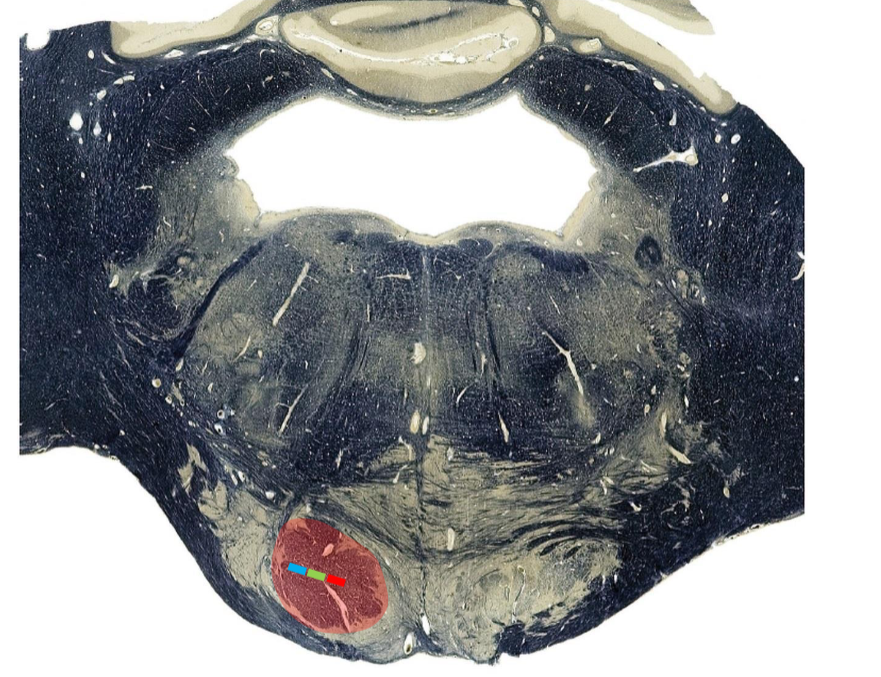
Pure motor hemiparesis
Medial pontine basis, caudal pons
Paramedian Basilar
Corticospinal tract: contralateral spastic hemiplegia (UMN)
Corticonuclear tract: dysarthria, dysphagia (UMN to contralateral tongue, palate)
commonly due to lacunar infarcts
sometimes hand involved to a greater extent than leg (somatotopic organization)
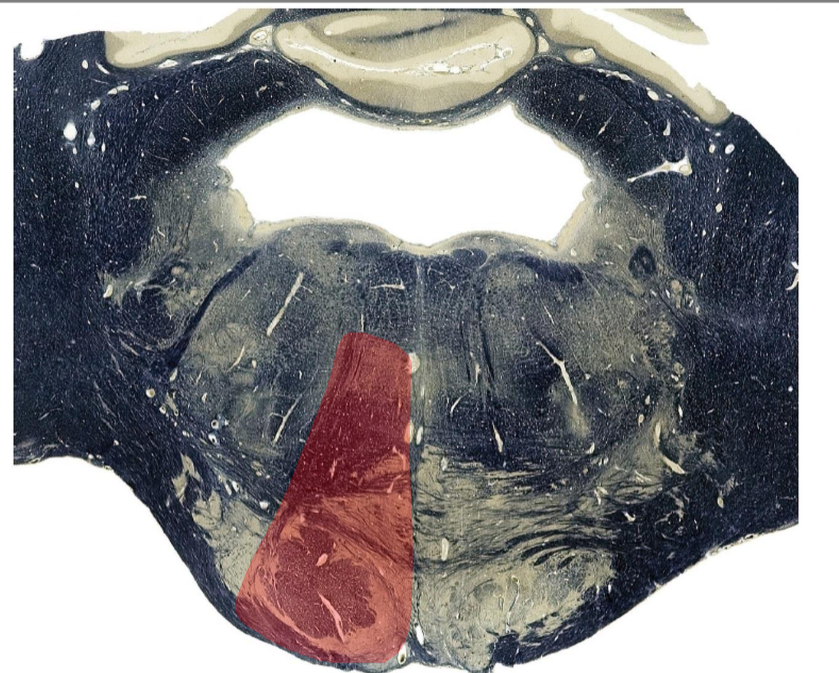
Middle alternating hemiplegia
Medial pontine basis and tegmentum, caudal pons
Paramedian Basilar
Corticospinal tract: contralateral spastic hemiplegia (UMN)
Corticonuclear tract: dysarthria, dysphagia (UMN to contralateral tongue, palate)
Pontine Nucleus/pontocerebellar fibers: contralateral ataxia, dysmetria, dysrhythmia
medial lemniscus: contralateral loss of discriminative touch
Abducens nerve fascicles: ipsilateral abducens nerve palsy- lateral rectus
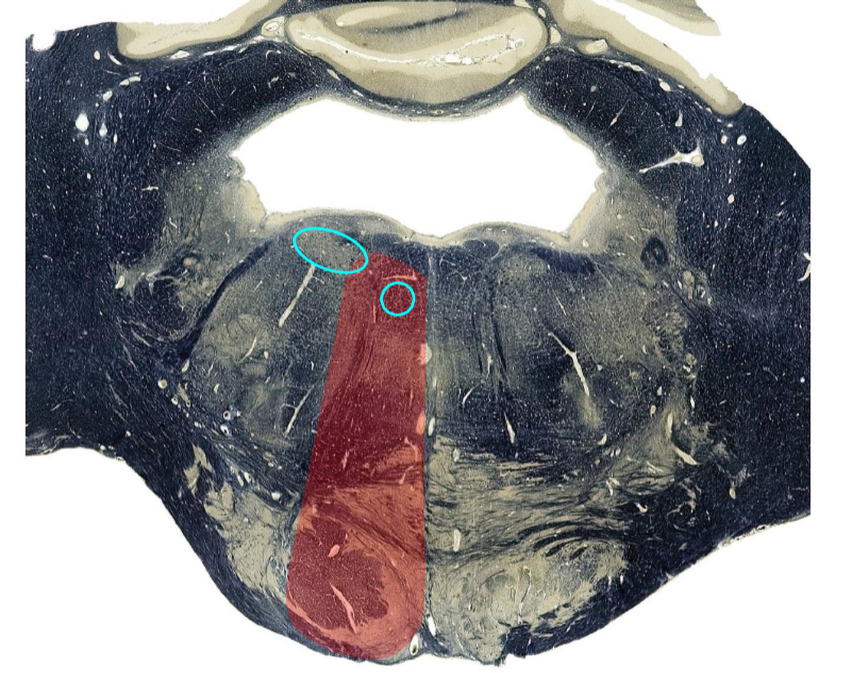
Medial pontine basis and tegmentum, caudal pons
Paramedian Basilar
Corticospinal tract: contralateral spastic hemiplegia (UMN)
Corticonuclear tract: dysarthria, dysphagia (UMN to contralateral tongue, palate)
Pontine Nucleus/pontocerebellar fibers: contralateral ataxia, dysmetria, dysrhythmia
medial lemniscus: contralateral loss of discriminative touch
PPRF: ipsilateral horizontal gaze palsy, contralateral gaze preference (Wrong way eyes)
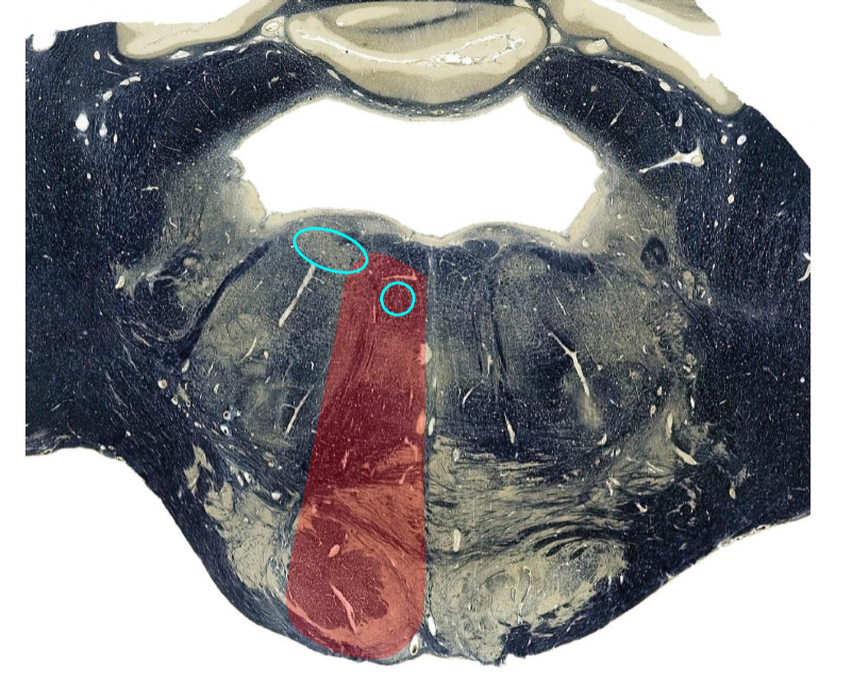
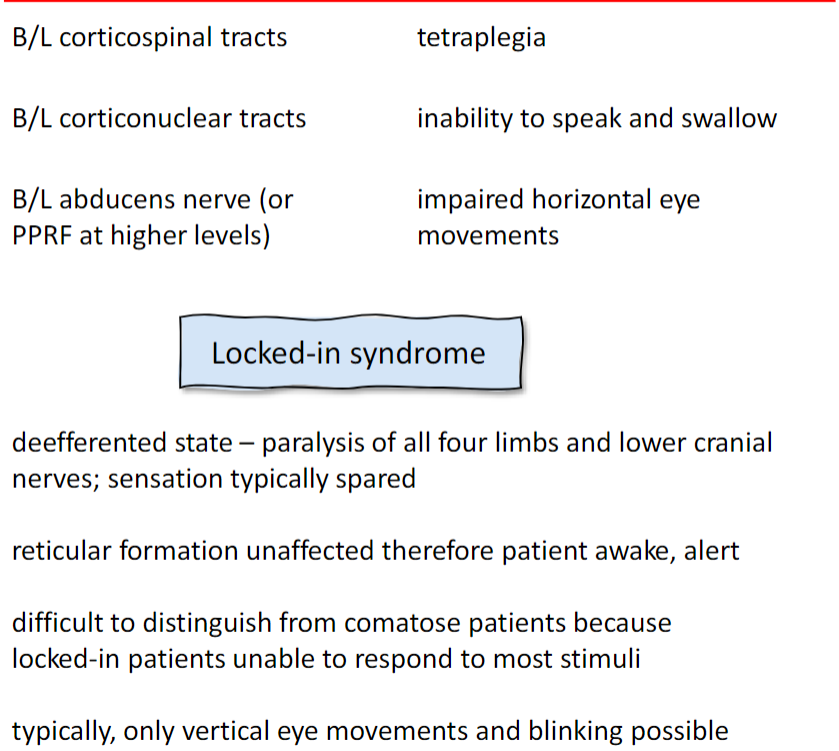
Abducens and PPRF
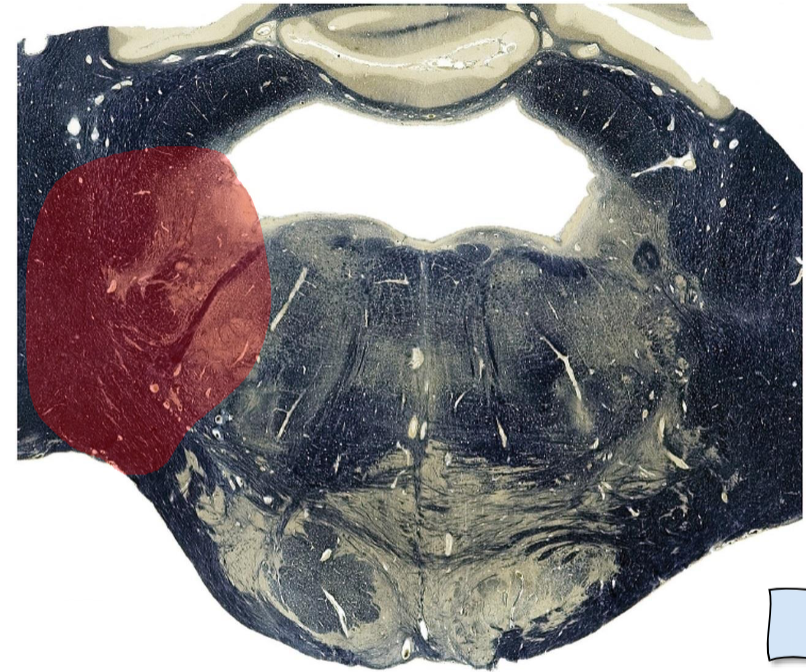
Lateral caudal pons
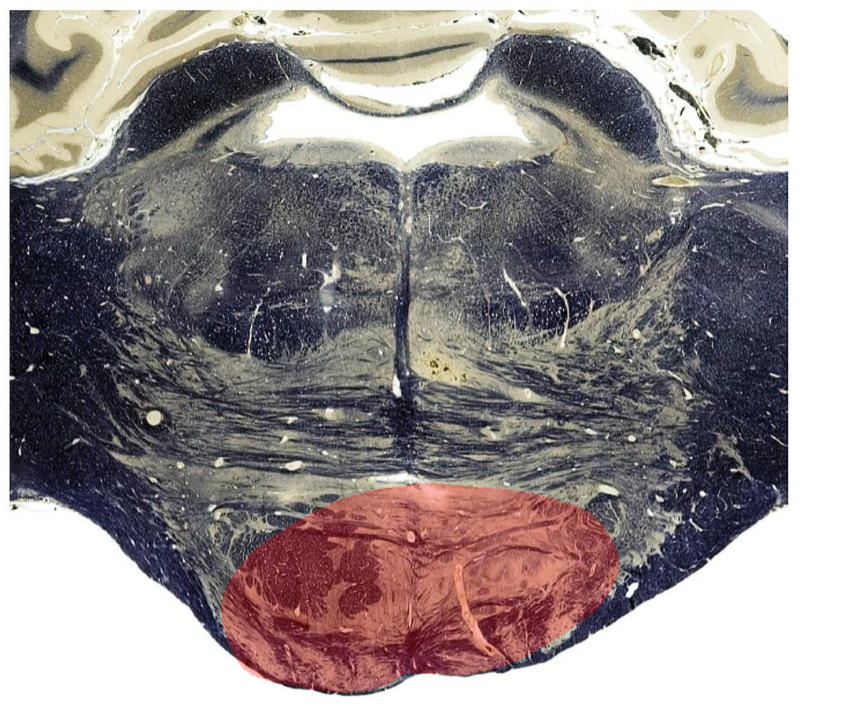
Bilateral ventral pons
Typically due to basilar artery infarct or thrombosis
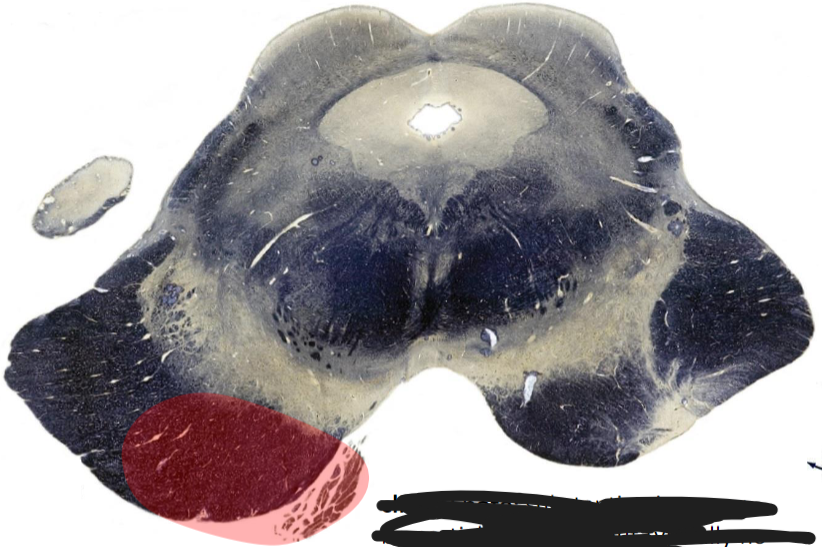
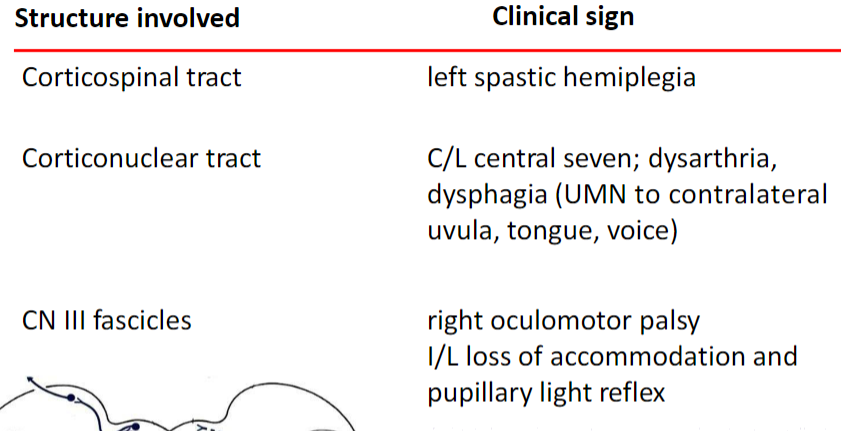
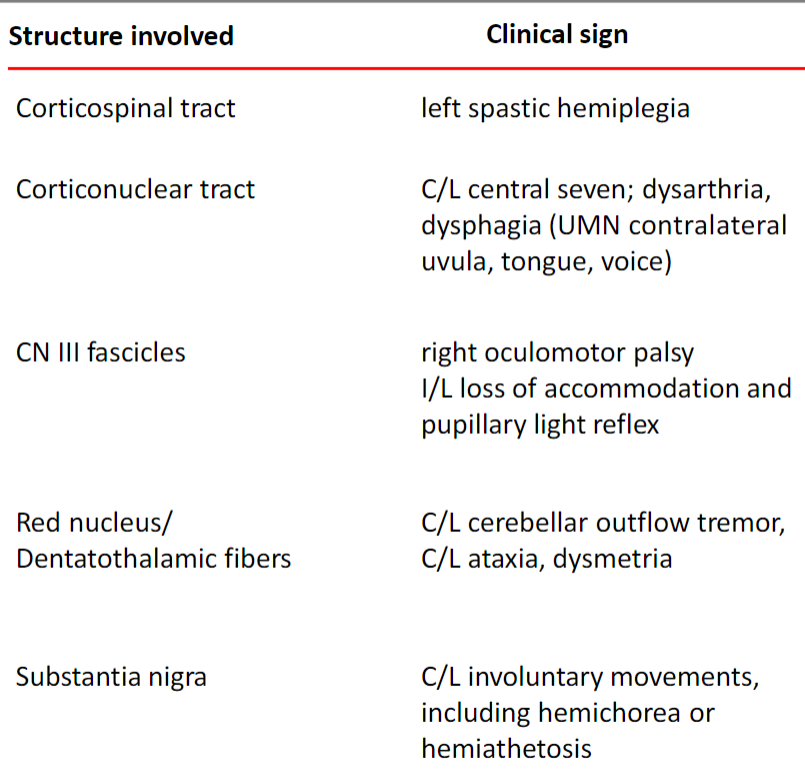
Weber syndrome/Superior alternating hemiplegia
Rostral Midbrain
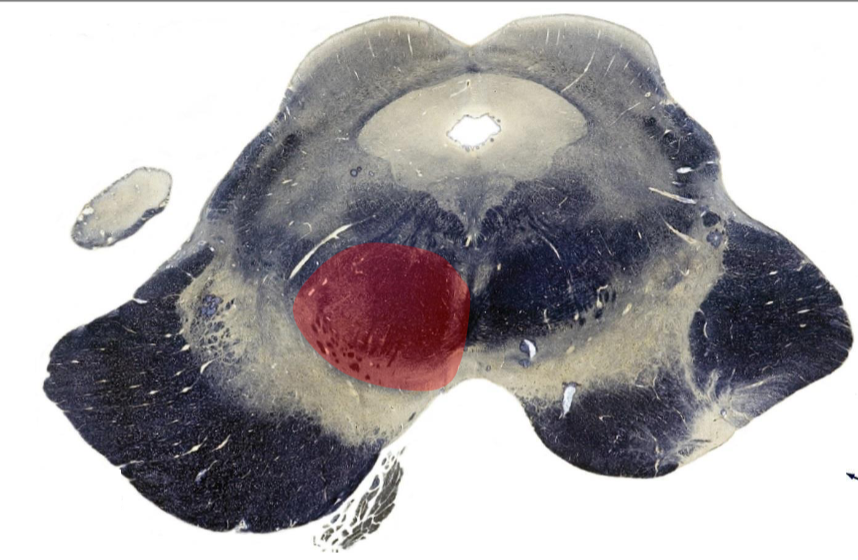

Claude Syndrome
Rostral Medulla
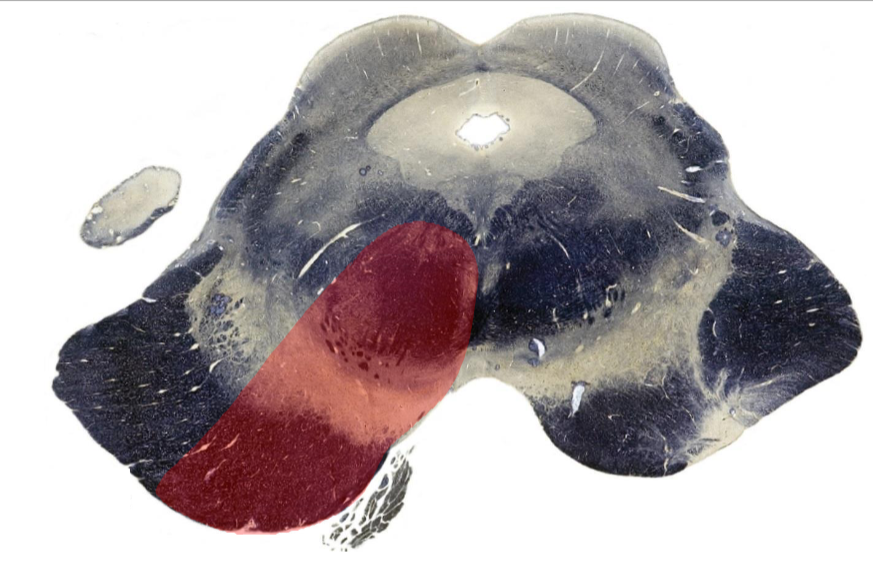
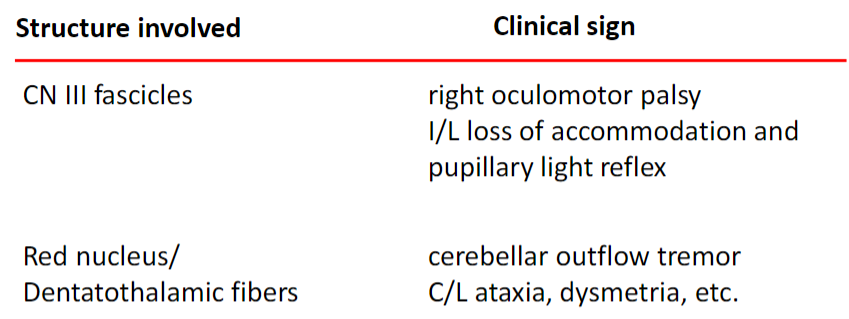

Benedikt Syndrome
Rostral Medulla
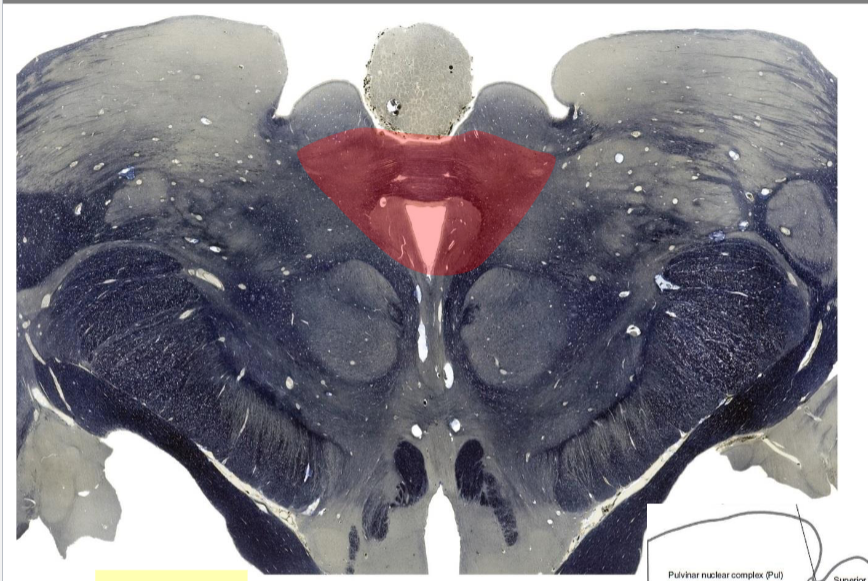
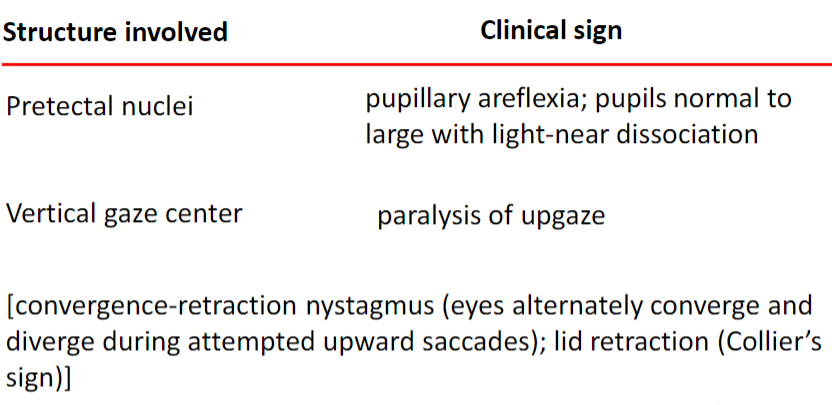
Parinaud syndrome
Midbrain-diencephalon junction
one and a half syndrome
lesion involved the MLF in addition to PPRF
horizontal gaze palsy + internuclear ophthalmoplegia
Only possible movement is abduction on side opposite gaze palsy